Changes in personal income tax
From 01/01/2018 the following changes apply.
1. Federal Law No. 335-FZ [1] amended:
– in Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation , which establishes a list of income not subject to personal income tax. A new clause has been added to it. So, according to clause 37.3 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not subject to personal income tax for the amount of payment of part of the down payment towards the cost of the purchased car, provided from the federal budget, when applying for a loan for the purchase of a car in the manner approved by the Government of the Russian Federation;
Provisions of paragraph 37.3 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation applies to legal relations that arose from January 1, 2017 ( Clause 9, Article 9 of Federal Law No. 335-FZ ).
– in Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation . It is supplemented by a new clause 5 , which states that in the event of failure by the reorganized (reorganized) organization (regardless of the form of reorganization) until the completion of the reorganization of the obligations provided for in this article, the information established by clauses 2 and 4 of this article must be submitted by the legal successor (successors) to the tax authority at the place of their registration. If there are several legal successors, the responsibility of each of them in performing the duties established by this article is determined on the basis of a transfer deed or a separation balance sheet.
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation , tax agent organizations submit to the tax authority at the place of their registration:
– a document containing information on the income of individuals for the expired tax period and the amount of tax calculated, withheld and transferred to the budget system of the Russian Federation for this tax period for each individual, annually no later than April 1 of the year following the expired tax period, according to Form 2 ‑NDFL, approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 30, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected] “On approval of the form of information on the income of an individual, the procedure for filling out and the format for its presentation in electronic form” ;
– calculation of personal income tax amounts calculated and withheld by the tax agent for the first quarter, six months, nine months no later than the last day of the month following the corresponding period, for the year - no later than April 1 of the year following the expired tax period, according to form 6-NDFL , approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 14, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected] “On approval of the form for calculating the amounts of personal income tax calculated and withheld by the tax agent (Form 6‑NDFL), the procedure for filling it out and submitting it, as well as the format for presenting the calculation of the amounts of personal income tax calculated and withheld by the tax agent in electronic form .
2. Federal Law No. 333-FZ [2] amended Art. 212 Tax Code of the Russian Federation . This law establishes the conditions under which material benefits from savings on interest for the use of borrowed funds are subject to personal income tax. So, according to the amendments, the material benefit received from savings on interest for the taxpayer’s use of borrowed (credit) funds (with the exception of the material benefit specified in paragraph 2 - 4 paragraphs 1 paragraph 1 of this article) is recognized as income of the taxpayer received in the form material benefit, provided that at least one of the following conditions is met in relation to such savings:
- the corresponding borrowed (credit) funds were received by the taxpayer from an organization or individual entrepreneur that is recognized as an interdependent person in relation to the taxpayer or with which he has an employment relationship;
- such savings are actually material assistance or a form of counter-fulfillment by an organization or individual entrepreneur of an obligation to the taxpayer, including payment (remuneration) for goods supplied by it (work performed, services rendered).
3. By Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 24, 2017 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected] new income codes were introduced for filling out a certificate in form 2‑NDFL:
– “2013” – compensation for unused vacation;
– “2014” – the portion of severance pay and other payments upon dismissal subject to personal income tax;
– “2301” – fine and penalty in accordance with the Law of the Russian Federation of 02/07/1992 No. 2300-1 “On the Protection of Consumer Rights” ;
– “2611” – bad debt written off from the balance sheet;
– “3021” – interest or coupon on certain types of bonds.
Please note that now all listed income has the code “4800”.
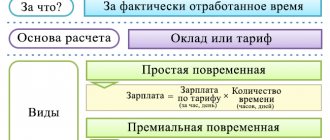
Forms of salary payment
All features of payment of wages to employees are strictly indicated in the Labor Code. Thus, the normative act indicates that salaries to your employees can be given both in cash and in non-monetary form. If the issue is made in cash, then the amount can only be paid in Russian rubles.
