The employer has a lot of responsibility to the employee in terms of creating safe working conditions, complying with the rules, standards for issuing PPE, including the provision of special clothing, safety footwear and other personal protective equipment.
And I will also immediately answer a frequently asked question: “is the employee obliged to compensate for the money spent by the employer on the purchase of personal protective equipment.” No, not obliged, if only for damage.
In order not to violate the law (Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the employer must, at his own expense, ensure the timely issuance of PPE. In addition to this, there is also their storage, washing, drying, repair and replacement, but more on that a little later.
Who is entitled to receive protective clothing?
To begin with, I would like to especially note that all purchased workwear, safety footwear and personal protective equipment must be certified or have a declaration of conformity with TR CU 019/2011 “On the safety of personal protective equipment”. Leave copies of certificates from each delivery of workwear and keep them in a folder. The inspector, coming with an inspection, can check their presence.
The employer is obliged to provide workers in professions whose activities are related to:
- harmful and dangerous working conditions;
- special temperature conditions;
- pollution.
It turns out that not only blue-collar workers should be provided with free PPE, but also managers and engineers who, while working, visit places where various types of pollution are possible.
What to do with contractors who may work on the territory of your enterprise, who should issue PPE to employees?
Employees of third-party organizations must be provided with special clothing and personal protective equipment at the expense of their employer (clause 18 of Order No. 290n of the Ministry of Social Health Development); special clothing is not required to be issued.
The following also have the right to receive special clothing:
- trainees of your company;
- employees who are temporarily transferred to another job;
- students studying under a student agreement.
Types of standards
The issuance of protective clothing at enterprises is controlled by government agencies. It is especially important to comply with the issuance rules at those enterprises where there is an increased risk of working with harmful and dangerous substances, as well as temperature conditions. Products that are designed to protect workers have appropriate standards.
Their variety is very large.
An example of some types of standards for PPE:
- Safety glasses . Serve to provide visual protection. Produced in accordance with GOST R12.4.013-97. This type of PPE can protect your eyes from any damage.
- Overalls. This includes all personal protective equipment that can be used in industry, production, namely vests, gowns, suits, etc.
- Protective clothing for hands. These are all types of gloves - rubber, cotton, which protect hands from exposure to harmful agents. As well as thermal or chemical damage.
- Shoes. Provides protection to the lower extremities. Large industries often use vibration-proof shoes that reduce vibration, which helps eliminate discomfort when walking.
Standards for issuing PPE
In order to understand in what quantity and what kind of protective equipment are required, it is necessary to use the standards for issuing workwear; for each production and each profession their own lists have been developed.
Let me give examples of some of them:
- Standards for issuing PPE in construction, approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated July 16, 2007 No. 477.
- Standards for issuing PPE for organizations in the food, meat and dairy industries, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated December 31, 2010 No. 1247n.
- Standards for issuing PPE for workers employed in metallurgy, mechanical engineering and transport production, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated December 14, 2010 No. 1104n.
- The standards for issuing PPE to workers in the trade and service sector were approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated October 3, 2008 No. 543n.
- And so on... for each position you can find a list of necessary workwear with regulated wearing periods.
There is also a document that defines the issuance standards for workers in cross-cutting professions - this is Order of the Ministry of Labor No. 997n dated December 9, 2014.
It takes precedence over the standards of individual industries for the issuance of workwear, and the positions specified in it must be provided with PPE, even if they are not specified in the industry standards!
There are a number of additional conditions under which the issuance of protective equipment against harmful factors is required, such as:
- working with high noise levels (headphones);
- work at height (safety harness);
- outdoor work in adverse weather conditions (raincoat);
- working outdoors in winter (insulated workwear);
- work in regions where blood-sucking insects appear in summer (repellents, encephalitis suits).
For each region, wearing protective clothing in winter is set at its own time depending on the climate zone. Moreover, the time period for wearing PPE used in special temperature conditions includes the time of their organized storage.
There are five of them in total from I to special. You can find your region and determine the climate zone here.
Only when the appropriate time of year arrives is the employee given seasonal protective equipment, and at the end the employer must organize storage.
PROCEDURE FOR STORING INSULATED PPE
The employer, at his own expense, is obliged to ensure the storage of PPE during its operation, before issuing it to employees and after handing it over after the wear period has expired.
Recommended storage conditions for PPE before and after use are established in the regulatory documents of specific types of PPE and are reflected in the product passport or operating instructions (information for the user).
PPE must have instructions indicating the purpose and service life of the product, the rules for its operation and storage.
