04.07.2019
0
1623
6 min.
Constantly changing conditions for the development of production and the lack of financial stability are pushing many private companies and enterprises to choose the most optimal wage system. One of them is a tariff-free procedure for settlements with employees of the organization. It allows for a more targeted distribution of earned funds among employees involved in the production process. This option is considered an alternative to tariff and piece-rate methods of calculation, since monetary remuneration is not tied to the amount of time worked, the qualifications of the employee, or the volume of products produced. Here, the KTU - labor participation coefficient - allows you to evaluate your individual contribution to the common cause.
Concept and scope of use
So, the coefficient of labor participation is inherently a relative indicator that characterizes the share of labor invested by a specific participant in the collective production process.
The scope of application of individual coefficients is team work, the result of which is directly influenced by both the total work of all team members and the personal contribution of each worker.
The limits of influence of the labor participation coefficient on the individual wage fund are dictated by the conditions of the team incentive system:
- the non-tariff system involves dividing the total amount allocated for remuneration of the team by the number of employees and adjusting the base indicator according to the calculated labor participation coefficient;
- A feature of the KTU when using the tariff system is its influence exclusively on additional payments accrued in excess of the established rates.
This is a convenient way to calculate the contribution of each employee to the result. Everyone receives as much as they have earned.
The salary agreed upon by the parties cannot be regulated in accordance with the Labor Code, since its size is fixed in the employment contract and is not subject to adjustment in the absence of significant changes in labor factors (job functions, mode and intensity of work, etc.)
There is a list of payments that are excluded from the wage fund, distributed using the labor participation coefficient:
- compensation accruals for work in conditions that are dangerous or harmful to health;
- payment of excess labor;
- additional charges for working on weekends, holidays and night shifts;
- regional allowances;
- accruals that are not related to labor results (compensations, financial assistance, bonuses for length of service, etc.)
The legislator does not close the list.
How funds are distributed
The legislative framework does not have clear and transparent definitions of how payments under the CTU are established. Calculations are made by the enterprises themselves, in the most acceptable ways, but it is important to know that this point does not contradict the law.
For a certain category of qualified employees, there should not be a downward change in wages when using KTU. That is, the employee must at least receive his tariff.
KTU is also used:
- With the introduction of a tariff-free system. The payment amount is divided by the number of employees working together. In this case, the average coefficient is one, and is adjusted on the basic basis of the KTU.
- Distribution of the amount of wages over the tariff. Employees receive wages in excess of tariff accruals, and then distribute the remaining amount to all employees.
Conditions of use
One of the varieties of the piecework system is the collective wage system, which allows you to distribute earnings among all employees, taking into account the corresponding prices and the total size of production within a specific structural unit.
The criterion for calculating the individual contribution of a particular employee is precisely the KTU, established in accordance with the qualification category and the number of shifts worked by him in the billing period.
The basic value of the labor participation coefficient, equal to one, is applied to those employees who, during the billing period:
- coped with planned tasks;
- did not allow disciplinary violations and strictly followed industrial safety rules;
- did not violate production technology, did not allow deviations from established quality standards;
- performed their duties in accordance with the provisions of job descriptions.
The basic indicator of each employee can be adjusted in one direction or another in accordance with the objective factors of his participation in the production process.
Reducing factors
The ability to lower the KTU allows you to adjust the remuneration of employees whose activities negatively affected the fulfillment of a collective task.
This happens if:
- Indicators of completed work are lower than planned.
- There were facts of violation of discipline or performance of official duties.
- There were defects or production of low quality products (works).
- Production or technology rules are not followed.
- Production equipment was not used in accordance with its intended purpose.
- There was a failure to comply with instructions from superiors.
- The equipment was operated with malfunctions.
- Neglect of protective equipment and other violations of labor safety rules were allowed.
If at least one of the circumstances exists, the employer has the right to reduce the amount of the initial payment.
Increasing factors
The labor participation coefficient used in calculating remuneration for labor allows motivating those employees whose personal contribution to the overall production process exceeds the level of other employees.
An employee has the right to apply for an increased KTU if:
- planned indicators for production or work are exceeded;
- he worked beyond the established standard time;
- performed public duties in the team, provided patronage and mentoring to new employees and young specialists;
- took initiative in carrying out labor-intensive processes and practiced an integrated approach to ensuring the best results.
Each employer has the right to adjust this list by adding something of their own to it.
Using the labor participation coefficient, you can calculate not only the wages of production team members, but also one-time remunerations, bonuses, additional payments for combinations and other charges.
