In the process of financial and economic activity, enterprises strive to make financial investments, using temporarily free funds for this. Such actions are taken in order to prevent inefficient use of available resources and maximize company profits.
Within the framework of this topic, we will talk about the concept and types of securities, about the work of position 59, consider the correspondence of accounts, standard accounting entries, and also focus on one of the practical examples.
Definition and classification of documents giving the right to a share in capital
By this category, experts mean monetary documents that confirm the right to own capital or indicate the nature of the relationship between the owner of the document and its issuer.
The functions of such monetary documents as an object of market relations are as follows:
- mobilization of savings of individuals and free resources of enterprises to cover expenses;
- regulation of money circulation;
- acting as a source of investment designed to create new companies or develop existing ones;
- fulfilling the role of a credit settlement instrument;
- redistribution of funds between industries and sectors of the economy;
- granting the right to capital;
- transfer of rights to manage the company;
- acting as a source of income.
In world practice, all existing financial instruments are divided into basic and derivative financial instruments or derivatives. In the first case, we are talking about documents based on the property right to a certain asset.
If we are talking about derivatives, then in this case we are talking about a non-documentary form of right to property that appears due to a change in the value of the financial instrument that underlies it.
If we take the form of issue as a basis, then we can distinguish issue-grade securities, for example, shares, and non-issue securities, for example, checks and bills.
If we classify documents according to the order of ownership, then we should distinguish between registered, warrant and bearer papers.
In practice, there are many other criteria by which designated monetary settlement documents can be classified.
What typical transactions contain the debit and credit of account 58?
Let's look at several examples of using accounts Dt 58 - Kt 58 .
Example 1
Zarya LLC issued a loan to another organization.
In this case, Zarya LLC will reflect the following entries:
Dt 58.03 Kt 51 - loan issued.
Dt 58.03 Kt 91 - interest on the loan has been accrued.
Dt 51 Kt 58.03 - the amount of interest was credited to the account of Zarya LLC
Dt 51 Kt 58.03 - the loan is repaid by the borrower.
IMPORTANT! An interest-free loan cannot be recognized as a financial investment due to the fact that it does not meet one of the criteria established by clause 2 of PBU 19/02 - the ability to bring economic benefit.
For information on the procedure for recording interest on a loan for the purpose of calculating income tax, see the article “How to recognize interest on a loan.”
Example 2
In March 2021, the organization acquired 120 shares of issuer X, of which 50 were worth 1,000 rubles. each and 70 pieces - 1,500 rubles. In April, 100 shares were sold at a price of 2,000 rubles. The accounting policy stipulates that the valuation of shares upon disposal is determined at the average initial cost.
Postings:
Dt 58.01 Kt 76 - shares worth 1,000 rubles. registered for a total amount of 50,000 rubles. (50 × 1,000).
Dt 58.01 Kt 76 - shares worth 1,500 rubles. capitalized for a total amount of 105,000 rubles. (70 × 1,500).
Dt 76 Kt 91.1 - sale of shares - 200,000 rubles. (100 × 2,000).
Dt 91.2 Kt 58.01 - expenses incurred in connection with the sale of shares - 129,167 rubles. (100 × (50 × 1,000 + 70 × 1,500) / (50 + 70)).
IMPORTANT! The cost of a retiring financial investment in accordance with clause 26 of PBU 19/02 “Accounting for Financial Investments” can be determined by the initial cost: the calculated average of the first acquired investments, each unit.
For information on the procedure for taxing VAT on sold shares, see the article “Is the sale of securities subject to VAT?”
The meaning of position 58 in accounting
The designated account is designed to provide detailed accounting of the company's cash investments.
Analytics for this account is carried out for separate sub-accounts, including:
- 1 – accounting for investments in shares and shares;
- 2 – investing in debt instruments.
Investments of a company or organization are reflected in the debit part 58 of the account and the credit part of those positions where the values that are subject to transfer on account of such investments are recorded. Thus, the company’s purchase of securities of third-party companies is recorded in the debit part of position 58 and the credit part of position 51 or 52.