All personal protective equipment must be stored in separate dry, heated, clean, ventilated rooms and protected from mechanical influences and direct sunlight.
Note!
It is prohibited to store PPE near heat-generating devices (less than 1 m), acids, alkalis, oils, gasoline, organic solvents and other aggressive chemical substances that cause corrosion of metal, damage to rubber or plastic structural elements of PPE.
To store and ensure the safety of personal protective equipment during operation, special rooms must be equipped - dressing rooms. Their size and design depend on the number of workers, groups of production processes and comply with the requirements of SP 44.13330.2011[6].
To organize the reception of storage and targeted issuance of PPE, it is recommended that employees label the PPE. Usually, for this purpose, a stamp is applied to the collar, collar of the jacket and the lining of the trousers' waistband with indelible paint - the employee's personnel number. Shoes can be packed in waterproof bags and also labeled.
The specific method of labeling and storage is established by the local act of the employer.
If it is not possible to organize centralized storage of insulated PPE, during the off-season period it is allowed to store them in specially equipped dressing rooms, provided that there is enough storage space.
Full range of labor protection, civil defense and emergency services
Enter your phone number and I will calculate an estimate for your tasks. Enter without the eight. “Bureau of Ekaterina Vorontsova” – professional solutions to your problems: with high quality and on time!
Procedure for issuing PPE
First you need to know the height and size of your employees. This information is determined from the employee’s words and entered into the PPE issuance card.
No matter how funny it may sound, it must correspond to the gender; intersectoral rules for providing workers with special clothing, special shoes and other personal protective equipment (Order No. 290n dated 06/01/2009) stipulate this in clause 12.
All issuance must be recorded in a personal PPE issuance card.

Sample personal PPE issuance card
On the front side are entered the names of workwear, safety footwear and protective equipment, which are provided for by the standards developed and approved by the head of the enterprise. The reverse side of the personal PPE card is filled out upon issue.
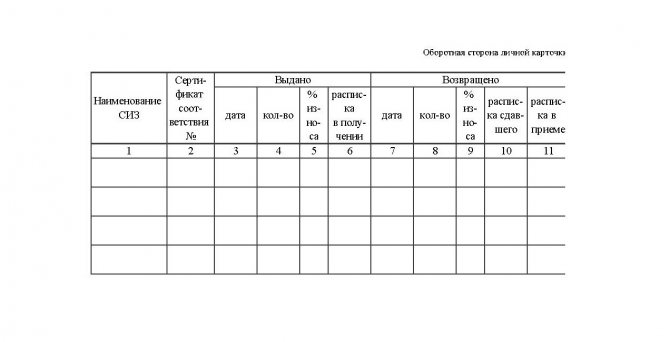
Reverse side of personal PPE card
The employee's signature on receipt of work clothes is required.
It is now popular to maintain an electronic form of a workwear issuance card, which is also allowed by law, but many continue to work the old fashioned way.
The distribution of work clothes and safety shoes to employees is carried out by the warehouse, and a labor protection specialist monitors compliance with standards and the correctness of maintaining cards.
To provide clarity on the wearing period, the amount of workwear issued per year, as well as where this information came from, a list of issuing workwear, safety footwear and personal protective equipment according to your staffing schedule is being developed. The list must be agreed upon with the trade union (if there is one) and approved by the head of the enterprise.
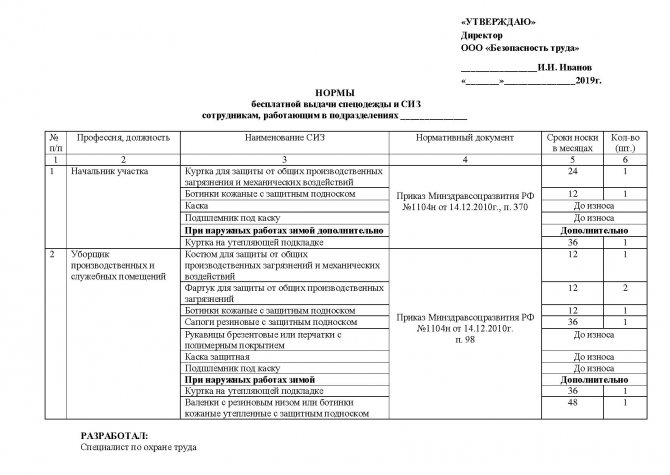
Sample standards for issuing PPE
The service life of PPE is regulated by regulations and cannot be extended, as this may worsen the working conditions of workers.
And an employer cannot simply replace one type of personal protective equipment with another. Only by agreeing on this replacement with the trade union body and the replaced PPE should be equally protected.
