Employer's name and representative
In the first part of the employment contract being analyzed, there is no information about the representative of the employer who signed the employment contract and the basis by which he is vested with the appropriate powers (paragraph 5, part 1, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Who is Lipatov? By virtue of what (Charter, power of attorney) is he entitled to enter into an employment contract?
By the way, it’s not critical, but advice to personnel officers, still check the endings in the text: “in the person of Sergei Dmitrievich Lipatov, referred to as.”
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation requires specifying the name of the employer, without deciphering in what form this should be done. If the constituent documents indicate both names of the legal entity (full, abbreviated), then it is better to indicate them.
“Profi LLC” is clearly not the full name of the organization, because usually the legal form is indicated in full. In my humble opinion, this is not a mistake, because... It is quite possible to identify the employer, especially since the employment contract must indicate the employer’s TIN and the employee’s place of work.
In accordance with Art. 56 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the parties to the employment contract are the employer and the employee. Therefore, in the specified employment contract, it is necessary to replace in the text “hereinafter referred to as “Organization”” with “Employer”, especially since there is an employee.
Basic provisions
Employment contract, according to Art. 56 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is a legally binding agreement between an employee and an employer, under the terms of which the employee performs work duties, and the employer, in turn, pays wages on time. In addition to the rights and obligations of the parties, the contract usually contains clarifications regarding vacations, working hours, compensation, etc.
Thus, in short, an employment contract will create a solid basis for protecting the rights of both the employer and the employee he employs.
By the way, an employee can quite legally perform labor duties on the basis of GPC agreements, for example, a contract or the provision of paid services. However, none of them gives the worker the same guarantees that an employment contract provides.
Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation prescribes a written form of an employment contract. However, in practice, a person often begins to perform work duties with the consent of the employer before the actual signing of the contract. In such cases, even an agreement not drawn up on paper will be regarded as concluded, and the employer will have exactly three days to conclude a written agreement with the employee allowed to work.
Place of work and job function

Place of work
Place of work is unclear. It doesn’t look like a structural unit - OJSC Profi (the difference with the employer is only in the organizational and legal form (LLC and JSC). Well, maybe it’s a branch (everything happens in this life) or a mistake (which is quite logical).
So, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation obliges to indicate exactly the place of work (does not disclose what is meant by it), and in the case when an employee is hired to work in a branch, representative office or other separate structural unit of the organization located in another area, the place of work indicating the separate structural unit and its location.
As a rule, as a place of work, indicate the name of the legal entity and its legal address or an indication of its location (for example, Vladimir). You will indicate the full address of the legal entity at the bottom of the employment contract (in the details of the parties).
In its letter (N 14-2/B-1012 dated November 17, 2017), the Russian Ministry of Labor expressed the opinion that the place of work should be understood as a specific organization (if the employer is a legal entity) that has its own name containing an indication of the organizational and legal form. In this case, the place of work can be either the location of the organization or a branch, representative office or other separate structural unit of the organization located in the same or in a different area.
Specifying the place of work indicating the structural unit is not a prerequisite for inclusion in the employment contract. Indication of the structural unit of the organization and its location is mandatory only in the case when the employee is hired or transferred to work in a branch, representative office or other structural unit of the organization located in another locality.
Labor function
Labor function (work according to the position in accordance with the staffing table, profession, specialty indicating qualifications; specific type of work assigned to the employee).
If, in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws, the performance of work in certain positions, professions, specialties is associated with the provision of compensation and benefits or the presence of restrictions, then the names of these positions, professions or specialties and the qualification requirements for them must correspond to the names and requirements specified in qualification reference books approved in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation, or corresponding to the provisions of professional standards (paragraph 3, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
According to Article 195.3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws, and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation establish requirements for the qualifications necessary for an employee to perform a certain labor function, professional standards in terms of these requirements are mandatory for application by employers.
The Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated June 27, 2016 No. 584 specifies the specifics of the application of professional standards in terms of requirements mandatory for application by state extra-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation, state or municipal institutions, state or municipal unitary enterprises, as well as state corporations, state companies and business entities , more than 50% of the shares (shares) in the authorized capital of which are in state or municipal ownership.
In the employment contract under consideration, the labor function is freight forwarder. According to the Qualification Directory of Positions of Managers, Specialists and Other Employees (approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation of August 21, 1998 N 37), a forwarder is an employee (technical performer) who receives and processes incoming and outgoing correspondence. There are no benefits or restrictions for this profession. There is also no professional standard.