The employer must record information about the minimum and maximum possible coefficient in its regulatory documents. At the same time, limiting the lower value of this indicator should not violate the legislative norm obliging the employer to calculate and pay its employees the minimum wage approved at the federal level.
Application of the labor participation rate
The basic value of the KTU is 1 or 100. This value applies to accruals to employees who, in the billing period:
- completed the task;
- followed the requirements for production technology, quality, labor safety;
- observed labor discipline;
- complied with job responsibilities and work instructions.
The base coefficient increases or decreases depending on indicators reflecting the individual contribution of a specialist to the collective result of work. Each organization determines the individual dimensions of the CTU. The decision is made by the brigade council (meeting) and documented in the appropriate protocol.
Subsequently, daily records of indicators are kept and the overall KTU is calculated.
Criteria that can reduce the size of the coefficient:
- failure to comply with the manager's instructions on time;
- violation of production technology;
- failure to fulfill the plan and established economic indicators;
- defects, low quality of work;
- violation of labor discipline;
- non-compliance with labor protection requirements; performing work without appropriate instructions, work permits, or personal protective equipment;
- use of faulty tools, equipment, faulty equipment;
- use of equipment for purposes other than its intended purpose, etc.
Indicators that increase the value of KTU:
- manifestation of initiative, creative activity when performing production, organizational and technical tasks;
- solving a complex and responsible problem;
- performing work in a short time;
- mentoring, etc.
KTU is most often used for piecework wages. The tariff part is calculated according to hourly tariff rates and time worked. The bonus and payment according to the labor participation coefficient are paid from the above-tariff part of the payroll (above-tariff part of the salary).
With the use of KTU, the following additional payments can be distributed:
- bonus for labor achievements (for exceeding the norm);
- one-time remuneration in connection with changes in standards;
- salary savings associated with the release of personnel.
The above-tariff salary, distributed according to the coefficient, is included in the cost of production.
Stages of implementation of CTU in an organization
The introduction of the labor participation coefficient in the workforce is accompanied by serious preparatory work, the result of which is the preparation of correct documents in accordance with the norms of current legislation.
The standard procedure includes three stages, but can be adjusted depending on the operating conditions of the organization:
- Development of the KTU structure. At the initial stage, a system is formed that determines the algorithm for using the coefficient, taking into account factors that increase and decrease its size. One of the options is a point scale, which implies the accrual of additional points for performing extremely complex work, producing above-plan products, etc., and deducting points for violations of labor discipline, production of defective products and other offenses that negatively affected the overall result.
- Creation of a local regulatory framework. The internal regulatory documentation of an organization planning to transfer its employees to a new incentive system must contain comprehensive information about what the KTU is in wages, what is the procedure for its formation and what factors influence the size of the coefficient. The specified information must be clearly formulated and available for review by all interested parties.
- Making changes to employment contracts by signing additional agreements. If a disagreement arises between employees and the employer regarding the need to introduce labor regulations, the latter must provide a comprehensive justification for its decision, which provides for structural, technological or organizational changes in working conditions under which the previous payment system is not appropriate. The document is brought to the attention of employees two months before it comes into force.
When distributing earnings taking into account the KTU, the amount allocated to each member of the workforce must not be lower than the amount established by the tariff schedule for performing similar work over a certain period of time.
Definition of KTU
There is no legal concept of the labor participation rate. At enterprises, it is understood as the degree of participation of an individual employee in the results obtained by an entire group - a team, unit or workshop. This means that, using KTU, the personal contribution of each worker is objectively assessed and the share of his remuneration is calculated.
KTU: concept and scope of application
KTU - coefficient of labor participation of employees in professional activities. Each team member contributes to the work. To evaluate the employee’s work, the concept of KTU was additionally introduced.
This value is determined in numbers to evaluate the employee’s work. This indicator is used to set increased or decreased wages, but it all depends on the employee himself.
That is, the amount of wages depends on this indicator. It is most common in team contracting. Under such circumstances, it becomes clear how employees work, which of them contribute more to the work, and which contribute less.
Definition
What is meant by the labor participation rate and where is it applicable?
KTU is a digital value that reflects the assessment of the participation of each team member in work activities. This indicator is used to stimulate payments in a collective form of labor organization, as well as to show the contribution of employees to the result of work.
KTU is applicable as a weighting factor for the distribution of funds received as a result of collective work.
The most common case of using the indicator is the work of a team. Here the result is achieved through joint efforts, and the KTU (labor participation coefficient, calculated according to the established standards of each team member) shows which of the workers performed their functions in what manner.
