Profit distribution
The amount that a JSC or LLC can allocate for distribution between participants or shareholders is listed in account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss).” In fact, these are funds remaining at the company’s disposal after all expenses, including payment of taxes on income (profit, simplified tax system or UTII). The distribution order is regulated:
- for LLC - by law dated 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ;
- for JSC – by Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ.
The company must pay dividends within certain periods:
- JSC - with a nominal holder, trustee is settled within 10 working days from the date of determination of persons entitled to receive dividends, and 25 working days - with other recipients;
- LLC - within 60 days from the date of the decision or within the period established by the Charter of the company.
Let's look at how dividend payments to the founders of an LLC and shareholders of a JSC are reflected in accounting.
Postings for accrual and payment of dividends to the founder and shareholders
To reflect any business transactions, entries recommended by the Chart of Accounts are used (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). Which entries when paying dividends to the founder of an LLC or to the shareholders of a JSC will be involved in a particular company depends on:
- from who the recipient is;
- depending on the method of calculation.
Let's figure out how to pay dividends in different situations.
Accrued dividends payable: posting
After the decision on payment is made, the funds due are distributed according to the list of recipients. In an LLC - in proportion to the share (contribution) of the participant. Joint stock companies determine the amount of dividends for each type of shares. The accrual is then reflected in the accounting accounts.
Postings for calculating dividends:
- for recipients who do not work for the company (it does not matter whether it is a legal entity or an individual) - Dt 84/Kt 75.2 (sub-account “Calculations for the payment of income”);
- for employees of the organization Dt 84/Kt 70 (for account 70 it is recommended to open a separate sub-account “Calculations for dividends”).
That is, from account 84, the profit received is distributed to the accounts of settlements with the founders in the context of specific individuals.
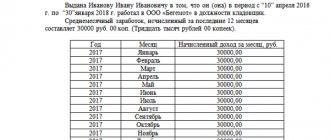
Example
For the payment of dividends to the shareholders of Alfa JSC for 2021, an amount of 3,300,000 rubles is allocated, the number of shares is 20 thousand, of which 11 thousand belong to Mir LLC, 9 thousand - to the head of the company, with whom an employment contract has been concluded.
For one share there is:
RUB 3,300,000 / 20,000 pcs. = 165 rub. dividends.
The company will accrue dividends to each shareholder based on the number of shares he owns - multiplying 165 rubles. per number of shares:
11,000 x 165 = 1,815,000 rubles. – dividends from Mir LLC,
9,000 x 165 = 1,485,000 – manager’s dividends.
The accountant will show that net profit is used to pay dividends by postings:
- Dt 84/Kt 75.2 – RUB 1,815,000, dividends accrued to Mir LLC;
- Dt 84/Kt 70 – RUB 1,485,000, dividends accrued to the head of Alfa JSC.
Example
, whose founders are Smirnov (share in the authorized capital 51%) and Potapov (share 49%), for 2021 received a net profit of 600,000 rubles. The organization is led by Smirnov as General Director (an employment contract has been concluded with him). At the end of the year, the founders decided to pay 400,000 rubles as dividends and leave the remaining funds in the company’s working capital. According to the shares of the founders, they were accrued dividends in the amount of:
- 400,000 x 51% = 204,000 rub. — Smirnov;
- 400,000 x 49% = 196,000 rub. - Potapov.
After dividends were accrued for payment, the accountant recorded the entries as follows:
- Dt 84/Kt 75.2 Potapov – 196,000 rubles;
- Dt 84/Kt 70 Smirnov – 204,000 rub.
The following entries will appear after the actual payment of funds or after the expiration of the claim period (3 years after the date no later than which the company should have paid).
When are payments made?
The period of time during which dividends must be paid depends on the legal form.
For an LLC, a period of 60 days is established from the date of registration of the minutes of the meeting of participants or the decision of the sole founder. At the same time, the law allows the establishment of a shorter payment period in the company’s charter.
If payment is not made within the specified period, the owner can directly contact the company and demand payment. If even after applying this is not done, you need to go to court.
You might be interested in:
Postings for the sale of goods and services: examples of which accounts are used
It is advisable to pay dividends to the LLC in non-cash form. There is no direct prohibition on performing this operation in cash, but at the same time, the instructions of the Central Bank do not include a purpose for which cash can be spent, such as issuing dividends.
When paying dividends to the shareholders of a JSC, it is necessary to take into account their status, as well as the moment of determining the recipients. The exact payment terms for each category of shareholders are established in Law 208-FZ. It is allowed to pay dividends to JSC participants only in non-cash form.
In practice, a situation may arise in which dividends will be accrued to the owners, but not paid. However, the statutory payment deadline has already passed.