Labor function is the basis of the employment contract
The most important component of an employment contract is the labor function (Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Labor function
– any work for a specific position in accordance with the staffing schedule, profession, specialty, indicating qualifications, as well as the specific type of work assigned. The specific type of work entrusted to an employee may constitute the content of the labor function both in itself and along with work in a particular position, profession, or specialty.
Job title
- this is an established set of responsibilities and the corresponding morals that determine the place and role of the employee in the organization. The name of the position is indicated in the employment contract in accordance with the organization’s staffing table.
This is important to know: Recognition of a civil law contract as an employment contract
Under profession
refers to the type of labor activity, occupation of a person who possesses a complex of special knowledge, skills, and abilities acquired through education.
Speciality -
This is a type of professional activity improved through special training (HR manager, surgeon), a certain area of work, knowledge.
Qualification
– level of preparedness, skill, degree of suitability for performing work in a certain specialty or position, determined by rank, class, rank and other qualification categories. The indicator that determines the level of qualification of an employee is the qualification category. The qualification category is established taking into account the complexity, responsibility and working conditions on the basis of the tariff and qualification reference book.
The performance of a labor function must be subject to the internal labor regulations of the organization. The employer's response to the performance of a labor function by an employee is the payment of remuneration in the form of wages.
Type of work and contract period
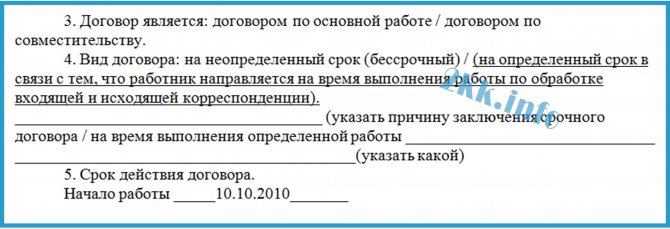
The contract in question does not emphasize what job the employee works (main or part-time). According to Art. 282 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employment contract must indicate that the work is part-time.
By the way, I don’t like it when a contract is drawn up for all occasions and is regulated by underlining.
The most common mistake encountered is not specifying the circumstances (reasons) that served as the basis for concluding a fixed-term employment contract. This is a mandatory condition (Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). All grounds are specified in Art. 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, you just need to choose and rewrite it into an employment contract.
There is no such basis, as stated in the contract (“due to the fact that the employee is sent to perform work on processing incoming and outgoing correspondence”). But, judging by the two months of work, there is: “for the duration of temporary (up to two months) work.” Here, after this sentence, you can clarify about the processing of correspondence. By the way, this should be a temporary job, i.e. it must be known that it will last no more than two months.
Start date and end date are available. If you wish, you can find fault with the deadline. From 10.10.2010 to 10.12.2010 - 2 months and one day, which is clearly more than two months of work. But the period is determined by a calendar date, so we dismiss the employee on December 10, 2010.
Contents of the agreement
There is no unified form of an employment contract, and therefore an organization can develop its own version of the document, based on which labor relations are formalized with employees.
However, in Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains a list of mandatory information that must be included in an employment contract. In particular, these are:
- personal data of the contracting parties;
- information about the employer’s representative who signs the contract and a link to the document granting him such authority;
- information about where and when the employment contract was concluded;
- place of work, if necessary, an indication of the location of the unit in which the employee is employed;
- employee’s labor function in the organization;
- work start date;
- in case of temporary labor relations - the duration of the contract, as well as a reference to the basis that served for its conclusion;
- the amount of wages, including various allowances and bonuses and the conditions for receiving them;
- working hours, as well as information about the employee’s rest;
- in case of dangerous working conditions, the required guarantees and compensation are indicated;
- the nature of the work, for example, traveling;
- working conditions;
- regulations on compulsory social insurance.
In addition, in addition to the essential conditions, additional information may be included in the employment contract at the discretion of the parties, namely:
- about the probationary period;
- on non-disclosure of secrets, commercial, official, etc.;
- about the obligation to continue working in the organization after training, if it was organized at the expense of the employer;
- about additional insurance;
- other conditions that do not put the worker in a worse position.
In addition, the employment contract may contain a section with grounds for bringing to financial liability. But if it is assumed that the employee will bear full financial responsibility, then one provision about this in the employment contract is not enough. It is important to conclude a separate agreement on liability. For example, this would be appropriate with a cashier who is being hired.
Important: if the organization does not have corporate standards regarding the preparation of documents, then the employment contract can be drawn up in accordance with GOST R 7.0.97-2016, which came into force on July 1, 2021.