Exactly how the employee will receive his earnings must be specified in the employment agreement with him. If there is no such clause in it, then the employee has the right to independently fill out an application addressed to the manager and write down in it exactly how he wants to receive the money he earned. The director cannot refuse such a request.
As a rule, in small companies salaries are paid in cash from the cash register. When receiving funds in hand, the employee must sign on the cash register or on the payroll. Funds that were intended for payment, but for some reason remained not issued, are returned to the current account. They must stay there for a period of time specified by law.
In large companies, salaries are most often paid by transfer to a plastic card. At the same time, the organization does not have the right to force an employee to use cards only from a specific bank. The employee has the right to fill out an application addressed to the director, in which he indicates the details for transferring wages. At the same time, the law gives him the right to change the bank at any time at will, to write a corresponding application no less than 5 days before the next transfer of funds.
Attention! The Labor Code allows the employee to be given part of their salary in kind (for example, in manufactured products). However, this can be done in no more than 20% of all accrued funds. In addition, the employee must fill out an application in which he expresses his desire to receive part of his salary in products - the employer himself does not have the right to impose this method of payment.
It is prohibited to issue salaries in the form of coupons or debt documents. It is also impossible to make payments in products the circulation of which is prohibited in the country or is subject to legal restrictions - alcohol, narcotic or poisonous products, weapons and ammunition, etc.
Changes in insurance premiums
, Russian Government Decree No. 1378 came into force , which established:
– the maximum value of the base for calculating contributions to compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity. For each individual it amounts to an amount exceeding RUB 815,000. cumulative total from the beginning of the year;
– the maximum value of the base for calculating contributions to compulsory pension insurance. For each individual it amounts to an amount not exceeding RUB 1,021,000. cumulative total since the beginning of the year.
How to count in a new way
Let's look at the example of calculating earnings for July. Let’s say that riding teacher Petr Petrovich Petrov works at the Allur sports school and has a salary of 40,000 rubles. Plus, he is entitled to a bonus of 10,000 rubles, but he has no regional additional payments. The production calendar suggests that July has 22 working days and 9 non-working days. Due to production needs (the school received new thoroughbred foals), Petrov had to work on July 7 and 8, that is, Saturday and Sunday. Let's calculate how much he needs to pay for these two days.
Previously, an accountant would calculate salaries like this:
Earnings for Saturday and Sunday = salary 40,000 / 22 working days in July × 2 days worked × coefficient 2 = 7272.73 rubles.
Now the basis for calculation will be salary plus bonus. It turns out the following:
Earnings for Saturday and Sunday = (salary 40,000 + bonus 10,000) / 22 working days in July × 2 days worked × coefficient 2 = 9090.90 rubles.
That is, now Petrov will receive almost 2,000 rubles more for Saturday and Sunday.
Social Security
Order of the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation No. 578[4] approved new forms of documents that must be used for the payment of benefits for temporary disability and in connection with maternity, as well as for making other payments and expenses, in particular, expenses of insurers for the payment of social benefits for funerals in the regions participating in the implementation of the pilot project.
Order of the FSS of the Russian Federation dated September 17, 2012 No. 335 was declared invalid.
From July 1, 2021, the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), Trans-Baikal Territory, Vladimir, Volgograd, Voronezh, Ivanovo, Kemerovo, Kirov, Kostroma, Kursk, Ryazan, Smolensk and Tver regions will join the FSS pilot project (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 21, 2011 No. 294 ).
Reporting to the Pension Fund and statistical authorities
1. Resolution of the Pension Fund Board of January 11, 2017 No. 3p approved the following reporting forms:
- SZV-STAZH “Information on the insurance experience of insured persons”;
- EDV-1 “Information on the policyholder transferred to the Pension Fund for maintaining individual (personalized) records”;
- SZV-KORR “Data on the adjustment of information recorded on the individual personal account of the insured person”;
- SZV-ISH “Information on earnings (remuneration), income, amount of payments and other remunerations, accrued and paid insurance premiums, periods of labor and other activities counted in the insurance period of the insured person.”
