The problem of purchasing and issuing workwear in organizations was, is and will be, because the budget is very sensitive to the cost of PPE.
Many people are constantly underfunded, and it doesn’t matter what amount you budgeted for during the annual budgeting. Upon review, they will definitely cut back, especially in the conditions of an eternal crisis in the country, when everyone survives as best they can.
Therefore, in this article we will look at how to extend the period of wearing PPE in order to save money without compromising the life and health of workers, and what documents need to be completed so that the employer feels protected.
If after reading the article you have something to add, then join in the comments, ask questions, give examples from practice and just keep up the dialogue.
Extending the wearing period of workwear
Extending the period of wearing special clothing is a very controversial issue, and if organized without adhering to the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 290n, then administrative liability is inevitable.
There is judicial practice that suggests that everything seems to have been done correctly, but there is no additional information and the employer faces administrative liability for failure to provide personal protective equipment to workers.
Therefore, think 100 times whether you really need it, and then decide whether you should save money due to risks in the future, because PPE comes in different classifications and not every type can be extended.
But it is necessary to talk about how to draw up an act for extending the period of wearing workwear and provide a sample because of the large number of questions, especially from budgetary organizations.
They have eternal problems with financing, and besides, workwear is purchased through a contract system in the procurement sector, and this is a very long process and it turns out that the period of wearing workwear for workers ends even before purchasing new ones.
How to extend the wearing period of PPE
All legal requirements concerning the procedure for the acquisition, issuance, use, storage and care of PPE are established by the Intersectoral Rules for Providing Workers with Work Clothing, Safety Footwear and Other Personal Protective Equipment (Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 290n).
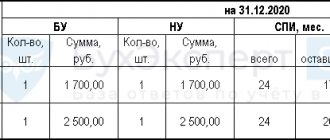
And to begin to understand how to extend the period of wearing PPE, you need to note that all issuance, as well as return of personal protective equipment by employees, must be recorded in a personal accounting card.
The period during which an employee uses the personal protective equipment issued to him is indicated in the industry standards for issuing PPE and those developed by the employer. You can read about how to prepare a list of issuing PPE for each position indicating the period of use in my other article.
And this period does not begin to be calculated from the moment of actual use, for example, you were issued winter workwear in the summer and accept for yourself that the wearing period must be counted from October.
This is fundamentally incorrect, because the use of personal protective equipment by an employee begins from the moment of actual issue and the date on the personal card (clause 13 of Order No. 290n).
And, of course, when the time comes to issue new workwear, but the old one is still in good condition, the employer’s natural desire to save money arises.
This situation often occurs among workers such as cleaners, janitors, cloakroom attendants, archivists, and including engineering and technical personnel.
And just like that, on the basis of the commission you created to determine the suitability of PPE, you cannot inspect the workwear, simply draw up a report and automatically allow further use by the employee. It's not that simple.
Because, on the basis of clause 22 of Order 209n, personal protective equipment that was returned by employees at the end of the period of use can be reissued, but after taking care measures, washing, cleaning, repairing, and so on.
That is, it turns out that the employee, in any case, must hand over the workwear to the warehouse when the deadline expires, for example, after 12 months.
Certificate of extension of the wearing period of workwear (sample)
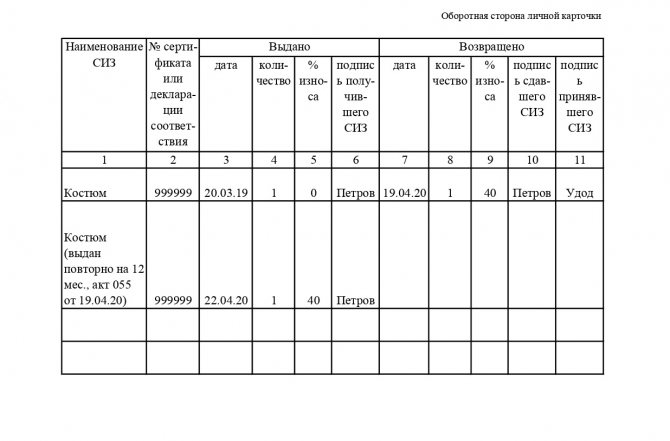
The return of workwear to the warehouse must be recorded in the acceptance certificate, and if it is still in a suitable condition for further use, then the commission must determine the percentage of wear.
