One of the most important resources of an organization is the labor of workers, which must be paid on time and in full. Thus, when forming a team of employees, the employer must take into account the potential of the company and the possibility of paying remuneration for the work performed.
Salary fund
This is the amount of monetary compensation for hired labor in the process of producing goods or providing services.
Composition of the wage fund:
- payment for time worked, additional payments, motivational bonuses;
- one-time payments;
- additional social compensation.
Payroll structure:
- calculation for hours worked (salary, tariff rates, payments in kind, additional payments for experience or skill, payments for overtime work, etc.);
- payment for unworked hours (vacation pay, compensation for training expenses, payments for downtime due to the fault of the employer).
Documents involved in the calculation:
- payroll of the enterprise (monetary expression of labor);
- time sheet (quantitative expression of labor);
- staffing table (list of rates, salaries).
Payroll or payroll?
Remuneration involves not only the regular receipt of wages by employees. In enterprises that care about their staff, employees usually receive not only the amounts intended to be paid according to the salary or tariff schedule, but also additional funds provided for by the internal policy and/or industry characteristics of the organization.
Thus, the wage fund includes all types of payments that the entrepreneur makes in favor of employees, that is, all expenses provided for the organization’s personnel in the planned, current or past period, regardless of the reasons for the accrual. If we compare this totality with the wage fund (WF), then the latter will be part of the payroll.
The main difference between the FW is that this fund includes only those payments that are directly related to the labor operations performed by employees and their results.
NOTE! These funds will match if the organization's employees do not receive any payments other than salaries. But in practice this happens quite rarely.
FW and payroll are calculated using identical algorithms.
How to analyze the efficiency of using the wage fund ?
Why is the payroll indicator needed?
The importance of payroll as an economic category, in addition to directly accounting for necessary expenses, helps in solving many management problems, such as:
- analysis of personnel costs of different structural divisions;
- adjusting the company's general expenses;
- a certain role in increasing profitability and reducing expenses;
- adjustment of product costs and, as a consequence, the company’s pricing policy;
- calculation of mandatory social payments - insurance contributions, pension contributions, etc.;
- budgeting expenses.
Composition of the wage fund
The wage fund is the totality of the wage fund and all other types of personnel costs. Includes the following categories:
- premium;
- “thirteenth” salary;
- sick leave;
- vacation pay of all types;
- business trips;
- bonuses for length of service;
- amounts for time that was not actually worked, but is legally subject to payment (for example, downtime);
- additional payments for part-time work, for odd or overtime work, for dangerous or harmful working conditions, etc.;
- employee compensation;
- expenses for providing the employee with discounted or free uniforms;
- preferential working hours for employed minors;
- medical examination costs;
- social payments;
- compensation (for example, for food, travel to work, etc.)
The wage fund does not include:
- annual bonuses;
- targeted payments in favor of employees;
- bonuses paid from special funds;
- separate pension benefits;
- reimbursement of vouchers, travel, etc.;
- gifts from the company;
- dividends;
- all types of financial assistance.
Hourly wages - how to calculate wages
Hourly wages are one of the types of time-based wage systems. For whom hourly wages can be set, how monthly earnings are calculated, what nuances need to be taken into account when drawing up a staffing table and an employment contract - read about all this in the material presented.
What types of remuneration systems are there and when are they used?
What is hourly wages and what are its forms?
When is hourly wages beneficial?
What are the nuances of establishing an hourly wage rate in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and how to calculate wages for hourly wages in 2021
How hourly wages are reflected in the staffing table - sample
What features need to be taken into account in an employment contract for hourly wages - sample
Results
What types of remuneration systems are there and when are they used?
For each group of workers in an enterprise and even for each specific person, the payment system for performing labor functions may vary. Let us highlight the following types of such systems:
- Time-based - an employee’s payment is directly dependent on the time he or she works. In this case, the employee is set an hourly or tariff rate and salary.
- Piecework - the amount of earnings depends on the amount of work performed. Piece rates must be approved here.
- Commission - when it is established, the employee receives a commission (percentage) on a certain indicator, for example, 5% of the store’s daily revenue.
- Variable salary system - an employee's salary is subject to periodic review, for example once a quarter or month. Such a review can be influenced by such an indicator as the completion of the planned amount of work.
- Chord - involves establishing a relationship between the amount of an employee’s salary and the package of work he performs in accordance with the chord assignment for a specific period.