For example, according to Art. 3 of the specified document, employment contract:
- formatted taking into account indents and spacing;
- has a text font from No. 12 to No. 14 inclusive;
- the text maintains a line spacing of 1-1.5;
- its headings and subsections are indented or centered in the document;
- The text must be aligned to the width of the sheet.
The rules set out in GOST are purely advisory in nature, so companies may not adhere to them.
Probation period and responsibilities

Test for employment (Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) is an additional condition, i.e. may not be specified. But dismissal due to an unsatisfactory test result (Article 71 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) will no longer work.
The absence of a probationary clause in the employment contract means that the employee was hired without a trial. But due to the fact that the term of the employment contract is 2 months (let’s not pick on one day), the test cannot be established at all.
But when concluding an employment contract for a period of 2 to 6 months, the trial cannot exceed two weeks. In other cases - 3 months (regular employee) and 6 months (manager, deputy, chief accountant).
Job responsibilities in this case are specified directly in the employment contract itself, which is not prohibited. Typically, responsibilities are defined both in the employment contract and in the job description.
The eighth point is about nothing. This is the employer’s responsibility, in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If you do not indicate in the employment contract about the employer’s obligation to provide safe working conditions, this will still be the employer’s responsibility (Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), if you do not indicate the timely payment of wages, the same thing (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Working conditions and working hours
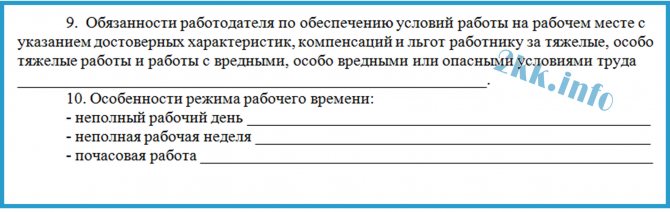
Paragraph 9 was not completed, apparently due to the absence of harmful conditions in the position of a freight forwarder.
According to the same article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to indicate in the employment contract:
- guarantees and compensation for work under harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, if the employee is hired in appropriate conditions, indicating the characteristics of working conditions in the workplace (annual additional paid leave (Article 117 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), increased wages ( Art. 147), reduced working hours (Art. 92));
- working conditions in the workplace.
The obligation to introduce working conditions in the workplace arose in 2014, but our agreement dates back to 2010. Currently, this is a mandatory condition; in the early years, there was generally a boom in fines purely for the absence of certain working conditions in employment contracts.
Here you need to indicate the working conditions based on the results of the special assessment (optimal (class 1), acceptable (class 2), harmful (3.1, 3.2, 3.3 and 3.4) or dangerous (class 4), you can also refer to the report details.
By the way, while there are no results of a special assessment of working conditions, it is still necessary to stipulate working conditions in the workplace in the employment contract. According to Letter of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated July 14, 2016 No. 15-1/OOG-2516, the department recommends that in the case of a new workplace, indicate the general characteristics of the workplace (description of the workplace, equipment used and features of working with it). Read more about working conditions in the workplace
The working time and rest time regime is prescribed only if it differs for the employee from the general rules in force for a given employer according to the Internal Labor Regulations (for example, the entire organization has a five-day workday, and our employee works on a staggered schedule or part-time, etc. .).
Employment contract with the employee
An employment contract with an employee is an agreement between the employer and the employee, according to which the employer undertakes to provide the employee with work for a specified labor function, to provide working conditions provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, a collective agreement, agreements, local regulations acts and this agreement, pay the employee wages in a timely manner and in full, and the employee undertakes to personally perform the labor function determined by this agreement in the interests, under the management and control of the employer, to comply with the internal labor regulations in force for this employer.
The employment contract specifies:
- surname, name, patronymic of the employee and the name of the employer (surname, name, patronymic of the employer - an individual) who entered into an employment contract;
- information about documents proving the identity of the employee and the employer - an individual;
- taxpayer identification number (for employers, with the exception of employers - individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs);
- information about the employer’s representative who signed the employment contract and the basis on which he is vested with the appropriate powers; place and date of conclusion of the employment contract.
The parties to the employment contract are the employer and the employee.
