Introducing additional grounds for conducting unscheduled inspections of employers
Article 360 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the procedure for conducting inspections by officials of the Federal Labor Inspectorate of employers on issues of compliance with labor legislation and the grounds for conducting inspections. Federal Law No. 272-FZ supplements the grounds for conducting an unscheduled inspection. Thus, from October 3, 2021, appeals containing facts of violation by employers of the requirements of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law standards, including labor protection requirements, resulting in a threat of harm to the life and health of workers, as well as leading to non-payment or incomplete payment of wages or other payments due to employees on time, or the establishment of wages in an amount less than the amount provided for by labor legislation, are grounds for an unscheduled inspection by labor inspectorate officials.
Employer's liability
When an employer is punished for delaying payment of wages, financial liability most often arises. More details about it can be found in Article 236 of the Labor Code.
Financial liability consists of paying the employee compensation in the amount of one three hundredth of the amount that is delayed for each day of delay.
Until 2006, the employer was exempt from paying interest if he could prove that the reasons for the delay were valid. For example, robbery or the employee’s reluctance to take money.
Since 2006, the legislation has changed, and no arguments are valid. Therefore, regardless of the reasons, interest must be paid.
And the size of payments can be indexed under the influence of the inflation rate in the region. To do this, you must obtain an official document in which this percentage is indicated.
How to do the calculation yourself
Calculating compensation yourself is quite simple - you need to know your salary and the exact number of days of delay. The last indicator must be correctly calculated from the day specified in local documents.
To calculate, you must use the following formula:
KV = ZrP * Class.St. / 150 * KDP, where
KV - compensation payment that the employer must make in favor of his employee;
Salary - the amount of wages that must be paid to a specific employee on a strictly established day;
Class.St. – this is the key rate (in percentage) of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the day the delay occurred. In the period from March 26, 2021 to September 16, 2021, the key rate is 7.25%;
KDP – number of days of delay.
Calculation example: At an enterprise, wages for the second half of the month are paid on the 6th of each month. For July, payment was made only on August 14. P.’s salary is 52,500 rubles. What amount should he receive on August 14? No additional payments were provided for July.
Calculation: CV = (52,500 * 7.5% 150) * 8 = 52,710 rubles, of which 210 rubles are interest for a delay of 8 days.
Where to go if your salary is delayed
If the situation with delayed wages could not be resolved through discussion with the management team, then you should seek protection of your interests in the authorities legally authorized to apply incentive measures to the violating party. Such authorities are :
- prosecutor's office;
- judiciary;
- labor dispute commission;
- labor inspectorate.
Appeal to these authorities is made by drawing up and submitting an application, which indicates the circumstances leading to this and a request to take measures regarding the employer in order to restore the legal rights and interests of the employee.
There is no single official form of writing, but there is a number of information that must be provided for a detailed consideration of the situation:
- the full name of the authority to which the employee applies;
- information about the plaintiff;
- a detailed statement of the current situation, the amount and circumstances of the delay;
- a request for compensation, taking into account interest penalties and moral damages;
- list of accompanying documentation (statements, certificates, checks confirming non-payment of funds on time).
If supporting documentation cannot be provided due to obstacles on the part of the employer, this fact must be reflected in the application. In this case, the competent authority has the right to fulfill the request for relevant documents.
The application is submitted:
- by personal appeal from the plaintiff;
- by registered mail with acknowledgment of receipt;
- with the help of an authorized third party, with the obligatory provision of a notarized power of attorney.
Labor Dispute Commission
At enterprises where the functioning of such a body is provided for, the resolution of disputes between the administrative apparatus of the enterprise and representatives of the workforce should occur with its participation. That is, the first instance for an employee to appeal in order to protect his interests and rights should be the labor dispute commission operating in this organization. It includes both representatives of the administration and members of the team, which implies equal consideration of conflicts.
The regulated response time to employee requests is 10 days. This period is counted from the date of creation of the commission on the application. The application must be registered and recorded by the enterprise trade union.
The commission meeting is held behind closed doors. All provisions adopted at it are not disclosed. If the employee’s appeal is satisfied, then the debt is paid in full and with any compensation due within the time frame approved by the commission.
If the employer ignores the decision of the commission and does not pay the debt, the employee has the right to receive a writ of execution, with which he has the right to apply to subsequent authorities.
Labor Inspectorate
If an appeal to the commission at the enterprise does not bring results, the employee or team can refer the situation to the labor inspectorate - a special government body authorized to resolve disputes between the employer and employees. Its powers include reviewing written appeals and taking action against unscrupulous employers.
The application must indicate:
- detailed information about the applicant;
- full details of the employer who violated the applicant’s rights;
- detailed details of payments, terms and duration of delay.
The application must be accompanied by originals or copies of supporting documentation. You can submit your application using any of the above methods.
The response time is 30 days from the date of acceptance of the application. At the end of this period, the inspection is obliged to inform the applicant in writing about the results of the inspection.
If during the inspection violations are discovered on the part of management and the fact of a delay in wages is confirmed, then the enterprise receives an order to eliminate the delay and pay wages in full.
