Defects in production and their accounting
During the manufacturing process, a company may produce defects. A manufacturing defect is considered to be products, goods, semi-finished products, finished products that do not meet the quality, technical specifications (TS) or certain enterprise standards (STP), therefore, the products cannot be used for their intended purpose.
Manufacturing defects can be divided into two types:
- Depending on the nature of the detected defects:
- Correctable defects are defective products, the correction of which is economically feasible and technically possible, after which they can be used for their intended purpose;
- An irreparable defect is a defective product that cannot be corrected, since correction is not economically feasible, since in this case it cannot be used for its intended purpose.
- At the location where the defects were found:
- An internal defect is a manufacturing defect discovered at the enterprise;
- External defect is a manufacturing defect discovered after sale during operation by the buyer:
To account for defective products, the technical control department (QCD) creates a document that reflects the fact that a defect was detected and what type it belongs to. The document is generated in any form, taking into account paragraph 2 of Article 9 of Law No. 129-FZ of November 21, 1996.
It is important to note that accounting for manufacturing defects is also necessary for tax accounting.
Losses due to manufacturing defects are recognized as costs that reduce the taxable income tax base. When calculating the costs of manufacturing defects, you need to take into account only those costs that were not written off for materials or for the employee who caused the defect.
In the event of an external defect, the company reduces the amount of VAT that was accrued and paid earlier by the amount of VAT on the sale of returned products.
Accounting for defective goods, products, materials in
10/13/2004 Accounting ZENsubscribe to our channel In the “Production + Services + Accounting” configuration (rev. 2.8) for “1C:Enterprise 7.
7″ a methodology for working with defective goods, products and materials has been implemented.
In this article, methodologists from the 1C company talk about how the configuration reflects operations for accounting for defective inventories, and also describes methods for working with correctable and irreparable defects.
Accounting for defective inventories in the warehouse
To account for defective inventories, the concept of “Quality” is used.
“Quality” in documents can take on two meanings:
- New – new MPZ
- Rejection – defective MPZ
Defective materials are identified separately in both warehouse and batch accounting. The cost of writing off defective goods from the warehouse is calculated separately from the cost of writing off new ones.
To register transactions with defective inventories in a configuration depending on the business transaction, you can use the following documents (see table).
Name of business transaction Document used to conduct a business transaction
It should be borne in mind that not all business transactions can use defective materials. The following transactions are processed only with new inventories:
- Receipt from the supplier;
- Receipt from processing;
- Transfer to production;
- Transfer into operation;
- Transfer to commission;
- Shipment without transfer of ownership.
Method for correcting manufacturing defects
A manufacturing defect can be correctable or irreparable. In the first case, it is technically possible and economically feasible to correct the product. If it is impossible or unprofitable to eliminate the shortcomings of defective products, then such a defect is considered irreparable.
We will describe methods of working with correctable and irreparable defects.
Application of account 28 in accounting
Account 28 “Rejects in production” in accounting serves to reflect all costs of rejected products in production. On this account you can keep analytical records that will allow you to track the causes of defects:
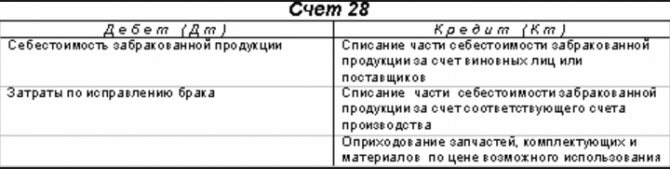
Subaccounts for which analytical accounting will be reflected must be indicated in the enterprise's accounting policy.
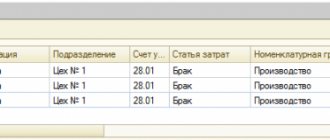
Defects were identified and recorded in the main wiring shop
Write-off of defects in production: postings Let's present in the table the main accounting records for write-off of defects in production: Operation Debit sub-account Credit of sub-account Defective products are capitalized at the price of possible use 10 “Materials” 28 Losses from defects are attributed to the guilty party 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations » 28 Losses due to correctable defects 20, 23, 29, etc. are written off. 28 Expenses in connection with final defects are written off Act on writing off defects in production There is no unified form of an act on writing off defects in production. An organization, taking into account its specifics, can independently develop the form of such an act and consolidate it in the Accounting Policy for accounting purposes.
