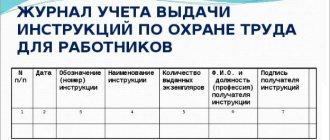
What is working time
The basic state law establishes the right of citizens to work, as well as the specifics of working hours and rest. At the same time, this right involves limiting the time that applies to a worker, as well as allowing workers to use weekends and holidays for rest.
The definition of “working hours” is reflected in Art. 91 of the Labor Code, it means the period of time during which the employee has the authority to perform labor duties determined by the internal labor regulations and the employment contract that forms the basis of the legal relationship that has arisen. Such time may also include other time periods that are established as such by legislative norms.
Other working periods may include the time employees are idle, the time of a paid break provided during work, the period of business trips, rest periods between shifts, etc.
Legislative regulation of working time aims to achieve:
- productive use of the time period for carrying out work;
- protecting the health and performance of workers hired under employment contracts;
- increasing the professionalism of performers engaged in joint hired labor.
Rest time at work: reminder
Instructions to help an employee
Working time belongs to the employer. Rest time belongs to you personally. Therefore, an employer interested in making a profit seeks to turn your rest time into working time. That is why every employee needs to know where the boundary between these concepts lies. For which, of course, it is necessary to have the following legal knowledge.
Rest time is the time during which the employee is free from performing work duties and which he can use at his own discretion (Article 106 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). These are breaks during the working day, daily (between shifts) rest, weekends, non-working holidays and vacations.
The following are legally defined: a break for rest and food (lunch break); special breaks for warming and rest; breaks to feed the baby.
The duration of daily rest between shifts must be, together with the lunch break, no less than double the length of work time on the working day (shift) preceding the rest.
Weekends are weekly and continuous rest, with a minimum duration of 42 hours (Article 110 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). With schedule 6/1, the duration of work on the eve of the weekend cannot exceed 5 hours (Article 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The days off for each employee are determined in accordance with the internal labor regulations, employment contract and shift schedule. At the same time, Sunday is a common day off for everyone, except in cases where production conditions make it impossible to suspend work on weekends.
The presence of holidays in a month (the list of all-Russian holidays is in Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) should not affect the salaries of employees: they do not work on their own initiative. For example, employees with daily or piecework wages for non-working holidays are paid a remuneration, the amount of which is determined by agreement (Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The working day on the eve of a holiday is either shortened by one hour, or this hour is regarded as overtime (Article 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Weekends and non-working holidays are untouchable days, forced involvement in work on which is allowed only in exceptional cases (described in Article 113 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In other cases, employment on weekends and non-working holidays is permitted with the written consent of the employee. However, the involvement of pregnant women and minors is prohibited, even with their consent. Important: when agreeing to work on a day off or a non-working holiday, do not forget to obtain a written order from the employer.
Work on a weekend or non-working holiday is paid at least double the amount. However, instead of double payment, you can take another day of rest (regardless of the number of hours worked on a weekend or non-working holiday, the employee is given a full day of rest), in this case the amount of payment will be one-time.
When accounting for working hours in aggregate, work on a weekend or non-working holiday is included in the monthly working time standard. This work is not taken into account when calculating overtime hours (it is already paid double).
All employees working under employment contracts are granted annual leave with preservation of their place of work (position) and average earnings (Article 114 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Annual paid leave can be basic (usually 28 calendar days) and additional. Additional leave may be provided for both in legislation (for example, a number of cases are listed in Article 116 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and at the organizational level. Non-working holidays falling during the period of annual leave are not included in the number of calendar days of leave.

The right to use vacation accrues to an employee after the first 6 months of his continuous work with a given employer.
In subsequent years, vacation is provided in accordance with the vacation schedule. The employer is required to approve the vacation schedule no later than two weeks before the start of the calendar year. If the organization does not have an approved vacation schedule, you should coordinate the time of going on vacation with the employer, and it is better in writing. If there is no vacation schedule and the employer does not provide vacation, then you can file a complaint with the state labor inspectorate or the prosecutor's office.
The employee must be notified of the start time of the vacation against signature no later than 14 days before its start (Article 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). And at least 3 days in advance - pay the employee vacation pay. If there is no order from the employer and you have not been paid vacation pay, you can demand that the vacation be transferred to another time convenient for you. Do not go on vacation in this case: the employer may present your absence from work as absenteeism.
The employer can divide the leave into parts and postpone it only with the consent of the employee. When dividing, one part of the vacation must be at least 14 days. Recall of an employee from vacation is permitted only with his consent. In this case, the unused part of the vacation must be provided to the employee at a time convenient for him in the current year or added to the vacation next year. Part of the annual paid leave exceeding 28 calendar days, upon written application of the employee, can be replaced by monetary compensation.
