System concept
Progressive remuneration is a special wage calculation scheme in which, until the established norm is met, the work of employees is assessed at direct piece rates, and if the standards are exceeded, then increased tariffs are applied.
Typically, at enterprises, standards are set within the limits of actual values determined over three months of the company’s operation. The main goal of such a system is to increase labor productivity. Each employee realizes that the more work tasks he completes, the higher his salary will be.
Piece-progressive wages assume that the same part made by an employee can be paid differently. Such actions motivate employees to work at a significant level of output.
Piece-progressive wages, calculation examples
07/13/201509/06/2018 17:14 Labor consultant
Many years of experience show that the piece-rate form of payment to personnel is very effective. It both stimulates employees to increase their work intensity and allows them to keep the total salary fund within certain limits. Piece-progressive wages significantly increase the motivation of workers, but require additional material costs.
The name “progressive” already suggests that there is some kind of movement forward. It consists in increasing the cost of work on producing units of production in excess of the standard. Almost every worker, knowing that it is possible to increase earnings by producing more products, will try to do this. Perhaps he will reduce the time for smoking breaks, come up with devices to speed up auxiliary and main operations, or, if this is permissible, will serve several work centers. All this will have a positive impact on the organization’s bottom line.
It may be easier to introduce a bonus system for additional motivation. But the piece-rate progressive payment system for employees is more attractive. This is because a premium is a fickle concept. It may not be issued if the final financial result of the activity is negative or zero. You can also lose it if, for example, you are late for work or violate safety rules. It is almost impossible to deprive a person of a “deal”.
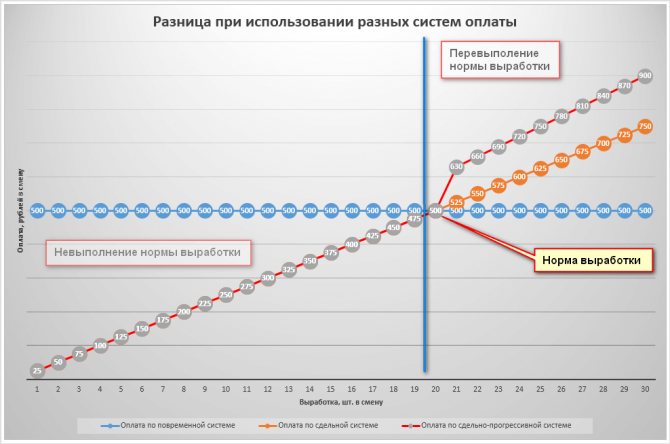
The figure below graphically shows the difference between wages under different systems. Here we clearly see that the piece-rate system stimulates the employee to increase labor productivity.
Methods for constructing a system of piece-rate progressive prices
Piece-progressive wages can be implemented in several variations. For example, consider a small production organization engaged in the manufacture of wooden furniture. The list of products, standard labor intensity and prices is as follows:
| Product type | Average labor intensity of production, standard/hour | Price per unit, rub. |
| Table | 2,5 | 250 |
| Chair | 1,2 | 105 |
| Stool | 0,9 | 85 |
| Rocking chair | 3,2 | 310 |
- If the production process is structured in such a way that each worker is engaged in the manufacture of one type of product (for example, he produces only tables all month), then a progressive pricing system can be constructed as follows:
| Product type | Planned monthly volume, pieces | Prices taking into account monthly output (pieces) | ||
| Table | 168/2,5 = 67 | Up to 67 | From 68-75 | Over 75 |
| 250 | 275 | 290 | ||
| Chair | 168/1,2=140 | Up to 140 | From 141-146 | Over 146 |
| 105 | 115 | 120 | ||
| Stool | 168/0,9=186 | Up to 186 | From 187-193 | Over 193 |
| 85 | 95 | 100 | ||
| Rocking chair | 168/3,2=52 | Up to 52 | From 53-60 | Over 60 |
| 310 | 340 | 350 | ||
* For calculations, we use the average monthly work duration – 168 hours.
