How data on unfinished construction is generated for balance
Initially, all costs for the acquisition and construction of fixed assets are accumulated in the account. 08 “Investments in non-current assets”. Its four subaccounts allow you to group costs:
On subaccount 3 counts 08 accumulate data on the costs of OS construction. Debit account 08 at the end of the period shows the amount of construction in progress, since even completed fixed assets that have not been put into operation are considered unfinished. With commissioning, the cost of fixed assets is transferred from the account. 08 on account 01 "Fixed assets".
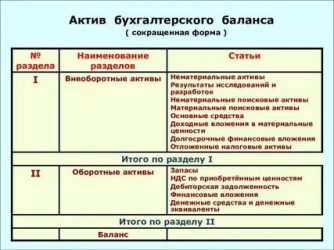
Account debit data 01 and 08 are entered into the balance sheet in line 1150. If the amounts of capital investments are significant, then a separate line is created in the balance sheet to reflect them (clause PBU 4/99).
You can learn more about accounting for investments reflected in account 08 in the article “Rules for keeping records of investments in non-current assets.”
Account 46 in accounting
The debit of account 46 “Completed stages of work in progress” takes into account the cost of completed stages of work (according to the established procedure) paid by the customer, and on the credit - funds received to the organization’s account from this customer:
Analytical accounting for account 46 is carried out by the organization by type of work.
Audit of unfinished capital investments: basic principles
In order to correctly reflect the value of unfinished capital investments (UCI) in the balance sheet and accounting records, it is necessary to periodically audit these investments. The purpose of such an audit may be:
- assessment of the reliability of accounting data;
- checking whether the cost of the NKV is formed correctly.
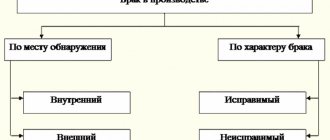
Since the entire construction process can be divided into 3 main stages: preparatory and permitting, construction stage, final stage, then the audit of unfinished capital investments can be divided into 3 types:
- Checking the correctness and availability of permits, checking design and estimate documentation.
- Checking the correct write-off of construction costs.
- Estimation of the value of an NKV object based on an inventory.
The first type of audit allows you to assess what documents are available at the construction site and whether they comply with technical requirements and standards. This type of audit is carried out by technical specialists. Together with them, at this stage, workers of economic services assess the correctness of the application of estimated prices and the cost of equipment included in the estimates. As a rule, this type of audit is carried out by the customer and investor.
IMPORTANT! Drawing up estimate documentation is mandatory and is provided for in Art. 743 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The second type of audit is also carried out by a complex group, which should include representatives of technical services and economists (accountants). At the same time, a check is made to ensure that actual costs correspond to the level of costs included in the construction cost. This type of audit is of greater interest to contractors.
The third type of audit is final. During it, the correctness of the assessment of the object of unfinished capital investment is checked. To do this, real costs are compared with estimates, actual balances of materials, equipment and the amount of written-off materials are checked. This type of audit is important for both the customer (investor) and the contractor.
The audit is carried out on the basis of documents that are located on the unfinished construction site. Such documents include work logs, hidden work logs, reports of financially responsible persons, reports on the write-off of materials for work, acts of work completed, accounting registers.
Learn more about how to organize an account audit. 08, read in the material “Audit of investments in non-current assets (account 08)”.
Reflection of unfinished capital investments in the balance sheet is carried out on line 1150, if the balance on the account is significant. 08 - on a separate line. Before drawing up annual reports, an enterprise is obliged to ensure the reliability of accounting data, for which an inventory is carried out, as well as an internal (and in cases established by law - external) audit of assets and liabilities.
Procedure for using account 46 accounting
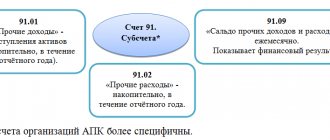
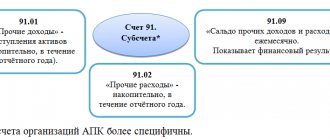
Accounting involves the use of a large number of accounts. One of the areas is completed stages of unfinished activities - score 46.
What is it used for?
The invoice is intended to provide information about work completed in accordance with the agreements drawn up, which have independent significance. If necessary, it is used by firms carrying out long-term work, the beginning and completion of which usually relates to different reporting time intervals. That is, more often we are talking about the field of construction, science, geology.