The following conditions are mandatory for inclusion in an employment contract:
- place of work, and in the case when an employee is hired to work in a branch, representative office or other separate structural unit of the organization located in another area - place of work indicating the separate structural unit and its location;
- labor function (work according to the position in accordance with the staffing table, profession, specialty indicating qualifications; specific type of work assigned to the employee). If, in accordance with this Code and other federal laws, the performance of work in certain positions, professions, specialties is associated with the provision of compensation and benefits or the presence of restrictions, then the names of these positions, professions or specialties and the qualification requirements for them must correspond to the names and requirements specified in qualification reference books approved in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation, or the relevant provisions of professional standards;
- the date of commencement of work, and in the case where a fixed-term employment contract is concluded, also the period of its validity and the circumstances (reasons) that served as the basis for concluding a fixed-term employment contract in accordance with this Code or other federal law;
- terms of remuneration (including the size of the tariff rate or salary (official salary) of the employee, additional payments, allowances and incentive payments);
- working hours and rest hours (if for a given employee it differs from the general rules in force for a given employer);
- guarantees and compensation for work under harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, if the employee is hired under appropriate conditions, indicating the characteristics of working conditions at the workplace;
- conditions that determine, in necessary cases, the nature of the work (mobile, traveling, on the road, other nature of work);
- working conditions in the workplace;
- a condition on compulsory social insurance of the employee in accordance with this Code and other federal laws;
- other conditions in cases provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
In this case, the missing information is entered directly into the text of the employment contract, and the missing conditions are determined by an annex to the employment contract or a separate agreement of the parties, concluded in writing, which are an integral part of the employment contract with the employee.
The employment contract with the employee may provide for additional conditions:
- on clarification of the place of work (indicating the structural unit and its location) and (or) the workplace;
- about the test;
- on non-disclosure of secrets protected by law (state, official, commercial and other);
- on the employee’s obligation to work after training for no less than the period established by the contract, if the training was carried out at the expense of the employer;
- on the types and conditions of additional employee insurance;
- on improving the social and living conditions of the employee and his family members;
- on clarification, in relation to the working conditions of a given employee, of the rights and obligations of the employee and the employer established by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms;
- on additional non-state pension provision for employees.
Sample employment contract with an employee
Wage

The employment contract must specify the terms of remuneration (including the size of the tariff rate or salary (official salary) of the employee, additional payments, allowances and incentive payments) (paragraph 5, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The monthly salary of an employee who has fully worked the standard working hours during this period and fulfilled the labor standards (job duties) cannot be lower than the minimum wage (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In our case, in 2010 the minimum wage was 4,330 rubles; according to the employment contract, the employee was given a salary of 10,000 rubles, which corresponds to the law.
Currently, throughout Russia, starting from 2021, the minimum wage is set at 12,130 rubles per month (approx. 2kk.info).
In a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, a regional agreement on the minimum wage may establish the amount of the minimum wage in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, which cannot be lower than the federal minimum wage (Article 133.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The specified regional agreement applies to all employers in the territory of the relevant entity. The law provides for the employer’s refusal to accede to the agreement if he submits a reasoned written refusal within 30 calendar days, which is subsequently sent to the State Tax Inspectorate.
According to the legal position set out in the Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated December 7, 2017 No. 38-P, employees working in special climatic conditions, including in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas, cannot be included in the regional coefficient and percentage increase in the minimum wage, and are accrued from above.
In addition to the employment contract, additional payments, allowances and incentive payments due to the employee (for example, for length of service) can also be specified in the local regulatory act of the employer, with which the employee must be familiarized with signature (Article 68 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
According to Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, wages are paid at least every half month. The specific date for payment of wages is established by internal labor regulations, a collective agreement or an employment contract no later than 15 calendar days from the end of the period for which it was accrued. Thus, the dates of salary payment may not be indicated in the employment contract, but set in the PVTR, but it is better, nevertheless, to duplicate them in both documents.
Compulsory social insurance
The employment contract in question does not contain a provision on compulsory social insurance of the employee in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws (paragraph 9, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), which is mandatory for inclusion in the contract.
Why the legislator included this condition as mandatory is a secret, because the absence of this condition cannot in any way affect the employee’s social insurance (all employers are required to pay contributions).
Many simply limit themselves to a general phrase, thereby fulfilling the requirements of the law: “for the period of validity of this agreement, the Employee is provided with all types of state and social insurance, he is subject to all guarantees and compensation provided for by the current Legislation of the Russian Federation.”
Although, if you wish, you can describe everything in detail.
Soap
Until June 12, 2018, there was a rule that prescribed that the standards for issuing flushing and (or) neutralizing agents should be fixed directly in the employment contract. Moreover, it was precisely this responsibility that caused a lot of fuss several years ago regarding administrative fines. The courts simply unanimously supported the position of some labor inspectorates, and there were positive court decisions on the norms in the employment contracts of office workers (as easily washable pollution).