Criteria
The indicator can decrease or increase depending on the individual contribution of each employee, his contribution to the overall result. Each organization has its own coefficient criteria. The procedure for determining and applying the labor participation coefficient must be submitted to a team meeting with the corresponding minutes drawn up.
When does the ratio decrease? These are cases such as:
- failure to comply with management orders;
- violation of production technology;
- failure to fulfill the established plan and indicators;
- faulty work or poor quality;
- violation of discipline;
- violation of labor protection conditions;
- performing work without instructions or permission;
- use of faulty equipment;
- use of equipment for purposes other than its intended purpose, etc.
When does the coefficient increase? These are the following cases:
- expression of initiative, activity;
- solving a responsible task;
- completing work in a short time;
- patronage, etc.
When applying the KTU, additional payments are distributed as:
- bonuses for performing work above the established norm;
- bonuses due to changes in regulations;
- savings on wages due to the release of employees.
The main condition for applying the coefficient is considered to be teamwork. KTU (labor participation coefficient), which is not calculated for individual payments, cannot be used when calculating:
- compensation for harm;
- overtime;
- additional payments for working on holidays and weekends;
- extra pay for night shifts;
- additional payments for leading a team or department;
- bonuses for qualifications;
- bonuses for professional finds;
- any type of benefits.
Labor legislation does not regulate clear positions regarding the calculation of earnings according to the labor participation rate (KTU). The calculation is made in a convenient way, the main thing is that there are no contradictions with laws and other regulatory documents.
It is important to know that no matter how earnings are distributed, the amount that each member of the work team receives cannot be less than what is due according to the tariff for similar work performed in a specific period of time.
Depending on the form of payment, the coefficient is applied in:
- Tariff-free system. The amount to be paid is divided by the number of employees, and then the average coefficient, equal to one, must be adjusted based on the KTU.
- Distribution in excess of the tariff. Each employee receives a fixed amount of money according to the tariffs, and the rest of the money must be divided taking into account the coefficient.
Calculation: formula
The procedure for calculating the KTU is based on the use of a system of established parameters, where each is assigned its own score. Each member of the team or department is assessed on all parameters, receiving a certain number of points for all parameters. Next, the number of points is summed up.
KTU = (0/1 2 3 ……. n) * N, where:
- KTU is the labor participation coefficient;
- 0 – parameter rating assigned to each team member;
- 1 2 3 ….. n – total points;
- N – number of workers in a team or department.
Let's look at the features of calculating the coefficient. Let's say there is a team where job evaluation parameters have been developed for each of its members. Main criteria:
- Difficulty of the work (very hard work - 3 points, moderate work - 2 points, easy work - 1 point).
- Temporary load (maximum – 3 b., average load – 2 b., minimum – 1 b.).
- Working with equipment (1 point for each type of equipment).
- Maintenance of tools or equipment (2 points for each case).
- Quality of work (1 point each for control and compliance).
- Responsibility for the result (up to 3 points, from which points may be deducted in case of violation)
You can calculate everything manually, or you can use Excel.
Calculation example
How to calculate KTU (labor participation rate)? Let's give an example. For example, there are 5 people in a team who make parts. For fulfilling the plan, the brigade is entitled to 1000 monetary units.
The first employee carried out his plan and complied with all standards. Its CTU is equal to one. The second employee exceeded the plan by a quarter and complied with all standards. His KTU is 1.25. The third worker made the quota, but because of him the machine broke down, which stopped work.
In addition, he was late several times. Its CTU is 0.5. The fourth worker repaired the machine, for which he received additional points. His overall KTU is 1.6. The fifth employee was forced to take time off on his last day of work. Accordingly, he worked less than others.
Its CTU is 0.65.
Now let's do the calculations: 1 1.25 0.5 1.6 0.65 = 5.
For non-tariff payments, the amount will be distributed as follows: 1000/5=200. This means that each employee is entitled to:
- 1 – 200 units;
- 2 – 200*1.25=250 units;
- 3 – 200*0.5=100 units;
- 4 – 200*1.6=320 units;
- 5 – 200*0.65=130 units.
It turns out that payments to each member of the team are distributed according to his work.
But this is not the only way to reward an employee for his work, especially if the result of the work was achieved through collective efforts.
In this case, we apply the KTU (labor participation rate). The calculation of this indicator, as well as the main nuances of application, will be discussed below.
An example of remuneration calculation according to KTU
Let our conditional team have five workers engaged in making stools for a set time period. For the implementation of the plan, their team is entitled to payment of 1000 monetary units (let’s take a conditional value for calculations).
The first employee fully fulfilled the plan, complied with all standards, working the required number of working hours, that is, his KTU is equal to 1.