Typical transactions for account 28 “Defects in production”
Typical entries for correctable defects on account 28:
| Dt accounts | CT account | Operation description |
| 28 | 10 (70;69;25;26) | Written off material (wages; insurance premiums; general production expenses; general business expenses) expenses for correcting defects |
| 73.02 | 28 | The amount recovered from the culprit of the marriage is reflected |
| 20 (23) | 28 | Expenses to correct defects are written off to the cost of production |
Typical postings for irreparable defects on account 28:
| Dt accounts | CT account | Operation description |
| 28 | 20 | The cost of defective products is written off |
| 41 (21) | 28 | Defective products (semi-finished products) are accepted for accounting |
| 73.02 (76.05; 60) | 28 | The amount recovered from the culprit of the defect (suppliers of defective material) is reflected. |
| 20 (23) | 28 | Losses from defects are written off to the cost of production |
Marriage assessment accounting account 28
Let's start with postings for correctable defects. Ivanov manufactured a defective part. Petrov corrected him. Costs for correcting defective products:
- cost of materials 100 rubles,
- Petrov's salary is 500,
- insurance premiums from Petrov’s salary 180.
500 was withheld from Ivanov’s salary at reduced rates.
What transactions need to be reflected? Postings for accounting for correctable defects Amount Debit Credit Name of transaction 100 28 10 Material costs for correction are taken into account 500 28 70 Costs for the salary of the employee who corrected the defect are taken into account 180 28 69 Accrued insurance premiums from the salary of the employee who corrected the defect are taken into account 500 73 28 Withheld from the salary of the guilty employee 280 20 28 Losses from defects are written off to the cost of production As we see from this example, if it is possible to correct the defect, then debit the account. 28 collects all costs for correcting defective products.
Account 28 in accounting: entries for accounting for defects in production
Losses from defects are written off monthly to the costs of the corresponding type of production and included in the cost of those works (services) for which defects were detected.
Losses from external defects related to products (works) produced in the previous reporting period are written off to the cost of similar products (works) produced in the current reporting period.
If no similar products (works) were manufactured during the reporting period, then losses from external defects are distributed among all manufactured products (works) according to the method established for the distribution of general business expenses.
As a rule, attributing losses from defective products to the cost of work in progress is not allowed. An exception may be allowed in individual and small-scale production, provided that the specified losses are attributed to a specific order that has not been completed in production.
Account 28. accounting for defects in production. example, wiring
Typical entries for correctable defects on account 28: Dt account Kt account Description of transaction 28 10 (70;69;25;26) Material (salaries; insurance premiums; general production expenses; general business expenses) expenses for correcting defects are written off 73.
02 28 The amount recovered from the culprit of the defect is reflected 20 (23) 28 The costs of correcting the defect are written off to the cost of production Typical entries for irreparable defects on account 28: Dt of account Kt of account Description of the transaction 28 20 The cost of defective products is written off 41 (21) 28 Accepted to accounting for defective products (semi-finished product) 73.02 (76.05; 60) 28 The amount recovered from the culprit of the defect (suppliers of defective material) is reflected 20 (23) 28 Losses from defects are written off to the cost of production Example and entries on account 28 for accounting for defects in production Let's look at more detailed example of recording transactions on account 28 “Defects in production”.
Count 28: production defects. example, wiring
Important Depending on the severity of product defects, repairable and irreparable damages are distinguished in production (final defects, the correction of which is impossible or economically impractical).
Attention! The amount of money spent on correcting defective products, the defects of which arose due to the fault of the customer and the repair is carried out at his expense, is not considered a manufacturing defect.
Account 28 in accounting is active.