The payment system is approved either in a local regulatory act at the enterprise, for example in the regulations on remuneration, or in a collective or labor agreement.
If you have access to ConsultantPlus, go to the Ready Solution and find out the features of payroll calculation in each wage system. If you do not have access to the legal system, get a trial demo access for free.
What is hourly wages and what are its forms?
The hourly wage system is one of the varieties of the time-based system. Here, wages are calculated depending on the amount of time worked - hours - and the established hourly rate.
On the topic of the article! Fixed assets in the budget in what accounts?
NOTE! With a time-based system, salaries or tariff rates may also be set, but these are usually tied to a month.
At enterprises, depending on the specifics of production and other factors, the hourly system can take the following forms:
- Standard hourly - when a fixed rate is set for one hour of work. At the same time, the volume and quality of work do not affect wages. This form is typical for the positions of security guard, operator, administrator, etc.
- Premium hourly wage - here the volume and quality of work performed will affect wages. That is, the time worked is paid and to this amount is added the amount of the bonus, the amount of which must be indicated in the regulations on remuneration, employment contract or in other regulations or agreements.
- Standardized hourly rate - in this case, in addition to the hourly rate, an additional payment is guaranteed for strict compliance with the conditions established by the employer. This form is convenient to use when exceeding production standards is undesirable.
Due to the 2021 coronavirus pandemic, the payment procedure has changed in a number of cases. We wrote more about this in the material “New in Payroll in 2020”.
When is hourly wages beneficial?
The benefit for employers when setting hourly wages is obvious: they only have to pay for the time worked. This type of payment is especially popular for those employees who do not work full time. Examples include:
- workers with an uneven workload involved in performing work at a specific facility;
- workers whose working hours cannot be regulated (for example, teachers who teach additional classes in educational institutions);
- employees employed on a flexible schedule;
- workers whose labor productivity is very difficult to determine.
However, this system has certain disadvantages. For example, in the absence of bonus payments, employees are usually not interested in working faster and more, i.e. production efficiency decreases. In addition, the employer needs to monitor every hour the employee works, which may require an additional employee to keep track of time, leading to new costs.
What are the nuances of establishing an hourly wage rate in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and how to calculate wages for hourly wages in 2021
Monthly earnings are calculated by multiplying the number of hours worked by the hourly rate. The employer can approve any size according to the qualifications of the specialist and the complexity of the work. However, when they are established for hourly wages, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the requirement must be met: when working the full norm (40 hours per week) in a month, the employee cannot receive less than the minimum wage (minimum wage).
IMPORTANT! From January 1, 2021, the minimum wage is set at RUB 12,130.00.
If the monthly payment at full production does not reach this amount, it is necessary to either revise the rate or make an additional payment to the minimum wage.
Let us illustrate with an example how to calculate wages at a set hourly rate.
For student Renata Vasilyeva, who came to work part-time at Romashka LLC as an assistant clerk, an hourly rate of 100 rubles was approved. Renata works on a flexible schedule during her free time. In February 2021, she worked 46 hours. Let's calculate her monthly salary:
46 hours × 100 rub./hour = 4600 rub.
If the student had worked the entire month of February - 159 hours, she would have received:
159 hours × 100 rub./hour = 15,900 rub.,
which exceeds the current minimum wage. Thus, Vasilyeva’s hourly wage rate complies with labor law.
ConsultantPlus experts explained how to pay an hourly employee for work on weekends. Learn the material by getting trial access to the system for free.
How hourly wages are reflected in the staffing table - sample
The staffing table is an internal document of the company, which collects all the information about the personnel structure, composition and number of employees, as well as the monthly payroll. When an employee is hired on an hourly basis, the staffing table must contain a corresponding note about this.
If we take as a basis the unified form T-3, put into circulation by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 5, 2004 No. 1, the hourly rate should be indicated in column 5 “Tariff rate (salary), etc., rubles,” and in column 10 “Notes » register “Hourly wages” with reference to the normative act establishing the payment system.
Use the link below to see how the staffing table is drawn up for those employees for whom the hourly form is approved.
staffing table
What features need to be taken into account in an employment contract for hourly wages - sample
When employing an employee, all aspects relating to the calculation and payment of wages are usually discussed between him and the employer, which must then be formalized in writing by signing an employment contract. In it (or an additional agreement to it), the Labor Code obliges to prescribe the conditions for hourly wages, if one is established for the employee.