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 11 of Federal Law No. 27-FZ [5], the insurer annually, no later than March 1 of the year following the reporting year (except for cases where other deadlines are provided for by this law), submits information about each insured person working for him (including persons who have entered into civil contracts). of a legal nature, for remuneration for which insurance premiums are charged in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on taxes and fees) information in the SZV-STAZH form together with the EDV-1 form.
Please note that policyholders will be required to submit these 2021 forms for the first time no later than March 1, 2021.
2. Order No. 772 of Rosstat dated November 22, 2017 approved instructions that are valid from January 1, 2021. This order also approved a new form P-4 “Information on the number and wages of employees.” Please note that the frequency of submission of this report (monthly or quarterly) depends on the average number of employees of the organization.
Despite the fact that form P-4 was approved by the new Rosstat Order No. 772 , the procedure for filling it out remains the same.
Labor legislation
Federal Law No. 359-FZ came into force on December 8, 2017 [6]. Let us note that before the amendments to the Labor Code, full financial responsibility was borne by:
– employees under 18 years of age only for intentionally causing damage, causing damage while under the influence of alcohol, drugs or other toxic intoxication, as well as as a result of committing a crime or administrative offense ( Part 3 of Article 242 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation );
– employees in cases where the damage, in particular, was caused as a result of an administrative violation, if such is established by the relevant government body ( clause 6, part 1, article 243 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ).
Taking into account those introduced in Art. 242 and 243 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation of amendments, the employee bears financial liability in the full amount of damage caused only if the damage was caused as a result of an administrative offense. This innovation was introduced due to the absence of the concept of “administrative offense” in the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
2. Order No. 655 of Rostrud [7] approved 107 checklists for routine inspections, which include lists of questions on the most important requirements of labor legislation, as well as regulations containing labor law standards. In particular, they are used to evaluate the correctness of:
– registration of employment;
– amendments to employment contracts;
– granting vacations;
– setting and paying wages;
– termination of employment relations.
Let us recall that clause 20 of Regulation No. 875 [8] states that scheduled inspections of the activities of legal entities, depending on the assigned risk category, are carried out with the following frequency:
– for the high-risk category – once every two years;
– for the significant risk category – once every three years;
– for the medium risk category – no more than once every five years;
– for the moderate risk category – no more than once every six years.
In relation to legal entities whose activities are classified as low risk, scheduled inspections are not carried out.
In addition, organizations can check themselves on the official website of the Federal Service for Labor and Employment on the Internet, since according to paragraph 21 of Regulation No. 875 , information on legal persons whose activities are classified as high and significant risk.
Order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation No. 805n will come into force , which establishes that the standards for issuing flushing and (or) neutralizing agents corresponding to the working conditions at the employee’s workplace are specified in the employment contract or local regulations of the employer, are communicated to the attention of the employee in writing or electronically in a manner that allows the employee to confirm his familiarity with the specified standards. This will simplify the procedure for issuing flushing agents to employees.
New rules for calculating advance payments in 2021
Advance payment is a preliminary payment of a certain amount of money, which is deducted from future payments. Most often we are talking about future payment; it is no more than 50% of earnings.
Thus, the employer interests the employee in continuing cooperation, guarantees receipt of the rest of the amount and helps the person out in case of emergency.
(What percentage of the salary is the advance? Amounts and payment procedure).
An advance is also called paying part of the amount for a product that they plan to purchase in the future, but for which they are not ready to pay in full (most often we are talking about expensive purchases, such as a car or real estate, expensive household appliances, etc.). In this way, the buyer reserves a specific item, reserving the right to pay the full amount later.
New advance payment calculation in 2021
In this article we will try to understand the regulatory framework and answer the most important questions regarding the timing, calculation and system for calculating advances in 2021.