If an amount is written off that exceeds the purchase price of debt obligations over their nominal price, then the accounting department reflects these funds as a debit of 76 and a credit of 58 positions.
If the company decides to sell existing securities or pay off their value, then these funds are recorded in debit 91 and credit 58 positions.
What does the score 58 show?
Dt 58 - Kt 58 in accordance with the instructions to the Chart of Accounts approved by the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation “On approval of the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities” dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n (hereinafter referred to as the Instructions) reflect information about investments, the company and loans provided by it :
- shares and shares (subaccount 58.01);
- securities (subaccount 58.02);
- loans (subaccount 58.03);
- deposits under simple partnership agreements (subaccount 58.04);
- other financial investments.
The above analytics for Dt 58 - Kt 58 are presented in the Instructions.
The organization also has the right to open its own sub-accounts to account 58 for the financial instruments it uses, which must be reflected in the working chart of accounts.
Dt 58 - Kt 58 are used in conjunction with the following accounts:
- 51 “Current accounts”;
- 52 “Currency accounts”;
- 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”;
- 80 “Authorized capital”,
- “Other income and expenses”, etc.
Count 58 – active or passive?
The placement of the organization's investments is carried out in the debit of account 58 in correspondence with cash or other accounts - 50, 52, 51, 80, 76, 75, 98, 91. The credit of account 58 reflects the repayment of loans, the excess of the purchase price of securities over the nominal, redemption and sale Central Bank, return of assets on deposits of a simple partnership and other operations. Correspondence is carried out with accounts - 52, 51, 76, 90, 80, 91, 99. The balance of active account 58 shows the balance of financial investments as of a given date.
Important! 58 account in the balance sheet is displayed together with the account. 73 and 55 (in terms of loans to staff and deposits) on lines 1170, 1240, depending on the validity period minus the account balance. 59, where reserves for impairment of investments are formed.
Characteristics of an accounting account 58
Account 58 in accounting is represented by balance sheet lines 1170 and 1240 “Financial investments” and reflects the implementation of various actions with changes in the size of the controlled company’s contribution to securities (hereinafter referred to as securities), shares and bonds of other enterprises, fixed capital of organizations, the cost of loans issued to other entities.
Analytical accounting for this account is structured in such a way as to provide access to information about short-term and long-term deposits. If investments are accounted for within several interrelated companies, the functioning of which is maintained by consolidated financial statements, then entries to account 58 are made separately.
Deposits in interest-bearing bonds and other types of securities, as well as loans issued to other organizations are reflected in account 58 if their repayment period is no more than 1 year. Investments in securities for which there is no set redemption period are also displayed on account 58, provided that these deposits were made without the purpose of generating income on them for more than 1 year.
The actual expenses for the purchase of assets as financial investments are considered:
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
- funds that are paid in accordance with the agreement to the seller;
- funds paid by enterprises for information and consulting services related to the intention to make financial investments;
- commission that is paid to the intermediary when carrying out a transaction for the acquisition of assets as investments, etc.
Account 58 “Financial investments”
Active accounts display information about the funds (in monetary equivalent) that the organization has at its disposal; these can be bank accounts, property in the warehouse and in operation.
Analytics for account 58.05 Acquired rights as part of the provision of financial services
Analytical accounting is maintained for objects in which investments are made (sub-account “Counterparties”) and grounds (sub-account “Agreements”). Each object is an element of the “Counterparties” directory. Each basis is an element of the “Contracts” directory.
| Subconto | Total accounting | RPM only | Accounting in currency |
| Counterparties | Yes | No | Yes |
| Contracts of counterparties | Yes | No | Yes |
Use of account 58.05 Acquired rights as part of the provision of financial services. Postings
According to Clause 44 of PBU, financial investments (investments) are taken into account in the amount of expenses actually incurred for their acquisition.
Example 1. Accounting for an assignment agreement.