To calculate piecework payment (PC), the following formula is used:
CO= Vn * Pn + Vn 1* Pn 1, where
Vn ( n 1) – volume of products produced according to the norm (above it);
Pn ( n 1) – cost of a unit of product at planned production (with excess production).
| FULL NAME. | Product | Output, pcs. | Calculation algorithm |
| Ivanov I.I. | table | 72 | 67*250+8*275+1*290=19 240 |
| Petrov P.P. | stool | 192 | 186*85+6*95=16 380 |
| Smirnov I.A. | rocking chair | 61 | 52*310+8*340+1*350=19 190 |
- If workers produce several types of products during a shift, then it is better to set the piece rate per standard hour. Since, in accordance with the production calendar, each month has a different number of hours, the gradation according to prices can be done conditionally.
| Type of work | Piece prices taking into account monthly output (RUB per standard/hour) | ||
| Furniture manufacture | norm | 15 hours above normal | Above normal for 16 or more hours |
| 120 | 135 | 140 | |
CO= H n *P n +H n 1* Pn 1, where
Chn(n1) – labor intensity on orders within the monthly norm (above it);
Pn(n1) – cost per hour within the norm (above the norm).
| FULL NAME. | Product | Output | Piece payment, rub. | |
| things | standard hours | |||
| Ivanov A.V. | 30 | 30*2,5=75 | 168*120=20 160 | |
| 18 | 18*0,9=16,2 | 15*135=2 025 | ||
| 30 | 30*3,2=96 | 4,2*140=588 | ||
| TOTAL | 78 | 187,2 | 22 773 | |
Documents confirming data on manufactured units can be piecework orders, production reports for a shift or other established reporting (necessarily with the signature of the responsible person - foreman, foreman, etc.).
Features of the piecework-progressive system
- Before approving and implementing a system of increasing prices, the employer must make a detailed calculation of the expected economic effect. The costs of increased wages should not exceed the amount of profit from the production of additional units of product.
- Employees must know and understand the rate increase system. In this regard, you should not make it too complicated (two or three gradations are enough).
- You need to immediately think through the question of how earnings will be calculated. In large enterprises with a large number of core workers, ideally this should be done by an economist or accountant using a program (1C:Enterprise, Excel, etc.). If there are not many people working on the transaction, then earnings can be calculated manually.
- The process of checking the quality of manufactured products must be clearly established. Indeed, often, a person, wanting to exceed the established norm, begins to neglect it. Substandard products should not be charged at higher rates.
- Planned labor intensity must be reliably calculated (using timing observations, technological calculations, etc.). The standards need to be reviewed periodically. It is possible that the equipment on which products are manufactured has become worse and slower over time and has become impossible to complete, much less exceed the planned target. Or vice versa. We introduced new technology that significantly reduces time spent on production operations. Then the production figures will be overestimated.
List of used literature:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation with comments
- Journal "Economist's Handbook", No. 4, 2011.
- Magazine "Salary", No. 8, 2013.
- Magazine "Human Resources Directory", No. 10, 2012.
- Magazine "Personnel Affairs", No. 2, 2014.
The nuances of this payment scheme
Progressive remuneration is a rather specific salary calculation scheme. Under it, a worker's earnings grow faster than output. This acts as a certain limitation for using the system everywhere in different enterprises.
Typically, piecework-progressive wages are used by companies for a limited period of time, not exceeding six months. It is considered effective for use in those areas of production where, for some reason, the established plan is not being implemented. Reasons may include laziness of workers, lack of motivation, outdated equipment, low wages or other factors. This adversely affects the performance of the entire manufacturing enterprise.
Progressive remuneration for a specific amount of work performed will motivate employees, so they will try to improve their performance in order to receive more money.
What kind of form is this - the basic concept
Progressive piecework payment is a form of wage calculation related to the piecework system, which is directly dependent on the amount of work performed at piecework rates and on its quality.
Within the piecework form, several types of payment can be distinguished:
- Straight. With this type, the employee is paid equal pay for each unit of goods produced.
- Indirect serves to pay wages to personnel who do not produce anything themselves, but serve those workers who create the main products, receiving a profit for them. Part of this income goes to pay these staff.
- Progressive. In this type, a standard is established for workers, upon fulfilling which they receive a salary at the minimum rate. And if this norm is exceeded, then a bonus is calculated.
- Premium payment is possible only if the employee not only fulfills the established norm, but provided that his products meet certain quality standards.
- Chord. This form is used when an employee must perform different tasks during the work process. They are paid for their implementation at a piece rate.
Under what conditions is the system effective?
It is advisable to use progressive remuneration systems if the following conditions are met:
- it is necessary to correctly establish the initial base from which the excess of the norm will be considered, since if it is too high, then employees will understand the meaninglessness of their own efforts, and if it is too low, this will lead to a lack of significant profit for the company due to the payment of high salaries;
- a special scale is being developed that will be understandable to all employees, on the basis of which wage rates will be raised;
- competent accounting of product output is carried out, and the time worked by each worker to perform a specific task is taken into account, which will ensure the correct calculation of the percentage of work performed, therefore progressive additional payments will be fair and effective not only for the workers, but also for the company itself;
- developing an economic justification for using such a remuneration system, since it is important to make sure in advance that its use will not lead to overspending of the wage fund, and will not increase the cost of manufactured products.