Employer's liability
If management refuses to provide employees with free protective equipment, the employee has every right to refuse to perform work.
At the same time, he cannot be brought to disciplinary liability or other penalties. True, many either do not know about this or are silent, because they could lose their jobs.
But the law provides for punishment of such managers in the form of a fine in the amount of:
- for officials and individual entrepreneurs - from 20 to 30 thousand rubles for each employee;
- for organizations - from 130 to 150 thousand rubles for each employee not provided with PPE.
For a repeated violation, the organization can be fined up to 200 thousand rubles, and its work can be suspended for up to 90 days.
Responsibility of workers for damage to personal protective equipment
According to the law, employees also have responsibility; not everything can be pinned on the employer. 

Employees of enterprises must take care of the protective clothing and personal protective equipment issued to them. If the fact of damage or loss of a set of PPE is revealed, they will have to compensate for the corresponding costs. Its use during work is mandatory (Article 214 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), otherwise disciplinary action may follow.
Moreover, in compliance with all safety rules - undone buttons or a robe carelessly thrown over the shoulders is considered exactly the same violation as a complete lack of overalls.
Order on the appointment of a person responsible for personal protective equipment
The employer is obliged to issue PPE to employees in strict accordance with current legislation, as well as with the standards established at the enterprise. Control over compliance with these requirements is assigned to the person responsible for issuing PPE, whose name and position are approved by the relevant order.
Who can be appointed responsible for issuing PPE
As a rule, the issuance of workwear is entrusted to an employee directly related to special working conditions (chief or senior production foreman). If we are talking about a large enterprise that has several categories of employees who need to be issued different PPE, then in this case the responsibility for issuing lies with the warehouse workers (warehouse manager or senior storekeeper).
The organization has the right to appoint several employees who will share responsibility for issuing PPE. For example, a warehouse employee may be responsible for the issuance procedure, monitoring the wearing period and replacement of PPE, while an employee of the household department may take on the work of ensuring the storage and maintenance of workwear.
In each case, the decision to appoint a responsible person/persons remains at the discretion of the company's management.
Drawing up an order to appoint a person responsible for personal protective equipment
The law does not approve the form according to which the employer is required to issue an order appointing a person responsible for personal protective equipment. The document is drawn up in free form, indicating the required details:
- name of company;
- date and document number;
- Full name and position of the manager approving the order.
The order must indicate the full name and position of the responsible person, as well as clearly and concisely list his responsibilities. For example:
- issuance of personal protective equipment;
- control over compliance with the wearing period;
- provision of storage and maintenance (laundry, repairs);
- maintaining a log of personal protective equipment;
- control over the return of personal protective equipment in specified cases (after the wearing period expires, upon dismissal of an employee, etc.).
Additionally, the employee may be assigned responsibilities for developing standards for accounting for personal protective equipment, as well as for monitoring changes in legislative norms regarding the procedure for issuing and accounting for protective clothing.
Conclusion
In the field of ensuring safe working conditions, a very important element is protective clothing, which helps not only to protect employees from harmful production processes, but also to ensure comfortable working conditions for workers.
In addition, compliance with these simple rules guarantees the correct and rational use of the enterprise’s budget, eliminating overexpenditures and losses due to the absence of workplace injuries and fines.
I wish you efficient and safe work.
If you have any difficulties in developing documents for the correct management of the issuance of workwear and PPE, please contact us and we will sort it out. I provide a full range of labor protection services.
PPE certification
Before purchasing PPE, the employer of the enterprise must make sure that the workwear has the appropriate quality certificate. The certification process ensures that PPE is safe for human use and can be used for human protection and safety.
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is the employer who is obliged to provide workers with safe working conditions. And therefore he is responsible for the acquisition and issuance of safe protective equipment.
In addition to having a certificate for PPE, when purchasing workwear, the employer must check the expiration date, which is also confirmed by the corresponding certificate.
All workwear must comply with GOST standards.
Caring for PPE
To ensure long service life of shoes, you must:
- after finishing work, clean it from dirt without damaging the material of the top and bottom, wipe it and leave it in a ventilated room at a distance of at least 30 cm from heating devices in an open form for ventilation and drying;
Note!
It is not allowed to clean shoes with organic solvents.
- systematically (at least once a week) lubricate it with shoe polish, followed by polishing with a bar brush;
- when cleaning, use: emulsion creams - for shoes made of chrome leather, fatty creams - for shoes made of yuft leather;
- avoid cutting the top of the shoe and the sole - this reduces its protective properties;
- When putting on shoes, unlace them, unfasten zippers, fasteners and always use a shoe horn (to avoid creasing the heel).