NOTE! When transferring employees to hourly pay from another salary system, the employer must notify them of this no later than 2 months before introducing the planned changes. Such changes, by the way, should be reflected in orders and other regulatory documents of the organization.
It is advisable to stipulate in the employment contract:
- the amount of the hourly wage rate (salary);
- the procedure for calculating wages for the month;
- bonus conditions;
- terms of payment for holidays, weekends and night hours;
- deadlines for issuing wages;
- other conditions, which may include a probationary period, social guarantees, etc.
Download a sample extract from an employment contract regarding the establishment of an hourly wage system and hourly rate from the link below.
agreement
Results
Hourly wages are one of the types of time-based systems, when, to calculate wages for each specific employee, a rate is set for one hour of work and the number of hours worked is calculated. In this case, the rate should be such that when working out the monthly quota, the employee is accrued no less than the minimum wage, which in 2021 is equal to 12,130.00 rubles.
All conditions relating to the calculation and payment of wages under the agreed system are included in the text of the employment contract or local regulations of the company. That is, the employee must be familiar with the principles on which his monthly earnings are calculated.
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 5, 2004 No. 1
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
Terms of formation of the wage fund
Depending on the needs of the organization, the payroll can be calculated for any period of interest, even for one day. In practice, other reporting units are more often used:
- Payroll for the year is calculated for the last calendar year period, this indicator is used to determine the entire amount of the wage fund;
- Monthly payroll is more often used for various types of reports;
- Payroll per day is used as a theoretical indicator for analyzing a company’s expenses;
- Payroll per hour will be needed for those enterprises where employees work on an hourly payment system.
An example of calculating the wage fund for a month .
How are taxes calculated?
The wage fund is the basis for calculating accruals to extra-budgetary funds .
According to current legislation, a business entity is obliged to accrue and pay within the time limits specified by law the following contributions:
- to the Pension Insurance Fund (PFR);
- to the FSS (Social Insurance Fund);
- to the MHIF (Health Insurance Fund).
In turn, contributions to the Social Insurance Fund are divided into two groups: contributions in case of temporary disability, and contributions related to injuries and occupational diseases. All listed contributions are charged to the accrued payroll of the enterprise (and fund) and are included in the cost of products (services).
Today the tariff in the Pension Fund is 22% , in the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund - 5.1% , in the Social Insurance Fund - 2.9% . Social contributions for injuries are an indicator established for each enterprise individually, taking into account the type of activity.
The legislation provides for regulation of the amount of payments to the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund. If the salary is more than 711 thousand rubles, then the amount exceeding this figure will be taxed at a rate of 10% . The Social Insurance Fund provides for zero contributions in case of excess of wages accrued in the amount of 670 thousand rubles.
Contributions are paid monthly , simultaneously with the payment of wages. The law provides for the payment of remuneration to employees twice a month , on days established by the enterprise (advance and settlement).
Reports to the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund are submitted quarterly , on an accrual basis. If payment deadlines or reporting deadlines are violated, administrative and financial penalties are imposed on the enterprise.
Let's look at an example :
The wage fund of Panorama LLC amounted to 215 thousand rubles in April 2015. Salary costs will be:
- Pension Fund – 47,300 rubles;
- in the Social Insurance Fund – 6235 rubles;
- in the Social Insurance Fund for injuries – 1290 rubles. (for the enterprise the deduction rate is set at 0.6%);
- in the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund – 10965 rubles.
All mandatory deductions are calculated by economists when forming the wage fund, and are included in the financial plan of the enterprise.
Calculation of annual payroll
In order to calculate the annual wage fund, you need to have the following data for calculations:
- the amount of wages paid to employees according to statements;
- number of hours worked (calculated using time sheets);
- indicators of additional costs enshrined in the company’s local regulations;
- the number of employees on the list and their salaries (fixed in the staffing table);
- forms of payment accepted at the company (salary, piecework, hourly).
Universal scheme
The universal calculation scheme involves the addition of all amounts intended for personnel. In order to calculate it as simply as possible, although somewhat approximately, use the following formula:
FOTyear = ZPs-m x Chsr-sp. x 12
Where:
- FOTyear – annual indicator of the wage fund;
- ZPs-m – average monthly salary (all amounts of payments for the year, divided by 12);
- Chsr-sp. – average number of employees (the summed number of employees for each day of the month, divided by the number of days in the month, repeated 12 times according to the number of months in the year).