The second employee exceeded the norm by a quarter, the rest of the indicators are the same as the first. KTU will be 1.25.
The third employee fulfilled the quota, but due to his fault (failure to comply with the rules for working with equipment), the woodworking machine was broken, which forced the suspension of work. In addition, he was late for the start of the work day several times. Therefore, several points were deducted from him, and his CTU was 0.5.
The fourth employee fixed a breakdown in a woodworking machine; his qualifications allowed him to do this. He was given points for equipment maintenance; in addition, management noted the quality of his work, and his KTU turned out to be 1.6.
The fifth employee asked for time off on his last day of work. His work did not cause any complaints, but in fact he worked somewhat less than the others, so the KTU decreased to 0.65.
Now let’s calculate the share of each employee that he will receive with a non-tariff payment method, or the additional remuneration due as extra income, with an established “fixed” tariff.
The sum of all KTUs: 1 + 1.25 + 0.5 + 1.6 + 0.65 = 5.
With tariff-free payment, the total amount will be distributed as follows: 1000 / 5 = 200 (average share corresponding to a KTU unit). Then employees are entitled to:
- The 1st employee will receive 200 (account units);
- 2nd – 200 x 1.25 = 250;
- 3rd – 200 x 0.5 = total 100;
- 4th – 200 x 1.6 = 320;
- 5th – 200 x 0.65 = 130.
Thus, thanks to KTU, earnings were distributed unevenly, with some employees receiving significantly more than others. However, this is due to objective factors, and therefore will not cause a feeling of injustice and discontent in the team.
What are the evaluation criteria
The KTU indicator can be lowered or, on the contrary, increased, and it all depends on each employee. Moreover, each enterprise presents its own KTU criteria in numbers. They are approved by regulatory documents.
The team must make a joint decision on the procedure for using the coefficient. In order for everything to be done correctly, it should be announced which coefficients are assigned to which employees, and the foreman does not need to do everything himself. Based on the results of the meeting, a protocol is drawn up.
Cases of decreasing the coefficient:
- the manager’s tasks were not completed at all or were not completed on time;
- violation of the route of operations during the execution of the technological process;
- failure to implement the approved work plan;
- failure to fulfill one of the points of the plan;
- allowing defects in work;
- quality does not meet standard requirements;
- violation of technological discipline;
- the work was carried out without permission and without instructions;
- use of faulty equipment;
- use of technological equipment for other purposes;
- failure to use PPE;
- violation of occupational safety requirements;
- providing false information;
- others.
An increase in KTU is carried out in the following cases:
- manifestation of activity in work;
- issuing initiative proposals;
- execution of a responsible task in a short time;
- and other criteria.
Additional payments when using KTU are distributed:
- As a bonus.
- From funds saved on the salaries of other employees.
There is no rule in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation that regulates the procedure for calculating the coefficient in question. This issue is left to the discretion of the employer. The algorithm for calculating KTU may be different. The main condition is that it does not contradict the law, in particular the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
IMPORTANT: Regardless of the algorithm for distributing wages between members of the workforce, the amount received by each of them should not be less than what is due for similar work at certain rates.
The unit is the base value for KTU. Indicator 1 means that the employee, performing work with other team members, performed his duties in good faith and was able to comply with all established standards for time, quantity and quality characteristics. In this process, the employee did not make any mistakes, did not make mistakes, did not make any inaccuracies, and complied with all requirements for labor protection.
During the calculation process, the resulting digital value may be in the range of 0. This means that the employee did not participate in the work of the team. The KTU criteria should be established as objectively as possible. For example, for each employee, their own criteria can be determined in the case of accounting for wages according to the KTU.
At the end of the working period, a special document (protocol) is used to calculate the KTU for each specific employee according to the established method. To calculate the CTU, certain parameters are used. Each of them is assigned a point. A specific person is assessed through each criterion, receives points, and they are summed up.
KTU = (O / O1 O2 ... On) x N
KTU - labor participation coefficient; O - evaluation indicator assigned to each specific employee based on the sum of points; O1 O2 On - is the sum of points for each specific employee; N - Number of members of the work team.
How is it counted?
The simplest and most common way is to calculate the contribution of each person to the overall result in shares or percentages. For example, a portion of all manufactured products, transactions or profits in rubles is determined.
KTU=(Personal result)/(General result)
A more complex and comprehensive option is to calculate points for each employee. Here, the result can be influenced by several criteria:
- experience;
- qualifications or rank, approvals (for example, electricians, installers);
- working hours;
- additional tasks (replacing a manager, patronage) and other criteria - everything that can somehow be measured and expressed in numbers.