Everything about how to determine the percentage of wear and detailed methods to simplify your work is given in this article.
Having determined whether the protective clothing is suitable for further use, it is necessary to record this fact with an inspection report of the personal protective equipment, in which the commission must make a conclusion about the possibility of further use, indicating the period and percentage of wear.
You can use it in your work.
Definitely needs to be duplicated
percentage of wear in the personal clothing issuance card, repeating this procedure for each personal protective equipment.
Because when issuing used PPE to an employee, you will need to indicate that it was issued second-hand with a certain percentage of wear.
For example, a janitor's suit expired in the spring, he returned it to a warehouse, and the commission determined that the percentage of wear and tear was 40%, recording this in the card and in the act.
It was washed, repaired and issued again in the fall, but this time indicating that the issue was used workwear.
Please note that the employer does not have the right to allow an employee to perform his or her job duties without personal protective equipment. After all, it turns out that the employee handed it in on Tuesday, and received it back on Friday, after washing and repairing, and during these three days you simply cannot allow him to work.
This is how the extension of the wearing period of workwear looks in a difficult way. But you need to act in exactly this sequence, because if it doesn’t:
- data on the return of personal protective equipment by the employee,
- documentary evidence that PPE is suitable for further use;
- confirmation of measures taken to care for PPE;
- percentage of PPE wear,
then if an accident occurs, the inspector or the court will come to the unequivocal conclusion that the employee was not provided with personal protective equipment.
The procedure for organizing the storage and care of personal protective equipment
In addition to how to hand over workwear, you need to know about the established rules for storage and care. According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, services are provided at the expense of the employer represented by the company.
Note! Storing personal protective equipment means keeping it in specially designated places that can ensure safety - for example, in a dressing room.
In situations where this is required by established working conditions, the direct employer (in particular in structural divisions) needs to install:
- specialized dryers;
- specialized chambers for drying, dust removal, degassing, decontamination and neutralization of personal protective equipment.
The procedure for caring for personal protective equipment includes a specially developed set of measures aimed at carrying out regular dry cleaning, washing, degassing (including disinfection), and in some established situations - repairing and replacing identified technically faulty equipment.
In the event that the employer does not have the appropriate technical capabilities for this, without which it is impossible to ensure the proper performance of work on the care of personal protective equipment, it is permissible to turn to specialized contractors for help. A mandatory criterion is the availability of an appropriate license and a signed agreement for the provision of services.
Note! Without documentary evidence, the contractor’s work is considered irrelevant with all the ensuing consequences.
Full range of labor protection, civil defense and emergency services
Enter your phone number and I will calculate an estimate for your tasks. Enter without the eight. “Bureau of Ekaterina Vorontsova” – professional solutions to your problems: with high quality and on time!
Employer's liability
The employer faces a fine for failure to provide PPE for employees, because if a serious, fatal or group accident occurs due to the fact that the organization decided to save, in the amount of:
- for officials and individual entrepreneurs – from 20,000 to 30,000 rubles;
- for legal entities – from 130,000 to 150,000 rubles.
Moreover, there has been similar judicial practice and the judge will adhere to a similar position when considering the case.
Therefore, either do everything right, or don't take risks.
What kind of PPE can be used to extend the wear period?
But, thus, absolutely all workwear that remains in good condition after the wear period has expired cannot be reused. And this begs the question: “What kind of PPE can be used to extend the wear period?”
You need to approach this issue with caution!
Because in addition to the percentage of wear, it is necessary to take into account the protective properties of workwear, which may decrease over time, and accordingly, proper safety of workers will not be ensured.
The Ministry of Labor even says this in its explanatory letter dated November 2, 2021 N 15-2/ОOG-3886, that the period of use of workwear should not exceed the permitted storage period.
And this applies to personal protective equipment that loses its protective properties during storage. This information is marked on personal protective equipment or on packaging; this information can also be found in the passport or instructions (clause 12 of TR CU 019/2011).
And if the passport indicates that the worker can use the PPE only for 2 years, then
the period of
use
cannot be
extended .
If you have simply stored PPE in a warehouse for quite a long time, then before issuing it to an employee, you will have to transfer it to the manufacturer or to a laboratory to determine the protective properties.
You cannot determine this “by eye,” and you should not take such responsibility for the life and health of personnel without knowing for sure whether the protective properties have been preserved or not.