Organization Alpha acquires the accounts receivable from Organization Betta. The amount of debt is 200,000 rubles, the purchase price is 180,000 rubles. Let's consider the reflection of the acquisition of debt and its subsequent repayment by the Betta organization in the accounting of the Alpha organization: 1. Acquisition of receivables:
Debit 58.05 Credit 76,180,000 rub.;
2. Transfer of money for acquired debt:
Debit 76 Credit 51,180,000 rub.;
3. Repayment of acquired debt by the Betta organization:
Debit 51 Credit 58,180,000 rub.
Debit 51 Credit 91 20,000 rub.
Example 2. Acquisition of receivables with subsequent assignment
Organization Alpha acquires the receivables of organization Betta, the amount of which is 100,000 rubles, for 60,000 rubles. and subsequently assigns it to the Gamma organization for 80,000 rubles. Let us reflect in the accounting records of the Alpha organization the acquisition of Betta’s debt and the assignment of the right of claim:
1. Acquisition of the right to claim:
Debit 58 Credit 76 RUB 60,000;
2. Transfer of money for the acquired right of claim:
Debit 76 Credit 51 60,000 rub.;
3. The fact of assignment of the right of claim to the Gamma organization is reflected:
Debit 76 Credit 91 RUB 80,000;
4. The assigned debt is written off:
Debit 91 Credit 58 60,000 rub.
To reflect in 1C Accounting, the document Debt Adjustment is used. In this case, the correct entries and amounts are reflected in the reporting, for example, in the income statement.

Account
Legislative basis for the balance sheet line “Financial investments”
All financial actions carried out by the organization are regulated by the relevant legislative acts of the state on accounting. The balance sheet line “Financial investments” is regulated by the following regulatory documents:
- Regulations on accounting audit PBU 19/02 based on order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 10, 2002 No. 126 (amended in 2010);
- Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ;
- Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In order to make financial investments fully and legally, an enterprise must comply with all standard requirements established at the legislative level. The legal regulation of this topic includes several stages. The decrees of the President of Russia are considered the highest, and the documents of the organization itself are considered the lowest, according to the industry direction and the amount of economic benefit received.
Wiring cannot be done: D 60 K 58
Financial investments"
58.1 - “Units and shares”;
58.2 - “Debt securities”;
58.3 - “Loans provided”;
58.4 - “Deposits under a simple partnership agreement”, etc.
UNIT - a share of the capital of a company, which gives the right to participate in general meetings of shareholders, to receive dividends and part of the company’s property upon its liquidation. P. is expressed in a specific document - a certificate, to which coupons for receiving dividends are attached.
SHARES are securities issued by a joint-stock company, the owners of which are granted all property and personal rights associated with the ownership of a share: a) the right to receive dividends, depending on the size of the corporation’s profit; b) the right to participate in the management of the corporation by voting at meetings; c) the right to receive part of the property after the liquidation of the corporation. Rights are exercised in an amount proportional to the size of the shares.
D 58 K 51 –
the emergence of a financial investment object is reflected (when transferring or paying for this object from a current account);
D 58 K 76 –
the occurrence of debt to counterparties is reflected (if payment for financial investment objects will be made after obtaining ownership rights to them, for example, in the case of securities).
D 76 K 91 —
D 91 K 58
– reflects the negative difference between the purchase and par value (or between the par and purchase value) of the acquired debt securities.
In account 58, investments are accounted for at actual cost (in the amount of costs incurred for their acquisition).
Financial investments are the second most liquid after cash in hand and in current accounts.
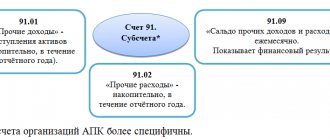
Account 59 “Reserves for the impairment of financial investments” is intended to summarize information on the availability and movement of reserves for the impairment of the organization’s financial investments.
The reserve is formed at the expense of financial results (as part of operating expenses), which is reflected in the accounting entry as a debit to account 91 “Other income and expenses” and a credit to account 59 “Provisions for impairment of financial investments.” A similar entry is made when increasing reserves in the event of a further decrease in the estimated value of financial investments.
The reserve is reduced (used) in the following cases: if the estimated value of the relevant assets in the reporting period has increased, if their value is no longer subject to a sustained significant decrease, as well as upon disposal of these assets. In this case, an entry is made in the debit of account 59 “Provisions for impairment of financial investments” in correspondence with the credit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”.