However, another period has been defined - the limitation period, which lasts three years. It starts counting from the first day after the end of the payment period. The company's charter may also stipulate a longer limitation period, but not more than five years.
If a participant applies for dividends while the statute of limitations has not expired, they must be issued according to the standard procedure with the calculation and withholding of tax. In this case, failure to comply with the payment deadline does not have any negative consequences. But the participant can go to court and collect interest for late payment of the amount.
Important! If the statute of limitations has expired, then the dividends are considered unclaimed. In this case, they are subject to inclusion back in profit, and the obligation to pay amounts to the owner ceases.
Payment of dividends: accounting entries
When paying dividends, the accounting accounts will vary depending on how the company will transfer the funds due to the recipient (founder, shareholder). There are quite a few ways:
- non-cash transfer through the company's bank account;
- cash payment through the cash register;
- transfer of company property - goods, materials, fixed assets.
A non-monetary form of payment must be provided for in the organization’s Charter.
In addition, when paying dividends, the company becomes a tax agent:
- for personal income tax, paying dividends to individuals (clause 3 of article 214 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
- for income tax when paying dividends in favor of legal entities (clause 3 of Article 275 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Therefore, even in one company, when paying dividends, there will be several accounting entries. Let's look at how different transactions are reflected in the accounting accounts.
Dividends: the procedure for their payment and features of their taxation
Dividends are part of the profit of an enterprise distributed among its founders. The size of dividends depends on the share participation of each of the founders - this can be a percentage in the authorized capital or the presence of a certain block of shares.
Dividends are paid in accordance with the approved procedure, which is determined at the meeting of shareholders (the corresponding act is drawn up). They can be paid at the end of the year, semi-annually or quarterly.
The form of dividend payment can also be different, as shown in the figure below:
At the legislative level, it is prohibited to pay dividends in the following cases:
- There is a threat of bankruptcy;
- Their payment leads to a decrease in the authorized capital;
- Not fully formed authorized capital.
Since dividends are income that an individual receives, it automatically becomes subject to taxation. The personal income tax rate for resident shareholders is 13%, for non-residents – 15%. Tax withholding occurs on the day of dividend payment.
Payment of dividends by property: postings
The company may choose a non-monetary form of payment. However, it should be borne in mind that transactions for the payment of dividends with property are equated to sales; accordingly, taxes on income must be charged:
- for companies under the general regime - VAT and income tax;
- for simplified people – a single tax under the simplified tax system.
With UTII, the calculation of dividends by property is not included in the tax base according to “imputation”, therefore the company charges taxes on dividends paid by property according to the general taxation system - becoming a payer of VAT and income tax.
Payment of dividends in goods - postings
When transferring goods, the organization draws up a consignment note TORG-12 or UPD. The legal entity reflects the payment of dividends in goods to the founder with the following entries:
- Dt 75.2/ Kt 90.1 – reflects the transfer of goods to founders (shareholders) who are not on the company’s staff;
- Dt 70/Kt 90.1 – goods were issued to the employee as dividends;
- Dt 90.2/Kt 41 – the cost of transferred goods is written off.
If finished products are transferred instead of goods, instead of 41 invoices, 43 is used.
Then the company must charge taxes on the transferred property:
- Dt 90.3/Kt68 – VAT on the amount of goods for companies on the OSN (later the organization will form a tax base for profit tax and calculate profit tax based on the results of taxable transactions);
- Dt 90.3 (99)/Kt 68 - income tax is charged (for payers of the simplified tax system - a single tax is charged).
The financial result from sales of the reporting period is formed by posting Dt 90.9/Kt 99.
A company on OSNO needs to remember to issue an invoice (UPD) and enter it in the sales book. Simplified people record the operation in KUDiR.
Fixed assets are transferred as dividends - transactions
Typically, companies part with fixed assets only if no other payment method is possible, or if it turns out that the fixed asset is idle (that is, there is no need for it in production). The payment of dividends by fixed assets of the LLC is reflected by the following entries:
- Dt 01Disposal/Kt 01 – disposal of an asset;
- Dt 02/Kt 01 Disposal - write-off of depreciation on the facility;
- Dt 91.2/Kt 01 – the residual value of the fixed assets is written off;
- Dt 75.2/Kt 91.1 – transfer of OS to a founder who does not work for the company;
- Dt 70/Kt 91.1 – if the OS is transferred to the founder-employee;
- Dt 91.2/Kt 68 – VAT is calculated by the organization using OSNO.
At the end of the year, 91 accounts will be closed to account 99. The company will also charge the tax due to the budget (on profit or single according to the simplified tax system): Dt 99/Kt 68.