Once the criteria are specified, all points are added up. The amount is taken equal to 100%. And then, for each employee, participation in the general process is calculated. The standard formula for calculating KTU for a specific person looks like this:
KTU=(Sum of points individual)/(Sum of points collective)
Let's look at the example of conducting lessons in an English language school:
| Teacher | Number of lessons completed | Specialist category | Certificates, advanced training | Participation in conferences | Student results | Total score |
| Anna | 95 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 103 |
| Alexei | 101 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 107 |
| Elena | 90 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 97 |
| Total | 287 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 13 | 307 |
The total points are 307, we take them equal to 1. Let’s calculate the contribution of each to the overall result:
- Anna - 103/307=0.34.
- Alexey - 107/307=0.35.
- Elena - 97/307=0.31.
When determining monetary incentives, the entire salary amount is multiplied by the coefficient of participation in the functioning of the institution.
If you use KTU in construction, you can use the following criteria:
| Employee | Qualification | Hours worked | Object completion date | Overconsumption of material | Total | KTU |
| 1 | 3 | 100 | 1 | 0 | 104 | 0,37 |
| 2 | 2 | 120 | 1 | -30 | 93 | 0,33 |
| 3 | 2 | 130 | 1 | -50 | 83 | 0,30 |
| Total | 7 | 350 | 3 | -80 | 280 | 1 |
For reverse criteria (when the lower the indicator, the better), an evaluation method is developed. If the object must be completed in 90 days, but the employee does it in 80, the points will be higher. And vice versa, the longer the period, the lower the coefficient.
In the table, delivery on time is taken as 1. Overconsumption of materials - if the employee met the estimate, 0 is awarded. Excess for every 5% of the calculated cost - minus 10 points.
You can also use KTU when conducting audits. If employees are financially responsible persons and the recalculation shows a lack of funds, you can calculate the KTU of each using the formula:
KTU = The entire amount of the shortfall / the total number of hours worked in the period * hours worked by a specific person.
For example, an audit revealed the absence of 10,000 rubles. The accounting period is 1 month, the team consists of 2 people - Andreev and Petrov. Petrov worked 186 hours, Andreev - 120 (was on sick leave). We calculate the amount of debt for Petrov:
KTU = 10,000 / (186+120) * 186 = 6078.43 rub.
KTU may not be used in audits, but this method is often used in areas with financial responsibility: in sales, in warehouses and factories.
Functioning wage systems and application of the KTU value
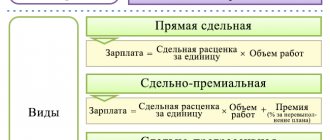
The organization has the right to autonomously predetermine the forms and methods of remuneration for its employees. Today, 2 key systems are widespread and functioning, which are divided into types and subtypes.
| The remuneration system (hereinafter referred to as SOT) and their formulation | Types of remuneration systems and their characteristics |
| Tariff-free: labor is paid taking into account the earned KTU | — |
| Tariff: payment is differentiated taking into account qualifications, experience, position, in accordance with the current tariff schedule (UTS), rates, tariff and qualification reference books (ETKS) in government agencies, and in commercial structures - identical to current documents | 1. Time-based SOT - pay is calculated taking into account the time actually worked (qualifications and working conditions are taken into account), divided into subtypes:
2. Piece work - earnings are affected by the volume of work performed and products produced. Includes subspecies:
|
Features of calculating KTU
Let’s imagine a team for which the following parameters for assessing its work have been developed:
- complexity of the work (on a three-point scale: the most difficult work - 3 points, average - 2 points, easy - 1 point);
- time load (maximum – 3 points, average – 2 points, minimum – 1 point);
- work on equipment (1 point for each type);
- equipment maintenance (2 points for each case);
- quality (1 point for compliance and 1 point for control);
- responsibility for results (up to 3 points, may be deducted for violations).
The Excel computer program is convenient for calculating KTU, where all indicators are visible in tabular form, and the last column displays the total for each employee.
Core differences between existing systems and forms of remuneration
The tariff system today remains the most familiar and optimal for most organizations. It seems more profitable for workers, since payment terms are determined before work begins and are not determined by the final result. In contrast, the tariff-free system is more attractive to employers. The reasons are obvious: this option of remuneration is interconnected with the results of the workers’ labor, the calculation is carried out after the work is completed, when there are concrete results.
The main criterion for distinguishing the piecework form of remuneration from the time-based form is the method of recording labor costs. Piecework is based on taking into account the number of finished high-quality products (and the volume of work - the number of operations). In the time-based form, the actual time worked is taken into account.