Rules for calculating advance payments 2021 according to the legislative framework. Officially, the concept of “advance” is absent in the Labor Code: the employer pays wages at least twice a month (the first of which we call an advance). Payment terms are set directly at the place of work, but the number of payments per month must be at least two.
However, some employers still make payments once a month. Moreover, this can be based both on their own desire and on the employee’s statement. In this case, the employer may face a fine for the first time from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles. (for managers and accountants), and from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles. (for legal entities).
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, payment must be made on one specific day, namely:
- necessarily on a working day,
- at least twice a month;
- the interval between payments should not exceed 16 calendar days;
- the salary delay can be no more than 7 calendar days;
- the duration and size are established by the collective agreement.
- It is unacceptable for the payment period to be defined as several days (for example, from the 20th to the 22nd).
These rules apply to both payments.
The amount of the advance does not depend on how long you have worked at this enterprise. Pregnancy also does not affect the timing or size of receiving an advance.
Is it possible to take vacation in advance?
Remember! If the delay in payment of advance payment or wages lasts longer than 15 days, you have the right to suspend work at this enterprise until full payment is made, notifying your employer in writing in advance.
The Ministry of Labor has changed the calculation of advance payments in 2021
The Ministry believes that when paying an advance, the following are taken into account:
- allowances for night work, for combining positions, professional skills, etc.;
- current salary size.
Here is a list of indicators that are not taken into account when forming an advance payment:
- bonuses;
- compensation payments (overtime, for work on days off, etc.).
All these accruals will be paid with the second half of the salary.
Now let's move on to the most important point. What are the rules for calculating an advance payment in 2021, when can you expect to receive it, and what responsibility does an employer bear if, for one reason or another, the payment is not made within the agreed time frame?
Interesting fact! When calculating the minimum advance amount, all bonuses, allowances, and additional payments are not taken into account - only the net salary. If these bonuses are permanent and not one-time, it is possible to recalculate the amount of the advance, taking into account all bonuses.
Salary advance calculation 2018
Depending on the company where you work, the advance payment in 2021 can be calculated as follows:
- the first salary will be proportional to the time worked, that is, the advance will be calculated as the sum of earnings for each day worked in the first half of the month;
- the first salary will be 50% of the current one; This is the most acceptable method for the employer, as it eliminates the possibility of overpayment and minimizes risks.
If during the specified period the employee was on vacation or sick leave, no calculations are made for this period. That is, the work is paid upon completion.
- advance payment in the form of a fixed amount; in many enterprises, the size and timing of the advance payment are agreed upon in advance and change only if the employee’s salary changes; its amount should not exceed 50% of the salary; It is believed that such an advance payment scheme is risky for the employer, since there is a possibility of overpayment (if the employee was on vacation or sick leave for the first half of the month).
Important! Advance payment at the time when you are on sick leave occurs in accordance with the labor act of the organization in which you work. This point must be discussed with the employer in advance. If in the period before receiving the advance you worked and then took sick leave, the settlement amount for the first half of the month must also be paid to you in full.
In order to calculate the amount of the advance starting in 2021, first clarify the organization’s internal rules on this issue.
How to earn a good pension - specific recommendations
Next, we calculate using the formula: tax is subtracted from the total salary (for the first and second half of the month), divided by the number of all working days and multiplied by the days already worked.
For example, you need to calculate the amount of the advance for April (let’s say the due date for payments is the 15th). Your salary is 30,000 rubles. In the first half of the month you had 11 working days.
(30,000 rub. - 3,900 rub.) / 21*11 - 13,671 rub.
3900 rub. - tax.
Advance and taxes
Another important point is the calculation of taxes. According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, it is considered that the taxpayer receives payment for his work only after the expiration of a full month.
Accordingly, receiving an advance is not considered to be receiving wages, and tax is levied only after receiving the second half of the salary.
The salary from which tax is deducted is the total salary for the first and second half of the month.