Losses from marriage: accounting and use
Defects in production lead to a decrease in the efficiency of resource use. Manufacturing defects are considered to be parts, components, semi-finished products, works, products:
- not meeting current standards or specifications;
- which can be used for their intended purpose only after additional costs for bringing them into compliance with standards or specifications, or cannot be used at all.
Accounting for defects in production for accounting purposes is carried out on account 28.
A marriage at the place of its detection can be:
- internal (directly at the enterprise);
- external (after sale to the consumer or intermediary).
If it is possible to correct the defect, it is divided into:
- correctable;
- incorrigible.
The detected defect must be documented in an act, the form of which is approved by the management of the enterprise.
Account 28 “defects in production”
Account Dt Account Kt Description of the posting Posting amount Document-basis 28 20.01 The cost of the defect was written off 2000 Certificate-calculation, act on the occurrence of the defect 10.
01, 21, 41 28 Rejected materials, semi-finished products, products were accepted for accounting at the price of their possible use 800 73.02, 76.05 (60.
01).
- confirmed costs for correcting defects from the consumer;
- costs of transporting defective products;
- reimbursement of other buyer expenses associated with defective products.
If the defect is corrected by the manufacturer, it is accounted for during the correction time in off-balance sheet account 002.
Accounting for losses from defects
It is important that the costs of rework are economically justified);
- irreparable defect (rework of rejected products is impossible, or the costs of rework are too high and not economically justified).
If a decision is made to eliminate product defects and the defect is considered correctable, then the product is sent to the workshop for revision. To the cost of repairable defects, the costs of materials, wages of employees with deductions, etc. are added.
p. Subsequently, the product is returned for sale.
If the defect cannot be corrected, the responsible employee determines what in the product can be usefully used in production, and what should be recycled? If the components retain their usefulness (for example, zippers in a tailoring workshop), they will be separated from the rejected product and used for their intended purpose in the production of similar products.
Postings for manufacturing defects - account 28
Attention On the debit of account 28, all costs for identified internal and external defects are accumulated, that is, the cost of irreparable (final) defects, costs for correcting defects and other expenses, as well as costs for warranty repairs.
On the credit side of the account, amounts attributed to the reduction of losses due to defects and amounts written off to production costs as losses due to defects are recorded.
Amounts that reduce losses due to defects include the cost of rejected products at the price of possible use; amounts actually withheld from those responsible for the defects, and amounts actually collected or awarded by arbitration (court) from suppliers for the supply of substandard products, raw materials, materials or semi-finished products, the use of which resulted in defects. If the returned product is corrected, it is included in the volume of commercial and sold products in the usual manner.
Defects in production
The cost of useful scrap parts is determined by the price of possible use. If an enterprise produces warranty products, then it is obliged to create a reserve for repairs. In this case, losses from defects are written off against the guarantee reserve (account 96).
When identifying rejected products, the person who caused the defect is always identified. The culprit may be a supplier of low-quality materials or an employee of the enterprise. A claim is submitted to the supplier.
If it is recognized by the supplier, the amount of compensation paid by him is counted towards the reduction of defective expenses.
If an employee is found to be at fault, then the amount of expenses related to the marriage is established and is subject to deduction from wages. By law, you can deduct no more than 20% from your salary each month. Account 28 for accounting for defects Account 28 is used for accounting for defects. The account is active.
Source: https://advokat-burilov.ru/brak-otsenka-uchet-schet-28/
The cost of the final defective wiring is written off
- materials - 100 rub.,
- transportation costs - 20,
- salary - 500,
- insurance premiums - 180,
- general production expenses - 30.
500 were withheld from Ivanov. Returnable waste after writing off the defective part amounted to 80 rubles.
What kind of wiring do we do? First of all, we calculate the cost of the final defect: 100+20+500+180+30=830 rubles.
Postings for accounting for irreparable defects Amount Debit Credit Name of transaction 830 28 20 The cost of the defective part was written off 500 73 28 Withheld from the employee who allowed the production of the defective part 80 10 28 Returnable waste from defects was entered into the materials warehouse for further use 250 20 28 The remaining losses from defects were written off to the cost of production Defects in production can also be grouped according to the location of the defect: internal and external.