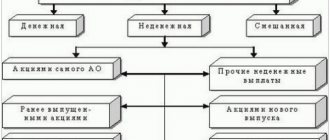
Composition of non-current assets
The property rights of this group include fixed assets and intangible assets that are planned to be used by the enterprise for more than a year. It consists of:
- OS owned by the enterprise and involved in the production process. At the same time, over a long period of time, the property does not lose its natural and material form.
- Investments of a long-term nature and in the form of capital.
- Any forms of intangible assets.
- Other noncurrent assets.
The property of an enterprise belonging to this category of funds occupies a leading place in the activities of the enterprise, especially in production cycles. During the period of its use, the cost is gradually transferred to the finished product in the form of depreciation charges.
There are active and passive parts of non-current assets. The first category includes the most mobile and dynamic means. For example, industrial equipment, company vehicles. The second group includes real estate objects: structures and buildings that create the initial conditions for the work of enterprise employees.
Account 08 08 and its purpose
We have sorted out the concept of non-current assets, but it remains unclear: why do we need a separate account for them if 01 and 04 have already been created? To understand the essence of the issue, let us recall the rules for accepting fixed assets and intangible assets for accounting.
According to the requirements of PBU, the accountant must reflect fixed assets and intangible assets on the account at their original cost, which includes all the actual costs of their acquisition. It often happens that information about all amounts is not received immediately. This is where the need arises to open accounting account 08, which will collect data on items of expenses for the acquisition of property. As soon as the accounting department has taken into account all the amounts and the property is ready for commissioning, the information can be written off to the main account 01 or 04.
Account 08: acceptance for accounting from the account
The receipt of goods or intangible assets on the balance sheet of the organization is carried out taking into account all the costs of their acquisition. This may include installation, delivery and other related costs.
The total resulting value of non-current assets is not subject to change, with the exception of possible cases of revaluation, completion, reconstruction and others.
Acceptance of fixed assets or intangible assets for accounting is accompanied by the determination of their useful life. Depending on the decision made, depreciation is calculated monthly, which reduces the initial cost of the object.
When registering intangible assets, there are options for determining and not determining the useful life. The useful life must be determined annually. The same applies to depreciation charges for intangible assets.
If fixed assets are considered in the future as an additional source of income reflected in account 03, then depreciation on them is accounted for separately in the general account for fixed assets - 02.
Tangible and intangible exploration costs involved in the development of deposits of natural minerals and other activities related to the development of natural resources are assessed based on the amount of actual costs incurred, which include:
- amounts paid to suppliers and intermediaries under the terms of contracts;
- consulting fees;
- customs payments;
- non-refundable taxes;
- remuneration of employees involved in development;
- depreciation of operating systems used to create search assets;
- other costs associated with activities of this kind.
The listed types of expenses do not include amounts of refundable taxes, as well as general business expenses, with the exception of situations where they are directly involved in the development of deposits and for performing other operations with minerals.
If the feasibility of development is subsequently confirmed, non-current exploration assets are transferred to the category of fixed assets or intangible assets on a general basis. Otherwise, further costs are stopped and the resulting assets are written off or disposed of.
Account structure
08 accounting account is active, because information about the company’s funds is collected on it. All related costs for the acquisition of property are reflected in a debit. When written off, the amounts are shown in the account credit. At the end of the reporting month, a debit balance may appear. As a rule, these are the amounts of expenses for unfinished construction projects and fixed assets that have not been put into operation. If there is no balance, the account is closed.

The debit balance, if any, should be reflected in the financial statements. Account 08 in the balance sheet is included in line 1190, which characterizes the amount of other non-current assets.
Definition and characteristics
Account 08 records investments regarding non-current resources for long periods.
Its purpose is to enter final information on the costs of the enterprise for property objects, land areas, natural objects, intangible property, the formation of domestic animals in the herd, excluding birds, rabbits, bees, dogs included in working capital. Costs for non-current assets are generated for the following reasons: main construction, new construction, restoration work, development and equipping of existing assets in the company with appropriate equipment. These measures, excluding the construction of new facilities, make it possible to change the goals for which they are carried out.
Costs may be associated with:
- acquired buildings, equipment, vehicles, agricultural technical equipment;
- purchased land areas, natural resources;
- purchase or production of intangible property;
- purchasing domestic animals for exploitation or breeding that are part of the main herd;
- directing grown young cattle into the herd;
- planting and caring for perennial vegetation.
Accounting for investments relating to property not involved in turnover serves to:
- timely, complete, accurate display of the costs incurred for construction work of various types of property;
- measures to control the construction process, the introduction of means of production, fixed assets;
- correct calculation, as well as display of price indicators for putting into use, acquired assets of property reserves, land areas, natural resources, intangible property.
Analytical accounting
To combine expenses of a similar nature into groups and systematize accounting, first-level subaccounts are additionally opened, which reflect information about the costs of:
- 08.1 – acquisition of land plots;
- 08.2 – purchase of environmental management facilities;
- 08.3 – construction of environmental facilities;
- 08.4 – purchase of individual OS by category;
- 08.5 – acquisition of intangible assets;
- 08.6 – transfer of livestock from one herd to another;
- 08.7 - purchase of adult livestock;
- 08.8 – carrying out scientific research, conducting experiments, the results of which will be used in the future at the enterprise.