The debit of this direction records the cost of stages of work paid by the customer. This is done in the manner prescribed by law, in correspondence with account 90 “Sales”.
At the same time, the amount of costly areas for completed and accepted stages of work is written off from account 20 “Main production”. Amounts of money received from customers are reflected in the debit of the direction in question in correspondence with account 62 “Settlements with customers”.
When the work process comes to an end, the price paid by the customer for the stages, appearing on invoice 46, is written off to 62. The cost of measures that have been completed in full is subject to repayment through advances and other amounts that were previously received from the customer. As a result, the final calculation is obtained, correspondence with the debit of the accounting accounts is observed.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wkdOEdv2Ips
Analytical accounting activities are carried out in accordance with the types of work. Based on the description given, we can conclude that the 46 account is often used with the following accounts:
- 90 – when reflecting the cost indicator of the stages of work that were paid by the customer;
- 62 – write-off of the cost of work stages after their completion in general;
- 20 – upon completion and acceptance of work that has been fully completed.
In addition, the direction is of a calculation nature and is used to calculate the cost of products, goods, works, services that were produced during the reporting time period. In order to calculate the financial result for intermediate types of work, two key directions are used:
- For construction projects, the determination is made strictly after the completion of construction of the facility.
- Based on the type of work that was completed - based on the completion of individual areas of work, when they can be objectively and fully assessed.
Thus, the account has many features and accounting subtleties taken into account.
Postings and business transactions
Business transactions on an account can be main and intermediate. The main elements include the account in question 46, while the intermediate ones are used solely for the purpose of detailing the information provided.
Here is an approximate list of transactions that are directly related to account 46.
- Dt 51 Kt 62 – receipt of advance payment from the customer.
- Dt 20 Kt 10 (69, 70) - a reflection of the contractor’s costly directions for the implementation of activities.
- Dt 46 Kt 90 – implementation of delivery based on the results of the first stage of work.
- Dt 90 Kt 20 – the fact of reflecting a write-off at the cost of the activities carried out.
- Dt 90 Kt 99 – reflection of the financial result based on the completion of the first stage.
- Dt 46 Kt 90 – delivery of the next stage of completed processes.
- Dt 20 Kt 10 (69, 70) – display of costly areas for fulfilling the conditions within the framework of the drawn up agreement.
- Dt 90 Kt 20 - when the write-off of the cost of work activities occurred within the second stage.
- Dt 90 Kt 99 – obtaining results of the financial result from the completion of the second stage of work.
- Dt 62 Kt 46 – the cost of measures taken by the customer was written off.
- Dt 51 Kt 62 - the fact of receipt of final payment for the work from the customer.
Determination of financial results must be carried out strictly monthly. But the profit parameter reflected during these operations is not used in the process of settlement actions for taxes, contributions, and fees. The remaining debt is closed using the advance received earlier.
If we consider without intermediate operations, the following activities can be distinguished:
- Dt 46 Kt 90 – the fact of acceptance of the work performed by the customer;
- Dt 90 Kt 20 - write-off of costs that went into performing production processes;
- Dt 51 Kt 62 – receipt of money from the customer, involving settlement activities;
- Dt 62 Kt 46 - a situation where the project has been completed and transferred to the customer with acceptance and payment.
On the topic of the article! How to put property received free of charge on the balance sheet?
Thus, there are quite a lot of transactions in the balance sheet for account 46. Their proper design will allow you to optimally calculate the cost of work and maintain accounting actions for other measures.
The use of this account is considered appropriate if organizations carry out activities and accept payment for them in stages.
The strictly negotiated price of the object is subject to reflection on the invoice. On the other hand, there are difficulties in the accounting process.
In the case of stage-by-stage delivery of the object, the transfer of ownership does not take place, so the company cannot say that all operations relate to direct sale.
The full amount of contractual terms reflected in the debit of account 46 is essentially revenue, but it is not presented to the customer. Therefore, these accruals relate to other assets and are recorded in line 1260.
The legislative framework
The application of this direction is carried out in accordance with the existing PBU. It is approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n. Contract agreements drawn up for a period of at least one year play an important role. For them, in addition, it is customary to apply PBU 2/2008 and other legislative acts.