Therefore, when calculating the amount of the advance, tax is deducted from the total salary (first and second).
Remember! If the advance has not been paid to you even after contacting the accounting department, you have every right to file an application with the prosecutor’s office against your employer or the labor inspectorate of your city.
Payroll
Let us turn to the Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated December 7, 2017 No. 38-P . The question of whether the regional coefficient and percentage premium are included in the minimum wage has not yet been legally regulated. For a long time, the RF Armed Forces expressed its opinion on this matter, based on where the workers directly work:
- the wages of workers who work in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas should be set at no less than the minimum wage, after which a regional coefficient and a percentage increase for length of service in these areas and areas must be applied. The arbitrators referred to the fact that Art. 315 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes: wages in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas are carried out using regional coefficients and percentage increases in wages ( Review dated 02/26/2014 , definitions dated 07/29/2011 No. 56-B11-10 , dated 06/24/2011 No. 3‑B11-16 );
- if employees work in areas with special climatic conditions that do not belong to the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas, the amount of the monthly salary paid to the employee, including the regional coefficient and percentage bonus, may be equal to the minimum wage. In this case, the arbitrators referred to Art. 146 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation , which establishes that the labor of workers engaged in work in areas with special climatic conditions is paid at an increased rate, thereby not violating the requirement of Part 3 of Art. 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation : the monthly salary of an employee who has fully worked the standard working hours during this period and fulfilled labor standards (job duties) cannot be lower than the minimum wage ( Definition dated 08.08.2016 No. 72‑KG16-4 ).
As for the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, in Resolution No. 38-P it explained the following: the minimum wage is recognized as a general guarantee provided to workers regardless of the location in which labor activity is carried out ( Part 3 of Article 37 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation ). According to Part 1 of Art. 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the minimum wage is established simultaneously throughout the entire territory of the Russian Federation without taking into account the natural and climatic conditions of various regions of the country. Thus, the regional coefficient and percentage bonus accrued in connection with work in areas with special climatic conditions, including in the Far North and equivalent areas, are not included in the minimum wage.
For setting wages in a smaller amount than determined by labor legislation, administrative penalties are provided. According to paragraph 6 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, non-payment or incomplete payment on time of wages or other amounts within the framework of labor relations, if these actions do not contain a criminal offense, or the establishment of wages in an amount less than that provided for by labor legislation shall entail a warning or the imposition of an administrative fine:
– for officials – from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles;
– for legal entities – from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles.
New rules for payment of wages from July 1, 2021
Regulation of wages is one of the main issues in labor relations between employer and employee. From July 1, 2021, legislative changes became valid in the Russian Federation, according to which a new remuneration procedure will apply.
All innovations will affect only municipal and budgetary organizations. Federal Law No. 88-FZ dated May 1, 2017 obliges employers to pay employees according to the rules that came into force on July 1, 2021.
As part of the new legislative framework, changes also affected funds whose financing does not come from the state budget.
From July 1, 2021, employers of municipal enterprises do not have the right to pay funds to VISA and Master Card payment systems.
New salary payment rules
Within the framework of the law, from July 1, 2021, Federal Law No. 88 dated May 1, 2017, new wage calculation criteria began to apply:
- All payments to workers are made only to the card of the MIR state payment system. Using cards with any other system will be illegal.
- If an employee does not have the opportunity to receive earned funds on a plastic card, then they can receive money at a bank cash desk.
These changes also apply to all government payments:
- pensions;
- scholarships;
- payment of sick leave;
- maintenance and financial remuneration of persons serving in public positions.
From July 1, 2021, new rules for paying overtime hours have been introduced:
- When going to work on a holiday or on their day off, the employee will receive double pay once. Previously, these hours had to be taken into account and paid twice: as time spent at the workplace in excess of the norm established by law. Moreover, the first 2 hours were paid at one and a half rates, and all subsequent hours at double rates.
- If on a weekday an employee worked 2 hours above normal, then this time is paid at double the rate.