If necessary, other analytical accounts of a similar nature may be opened.
Receipt of non-current assets
Most often, a company acquires property through a purchase and sale agreement. In this case, the algorithm for registering it is clear: you need to collect all expenses on account 08, and then write them off during commissioning to the main accounts. But there are other ways in which assets are transferred to the ownership of a business. This is mainly the result of barter or a contribution to the initial capital; gratuitous receipts are not uncommon.

For each method of obtaining property, a method for registering 08 accounts and a method for calculating the initial cost are determined. When making an act of donation, a corresponding agreement is drawn up, which indicates the market value of the transferred objects. This will be the amount that should be reflected by posting Dt 08 Kt 98 “Gratuitous receipts”.
Asset or liability
Investments in long-term non-current funds, when reflected in the balance sheet, are considered active operations that take into account the overall indicator of the company's financial costs associated with fixed assets.
Its task is to register movements and changes in property objects in accordance with their types. It denotes data on the financial capital possessed by the enterprise. Maintaining an analytical system of accounting records relating to account 08 is carried out according to the costs of finished property objects under construction.
Generated analytical accounting allows you to obtain information on the costs of restoration work and the formation of fixed assets. These costs may relate to:
- drilling, installation, tools, equipment, which are taken into account in the estimate of the main construction;
- acquisition of intangible property;
- creating a herd of working, productive livestock, which can consist of horses, representatives of the cattle family, sheep, pigs, and so on;
- costs of carrying out research, technological, experimental and design work.
Contribution to capital and transfer of goods for the needs of the enterprise
If one of the founders of an enterprise makes a contribution to the authorized capital in the form of fixed assets or intangible assets, they should be registered based on the following rules:
- The assessment of incoming assets should be carried out in agreement with the participants of the PA or JSC. In this case, the value of the property should not exceed the market value.
- After determining the amount of the initial cost, carry out account assignment Dt 08 Kt 75.
Thus, fixed assets from the founders were accepted for accounting in account 08. The information will be kept in debit until the property is put into operation.

Goods or finished products transferred within the enterprise to fulfill its needs are accounted for at their actual cost, the amount of which can be found in accounts 41 or 43. The posting looks like this: Dt 08 Kt 43 (41).
Which accounts does it correspond with?
Account 08 can correspond with the following accounts.
From the debit of account 08 to the credit of accounts:
- Account 02 - when calculating depreciation of fixed assets that are used for modernization or creation of other operating systems;
- Account 05 - when calculating depreciation of intangible assets that were used to create other fixed assets or intangible assets;
- Account 07 - regarding the cost of equipment that was transferred for installation at the site;
- Account 10 - regarding the cost of materials that were used for the construction or modernization of the OS facility;
- Count 11 - when transferring young animals to the main herd;
- Account 16 - regarding the deviation in the price of inventories that were used in the creation of the fixed asset;
- Account 19 - when writing off VAT tax, which is not subject to reimbursement from the budget;
- Account 23 - when writing off the costs of auxiliary production to increase the cost of the capital investment object;
- Account 26 - when writing off general business expenses to increase the value of the capital investment object;
- Account 60 - when reflecting non-current assets received from suppliers, reflecting construction costs;
- Account 66 - when calculating interest on short-term loans and credits with the help of which the capital investment object was acquired (until it was accepted for operation);
- Account 67 - when calculating interest on long-term loans and credits with the help of which the capital investment object was acquired (until it was accepted for operation);
- Account 68 - when writing off amounts of non-refundable taxes on a capital investment object;
- Account 69 - when reflecting the accrual of social contributions on the salaries of workers who were involved in work with the object of capital investment;
- Account 70 - when calculating wages to employees who were involved in work with the investment object;
- Account 71 - when writing off expenses for accountable persons for a capital investment object;
- Account 75 - when one of the founders of the capital investment object makes a contribution to the authorized capital;
- Account 76 - when reflecting other services related to the commissioning of a capital investment facility;
- Account 79 - upon receipt or transfer of capital investment objects to the parent organization or branch;
- Account 80 - when transferring a capital investment object as a contribution under a joint activity agreement;
- Account 86 - upon receipt of a capital investment object in the form of investments or financing;
- Account 91 - when capitalizing MTs that were identified as a result of inventory and are intended for use when working with a capital investment object;
- Account 94 - the amounts of previously identified shortages and losses are written off to the capital investment object;
- Account 96 - when creating reserves at the expense of the investment object;
- Account 97 - deferred expenses are written off to the cost of the capital investment object;
- Account 98 - capital investment items received for free are taken into account.
You might be interested in:
Account 03 in accounting “Profitable investments in material assets”, what is taken into account, correspondence of accounts, postings
According to the credit of the account, it corresponds with the debit of the following accounts:
- Account 01 - when commissioning a capital investment as an OS object;
- Account 03 – when commissioning a capital investment that is supposed to be rented out;
- Account 04 – when commissioning a capital investment as an intangible asset;
- Account 76 - when writing off part of the cost of capital investment as insurance compensation, when making claims to contractors, etc.
- Account 79 – upon receipt or transfer of capital investment objects to the parent organization or branch;
- Account 80 - upon return of the investment object upon termination of the joint activity agreement;
- Account 91 - when writing off losses, selling part of the capital investment, disposal, etc.
- Account 94 - identified shortfalls or losses in investments in assets are written off;
- Account 99 - writing off part of the cost of the investment object as a loss (as a result of an emergency, natural disaster, etc.)
Barter agreement
The registration of property received after barter differs depending on the conditions of its implementation. Thus, if both parties recognize the objects of exchange as equivalent, then they do not undertake any additional obligations. No additional payment is required, but what amount should be entered into the account on 08/08 when the asset is received? In this case, the initial price is the market value of the property being disposed of for exchange. If it is impossible to determine it, use the indicator of the possible purchase price of the incoming property.