The procedure for issuing KTU to collective workers
The monthly value of the KTU has the right to determine and approve the head of the team (team) or the general meeting of workers. It all depends on which of these options is fixed in local documents. In the first option, the head of the group (team, collective) or the personnel officer does the calculations on a monthly basis. BEFORE the CTU is approved by the manager, each participant in the collective work is familiarized with the set value of the multiplier.
At this point, in case of disagreement, the employee has the right to challenge the value of the KTU and express his claims. The second version of the calculation is carried out by the council of the brigade (department, etc.). It is within his competence to consider the need to apply increasing or decreasing criteria and calculating the final value of the KTU.
The results of the meeting are recorded in a protocol, which is signed by all participants and given to the employer for final approval of payments.
Documents required for acceptance and registration of the CTU
The fundamental documents that are necessary to determine the value of the CTU for each participant in the collective labor process are:
- Regulations on KTU.
- Minutes of the meeting on the application of the coefficient.
- Order to establish KTU.
These documents are developed by the organization taking into account basic legal requirements. So, in a standard version of the protocol, the name of the organization, department (site, management unit, trust, etc.), and the date of the meeting are written down.

Minutes of the meeting on the application of the coefficient
Also included are the details of those present, the agenda and the decision (resolution) of the meeting. The minutes are signed by the chairman of the meeting and the secretary.
The order to establish the KTU must include the name of the organization, the date, the essence of the order (what values of the multiplier are established and to whom). It must be signed by the head (director) of the organization. Only after this the order comes into force (on the date indicated in the text header). Next, the agreed document is presented with the signature of each employee, after which it is sent to the accounting department for accruals.
Where is the coefficient applied?
The labor participation rate is a rather specific tool. The fact is that its use is possible only in work collectives that perform some kind of work together. That is, in such a team, everyone seems to be doing the same job, but the effectiveness of such collectivism, as a rule, is always different. Output should be assessed based on the quantity of products produced over a certain period of time. Most often, the calculation period is considered to be a month, but it also happens differently. For example, a team may be working on a project, and the monetary result is achieved only after the final delivery of the finished product. In this case, everyone can be paid a basic salary every month, and an additional payment is given based on the results achieved.
It is impossible to apply this coefficient outside of team work. In addition, this value cannot be replaced by:
- Payment for overtime hours worked.
- Payments for work on weekends and holidays.
- Additional payments for hazardous work.
- Compensation for night work.
- Allowances for length of service and qualifications.
- Additional payments for mentoring or leading a team.
- Rewards for rational proposals made.
The labor participation coefficient is calculated to individualize the merits of each team member in the team.
What is KTU in wages
The abbreviation KTU stands for “labor participation rate”.
It allows you to fairly distribute a certain amount of money earned by the whole team among individual participants. KTU is used when calculating remuneration that is intended for a group of people. Classic examples: bonus to the crew upon completion of work; bonus to the department upon completion of the project, etc. If we are talking about remuneration that is accrued to only one employee, it makes no sense to use the labor participation coefficient.
Calculate your salary and benefits taking into account the increase in the minimum wage from 2021 Calculate for free
Impact on wages
The basic indicator of this coefficient is unity. That is, this is exactly the amount of payments due to an employee who fulfilled his work standards in full, without increasing or decreasing them.

The level of accrued wages is affected by the established minimum and maximum indicators of this coefficient.
These levels are prescribed in the general regulatory documentation of the organization. The employer is obliged to take into account that the establishment of minimum values should not violate legal norms by reducing the required payment for time worked. For example, in the Regulations you can determine that the minimum possible value is 0.5 and the maximum is 2.0. This definition is rather conditional, and each individual case considers its own values.
Thus, the employee will receive the established minimum wage for his work in any case, but in order to increase it, he will have to perform a number of additional measures. There are quite a lot of factors that influence the increase or decrease of the coefficient, but each individual organization can apply them selectively and not in full.
Calculation rules
The labor participation coefficient is a value for the calculation of which a special formula is used. If you want to calculate the KTU, you must:
- Calculate the amount to be distributed among the team members.
- Find out the number of team members into whom the due amount will be divided.
- Calculate the coefficient of each individual employee based on the results of the worked period.
Let's look at an example. A team of four people produced products for a month. As a result, they calculated the following coefficients:
- The 1st employee received 1.
- The 2nd employee earned 1.5.
- The 3rd person is rated 1.2.
- The 4th employee received only 0.7.
The final indicator is 4.4, and the amount to be distributed is 42,000 rubles.