- When going to work on a day off, the employee is paid at a double rate based on the number of hours worked.
- In case of a part-time working week or a shortened working day, the employer does not have the right to establish irregular working hours.
Normative base
Payments to employees who work in the budgetary, municipal sector and extra-budgetary funds are regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Federal legislation:
- Federal Law No. 272 of 2021. This regulates the liability of organizations to an employee in case of non-compliance with payment deadlines. The employer's responsibilities are described, according to which he must specify the dates for the transfer of funds.
- Federal Law No. 125 of 2021. Amendments have been made to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation that regulate the accrual of wages to employees in accordance with Federal Law No. 125.
- Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, part 6, regulates the obligations of the employer in case of non-compliance and incorrect execution of wage laws.
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation Art. 136. The terms and dates for the accrual of funds to workers in an institution that is funded by the state are directly indicated here.
- Federal Law dated May 1, 2017 No. 88-FZ.
What has changed with the innovations on July 1, 2021?
How was the issuance of the salary earlier [/td]
| Changes from July 1, 2021 for organizations financed from the state budget and extra-budgetary funds | |
| Employees had the right to use cards with other payment systems, such as Visa and Master Card. |
|
| The employer had to pay double the rate for weekend work and count the same hours as overtime. | With a shortened week or day, additional irregular working hours cannot be established. Remuneration for work on a day off is doubled once. |
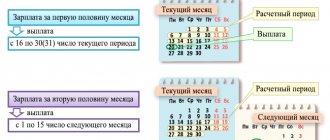
Terms and criteria for transfers of earned funds under the Labor Code from July 1, 2018
From October 3, 2021, the rules and procedure for transferring earned funds have changed. In July 2021, there were no innovations in this area. Therefore, the payment terms and criteria will remain the same.
As part of changes in legislation in 2021, payment of earned funds and advance payments to municipal, state institutions and extra-budgetary funds must be issued once every 15 calendar days.
Organizations must pay the remaining share of the salary in full no later than 15 calendar days from the end of the month for which funds are accrued.
Consequently, the employer has no right to transfer the advance portion on the 20th of the current month, and the remaining share of the salary on the 15th of the next month.
Because between the 20th and 15th there will be approximately 25 calendar days, and this is contrary to the new legislation. If the specified deadlines are not met, the organization will be fined.
Thus, when transferring salary to an employee, the employer must comply with two key criteria:
- The temporary break between the advance payment and the rest of the payment is no more than 15 days.
- Full payment of earned funds is carried out no later than fifteen days from the end of the month for which wages are transferred.
It is possible to set the dates for issuing the PO in the following way: 20th and 5th, 23rd and 7th, 25th and 10th. It is important for managers to take into account that each month has a different number of days: from 28 to 31. Here, any organization is obliged to independently calculate the time frame from the advance to the full transfer of earned funds.
The procedure for issuing wages in 2021 from July 1 for government agencies
Municipal institutions and organizations financed from the state budget, from July 1, 2021, as part of changes in Federal legislation dated May 1, 2017 No. 88-FZ, must pay wages to employees in accordance with the following points:
- Payment is made only to the national payment system - the MIR card. The organization is obliged to enter into appropriate contracts with banks for issuing salary cards to employees. But the employee has the right to independently determine the bank in which the salary account will be located. The employee must notify about the choice of bank no later than 5 days before the date of the next advance or salary. And draw up a corresponding application, which will indicate all bank details.
- The employee has the right to receive funds through the cash register.
How has the procedure for paying wages changed since July 1, 2018 for individual entrepreneurs?
If the organization is not financed from the municipal or state budget, or is not an extra-budgetary fund, then the innovations introduced into the legislation from July 1, 2021 will not affect private sector employees.
The terms, dates of issuance of the advance share and full payment of labor are established by the employer. Individual entrepreneurs have the right to transfer wages to a card with any payment system (Visa, Master Card or MIR). The boss independently determines the dates for issuing the advance payment and the full part of the payment.