For family reasons and other valid reasons, an employee, upon his written application, may be granted leave without pay. The duration of this leave is determined by agreement between the employee and the employer. For some categories of employees, for example, pensioners, the employer is obliged to provide unpaid leave (Article 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In other cases, the employer may refuse. But he also does not have the right to demand that you go on unpaid leave. If you were sent on such leave by order of your employer, but you did not write a corresponding application, ask for a written order: you will prove that you are not absenteeizing, and you will be able to recover the average earnings for the period of illegal removal from work (Article 234 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). You have the right to withdraw your application and demand that the employer provide you with work. If the employer refuses to provide you with work, you can write a statement to the employer about the beginning of downtime due to his fault and demand payment in the amount of 2/3 of the average salary (Article 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Don't let your employer take advantage of your time. Demand fair payment for your work. Improve your legal literacy. All agreements with the employer must be drawn up in writing in duplicate.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Mode elements
Working hours refer to the period of time during which an employed employee has an obligation to perform the functions assigned to him by the employer. The legal standard for such a time period must be understood as the standard work time established by the legislator.
The provisions of the Labor Code establish as time standards in which employees can be busy performing the functions assigned to them: working week, shift (day), accounting period.
A working week is understood as a period of working time falling within a calendar week. Legislative norms limited this time period to 40 hours. This standard applies to the work week, regardless of whether it is 5 or 6 days. This standard of hours falls under the definition of a normal working week, which, as a rule, contains 2 days off.
A shortened or incomplete week can be established by agreement of the parties and represents a part-time working regime.
The establishment of six-day work is preceded by a necessity determined by the conditions of production or performance of work. This standard is typical for educational, medical or social institutions. A distinctive feature of the “six-day week” is the reduction of the working day preceding a weekend or holiday to 5 hours.
The presence of shift work conditions implies the establishment of work shifts, that is, such work intervals during which some workers performing the functions necessary for a single technological process are replaced by others. In this case, we can talk about day and night shifts. Shift work is typical for those types of production that are considered continuous.
It is necessary to change the working hours if there are shifts, within the framework of current legal norms, on the eve of a non-working day, holiday and day off, as well as when performing work on the night shift.
Working hours according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The normative basic Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the understanding of the time required for a worker or employee to perform direct duties. Actions take place according to the conditions regulated in the contract with the employer, according to the internal regulations of the company, including rest periods and other breaks. For unworked hours, you may face disciplinary action if such a clause is specified in the contract.
Breaks are regulated by legislative and legal acts of the Russian Federation, including types of interruption of the work process: rest breaks, heating during the cold season, feeding and caring for young children, lunch, downtime, etc.
Basic accounting of working time, its division into standard intervals (years, months, quarters, days) is determined by government authorities at the federal level.
Actual accounting of time worked in production or service is carried out by the enterprise's control bodies. According to the regulated legislation of the Russian Federation, the standard working time per week should not exceed forty working hours.
Legislatively in the Russian Federation, working hours are divided:
- By duration per working week.
- According to the rules for establishing labor order.
- According to legal and legal standards.
An employee's working time is divided into:
- Normal working period.
- Shortened working period.
- Underemployment.
- Extended working hours.
The first three are standardized labor time, the fourth is irregular.
Types of working hours
The provisions of the Labor Code define the types of working time used:
- usual - depending on the system by which work time is recorded. Most often it is reflected in a 5 or 6-day work week.
- Irregular – established for certain categories of workers, by order of the manager. This type cannot be installed on a permanent basis.
- Flexible - allowed in individual teams and departments, on the basis of self-regulation. The flexible working time regime should not contradict the legislative principles on the total number of hours worked. Flexible working hours may be temporary.
- Shift work is a working time regime in which employees can work in several shifts and in an equal number of hours.
- Shift work is a regime and recording of working hours of a special type, which is typical for performing work outside the place of primary residence, which means it is impossible to return to the place of residence every day.
- Divisible – characteristic of work with different types of intensity.
Part-time working hours can be established at the request of the employee. Pregnant women, parents of children (under 14 years of age) and persons caring for sick relatives can petition management and ask for a part-time working schedule.
The introduction of a part-time working regime falls within the competence of the company’s management, which is formalized by order. An order to change working hours, based on an exclusive decision of management, may have signs of a change in significant working conditions.
Common violations when providing rest time
Labor law standards are often violated. This is largely the responsibility of the employee. Many employees simply do not know about their rights, and therefore do not file complaints with the labor inspectorate. Let's consider the most common violations of the Labor Code in the field of providing rest time:
- Internal regulations have not been established. There are no approved vacation schedules.
- The employer recalls the worker from vacation without his written consent.
- Issue of leave, the duration of which is less than the norm.
- Compensation for unused vacation is not paid upon dismissal.
- Working time standards for persons working part-time are not met.
- The norms for the duration of weekly rest are violated.
- Persons who may qualify for additional days of rest do not receive them. For example, parents of children with disabilities are not given the required 4 days of rest.
- Donors' rights are violated. For example, a person went to donate blood and therefore did not show up for work. The employer was provided with all the necessary documents. The manager fires an employee due to absenteeism. This would be a gross violation of the law.
As a rule, all violations are detected during scheduled and unscheduled inspections.