To correctly calculate the coefficient, we use the formula:
(C/OK) * IR
Where,
C is the total amount to be distributed;
OK – general collective indicator; IR – individually obtained KTU.
So, each of them will receive accordingly:
The first one will receive 9545.45 rubles.
2nd – 14318.18 rub.
3rd – 11454.54 rub.
4th – 6681.82 rubles.
Thus, there is individual reward for merit and payment in proportion to labor productivity.
Example of KTU calculation (table)
The trading company has adopted a provision on bonuses. It specifies the increasing and decreasing criteria given above in Tables 1 and 2.
The staff has four employees: Ivanov, Petrov, Sidorov and Kuznetsov.
At the end of December, a bonus was awarded in the amount of 300,000 rubles, which must be distributed among employees. A statement for December was compiled, which reflects the assessments received by employees (see Table 3).
Table 3
KTU statement for December
| № p/p | Full name of the employee | KTU base part | Reducing factors | Increasing factors | KTU | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | |||||||
| 1 | Ivanov I.I. | 1 | -0,3 | 0,8 | 0,7 | 2,2 | |||||
| 2 | Petrov P.P. | 1 | -0,6 | 0,4 | |||||||
| 3 | Sidorov S.S. | 1 | -0,2 | 0,6 | 1,4 | ||||||
| 4 | Kuznetsov K.K. | 1 | -0,6 | 0,7 | 0,4 | 1,5 | |||||
| Total: | 5,5 | ||||||||||
We see that Ivanov received a deduction of 0.3 (lateness), as well as an increase: 0.8 (conclusion of new contracts) and 0.7 (extension of contracts). His personal score was 2.2 (1 - 0.3 + 0.8 + 07). The scores of other employees are calculated in a similar way.
All that remains is to distribute the prize:
- Ivanov 120,000 rub. (RUB 300,000 / 5.5 × 2.2);
- Petrov RUB 21,818 (RUB 300,000 / 5.5 × 0.4);
- Sidorov RUB 76,364 (RUB 300,000 / 5.5 × 1.4);
- Kuznetsov RUB 81,818 (RUB 300,000 / 5.5 × 1.5).
To check, we will find the amount of bonuses accrued to each employee. We will receive: 120,000 rubles. + 21,818 rub. + 76,364 rub. + 81,818 rub. = 300,000 rub.
Calculate “complex” salaries under different remuneration systems Try for free
Advantages and disadvantages of KTU
Like any remuneration system, KTU, as a complex, has certain advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of using the labor participation rate include:

High level of fairness. Ensuring a fair ratio of labor costs to wages is one of the main factors motivating workers, and this system assumes a fairly transparent and fair distribution of income between participants in the labor process, both in the event of a decrease in their earnings and in the event of an increase.- The relationship between enterprise income and employee productivity. In the case when the CTU is applied, the employee’s income directly depends on the benefit his work provides to the employer and, accordingly, the employer does not have to pay for ineffective workers at his own expense or spend excessively on bonuses for workers.
- Ease of implementation. KTU is a fairly simple system and its implementation will not require significant costs. Accordingly, this aspect of using the labor participation coefficient greatly simplifies the use of its other advantages.
However, KTU also has certain disadvantages:
- Collective component. The use of KTU is relevant only in relation to certain groups of employees. Thus, this method of remuneration cannot be applied in principle to all positions and specialties.
- Inapplicability in certain areas of activity. The labor participation coefficient is used primarily in those areas of work where the labor of employees directly affects the formation of the organization’s income and has a certain material embodiment, and can also be fairly easily assessed according to the provided criteria. For workers who are not directly involved in the production process and have a direct impact on the economic performance of the enterprise, the use of CTU is ineffective.
- Risks of subjective assessment. The use of KTU with an incorrect choice of factors influencing the coefficient or with imperfect assessment methods can lead to an extremely subjective use of the said system, when the actual value of the distributed coefficients is not carried out in accordance with the real achievements of employees, but is used by managers for personal interests.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of using the CTU include the objective distribution of money between the participants in the process. Of course, only if objective quantitative indicators are taken into account, and not the degree of relationship or friendship with the leader. Another positive is that employees strive to improve their performance and contribute to business growth.

For managers, this is an opportunity to identify problem areas in the overall process and for each subordinate and correct them. For employees - a clear understanding of the requirements for the tasks performed.
The disadvantages include discord in the team. Even with objective differences in the work of employees, misunderstandings, envy and conflicts can arise. The result is an outflow of personnel.
This also includes the lack of a real picture. Employees can agree among themselves to divide the results evenly among all participants. In this case, management will not be in the know.