FOR EXAMPLE. From January to March 2021, Tradition LLC employed 12 people; in April, 2 more workers were hired; the staff did not change until October, when 1 person was fired, and in December, three more were hired. The average monthly salary of personnel, including bonuses, additional payments and bonuses, pre-calculated from the statements, amounted to 456 thousand rubles. First, we determine the average number of employees: (12 x 3 months) + (12 + 2 (April)) + (14 x 6 (until October)) + (14-1 (October)) + 13 (November) + (13 + 3 (December)) / 12 = 13. Let's calculate the payroll for Tradition LLC for 2021: 456,000 x 13 x 12 = 71,136,000 rubles.
When paid hourly
Payroll calculation for hourly wages is carried out according to the following scheme:
FOThour = ∑st. x RF
Where:
- FOThour – wage fund for hourly workers;
- ∑st. – the sum of the rates of hourly workers;
- RF – number of working hours.
With piecework payment
Payroll calculation for piecework wages is carried out as follows:
FOTsd. = (Vpl. x Tsed.) + K + N + Pr. + Social
Where:
- FOTsd. – wage fund for workers with piecework wages;
- Vpl. – volume of production according to plan;
- Tsed. – price per unit of production;
- K – various compensations;
- N – allowances;
- Etc. – bonuses;
- Vsots. – social payments.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! If you need to calculate not the annual, but the monthly payroll or use another reporting unit, you need to take the corresponding indicators for the formulas, that is, do not multiply the average monthly salary by 12, but determine the average number of employees for 1 reporting month.
Formula for calculating the wage fund, analysis and optimization - Business

22.11.2019
On the topic of the article! The profitability of production assets is determined by the ratio
Online calculators
Our website contains more than 100 free online calculators for mathematics, geometry and physics.
Directory
Basic formulas, tables and theorems for students. Everything you need to do your homework!
Order a solution
Can't solve the test?! We will help! More than 20,000 authors will complete your work from 100 rubles!
The payroll formula allows you to analyze and optimize the following data:
- Costs for wages of personnel of all structural divisions (all categories of employees),
- Amount of costs, adjustment of rates, salaries, rates.
Using the payroll formula, the amount of the fund is calculated, through which all payments provided for by law are calculated (pension contributions, contributions to various insurance funds, etc.).
The wage fund is the main tool for rationalizing the costs of an enterprise and stimulating its employees.
Payroll Formula
When calculating the annual payroll, the following documents are required:
- Annual pay slips reflecting all amounts of payments accrued to employees.
- An annual time sheet indicating the number of hours worked.
- The staffing table, which indicates tariff rates, salaries, including the list of personnel of the organization.
- The payroll formula is calculated as follows:
- Фзп = Зср*Чср*12
- Here FZP is the wage fund;
- Zsr - average monthly salary;
- Chsr - average number of employees.
- The average salary can be determined by the sum of all accruals and payments included in the wage fund, then they must be divided by 12.
- The average number of personnel can be calculated by determining the amount of employees for each day of the month (then must be divided by the number of calendar days).
- The annual payroll formula includes the above actions for the period January-December, then the resulting number is divided by 12.
Composition of the wage fund
The wage fund usually includes amounts to be paid to employees in cash or in kind.
The composition of the wage fund is reflected by the following indicators:
- Salary accrued;
- The cost of products issued to employees of the enterprise;
- Additional payment for going out on holidays and weekends;
- Allowances for overtime work, including night work;
- Bonuses and rewards (for example, for continuous work experience);
- Hazard pay;
- Remuneration for part-time workers and persons not included in the payroll, etc.
The wage fund also includes payments for unworked time, which may be as follows:
- Time for performing public duties or agricultural work;
- Employee training time (retraining, advanced training);
- All types of vacation, excluding unused vacation, etc.
Payroll calculation period
There are several periods for calculating the wage fund in accordance with the reporting time unit:
- The annual fund, which is used to determine the amount of the wage fund. In these calculations, the payroll formula must include data for the last calendar year.
- Monthly fund, which calculates the amount of the wage fund for each month.