Responsibility for violations
The employer is responsible for violations in the area of rest time. As a rule, this is an administrative responsibility. For example, it is precisely this that is imposed in the absence of schedules and vacation that was not granted. This offense is regulated by Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. If the employee is not paid compensation for unused vacation, the employer is liable to a fine:
- For legal entities – 30-50 thousand rubles.
- For individual entrepreneurs – 1-5 thousand rubles.
IMPORTANT! If a violation is detected again, the fine will be large.
Duration of daily work (shift) for certain categories of workers
The legislator has determined the maximum amount of time that certain categories of employed people can spend at work.
Young people aged 15 to 16 years and from 16 to 18 years old cannot have a work shift of more than 5 and 7 hours, respectively. Teenagers who are students, as well as those whose age is between 14 and 16 years old - no more than 2.5 hours, and students whose age is 16-18 years old - no more than 4 hours. The duration of the shift for disabled people is determined by a medical report.
The harmfulness or danger of work is a reason to reduce working hours to 8 hours per shift, with 36 working hours per week, and to 6 hours per shift, with 30 working hours per week.
Certain features also exist regarding the work of creative teams. Such persons carry out their work under the conditions established by local acts, collective and labor agreements.
Overtime time
The basic legislative document in the field of employment of citizens is the labor legislation of the Russian Federation, which allows the employer to attract potential employees to perform work outside the main working hours. This time is regulated by legislative acts of the Russian Federation, an employment contract, and other official protocols.
Busy time at work increases for the following reasons:
- Precedents for important overtime work, with the consent of the employee.
- Regimes of irregular periods of work, fixed by the employment agreement.
Independent working hours are defined as work outside the standard duration of the work period. Legislatively, it is independent in relation to the other types of labor described above.
Equally, any categories of employees, of different ages, having different benefits, are involved in the same type of labor activity, if necessary and by consent.
Long-term work is considered an additional type of labor that exists in conjunction with any type of human labor activity. Legally, work outside the standard time is characterized as an independent type:
- An additional, auxiliary role relative to the basic types of labor.
- Involvement in work activities based on the voluntary desire of the employee.
- Receiving wages based on the results of irregular work (volume, hours).
Regulation of working hours
Carrying out actions entailing a change in working hours falls within the competence of the management of the legal entity. As a rule, such changes are based on local or national legal acts.
Working hours, as well as part-time working hours, are established at each specific enterprise, depending on the specifics of its work.
The approval of the features of the working time regime is within the competence of the governed by and is a change in essential working conditions, in the event that before the change in the working time regime occurred, there was a different regime.
Part-time working hours are established for individual categories, based on their application. It is possible to establish a part-time working regime for the entire workforce only in accordance with the procedure for making changes related to essential working conditions.
Cancellation of the part-time working regime may be established by an order establishing it, and in relation to certain categories of workers, by a separate order based on their application.
Shortened working hours
The legally regulated period of work of a worker or employee, for a period less than the normative one, with full pay, is usually defined as shortened. And according to the Labor Code, the limit on the duration of work per week is established:
- Up to sixteen years – twenty-four hours.
- Up to eighteen years – thirty-five hours.
- Disabled people of the first and second groups – thirty-five hours.
- Life-threatening and harmful working conditions – thirty-six hours.
- Students of educational institutions during the training period – eighteen hours.
The simplified working time standard is not accepted for all types of work; it is used according to the legislation of the Russian Federation. It defines the basic legal relationship between the worker and the employer, in accordance with the internal labor regulations of the enterprise, and is the responsibility of the employer. Contractual regulation of labor relations provides for all this.
All expenses that are necessary will follow after the reduction of labor of a worker or employee. They are borne by a company, firm, or private enterprise. The employee retains the benefits provided by law, benefits, the minimum salary, which is regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, its basic norms and rules.
Despite the fact that the amount of time a person works per week is reduced, the basic rights of the employee are not limited. Sometimes compensation for unworked time occurs (more the exception than the rule).
Legally important factors regarding the shortened period of work are highlighted, such as:
- The determination of the working day is regulated by the actual law of the Russian Federation.
- Compliance with basic rights, benefits, and other worker preferences specified in the law.
Internal labor regulations
These rules relate to local acts adopted and approved at each individual enterprise. When approving the specifics of working hours, they are reflected in the VTR rules. Employees of enterprises are obliged to perform their labor functions in full compliance with established rules.
Familiarization with them is carried out by the person employing the employee, of which the latter is notified against his signature. Failure to comply with these rules may be grounds for dismissal of an employee who violates the company’s work schedule.
Regime of working hours and rest time for employees with a special nature of work
Features of the production cycle and the nature of labor, categories of workers, their age and other factors are the basis for the use of different regimes of work and rest time.
Some types of work are characterized by the presence of special breaks, which are based on the complexity or harmfulness of the work functions performed. A separate work and rest regime established for certain categories of workers engaged in special work is reflected in industry and federal industry agreements that extend to certain production areas.