After June 2021, clause 9 of the Labor Safety Standard “Providing workers with flushing and (or) neutralizing agents”, approved. by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated December 17, 2010 N 1122n.
Currently, it reads like this: “The standards for issuing flushing and (or) neutralizing agents that correspond to the working conditions at the employee’s workplace are specified in the employee’s employment contract or in the local regulatory act of the employer, and are brought to the attention of the employee in writing or electronically in a manner that allows confirm that the employee is familiar with the specified standards.”
Thus, soap can no longer be prescribed directly in the employee’s employment contract, but everything can be noted in the local regulatory act of the employer. More details at
Additional terms
The employment contract may include additional conditions that do not worsen the employee’s position in comparison with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts, collective agreements, agreements, local regulations, etc.
Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in particular, lists the following conditions:
- on clarification of the place of work (indicating the structural unit and its location) and (or) the workplace;
- on non-disclosure of secrets protected by law (state, official, commercial and other);
- on the employee’s obligation to work after training for no less than the period established by the contract, if the training was carried out at the expense of the employer;
- on the types and conditions of additional employee insurance;
- on improving the social and living conditions of the employee and his family members;
- on clarification, in relation to the working conditions of a given employee, of the rights and obligations of the employee and the employer established by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms;
- on additional non-state pension provision for employees.
By agreement of the parties, the employment contract may also include the rights and obligations of the employee and employer established by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, local regulations, as well as the rights and obligations of the employee and employer arising from the terms of the collective agreement and agreements .
Failure to include any of the specified rights and (or) obligations of the employee and employer in the employment contract cannot be considered as a refusal to exercise these rights or fulfill these obligations.
Even if you do not specify these rights and obligations in the employment contract, the parties will still be required to fulfill them. Thus, the basic rights and obligations of the employee and the employer are specified in Articles 21 and 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Contents of the employment contract
The most important document in the relationship between employer and employee is the employment contract . Properly drawn up, it is able to protect the rights of both the employee and the employer. The structure of Section III “Employment Contract” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is presented in Fig. 2.4.
Rice.
2.4. Structure of Section III of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The content of an employment contract refers to the rights and obligations of the parties. Its contents consist of information and conditions. According to Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employment contract specifies:
- – last name, first name, patronymic of the employee and name of the employer (last name, first name, patronymic of the employer - an individual) who entered into an employment contract;
- – information about documents proving the identity of the employee and the employer - an individual;
- – taxpayer identification number (for employers, with the exception of employers - individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs);
- – information about the employer’s representative who signed the employment contract, and the basis on which he is vested with the appropriate powers;
- – place and date of conclusion of the employment contract.
The following conditions are mandatory for inclusion in an employment contract:
- – place of work, and in the case where an employee is hired to work in a branch, representative office or other separate structural unit of an organization located in another area – place of work indicating the separate structural unit and its location;
- – labor function (work according to the position in accordance with the staffing table, profession, specialty indicating qualifications; specific type of work assigned to the employee). If, in accordance with federal laws, the performance of work in certain positions, professions, specialties is associated with the provision of compensation and benefits or the presence of restrictions, then the names of these positions, professions or specialties and the qualification requirements for them must correspond to the names and requirements specified in the qualification reference books approved in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation;
- – the date of commencement of work, and in the case where a fixed-term employment contract is concluded, also the duration of its validity and the obligations (reasons) that served as the basis for concluding a fixed-term employment contract in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other federal law;
- – terms of remuneration (including the size of the tariff rate or salary (official salary) of the employee, additional payments, allowances and incentive payments);
- – working hours and rest hours (if for a given employee it differs from the general rules in force for a given employer);
- – compensation for hard work and work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, if the employee is hired in appropriate conditions, indicating the characteristics of working conditions in the workplace;
- – conditions that determine, in necessary cases, the nature of the work (mobile, traveling, on the road, other nature of the work);
- – a condition on compulsory social insurance of the employee in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
- – other conditions in cases provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
This is important to know: Is it possible to terminate a fixed-term employment contract early?
If, when concluding an employment contract, it did not include any information and (or) conditions from those provided for in Parts 1 and 2 of Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, this is not a basis for recognizing the employment contract as not concluded or for its termination. The employment contract must be supplemented with missing information and (or) conditions. In this case, the missing information is entered directly into the text of the employment contract, and the missing conditions are determined by an annex to the employment contract or a separate agreement of the parties, concluded in writing, which are an integral part of the employment contract.