And this event is costly and troublesome, so I do not advise you to take risks and renew only those personal protective equipment that will not be used in harmful and dangerous working conditions.
Why is working at height dangerous?

There is a high probability that the employee may fall down himself or something will fall on him from above. There are many reasons for this:
- improper organization of work;
- suddenly changing weather conditions;
- fatigue from heavy physical activity;
- incomplete set of personal protective equipment;
- falling of tools, piece goods from lifted containers, structural elements, etc. onto the employee.
EXAMPLE:
In the Oryol region, at ZAO Mir Roofs, workers were installing a metal covering on a hangar building. One of the roofers in safety equipment climbed to a height of about five meters using a makeshift ladder, could not resist and fell down. The worker's safety belt was not connected to the safety rope, and the safety helmet fell off his head because it was not fastened properly. The roofer died on the spot.
EXAMPLE:
In Orenburg, employees of SK Promyshlennaya - 1 inspected the roofs. Having discovered massive icicles, one of them, without using a safety net, began dumping snow and ice onto the sidewalk adjacent to the building. The worker could not stay on the sloping metal roof and died as a result of the fall.
The risk of injury to workers due to falls is greatly reduced when modern fall protection equipment is used. According to Rosstat, one of the most common types of occupational injuries is falling from a height (more than 30% of accidents). The consequences of such falls are severe and lead to severe injuries or even death to workers. Accidents when working at height most often occur for several reasons, including:
- violation by the employer of legislation obliging workers to provide free necessary personal protective equipment, etc.;
- employee ignorance of safety rules when working at height;
- lack of awareness of the types and purposes of fall protection equipment;
- ignorance of the rules for using such protective equipment.
In order to reduce injuries when working at height, the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation issued Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated March 28, 2014 No. 155n (as amended on June 17, 2015) “On approval of the Rules for labor protection when working at height.” The rules regulate work during which the employee must wear a safety harness, and work in which the use of safety harnesses is necessary. In accordance with current regulations, when restraint or work positioning is necessary, the employee must, at a minimum, use a safety harness. For work involving the risk of falling from a height, the employee is required to wear a safety harness and be secured to it with a lanyard with a shock absorber that absorbs the force of the fall. It should also be noted that, according to this Order, verification of belts and harnesses with a static load is canceled, since during such verifications the protective properties of PPE from falling from a height are significantly reduced.
It should be noted that 18% of deaths occur from falls from a height of less than 2 m, and 60% of cases of falls from height cause subsequent disability of workers. In 80% of cases, a person is seriously injured or killed due to failure to use personal protective equipment (PPE). The main reasons for not using fall protection PPE in the workplace are the following: “the models of belts/harnesses provided are inconvenient when working at heights, cause discomfort, have an incomprehensible design, and take too long to put on.” Labor safety services of enterprises must constantly work with employees, informing them about the rules for working at height, the risks of not using PPE, choosing high-quality, comfortable safety harnesses, equipment for working at height, and monitoring the use of PPE by employees in accordance with standard industry standards, working conditions and corporate standards.
Today, the Russian fall protection market offers modern, high-quality and inexpensive models with improved ergonomics and accessories for fall protection (anchor lines, carabiners, slings, locking devices, etc.) - an affordable and high-quality solution to ensure safety when working at height.
You can get acquainted with a large range of fall protection equipment by following the link to the Fire Safety online store in the “Insurance Equipment” section
Criteria and concepts when working at height
Work at height includes work when:
a) there are risks associated with a possible fall of an employee from a height of 1.8 m or more; b) the employee ascends a height exceeding 5 m or descends a height exceeding 5 m along a vertical ladder, the angle of inclination of which to a horizontal surface is more than 75 degrees; c) work is carried out on sites at a distance closer than 2 m from unfenced differences in height of more than 1.8 m, and also if the height of the fencing of these sites is less than 1.1 m; d) there are risks associated with a possible fall of an employee from a height of less than 1.8 m if work is carried out on machines or mechanisms, water surfaces or protruding objects.