All insulated PPE must be dried after work. Drying work clothes and safety shoes on heating radiators is prohibited.
During operation, insulated workwear must be promptly washed, dry cleaned, repaired and replaced in case of premature failure. All this work is carried out at the expense of the employer.
In accordance with the requirements for the organization of dry cleaning and laundry facilities[7], the laundry must have:
- rooms for receiving, sorting and tagging dirty linen;
- washing shop;
- drying and ironing shop;
- room for disassembling and storing clean linen;
- linen collection point;
- repair shop;
- storage room for washing materials and equipment.
Employees can hand over their workwear for washing on their own, or each department can appoint someone responsible for handing over their workwear for washing (cleaning) and repair, who will collect the workwear from employees and deliver it to the laundry, and return it to the employees after washing and repairing.
To simplify the procedure for handing over and returning workwear from washing and repair, you can mark work clothes (apply a personnel number) or install individual lockers for handing over and receiving.
In addition, a schedule for the delivery and return of workwear from washing and repair must be drawn up.
The current legislation does not establish the frequency with which work clothing must be washed. However, such clothes must be washed in a timely manner (as they get dirty), so the washing schedule is set taking into account the working conditions at the workplace.
For example, when operating industrial vehicles[8], it is recommended to wash workwear once every six days for heavy contamination and once every 10 days for moderate contamination.
For your information
In order to promptly wash and care for PPE, you can issue employees two sets of identical PPE with double the wearing period
It must be remembered that frequent dry cleaning and washing can damage protective coatings and damage the special properties of the fabric. Generally accepted practice for washing (dry cleaning) workwear: for moderate soiling - once a month, for heavy soiling - 2 times a month.
The frequency of dry cleaning, washing, and repairs is prescribed in the employer’s local act and, based on it, a schedule is developed that also includes accounting for the delivery and issuance of PPE.
When washing, you need to pay attention to the composition of the fabric indicated on the label, the presence of dyes and special impregnations - they may require special care. For example, natural plant fabrics (cotton, linen, etc.) are washed with any reagents at a temperature not exceeding 40 °C to avoid shrinkage; To wash natural fabrics of animal origin (wool, silk), you need to carefully wash at a temperature not exceeding 50–60 °C, and do not use products with enzymes that decompose proteins, chemical bleaches, or alkali salts.
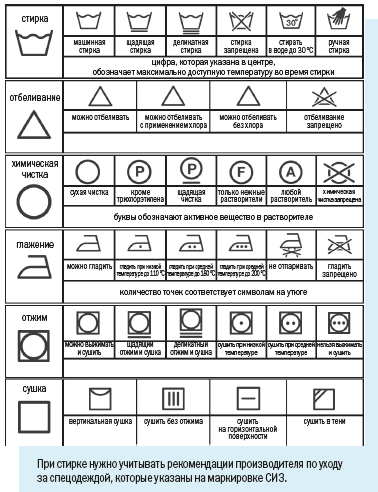
Do not force employees to wash their personal protective equipment at home - employees are prohibited from taking work clothes outside the production premises and washing workwear sets in household machines:
- firstly, unsuitable equipment can damage the protective impregnation of workwear;
- secondly, in order to remove industrial stains, professional detergents are needed - household detergents are simply not able to cope with them;
- thirdly, sources of chemical pollution contained on fabrics may enter wastewater. In specialized organizations that process large batches of workwear, the water remaining after washing must undergo a filtration stage.
Thus, washing (dry cleaning) and repairing workwear at the enterprise itself requires financial costs and the implementation of certain technical procedures, which are not always easy to perform. Therefore, each enterprise calculates the profitability of introducing its own service, whose responsibilities will include washing, dry cleaning and repair of workwear.
If the employer does not have the opportunity to carry out such work, a civil contract should be concluded with an organization specializing in the provision of such services[9]. The procedure for their organization and implementation should also be regulated by the employer’s local act.
In this case, the procedure for collecting PPE and delivering it to the laundry (dry cleaning) must be stipulated in the local act of the employer and in the agreement with the organization providing this service. These can be various options:
- appoint a responsible employee for collecting and handing over workwear for washing and repair. According to the approved schedule, he will collect work clothes from workers, deliver them to the laundry and bring them back. In this case, the responsible employee must be paid for additional work;
- negotiate with the laundry so that their service is responsible for the delivery of workwear, and stipulate this in the contract.
We remind you that employees cannot take dirty workwear to the laundry themselves, as they are prohibited from taking PPE outside the employer’s premises.