In the financial statements, financial investments for which an impairment reserve has been created are reflected at their book value less the amount of the reserve.
In the net balance sheet, when reflected in the asset, the difference between 58 and 59 accounts is reflected. Those. There is no account in the liabilities side of balance 59!
Reserve for depreciation of financial investments” (passive, contractual to account 58).
If we have a large number of shares of one company, and its shares have sharply decreased in price, we cannot reflect these changes in account 58, because this will lead to misstatement of the financial statements.
The reserve for impairment of financial investments is created by the following entry:
D 91.2 K 59
D 59 K 91.2 –
reserve amount restored
As soon as financial investments are disposed of, the corresponding reserve amounts are written off to other income of the enterprise (91.1).
Regulatory regulation of the accounting of bills of exchange is carried out by the “Regulations on promissory notes and bills of exchange” dated August 7, 1937.
When purchasing bills of exchange, they are accounted for at actual cost on account 58, disposal is reflected through account 91.
D 60 K 91
– we pay the supplier with a bill of exchange.
If we purchased a bill with a face value of 1000 rubles, and with a discount it was transferred to us for actually 900 rubles, then we will reflect the acquisition price in accounting - 900 rubles.
Upon disposal of this bill, we will make the following entries:
D 60, 76 K 91.1 1000
D91.2 K 58 900
A credit balance of 100 rubles is formed, and income tax is paid on it.
If we provide a loan, we make the following entries:
D 58 K 51
If our main activity is the purchase and sale of financial investments, then income and expenses are charged to account 90, otherwise - to account 91.
When transferring shares, bills, i.e. When they are disposed of and sold, the following entry is made:
D 90.1, 91.2 K 58
Wiring cannot be done: D 60 K 58
D 76 K 91.1
– interest accrued on loans is reflected;
If the loan is provided to an employee, then interest will be accrued to account 73.
D 73 K 91.1
If we have been accrued dividends on the objects of any financial investments, then we will reflect their receipt by posting:
D 51 K 91.1
58.4 — “Deposits under a simple partnership agreement”
(joint activity of enterprises, which is carried out on the books of one of the enterprises);
When depositing assets, account 58 is used.
Under the simple partnership agreement, funds were deposited from the current account:
D 58 K 51
The following materials were included under the simple partnership agreement:
D 58 K 10
And if we contribute them at a higher price, then the transfer of materials will have to be reflected as follows:
D 58 K 91.1
Accounting for loans from the lender - entries for issuing loans
If a company issues a loan to another organization, then the transactions will be as follows:
- Debit 58 Credit 51 (50, 52, 40 ...) – entry for the loan issued.
As can be seen from the posting, a loan can be provided not only in the form of a sum of money, but also in the form of property (materials, fixed assets, etc.). The amount that will be taken into account in this case is the value of goods/materials, etc.
When issuing an interest-free loan to a legal entity, the amount is taken into account in the debit of account 76 and the credit of the account for issuing funds or property (50, 51,10, 40, etc.).
Loan repayment is documented by posting:
- Debit 51 (50, 40...) Credit 58 (76).
Regarding the taxation of loans with VAT, there are two opposing points of view. The first is based on the fact that there is a transfer of ownership, which is an implementation (Article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Sales are subject to VAT. The opposite point of view: when receiving and returning a loan in the form of goods, there is no object of VAT taxation.
Entries for VAT accounting on loans in kind:
- Debit 91.2 Credit 68 VAT – when issuing a loan
- Debit 19 Credit 58 (76) – accounting for input VAT when repaying the loan.
The issuance of a loan to an employee of an organization is documented by posting:
- Debit 73 Credit 50 (51).
The return is processed by return posting.
Example:
The organization issued an interest-free loan to a legal entity in the amount of 320,000 rubles.
Postings for issuing a loan:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 76 | 51 | Issuing an interest-free loan | 320 000 | Payment order ref. |
| 51 | 76 | Loan repayment | 320 000 | Bank statement |