In addition to the local documentation base, in practice the norm of state legislation is often applied. For example, various acts, resolutions, orders. Through these documents, accounting activities are regulated and regulated. Various accounting statements, forms, samples and templates are also used to help reflect certain transactions.
Thus, the count of 46 has many uses and is significant.
We recommend other articles on the topic
2.1. Features of accounting in construction using account 46
According to accounting rules, revenue is always recognized on an accrual basis.
This is reflected in the credit of account 90.1 “Sales revenue”. And the moment of recognition of revenue for tax accounting may depend on the accounting policy adopted by the organization (accrual, cash basis, simplified tax system or UTII).
However, there is a very interesting and economical accounting in construction using account 46 “Completed stages for work in progress.” A peculiarity of using account 46 is the fact that revenue for both accounting and tax accounting is recognized not on an accrual basis, not on a cash basis, but somewhat differently.
1. Revenue for accounting and tax accounting is recognized at the time of completion of work under the act, but subject to payment for these works by the customer (under the contract, ownership begins at the time of payment for work performed under the act by the customer).
2. Revenue for accounting and tax accounting is recognized at the time of completion of all work under the contract, but subject to payment for these works by the customer (under the contract, ownership begins at the time of payment for work performed under the contract as a whole by the customer).
3. Revenue for accounting and tax purposes is recognized at the time of completion of the project as a whole, but subject to payment for all work by the customer (under the contract, ownership begins at the time of payment for work performed on the project as a whole by the customer). Revenue for accounting and tax purposes is recognized at the moment of transfer of ownership upon delivery of the object (according to the contract, ownership begins at the moment the object is put into operation to the customer).
Using all these options for recognizing revenue allows you to use account 46 “Completed stages for work in progress” in accounting. Until revenue is recognized in the first case, the completed stages of work are reflected on the credit of account 46. After receipt of payment for the work performed, i.e. at the moment of transfer of ownership, revenue is credited, which is reflected on the credit of account 90.1 and the debit of account 46.
In other cases, revenue is transferred to the credit of account 90.1 at the moment when it is recognized according to the accounting policy adopted by the organization.
It should be noted that such recognition of revenue for both accounting and tax accounting purposes is very progressive for Russian accounting and significantly brings our accounting closer to international standards. Agree, after all, at the moment of recognition of revenue, we will already have generated all the expenses for this object or stage of work, which means that the profit will be fair and finally determined. And at this moment it is not a sin to share this profit with the budget in the form of income tax.
In addition, such accounting significantly brings accounting and tax accounting closer together and puts accounting in an organization at a higher level.
All receipts of funds from the customer until revenue is recognized are considered as advances.
Using the example of Vector LLC, let's consider accounting, tax accounting and reporting using account 46, as well as elements of management accounting.
Account 46 in accounting: application of accounts and postings
Accounting account 46 is the active account “Completed stages of work in progress”, provides information about the “independent” stages of work completed, according to the terms of the concluded agreement, so that they can be calculated by the organization.
The debit of account 46 “Completed stages of work in progress” takes into account the cost of completed stages of work (according to the established procedure) paid by the customer, and on the credit - funds received to the organization’s account from this customer:
[1]
Analytical accounting for account 46 is carried out by the organization by type of work.
Postings to account 46 using the example of a construction contract
Let's say that IC "Vernex", according to a construction contract, where the price of work is 250,000 rubles, is the contractor.
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
- construction costs - 180,000 rubles;
- period – from December 2021 to January 2021;
- advance payment (before the start of work) – 110,000 rubles.
Based on the results of December 2021:
- completed - 75% of the total scope of work under the contract;
- expenses incurred - 130,000 rubles.
Postings on account 46 in construction: long-term construction contract:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 51 | 62 | 110 000 | The advance received from the customer of the work is reflected | Bank statement |
| 62 | 68 VAT | 18 780 | VAT charged on advance payment | Invoice |
| 46 subaccount “Revenue not presented for payment” | 90.01 | 187 500 | Reflection of the cost of work performed “as ready” (revenue for December 2021) | Bank account statement, Certificate of acceptance of work performed and services rendered |
| 90.03 | 76.N.1 | 28 602 | The amount of VAT not claimed is reflected on the recorded revenue. | Invoice |
| 90.02 | 20 | 130 000 | Expenses written off (construction in December 2021) | Accounting information, |
Act on the provision of production services