- The daily wage fund is used less frequently, but is necessary for a more thorough analysis of wage costs.
- Hourly fund, which is used in organizations where hourly wages are used.
Examples of problem solving
| Did you like the site? Tell your friends! |
Payroll utilization analysis
Analysis of the use of labor resources and the growth of labor productivity must be considered in close connection with wages. When starting to analyze the use of the wages and salaries, first of all it is necessary to calculate the absolute and relative deviation of its actual value from the planned (base) value.
- The absolute deviation (ΔFZPabs) is calculated as the difference between the funds actually used for wages and the basic FZP for the entire enterprise, production divisions and categories of employees:
- ΔFZPabs = FZP1 - FZP0.
- Since the absolute deviation is determined without taking into account changes in the volume of production, it cannot be used to judge the savings or overexpenditure of the FZP.
Relative deviation (ΔФЗПтн) is calculated as the difference between the actual accrued salary amount and the base fund, adjusted for the production volume index.
It should be borne in mind that only the variable part of the wages and salaries is adjusted, which changes in proportion to the volume of production.
The constant part of wages does not change with an increase or decrease in production volume.
- ΔFZPotn==FZP1 - FZPSK= FZP1 - (FZPper0 *Ιvp + FZPpost0),
- where ΔФЗПтн is the relative deviation in the wage fund;
- FZP1 - salary fund of the reporting period;
- FZPSK - base salary fund, adjusted to the output volume index;
- FZPper0 and FZPpost0—variable and the amount of the basic salary fund, respectively;
- Ιvp is an index of production volume.
- In the process of subsequent analysis, it is necessary to determine the factors of absolute and relative deviation according to the FZP.
- The variable part of the wage depends on the volume of production (VVP), its structure (Udi), specific labor intensity (TE) and the level of average hourly wages (OT).
- The constant part of the wage depends on the number of employees, the number of days worked by one employee on average per year, the average length of the working day and the average hourly wage.
- The following models can be used for deterministic factor analysis of the absolute deviation in the FZP:
- 1. FZP = CR* GZP,
- 2.FZP=CR*D*DZP,
- 3.FZP=ChR*D*P*ChZP,
- where CR is the average annual number of employees;
- D - number of days worked by one employee per year;
- P is the average working time for;
- GZP - average annual salary of one employee;
- DZP - average daily salary of one employee;
- NWP is the average hourly salary of one employee.
- Calculation of the influence of factors according to these models can be done using the method of absolute differences:
- ΔФЗПЧР = (ЧР1 - ПР0) *Д0*П0* ФЗП 0;
- ΔFZPD= CR1 * (D1 - D0) * P0 * CHZP0 ;
- ΔФЗП=ЧР1 *Д1 *(П1—П0)*ЧЗП0;
- ΔФЗПЧЗП = ФП1 * Д1 * П1 * (ЧЗП1 - Ш3П0).
- In the future, the reasons for changes in the average salary of employees by enterprise, divisions, categories and professions should be analyzed.
- The average annual wage of workers (AWW) depends on the number of days worked by each worker, the average length of the working day and the average hourly wage:
- GZP=D*P*P*P,
- and the average daily wage (ADW) - from the length of the working day and the average hourly wage:
- DZP=P*ChZP.
- Calculation of the influence of factors on changes in the average annual salary of employees for the enterprise as a whole and for individual categories can be done using the method of absolute differences.
The analysis process should also establish a correspondence between the growth rate of average wages and labor productivity.
For expanded reproduction, obtaining the necessary profits and profitability, it is important that the growth rate of labor productivity outstrips the growth rate of its remuneration.
If this principle is not observed, then there is an overexpenditure of the wage fund, an increase in production costs and a decrease in the amount of profit.
The change in the average earnings of workers over a given period of time (year, month, day, hour) is characterized by its index (IZP), which is determined by the ratio of the average salary for the reporting period (ZP1) to the average salary in the base period (ZP0). The labor productivity index (IGP) is calculated in a similar way:
On the topic of the article! What is the working capital of an enterprise?
The advance coefficient (ECF) is equal to COF = ΙGV /ΙZP.
To determine the amount of savings (-E) or overexpenditure (+E) of the wage fund due to changes in the relationship between the growth rate of labor productivity and its payment, you can use the following formula:
To assess the effectiveness of using funds for wages, it is necessary to use such indicators as the volume of production in current prices, the amount of revenue and profit per ruble of salary, etc.