Judicial authorities
An employee can also restore his rights and interests by filing a claim with the judicial authorities. The drawn up claim, together with copies of supporting documents (employment contract, appointment order, bank statements and other documentation proving the facts of employment and delays in wages) is transferred to the district or magistrate court for the purpose of further consideration of the employer’s failure to fulfill obligations to remunerate employees, and also forcing him to repay the debt.
The consideration period is 2 calendar months for district courts and 1 calendar month for magistrates' courts. The countdown starts from the date of filing the claim.
note
The time period within which a claim can be filed in court is limited by Article 392 of the Labor Code. To consider a labor dispute, they take 1-3 calendar months (depending on the type of claim). The period for reviewing wage arrears is 12 months. At the same time, plenary Resolution No. 2 additionally indicates that if the salary was accrued but not issued to the employee, then the claim must be accepted and considered regardless of compliance with the above deadlines. This category of violation is included in the list of those with no finite duration, therefore the refusal to accept the claim and satisfy the claims is unlawful.
If the claims specified in the claim are subject to satisfaction, collection of the debt and compensation accruals is carried out forcibly.
Compensation for delayed payment of salary
If you fail to fulfill your obligations to accrue and pay wages, the employer will have to answer primarily financially. In addition to transferring the debt, the company must assign compensation to the employee, as stated in Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Let's consider what compensation employees are entitled to when salary is delayed and whether such payments are taxed.
Tax and insurance premiums
If wages are paid without delay, a special tax, personal income tax, is deducted from the employee. It is 13% of the amount accrued for labor. Such interest is not deducted from compensation. A similar clarification was given by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in Letter No. 03-04-05/11096, published on February 28, 2021. Accordingly, filling out reports in Form 6 of personal income tax on transferred taxes for employees is simplified; the income code “compensation” is not indicated in the document.
So, taxation does not apply to such payments. But when considering insurance premiums, it is difficult to answer the question about the need to pay. Until 2021, based on the decision of the Supreme Arbitration Court No. 11031/13 of December 10, 2013, the employer could refuse to transfer contributions. But on March 21, 2021, another letter from the Ministry of Finance No. 03-15-06/16239 was published. And officials explained that insurance payments from compensation are transferred without fail. This complicates accounting because you need to know how to calculate and pay contributions.
Compensation calculation
Before calculating compensation, you need to know a special formula. It follows from the provisions of Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which states how much an employee can receive as compensation. But it is worth remembering: the regulation indicates the minimum amount of payments. The maximum amount of penalties can be calculated only after studying the local acts of the enterprise, which can increase the compensation established by law.
How much employees are entitled to under the labor code can be calculated using the formula:
salary debt*1/150 refinancing rates*number of days of non-payment
In order not to make mistakes in calculations in 2021, it is better to use an online calculator that knows what refinancing rate is currently in effect and is able to display current figures. The value is not constant, so when you calculate it yourself it is more likely to make a mistake than using a special service.
What should an employee do if wages are delayed?

Employees of an enterprise are not required to wait until their salaries are delayed by 15 or more calendar days. Starting from the first day of the delay, you can begin to take measures to protect your interests. At the initial stage, it is recommended to draw up and submit to management a collective appeal on this matter. There is no single format for compiling, therefore such an appeal can be compiled in any form.
The main task of the appeal is to formulate claims and provide the data necessary to adequately resolve the situation:
- to whom the appeal is intended - branch, company, enterprise, full name;
- who sent the appeal - team, employee, full data;
- a full statement of the current situation - the fact of the delay, the set date and the period for which the salary was delayed;
- a request to begin a negotiation process that will allow the situation to be discussed and measures to be taken to eliminate it, with relevant reports in writing.
The appeal should be completed by indicating the date and the signature or signatures of the applicant.
If the document is ignored and there is no response, then employees have grounds for temporary suspension of professional duties. This action is stimulating in nature and is intended to encourage the employer to solve the problem.
Temporary suspension of professional duties
After reaching a delay of 15 days or more, employees have the right not to show up for work, suspending the performance of their professional duties and functions, until the employer pays the delayed wages. This is provided for in Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
To implement this measure, the employee must notify the employer by sending him a written notice. During the suspension of activities, the employee has the right to either be present at his workplace or not to go to work. Resumption of work must occur the next day after management informs that the debt will be paid on the day of returning to work.
In some situations and certain professions, it is prohibited to apply such a measure as suspension of professional duties:
- during an existing state of emergency or emergency situation;
- employees of strategically important enterprises and services (water, heat, communications, rescuers, doctors, emergency services, etc.);
- law enforcement officials;
- civil servants;
- worker in hazardous areas (nuclear power plants, mines, chemical plants, etc.).
Since suspension is a legal right of the employee, he, in turn, has the right to receive payment for this period. This right is stipulated by Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Important
To avoid disagreements with the Federal Tax Service regarding the accounting of payments of this kind as an expense item for remuneration, these points should be indicated in advance in the contract or additional agreements with the workforce.
