What does the Labor Code of the Russian Federation say about the timing of payment of wages in 2021 - 2021
Salary terms are fixed in Art. 136 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. According to it, money for employees’ work should be transferred to:
- at least every half month; And
- no later than 15 calendar days from the end of the period for which the payment was accrued.
If the salary date approved by the employer falls on a weekend, the money is issued the day before.
IMPORTANT! Norms Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are mandatory and cannot be violated even at the written request of an employee who wishes to receive money once a month.
As a rule, employers pay wages according to the following scheme: once a month they issue an advance and once a month the final payment, adjusted to the previously issued advance. With such a schedule and taking into account the norms of Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the deadlines for salaries for the first half of the month fall on the 16th–30th (31st), and for the second half - on the 1st–15th.
IMPORTANT! For large companies with a large number of structural divisions and a large staff, it is not prohibited to approve different salary payment dates for different departments (letter of Rostrud dated June 20, 2014 No. PG/6310-6-1).
All aspects of paying advances to new employees are in the article “Advance to a new employee in the first month of work.”
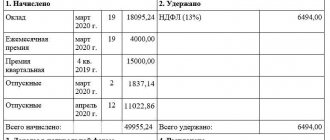
Example of calculating the advance payment

Fillipova A. N. Works as a cashier at Rassvet LLC. Her salary is set at 18,000 rubles. She also receives an additional payment for combining the position of an accountant - 8,000 rubles. If the sales department fulfills the plan for selling products, all employees are also awarded a bonus in the amount of 30% of the salary.
You might be interested in:
Salary: payment procedure, when, in what amount
There are 21 working days in a billing month, the advance is paid for 11 days worked.
We will calculate the advance payment. It will include the salary and the amount of additional payment. Since the bonus is calculated only based on monthly sales results, it is not included in the calculation of the advance payment.
The salary for the first half of the month will be: 18,000 / 21 x 11 = 9,429 rubles.
The additional payment for the same period will be: 8000 / 21 x 11 = 4191 rubles.
Total total advance amount: 9429 + 4191 = 13620 rubles.
bukhproffi
Important! Income tax is not deducted from the advance payment, therefore the entire calculated amount must be issued to the employee on the day established in local regulations.
What documents indicate the days of payment of wages?
The employer is obliged to fix a specific schedule for the transfer of salary money in its local regulations (LNA): internal labor regulations (ILR), collective or labor agreement. It is these 3 documents that Art. 136 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The wording of this article is designed in such a way that the question often arises: is it necessary to fix salary terms in all of the above documents or is one of them sufficient? The answer to it was repeatedly given by both officials and judges (letter of Rostrud dated March 6, 2012 No. PG/1004-6-1, ruling of the Moscow City Court dated December 24, 2012 No. 4g/5-12211/12).
For information on what to include in an employment contract, read the article “Procedure for concluding an employment contract (nuances).”
According to the explanations, it is enough that the deadlines are fixed in one of those given in Art. 136 Labor Code of the Russian Federation documents. Moreover, according to Rostrud, PVTR is a priority. He explains this by saying that the PVTR is a general document, the norms of which apply to all personnel, while an employment contract regulates relations with a specific employee, and a collective agreement may not be concluded at all.
In order to completely eliminate disputes with inspectors, you can do the following: fix the rules for issuing wages in the PVTR, and add a phrase in labor or collective agreements that refers to the PVTR: “salaries are issued in accordance with clause (here we indicate the clause number of the PVTR) of the rules labor regulations..."
Want another expert opinion? Sign up for a free trial of ConsultantPlus or, if available, proceed to the Salary Guide.
Does an employee have the right to demand payment of wages in cash and not on a card?
- Current account of the organization. An authorized employee, for example a director or accountant, can withdraw funds from the company's current account in advance to ensure payment of wages, which must be reflected in the withdrawal receipt.
- Cash received by the organization's cash desk. It is not prohibited to use the cash available in the company's cash register to pay salaries, subject to one limitation. Thus, it is not allowed to issue as salary cash transferred for the performance of intermediary services - the purchase of goods, transfer to third parties, payment for the services of mobile operators or repayment of debt to third parties.
A bank salary card is a tool for receiving cash payments from an employer. The company significantly reduces its costs when paying wages to employees in non-cash form. But salary cards have a number of advantages for holders:
- Free service (if simple conditions are met).
- Additional income due to interest accrual on the balance.
- Refund of part of the cost of purchases under cashback programs.