In the process of analysis, it is necessary to study the dynamics of these indicators and the implementation of the plan according to their level. An inter-farm comparative analysis will be useful, which will show which enterprise operates more efficiently.
After this, it is necessary to establish the factors for changing each indicator that characterizes the efficiency of using the wage fund.
For factor analysis of production per ruble of wages, you can use the following model:
- where VP is output at current prices;
- FZP - personnel wage fund;
- T - the number of hours spent on production;
- ∑D and D are the number of days worked by all workers and one worker, respectively, for the analyzed period;
- CR - average number of workers;
- PPP - average number of production personnel;
- PV - average hourly output per worker;
- PD—average working day;
- Ud - the proportion of workers in the total number of production personnel;
- GZP is the average annual salary of one employee.
- Revenue per ruble of salary, in addition to the listed factors, also depends on the ratio of sold and produced products (PSP):
- V/FZP=DRP*ChV*PD*D*Ud: GZP.
- Profit from sales of products per ruble of salary, in addition to the above factors, also depends on the level of profitability of sales (the ratio of profit to revenue):
- P/FZP=ROB*DRP*ChV*PD*D*Ud: GZP.
- When analyzing the amount of net profit per ruble of wages, another factor is added as the share of net profit in the total amount of gross profit (GP):
- PE/FZP=DChP* ROB *DRP *ChV*PD * Ud : GZP.
- To calculate the influence of factors using the above models, the chain substitution method can be used.
The analysis can be deepened by detailing each factor of this model. Knowing, for example, due to what factors the level of average hourly output or profitability of sales has changed, you can calculate their impact on the amount of profit per ruble of salary using the method of proportional division.
The analysis will show the main directions for searching for reserves for increasing the efficiency of using funds for labor costs. At the analyzed enterprise, this is a reduction in daily and intra-shift losses of working time, as well as an increase in the share of net profit in its total amount.
Didn't find what you were looking for? Use the search:
Payroll calculation formulas for the year, for the month, according to the balance
What is the wage fund, how does it differ from the wage fund, what is its structure, how to calculate the annual and average monthly indicator, examples.
There is no strict legal definition of payroll in Russian legislation. Essentially, the wage fund is all expenses for personnel wages, including bonuses, allowances, and compensation from any source of financing.
Download and use it
:
Difference from FZP
If payroll is a broad concept of various items of compensation payments to an employee, then the wage fund is the basis for calculating payroll. This is remuneration for work in accordance with the qualifications of the personnel, intensity, quantity, quality of work and under what conditions it is performed, as well as compensation and incentive payments.
Wages are generally paid in cash. In accordance with the employment contract, it can be carried out in another form (for example, in the form of products manufactured by the enterprise). It is important to know that the share of wages paid in another form, that is, not in money, cannot exceed 20% of the total wage fund.
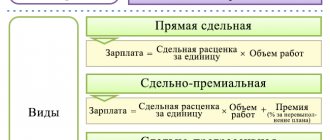
The remuneration system is built by each company. The system can be:
- temporary,
- piecework,
- periodic (earnings depend on completing certain stages of work or producing a certain volume of products).
The first two types have their own subtypes:
- regular temporary (monthly salary);
- temporary – bonus (salary + bonus as a % of salary or hourly rate);
- piecework (fixed rate of remuneration for the number of units of products manufactured, work performed);
- piecework-bonus KPI (previous point + bonuses for achieving qualitative/quantitative indicators, for example, reducing the proportion of rejected products, reducing complaints, etc.);
- piecework-transfer (payment increases for production in excess of the agreed quantity of products, exceeding the business plan indicators);
- side-piece work (usually the wages of workers in auxiliary and service industries - determined as a percentage of the wages of main workers).
Don't save on payroll
Any entrepreneur strives to reduce his expenses, including through salary funds and wages. Of course, you can cut salaries, cancel compensation payments, remove bonuses, etc.
However, one should not get carried away with such a reduction. An employee has the right to expect fair remuneration. Financial motivation is one of the strongest factors influencing staff turnover, their qualifications, and the efficiency of performing work duties. A meager wage fund can provoke workers to commit crimes in order to somehow make up for the lost funds in an illegal manner.
To put it simply, the vast majority of employees work exactly as their employer pays them.