The employment contract may provide for additional conditions that do not worsen the employee’s position in comparison with established labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreements, agreements, local regulations, in particular:
- – on clarification of the place of work (indicating the structural unit and its location) and (or) the workplace;
- – about the test;
- – on non-disclosure of secrets protected by law (state, official, commercial and other);
- – on the employee’s obligations to work after training for no less than the period established by the contract, if the training was carried out at the expense of the employer;
- – on the types and conditions of additional employee insurance;
- – on improving the social and living conditions of the employee and his family members;
- – on clarifying, in relation to the working conditions of a given employee, the rights and obligations of the employee and the employer established by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
By agreement of the parties, the employment contract may also include the rights and obligations of the employee and employer established by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, local regulations, as well as the rights and obligations of the employee and employer arising from the terms of the collective agreement and agreements . Failure to include any of the specified rights and (or) obligations of the employee and employer in the employment contract cannot be considered as a refusal to exercise these rights or fulfill these obligations.
Employment contracts, depending on their duration, can be concluded for an indefinite or definite period.
When concluding an employment contract for an unlimited period, the parties do not stipulate its duration at all. The agreement determines the date of its entry into force.
When concluding an employment contract for a specific period (fixed-term employment contract), the parties must provide for a specific period of its validity: one, four years, etc. As a rule, a fixed-term employment contract is concluded for a period not exceeding 5 years.
It is prohibited to conclude fixed-term employment contracts in order to evade the provision of rights and guarantees provided for employees with whom an employment contract is concluded for an indefinite period.
The written form of the employment contract is mandatory (Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The agreement is drawn up in two copies, each of which is certified by the signature of the employee and the representative of the employer or the employer - an individual. One copy of the employment contract is given to the employee, the other is kept by the employer.
When concluding an employment contract, by agreement of the parties, it may provide for a condition on testing the employee in order to verify his compliance with the assigned work (Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The probationary agreement must be specified in the employment contract. The employer may recognize the test results as unsatisfactory and terminate the employment contract with the employee. With an employee who fails the test, the employment contract is terminated on the basis of Art. 71 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation without taking into account the opinion of the relevant trade union body and without paying severance pay.
The grounds for termination of an employment contract are (Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- – agreement of the parties;
- – expiration of the employment contract, except for cases where the employment relationship actually continues and neither party has demanded its termination;
- – termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employee;
- – termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer;
- – transfer of an employee, at his request or with his consent, to work for another employer or transfer to an elective job (position);
- – the employee’s refusal to continue working in connection with a change in the owner of the organization’s property, a change in the jurisdiction (subordination) of the organization or its reorganization;
- – the employee’s refusal to continue work due to a change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties;
- – the employee’s refusal to transfer to another job, required for him in accordance with a medical certificate issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, or the employer’s lack of relevant work;
- – the employee’s refusal to be transferred to work in another location together with the employer;
- – circumstances beyond the control of the parties;
- – violation of the rules for concluding an employment contract established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other federal law, if this violation excludes the possibility of continuing work.
An employment contract may also be terminated on other grounds provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws.
Let's summarize what has been said:
- The content of an employment contract can be divided into three parts: mandatory information, mandatory conditions, additional conditions that the parties can establish at their own discretion.
- All information and conditions that must be specified in the employment contract are mainly established in Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in other articles of the code and in other legal acts containing labor law norms.
- Based on the content of the employment contract in question, the employer may well face an administrative fine (Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code) in the amount of 50,000 to 100,000 rubles (as for a legal entity), due to improper execution of the employment contract (lack of circumstances (reasons), served as the basis for concluding a fixed-term employment contract, the absence of a condition on compulsory social insurance, etc.).
- The employer has the right to regulate the content of the employment contract only taking into account the above-mentioned features. It is prohibited to establish conditions that contradict or worsen the employee’s position in comparison with labor legislation (for example, a 15-minute lunch break, fines, etc.).
Share
Related Posts
- Error or typo in the employment contract Errors in the employment contract. How to correct a mistake in an employment contract? Arbitrage practice.
- Working conditions at the workplace in the employee’s employment contract Read more about working conditions in the employment contract. Example of wording. Arbitrage practice.
- Salary of a part-time worker in an employment contract What salary should be indicated for a part-time worker in an employment contract? Is it possible to set a full salary? Examples from...