- Preferential lending conditions in some banks when connecting an individual salary project.
Directly in the standards of Russian legislation there are no restrictions on the payment to citizens of the Russian Federation of their wages in cash. Thus, the employer establishes the general procedure for paying wages in the internal documents of the organization, and also necessarily reflects this fact in the employment contract with the employee - wages can be paid either in cash or by crediting funds to the employee’s bank account.
At the same time, if the employer ensures payment of wages in cash in 2021, he must also follow a certain procedure - certain restrictions are imposed on the source of funds, the time of settlements with the employee and the procedure for processing accounting entries and cash orders during the issuance of wages.
The right to choose a bank for paying wages appeared thanks to the Law of November 4, 2014 No. 333-FZ, which supplemented Part 3 of Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to pay wages to the employee to the credit institution specified in his application. The conditions for payment of wages must be established by a collective or labor agreement. In addition, the employee has the right to change the credit institution by notifying the employer in writing in advance about the change in the details for transferring wages no later than 5 working days before the payday.
What to consider when setting payroll dates
Before approving salary dates, consider the possible risks and tax consequences. There are a number of slippery points that you should pay attention to:
- The expressions “every half month” and “twice a month” should not be confused. For example, the numbers 3 and 16 fit the definition of “twice a month,” but the rule of not exceeding a gap of 15 days is not followed here, since from the 16th to the 3rd it is more than half a month.
- It is dangerous to choose not clear dates, but a time period - for example, from the 1st to the 5th, as well as deadlines, for example, no later than the 5th and 25th. Firstly, Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation speaks of the need to establish specific dates, and secondly, there is a risk of confusion and exceeding the six-month interval between payments. The illegality of this approach is stated in the letter of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated November 28, 2013 No. 14-2-242, the resolution of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated May 15, 2014 No. 3-AD14-1, the ruling of the Trans-Baikal Regional Court dated September 5, 2012 No. 33-2867-2012.
- An insufficiently defined phrase will also be unsafe, for example: “salaries are paid no later than the 5th and 20th of each month.” After all, it is impossible to understand from such a phrase when an advance is given and when the final amount is given.
- When choosing convenient dates, you need to take into account the requirements of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, the 15th day for the final payment turns out to be inconvenient, since the advance payment in this case falls on the 30th day, and this is the last day in many months. From the advance paid on the last day of the month, personal income tax will have to be withheld (clause 2 of Article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, determination of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated May 11, 2016 No. 309-KG16-1804). But in months that have 31 days, this is not necessary. This will create confusion for both the accountant and controllers.
To learn how to reflect the tax withholding date in 6-NDFL, read this article.
Deadlines for payment of advance payments and wages in 2018
The days on which it is necessary to issue an advance and salary must be clearly stated in the employment contract with the employee, as well as in the local acts of the organization (for example, in the regulations on wages).
The law clearly states that no more than 15 days should pass between the issuance of these two parts. In addition, it is established that earnings for the first part of the month must be issued between the 15th and 30th days of the current month, and the final payment must be made between the 1st and 15th days of the month following it.
The administration does not have the right to establish in the documents a period of days during which the payment is expected to be made. However, it can be stipulated that the payment must be made before the specified date. Also, inaccurate dates should not be recorded. The document must clearly indicate the days on which the payment is made, and exactly what part of the salary is paid at that moment.
The law does not prohibit payments at more frequent intervals, for example every 10 days. But in any case, these dates must be indicated in the documents.
Attention! If the day on which the payment of one of the earnings falls falls on a non-working day, then the employer is obliged to make the payment on the previous working day.
It is not recommended to indicate the 15th and 30th as days of issue. This is due to the fact that in many months of the year the 30th day is the last, and therefore on this day the accountant will have to calculate and withhold personal income tax from the advance payment.
You might be interested in:
Online salary calculator for [year] year
Is it permissible to pay salaries more than twice a month?
Yes, definitely. The Labor Code directly states that salaries are paid “at least every half month.” This means that restrictions are placed only on rarer payments to employees, but not on more frequent ones (letters from the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated 02/03/2016 No. 14-1/10/B-660, dated 12/06/2016 No. 14-1/B-1226 ).
If you wish, you can issue money not twice a month, but weekly and even daily. However, before switching to a more frequent frequency of salary payments, it is worth considering the feasibility of this: whether such a schedule will be convenient and beneficial for both employees and the employer himself.
Practice shows that this is beneficial for those employers who employ temporary staff; in other cases, the benefits of more frequent payment of money are completely unobvious, if not completely absent.