For example, when working with a cash register, sales are recorded under the selected person. Managers can calculate the numbers and “finish off” the goods for the seller who does not reach the average KTU.
To avoid the negative impact of the indicator on the team, you need to define clear criteria. They must be transparent and understandable to every member of the team.
Features of application
This indicator shows the overall qualitative and quantitative assessment of the work of employees, specialists and management in an overall positive result, that is, in the intensity and productivity of work.
In the basic value, KTU is expressed as one whole unit or 100%. This contributes to the calculation of the average assessment of employee performance and relates directly to those employees of the general team who fulfilled the production plan for the reporting period, had no recorded violations of labor protection rules, and were not involved in disciplinary punishments.
The basic labor participation rate has the ability to decrease and increase depending on the indicators that influence it. Indicators reflect the contribution of one employee to the overall collective result.
This coefficient can be calculated based on the results of a monthly period. Indicators that have an impact on the KTU are taken into account daily for a complete and high-quality calculation.
The additional payment for participation is applied to remuneration for work activities when distributing team additional income, bonuses and remunerations that are assigned to a specific area, workshop or team.
The tariff is calculated based on the salary and time actually worked by the team, despite the labor participation coefficient established for the employee.
The following are not collective income and, accordingly, are not distributed with the help of the CTU:
- Additional payments for night work, harmful and difficult working conditions, overtime and management of a team or unit.
- Allowances for qualifications and work experience.
- Rewards related to inventions.
- Disability benefits or any other type of individual benefits.
At established tariffs
The labor participation coefficient can be used not only in non-tariff wage rates, but also taking into account the tariff salary. KTU can be used to divide the wage fund into parts. Additional payments that may be included in the calculation of the indicator at established tariffs:
- bonus for exceeding the plan by the team;
- saving money related to the wage fund;
- one-time benefit when revaluing temporary standards.
According to the accruals that are made taking into account the tariff, the part of the funds that is subject to payments to the KTU is deducted from the earnings of the team’s employees.
Distribution of funds
Based on the way in which the form of remuneration, both individual and collective, is laid down in the enterprise’s Charter, as well as on the orders of the immediate supervisor, the use of the indicator of collective labor participation looks like this:
- Tariff-free earnings accrual system. In this case, the total amount earned by the entire team is distributed by calculating the average income for each employee, then the resulting result is adjusted using the labor participation indicator.
- Remuneration made in excess of established standards. Each of the employees of the team receives a salary depending on the tariff distribution rate, and the funds that are on the balance are transferred to the employees’ accounts taking into account the coefficient.
Where not to use
The indicator of distribution of funds from labor participation is applicable only in the case when labor activity is carried out collectively. According to the Regulations for the application of this coefficient, it is applied only in the area that is regulated. The participation fee does not include:
- Compensation to an employee for harmful working conditions.
- Cash surcharges above the norm.
- Additional payments for going to work on weekends and non-working holidays, at night and in the evening.
- Type of cash benefits.
When not to use KTU
In what cases does KTU not apply?
Collective work is the main condition for using this coefficient. But it is not always used; it cannot be used under the following circumstances:
- when calculating compensation payments for work in hazardous conditions;
- when calculating wages for overtime work;
- additional payment for work on holidays and weekends;
- with established additional payments when working at night;
- if, when calculating wages, an additional payment to the foreman is established;
- with individual bonuses for employee qualifications;
- when calculating bonuses;
- other types of benefits.
Payroll for all listed cases is carried out separately and KTU cannot influence this circumstance in any way.
How is KTU calculated? basic principles
- Compliance with labor discipline standards. If an employee is late for work and other violations, the KTU for him is reduced, and this will lead to a decrease in the final salary.
- Meeting deadlines for completing assignments. If they are completed on time or ahead of schedule, the CTU increases.
- Quality of work performed. It is determined by indicators for each specific type of activity; the employer must develop clear criteria for the quality of work performed so that employees clearly understand what result needs to be achieved.
- Performing overtime tasks. If workers show increased zeal and perform tasks beyond the plan, this is also rewarded according to the KTU.
- The desire to improve qualifications and grow professional skills. The employer is directly interested in the professional growth of employees; their desire to improve their skills should be financially encouraged.
- Mentorship of young employees. participation in mentoring programs. Encouraging mentors improves the training of young staff, which is beneficial for any enterprise, so such work must be encouraged.
Passivity, failure to meet deadlines, a decrease in the quality and pace of work, and disinterest in achieving results by the team can lead to a decrease in the employee’s performance level. In practice, the coefficient is often reduced for lateness, unnecessary breaks, absenteeism and other violations; this is one of the effective disciplinary measures.