In addition to payment, the employee has the right to compensation, which is determined by Article 236 of the Labor Code.
That is, by creating delays in wages at the enterprise, the owner bears the costs not only of full reimbursement of funds, but also pays an additional compensation amount.
What threatens the employer?
To find out what responsibility the employer bears for the delay in payment of wages, it is necessary to refer to the text of the Labor Code, which spells out the obligations of the employer and penalties for violating them. The manager may be subject to monetary penalties and fines or a decision to suspend the activities of his enterprise.
If violations continue regularly, this threatens the organization with disqualification for a certain period.
.
Long delays in salaries may result in criminal penalties for managers and officials
with imprisonment or a ban on engaging in certain activities. In this case, the responsibility for paying average earnings for this period will fall entirely on the manager and he will be obliged to compensate it.
The main document legally confirming the employer’s violations is a certificate of delayed wages in Russia. A sample form is available for free viewing on the Internet or can be provided by a professional lawyer or an attorney defending the interests of the plaintiff in court.
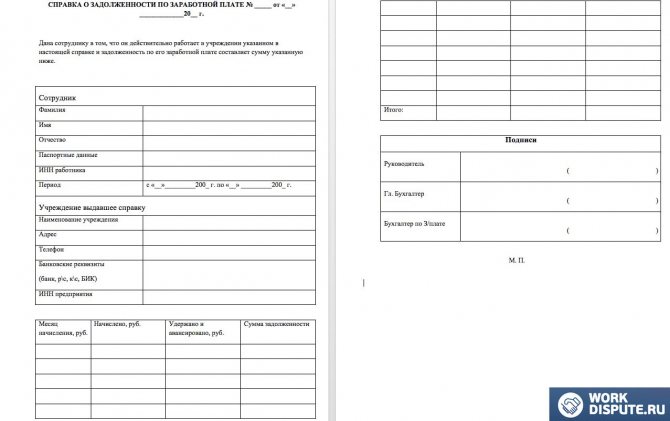
A delay in wages under the labor code in 2021 is a serious violation of constitutional freedoms, therefore every injured employee has the right to seek justice through legal means.
Acceptable delay: timing
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that an employee must receive remuneration for work performed at work every 15 days. This is reported in Article 136, as well as Article 142. Additionally, the situation is recorded in Letter No. 14-2-242, issued on November 28, 2003 by the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation.
Free consultation with a lawyer on salary delays>>
Usually payments are made 2 times a month on days determined in advance. The latter usually records:
- labor contract
- collective agreement
- local regulatory act of the company - order
If postings are made less frequently, or the employer delays the transfer of wages, he is violating current legislation. And it doesn’t matter how late the payment is - by a day, a week, a month or a year. The reasons why such a situation has arisen are also rarely taken into account. A one-time, or even more so a permanent delay is a direct violation of the law. Only the responsibility of the enterprise depends on the timing.
Administrative responsibility of the employer
For a delay in paying wages, the employer may be held administratively liable under Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses.
The fine imposed on the employer is small - from one thousand to five thousand rubles for officials.
If an employer is engaged in business without forming a legal entity, he faces a similar fine, as well as suspension of the organization’s activities for up to 90 days, and for a legal entity, that is, for the enterprise itself, the fine will be no more than 50 thousand rubles or suspension of work for 3 months .
Punishment in the form of an administrative fine is imposed by a court or an authorized executive body, that is, a labor inspectorate.
How to submit an application
The claim sent to the director of the enterprise must include the following information:
- Full name and position of the applicant.
- A link to the employment contract and work record book as confirmation of the employee’s hiring.
- The period for which wages have not been paid.
- Regulatory acts confirming the commission of an offense.
- Amount of wage arrears.
- Applicant's requirements.
The lawsuit and complaints to the labor inspectorate and the prosecutor's office are drawn up according to a similar plan. A strict model has not been established in Russia, but it is important to display all the information necessary for the proceedings.
Consequences of a delay of 1 day
According to the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a delay in wages even by 1 day can lead to unpleasant consequences for the employer in the form of compensation payments. Compensation is accrued from the 1st day of delay in the amount of 1/150 of the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, which is set on the day the debt arose. To receive compensation, the employee does not need to fill out any paperwork or write additional statements. All calculations and payments are made by the employer independently. They must be carried out together with the payment of delayed wages.
If the delay is 1 or several days, you can write a claim addressed to the employer demanding to pay not only wages, but also compensation for each day of delay. If the letter is ignored, you can complain to higher authorities.
However, the claim must be submitted in writing and must be properly recorded as an incoming document. The employer will then have to provide a formal written response.
Criminal liability of the employer
For late payment of wages, the employer can be punished under Article 145 of the Criminal Code.
Employers are rarely brought to such liability; in this case, the employer must delay wages for more than two months for selfish reasons.
It is very difficult to prove the selfishness of an employer’s actions. The prosecutor's office is investigating the case of non-payment of wages.
The employer brought to justice will be required to pay a fine of up to 120 thousand rubles, and may also be imprisoned for up to two years.