After agreeing on the terms of a barter transaction between enterprises, the acquired assets cannot yet be considered their property. The right to ownership passes after the fulfillment of obligations by each of the counterparties. Until this moment, the amounts are registered in off-balance sheet account 002. After all points of the agreement are fulfilled and property rights are received, the accountant writes off the amounts in Kt 002.
Further registration of the receipt is carried out according to the usual procedure for receiving fixed assets or intangible assets:
- Dt 08 Kt 60 – the amount of incoming fixed assets is taken into account (amount excluding VAT).
- Dt 19 Kt 60 – VAT on acquired property is reflected.
- Dt 01 Kt 08 – the object was put into operation and accepted for accounting.
What connection do accounts 90, 62 and 63 have in the balance sheet with account 08?
The organization can realize unfinished capital investments. Their sale will be reflected in accordance with the financial policy adopted by the organization:
- Dt 62 Kt 90 (91).
The actual cost of such investments is written off, accordingly, as a debit to one of these items:
- Dt 90 (91) Kt 08.
A contract for the purchase of property may provide for payment in installments. If the purchasing company fails to repay the obligation for a long time, its debt may be considered doubtful. A reserve is created for it:
- Dt 91 Kt 63.
Account 08 08: typical transactions
Having studied the features of determining the initial cost of assets and registering them, we will consider the main account assignments:
Typical entries for account 08
| Dt | CT | Characteristics of a business transaction |
| 08.1 | 10 | The costs of materials for the acquisition of a plot of land are taken into account |
| 08.4 | 75.1 | Intangible assets were accepted from the founders as a contribution to the initial capital |
| 08 | 02 | Accrued depreciation amounts for fixed assets |
| 08.3 | 10 | Materials used in construction were written off as the cost of fixed assets |
| 08.6 | 11 | Young cattle were transferred to an adult herd |
| 08.8 | 70 | The costs of developing innovations include the salaries of researchers |
| 08.8 | 08.3 | Equipment transferred for conservation |
| 08 | 19 | The costs of purchasing fixed assets include VAT paid on it and not reimbursed by the state |
| 08 | 60 | Invoices from suppliers for purchased property are accepted for payment |
| 08 | 66 | Interest accrued for the use of short-term loans for the purchase of fixed assets and intangible assets is taken into account |
| 08 | 69 | Insurance payments have been accrued to employees involved in the creation of intangible assets |
| 08 | 80 | Assets received as a contribution to joint activities |
| 08 | 98.2 | Assets received free of charge were registered at market value |
| 08 | 86 | Property received as an investment |
08 accounting account for the loan reflects the amount of write-off of property when:
- putting it into operation;
- losses as a result of an emergency;
- shortages identified after inventory;
- sale or partial liquidation.
Indicators of non-current assets mainly characterize the activities of the enterprise. The further organization of accounting for fixed assets and intangible assets depends on the accuracy of the calculation of the initial cost of property. Account 08 was created to collect the necessary information about incoming assets in order to reflect as fully as possible all types of expenses for their acquisition.
R&D accounting
In March 2015, Technocrat JSC carried out work to create an improved wood processing technology. The work was carried out with the involvement of employees of JSC "Technocrat", in connection with which expenses were incurred for:
- salaries of employees of the innovation and development department - 184,300 rubles;
- insurance premiums from the salaries of employees of the innovation and development department - .215 rubles;
- materials used in the development process - 177,250 rubles.
The accountant of Tekhnokrat JSC made the following entries:
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Document |
| 08.8 | The calculation of wages for employees of the innovation and development department is reflected | 184,300 rub. | Payroll | |
| 08.8 | 69.1, 69.2, 69.3 | The amount of accrued insurance premiums on the salaries of employees of the innovation and development department is reflected | .215 rub. | Payroll |
| 08.8 | 10 | The cost of materials spent in the development process is reflected | 177.250 rub. | Sales Invoice |