According to Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee of the private sector has the right to receive payment on any card, including “MIR”.
An individual entrepreneur does not have the right to refuse transfers to the national card of the Russian Federation. Regardless of whether the organization is financed from the state budget or by private individuals.
The employee is required to submit an application to change payment details no later than 5 days before the issuance of the salary or its advance part.
The procedure for transferring wages for legal entities
If a legal entity is financed from the state or municipal budget, then from July 1, 2021, the following procedure for transferring salary to employees is established for the institution:
- The payment period must be clearly stated in the employment and collective agreements, as well as in the regulations on the payment of salary.
- All financial payments must be transferred to a card with the domestic MIR system. An employee has the right to independently choose the bank in which his salary account will be registered. He must notify the employer of his decision 5 days before the advance payment or payday.
If the legal entity is a non-budgetary institution, the payment of funds is carried out in the following order:
- An individual entrepreneur has the right to make transfers to Visa or Master Card. But refusing to choose a bank is illegal. Employees also have the right to receive salaries on the card of the MIR state payment system. The employee must provide management with the details 5 working days before receiving wages.
- The terms, amount of advance payments and wages are specified by the employer.
How is the advance paid?
There is no clear definition of the concept of “advance” in the legislation of the Russian Federation. On October 3, 2021, new criteria came into law, within the framework of which an employee has the right to receive earned money at least once every six months. There will be no changes in 2021. The rules affect municipal and state institutions, as well as funds not financed from the state budget.
Payments of the advance share in 2021 are made in the following order:
- The advance payment is issued strictly until the 30th day of the current month. The employing organization has the right to transfer earned funds to employees more than 2 times in one month. Every 10 days or every seven days.
- The dates of advance payments are clearly stated by the employer in regulatory documents, collective agreements, and regulations on the payment of wages. Payment periods cannot be set. For example, “...from the 25th to the 27th” or “...from the 3rd to the 7th.”
Employers should note that the salary payment deadlines set for the 15th and 30th are not a safe option due to the need to pay personal income tax.
Payment of settlement funds upon dismissal from July 1, 2018
According to Art. 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, full settlement with the employee is carried out on the last working day. If the employee is absent, all transfers are made the next day.
Violation of wage payment rules
According to Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, Part 6, if the rules for paying salaries are not followed, the institution will be fined. The fine is up to 50,000 rubles.
What should an employee do if he doesn’t yet have a MIR card?
If an employee has not issued a card before July 1, 2021, and money from the budget has been deposited into the account, then the bank will define it as funds of “unexplained purpose.” The bank is obliged to notify the client about the presence of money in his account, and also offer two ways of developing events:
- Open an account and link a MIR plastic card to it.
- Open a simple account without a card, and then receive funds from it in cash.
If the client does not open a new account and does not appear at the bank within ten working days, the money will be returned to the payer.
Should the employing institution inform employees about innovations?
The employer is obliged to inform subordinates about new changes in legislation, according to which a new procedure for issuing earned funds comes into force on July 1, 2021. Employees need to order a MIR card on time and become familiar with the timing and nuances of salary transfers.
Some nuances of salary payments after July 1, 2018
- If payment deadlines are not met, the employing government agency may be fined.
- An employee has the right to choose the bank where his salary account will be registered. But the payment system is only “MIR”.
- The employer must clearly state the dates of salary payments in regulatory documents.
- If the payment day falls on a weekend, then the salary should be transferred a day earlier.
- The innovations concern organizations that are financed from the municipal or state budget, as well as extra-budgetary funds.
- Accrual of funds on weekends at a double rate. There is no need to count these hours as overtime.
- It is impossible to establish irregular working hours during a shortened week or during a shortened day.
Source: https://rabotnik-info.ru/zarabotnaya-plata/novye-pravila-vyplaty-zarplaty-s-1-iyulya-2018-goda/