For information on how to conclude an agreement with a temporary worker, read the material “Art. 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: questions and answers.”
The weekly payment does not excite the staff either: according to repeated statistical surveys, the majority of employees would like to maintain a 2-time salary schedule.
Is it legal to pay wages ahead of schedule?
It is only legal if the payday falls on a weekend. In other cases, despite the fact that there is no violation of the rights of employees, it is not recommended to pay money earlier than approved by the employer’s LNA. This is fraught with claims from the labor inspectorate and the imposition of a fine.
As we have already found out, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation requires that the dates of payment of wages be clearly recorded in the employer’s LNA. By paying wages ahead of the approved date, strictly speaking, you will have to make appropriate changes to the LNA. However, it is unlikely that anyone will think about a global reworking of documents if the manager occasionally wants to meet employees halfway and issue, for example, a salary before the holidays (while the salary payment period falls on the day after the holiday). In addition, this may lead to an increase in the half-month period between payments, which is also not allowed.
Therefore, although the manager allowed the earlier payment of wages in the interests of the employees themselves, formally this situation is considered a violation (Part 1 of Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and may lead to fines (Part 1 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). However, the risk of prosecution here is still small.
What are the consequences of violating wage payment deadlines?
The employer's liability for such violations can be of two types: material and administrative.
Administrative liability applies only if the employer is at fault.
Primary administrative punishment (clause 1 of article 5.27 of the Administrative Code):
- warning or fine of 1,000–5,000 rubles. for officials;
- fine for the culprit - individual entrepreneur - 1,000–5,000 rubles;
- fine for the culprit legal entity - 30,000–50,000 rubles.
Repeated administrative punishment (clause 2 of article 5.27 of the Administrative Code):
- disqualification for 1–3 years or a fine of 10,000–20,000 rubles. for officials;
- fine for the culprit - individual entrepreneur - 10,000–20,000 rubles;
- fine for the culprit legal entity - 50,000–70,000 rubles.
Financial liability (Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) is expressed in monetary compensation for each day of delay, calculated from 1/150 of the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation of the amount due for payment (minus personal income tax). This is the minimum amount of compensation, but the employer has the right to assign a larger amount. No application from the employee is required to receive it - it must be paid along with the delayed amounts.
IMPORTANT! Maternity compensation is paid regardless of whether the employer is to blame for violating salary deadlines.
In what other cases is the employer liable for financial liability? This publication will tell you.
Responsibility of the employer for failure to pay the advance
The Labor Code does not establish the concept of advance payment. What we call this word is one of the parts of the salary. Therefore, failure to pay an advance is subject to the same liability as failure to pay all earnings.
The law determines that the culprit may be subject to three types of liability:
- Material - occurs immediately the next day after the fixed date of issue. The amount of the fine is calculated based on the amount not paid and the total period of delay as 1/150 of the debt for each day of delay. This compensation must be accrued and paid to each employee, regardless of the reason for which he was not paid on time.
- Administrative - imposed by inspection bodies when they detect a delay in payment of wages. Can be awarded to a responsible person, company or individual entrepreneur. The maximum amount of punishment is 50 thousand rubles, which can be increased if a similar violation is repeated.
- Criminal - imposed by a court decision in case of deliberate non-payment for more than 2 months. Applies to the director of the company or entrepreneur. The maximum penalty is a fine of 500 thousand rubles, or imprisonment for up to 3 years.
How to make changes to documents and set the correct deadlines for paying wages
If for some reason you do not have LNA regulating the timing of salary transfers, they need to be done as quickly as possible. If the necessary LNAs exist, but the dates in them are indicated incorrectly, this should be promptly corrected:
- If possible, redo the document, but only if doing so will not cause inconsistencies with your other documentation.
- In order to change the collective agreement, assemble a commission of representatives of both parties - employees and employer. Document the results of the negotiations between the commission members in an additional agreement, in which you indicate the new salary terms.
- If salary dates were included in employment contracts, you will have to draw up additional agreements for each of them.
- Changes in the terms of payment of wages included in the PVTR are the easiest to formalize - to do this, it is enough to issue an order, which should be familiarized to each employee against signature.
You can see what such an order looks like here:

Results
The frequency of payment of wages is established by Art. 136 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It also obliges employers to set clear deadlines for issuing wages in the LNA. Failure to comply with these deadlines (or the absence of regulatory deadlines) falls under the articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation on material and administrative liability.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.