Accounting for dividend payments using materials
Dividends can also be paid in materials. The postings will be similar to those shown when transferring fixed assets, with the exception of writing off the cost - instead of account 01, the accounting department uses account 10:
Dt 91.2/Kt 10 – the cost of materials transferred as dividends is written off.
Postings for personal income tax and income tax for the dividend payer
As noted earlier, when paying dividends, the company acts as a tax agent - withholds personal income tax when paying individuals (13% from residents, 15% from non-residents), income tax - when paying legal entities, regardless of the taxation system they use (13% - Russian companies, 15% - foreign, 0% - with ownership of at least 50% during the year).
The company must transfer the withheld tax amounts to the budget no later than the next business day. When calculating and paying dividends, accounting entries are used:
- Dt 75.2 / Kt 68 Personal Income Tax - to reflect accrued amounts withheld from the founder (shareholder) - an individual who does not work in the organization;
- Dt 70 / Kt 68 Personal income tax – tax accrual on payments to the founder (shareholder) - employee of the company;
- Dt 75.2 / Kt 68 NNP - income tax on payments to the teacher (shareholder) - a legal entity.
Dividends are not subject to insurance premiums.
Posting payment of dividends and withheld personal income tax and income tax when transferred to the budget:
- Dt 68 Personal Income Tax/Kt 51 – transferred to the personal income tax budget, withheld from dividends of the founder (shareholder) - an individual;
- Dt 68 NNP/Kt 51 – transfer of the amount of income tax withheld from dividends of the founder (shareholder) of a legal entity.
Covering losses on account 84 at the expense of the founders
At the end of 2015, JSC Fiesta received losses in the amount of 841,800 rubles. The founders of JSC “Fiesta” are Savelyev R.N. (58% share in the authorized capital) and Markov K.L. (42% share in the authorized capital). By decision of the board it was established that the losses of 2015 would be covered at the expense of the founders:
- at the expense of Savelyev - 488,244 rubles. (RUB 841,800 * 58%);
- at Markov’s expense - 353,556 rubles. (RUB 841,800 * 42%).
The protocol of the board’s decision was signed in February 2021. In the same month, funds were received from Savelyev and Markov into the current account of JSC Fiesta.
To reflect operations to cover losses at the expense of the founders’ own funds, the following sub-accounts were opened in the balance sheet of JSC Fiesta:
- 75.1 - Savelyev’s funds aimed at repaying the loss;
- 75.2 — Markov’s funds used to repay the loss.
The following entries were made in the accounting of JSC Fiesta:
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Document |
| 75.1 | 84 | Savelyev's debt to repay the loss with his own funds is reflected | RUR 488,244 | Minutes of the board's decision |
| 75.2 | 84 | Markov's debt to repay the loss with his own funds is reflected | RUR 353,556 | Minutes of the board's decision |
| 51 | 75.1 | Funds from Savelyev were credited to repay the 2015 loss | RUR 488,244 | Bank statement |
| 51 | 75.2 | Funds from Savelyev were credited to repay the 2015 loss | RUR 353,556 | Bank statement |
| 99 PNO | 68 Income tax | The amount of permanent tax liability is taken into account (RUB 488,244 * 20%) | RUR 97,649 | Minutes of the board's decision |
Unpaid dividends: entries
On the date of expiration of the claim period, dividends not paid to the founders are returned to net profit. In this case the following transactions are made:
- Dt 75/Kt 84 - dividends not claimed by legal entities and individuals who are not employees of the payer company;
- Dt 70/Kt 84 - dividends not claimed by employees.
Thus, the balance of unused profit on account 84 will increase.
When calculating and paying dividends, the organization uses accounts and entries that will reflect business transactions actually performed by the company. Accounting must keep records of both accrued and paid amounts - in an analytical context for each founder, participant, and shareholder.
Retained earnings: entries
Operations carried out on account 84 and necessary to account for retained earnings and uncovered losses are carried out at the end of the year. NP is reflected by credit turnover, and NU by debit turnover. In both cases - according to account 84 in correspondence with account 99. In the latter, by the way, the financial result is displayed throughout the year.
In this regard, we recall that the accountant must make closing entries with the following content at the end of each month:
| Dt | CT | Operation description |
| Profit from core activities is taken into account |
Or
| The loss incurred from the main activity is taken into account |
| Profit received from other activities is taken into account |
Or
| The loss arising from other activities is taken into account |
When the year ends and the balance sheet accounts are closed, the ending balance of account 99 should be transferred to the retained earnings account by posting:
| Dt | CT | Operation description |
| The company's emergency is taken into account |
Or
| The company's loss is taken into account |
As a result of postings at the beginning of the next year, account 99 should be reset to zero. This sequential closing of accounts with the writing off of retained earnings to account 84 and revealing the result is called balance sheet reformation.