Procedure for undergoing periodic inspections

As part of the new rules, the main document accompanying PPE, including defining the procedure for inspections, is “Instruction Paragraph 92 of the Rules” states that “PPE of workers must be taken into account and maintained in technically sound condition with the organization of their maintenance and periodic checks specified in documentation “Competent person” (these are persons with safety group 3 when working at height and who have undergone appropriate training in PPE inspection). Based on the results of inspections, based on the conclusion of a competent person, PPE is allowed for further use, otherwise it is prohibited, rejected or written off. According to paragraph “95 of the Rules”: “...Dynamic and static tests of PPE against falls from a height, with an increased load in operating organizations are not carried out...”. It turns out that from May 5, 2015, any personal protective equipment must undergo periodic testing of suitability for further use. Periodic inspections must be carried out by competent personnel who have undergone appropriate training or by organizations accredited by the manufacturer. Depending on the operating conditions and taking into account the manufacturer’s requirements, based on his conclusion, PPE is either allowed or rejected.
3. Fines
If, during an inspection of your enterprise, the Labor or other Inspectorate discovers that PPE is not certified or has not undergone periodic inspection, much less the absence of the necessary PPE, then this can lead to serious consequences.
Since 2015, fines for violations of labor safety rules and, specifically, for failure to provide workers with personal protective equipment have increased. According to Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, these violations are subject to the imposition of an administrative fine on officials in the amount of 20,000 - 30,000 rubles; for organizations 100,000 - 150,000 rubles.
Maximum service life of PPE when working at height
! The shelf life of protective equipment made of synthetic materials, subject to the rules of operation and storage, is determined in the manufacturer’s documentation, and usually does not exceed:
a) for synthetic ropes - 2 years or 400 hours of operation; b) for personal protective equipment against falls from a height that has non-metallic elements - 5 years; c) for helmets - 5 years.
Prohibition of the use of mounting and safety belts
! When using a mounting belt, in the event of a fall, there is a large load on the spine, a high risk of paralysis of the lower extremities and a high risk of falling out of the belt during a jerk.
Paragraph 104: The Rules prohibit the use of strapless safety belts when carrying out work with a possible risk of falling due to the risk of injury or death to the worker due to the shock load on the worker’s spine.
Clause 98: The Rules defines the elements of safety systems for working at height: harnesses (safety, restraining, positioning, sitting).
Belts can only be used to hold you in a working position without the risk of falling in a safe area!
Solutions for organizing safety systems using modern fall protection equipment
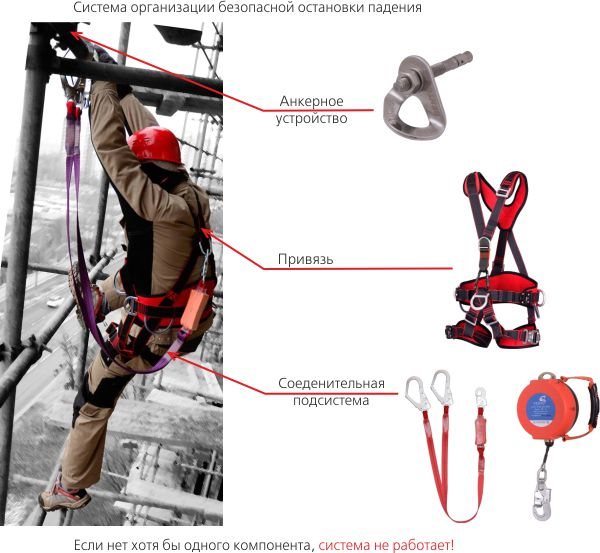
A fall protection system is a set of fall protection equipment aimed at preserving a person’s life and health in the event of a fall.
The safety system consists of:
- Anchor point.
- Connecting element (carabiner, loop) - in the online store section.
- Shock absorption systems (shock absorber).
- Intermediate connection (sling, fall arrester) - in the online store section.
- A full body harness with shoulder and hip straps or a belt - go to the online store section.

Main conclusions
All employers have a great desire to somehow save money on issuing personal protective equipment, because staff turnover, transfers within the organization, and simply the desire to invest this money in the business so that the margin is larger can put a large burden on the budget.
But everything is not as simple as it seemed at first glance, and extending the period of wearing workwear is not just about drawing up an act and continuing to wear it. No, there is one very significant detail here, without knowing which the employer can be held administratively liable.
A properly organized procedure, a sample of actions and a formalized act of extending the period of wearing workwear will allow the enterprise to save a little on the budget.
I wish you efficient and safe work!
If you have any questions or perhaps you have something to add or complement, write in the comments, this is important for both the author and the readers. If you need help with paperwork, please contact us.