Only if the above conditions are met is it possible to achieve high efficiency from using this method of calculating payroll. Therefore, before using it, economists and accounting workers of an enterprise must carefully analyze the situation, predict the results of changes, and also draw up the necessary documentation.
Summarizing
The piece-rate progressive wage system is convenient for both parties to the employment contract. Employees are interested in exceeding the established minimum amount of work; depending on exceeding the plan, salaries can increase significantly.
The employer pursues his own benefit: there is no need to create additional jobs, employ and train new people who are not interested in increasing the quantity of products produced, and pay them a fixed salary.
At the same time, the piece-rate progressive form of remuneration is not yet widely used in the market, which is caused by some complexity in calculations, and is also associated with the risk of deterioration in product quality.
Registration of piecework wages in 1C is presented in the video below.
Advantages and disadvantages
There are pros and cons to progressive pay, so you should consider both the positives and the negatives before implementing one.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Remuneration is closely related directly to the number of products created by one employee | Workers will try to produce goods as quickly as possible, which may negatively affect their quality |
| The ability to significantly motivate employees, which directly affects the increase in labor productivity, which is a significant indicator in any enterprise | The rhythm of the production process, established before the introduction of progressive wages at the enterprise, is artificially disrupted |
| The turnover of working capital accelerates and the quantity of products sold increases, which leads to higher net profit | The amount of funds paid to employees increases, so there is an overspending of the wage fund |
| You can quickly remove bottlenecks in the enterprise | Often, the introduction of such a system even leads to a violation of discipline and a deterioration in relationships between employees |
Thus, the use of this payment method can result in both positive and negative consequences, so it is important to rationally evaluate the result. It is advisable to make a special forecast in advance by specialists.

When is it appropriate to use it?
Progressive remuneration is a rather specific salary calculation scheme, so it is not used very often. It is most effective for enterprises that specialize in mass production of a large number of different goods, parts or other small items. They should be easily identifiable using a standard description. They must have certain distinctive features so that they cannot be confused with other products.
It is most optimal to use this system under the following conditions:
- it is possible at the enterprise to accurately determine all the qualitative criteria for the result of the work of each specialist, and it is also possible to calculate without difficulty how many products were made by him over a certain period of time;
- the company has an urgent need to increase production volume, and at the same time it is impossible to attract new workers, for example, one large order has been received from the state or a large commercial organization;
- The company creates special accounting for the release of goods, which allows you to control the quality and quantity of products produced;
- on the part of the management team, a decision is made on strict control over labor intensity, the cost of manufactured elements, the profitability of the enterprise and other performance indicators.

It is to increase motivation that progressive remuneration is used. Its areas of application are numerous, so it can be used in different enterprises. Due to the fact that each employee will strive to ensure that his labor productivity grows, which will lead to an increase in his salary, it will not be difficult to increase almost all the economic indicators of the company.
What formula is used for the calculation?
When using this system, a certain standard is established in advance. Upon completion, the employee can receive the previously agreed amount. If he has the strength and ability to exceed this norm, then remuneration is carried out at increased rates.
A simple formula is used for calculation:
The salary amount = the norm for the quantity of products produced * the rate within the norm + the volume of products produced after the plan is fulfilled * the rate above the norm.
Calculation example
Every entrepreneur planning to use this system in his company must understand how progressive wages are calculated. An example of this process is considered quite simple.
For example, the company uses a piece-rate and progressive wage scheme. For one unit of output, the employee is paid 250 rubles. The norm per day is 4 units. If the plan is exceeded, then 300 rubles are paid for each additional unit. A worker can expect a different salary depending on monthly output:
- in March (21 working days) 89 units of products are produced, so the salary at a rate of 84 units will be equal to: 250*84+300*5=21000+1500=22500 rubles;
- in April, 80 units of products are produced in 22 working days, therefore, with a norm of 88 units, the employee receives a standard salary: 80 * 250 = 20 thousand rubles;
- in May, 108 units are produced in 21 working days, so the salary at a rate of 84 units is equal to: 250*84+300*24=21000+7200=28200 rubles.

Thus, the calculation will indeed be simple if it is possible to accurately determine how many units of product are produced by a particular employee per month or other amount of time.
Types of calculation
Piece-progressive remuneration can take several forms, which are used to simplify calculations or reduce risks:
- Bonus: for additional output or revenue, the employee receives a bonus, the size of which is higher, the greater the excess of the norm. This method is simpler, since the premium amount is clearly stated in the documents in advance and does not require additional calculations.
- Piece-time: used in those industries where the risk of downtime is high. Here the salary is conventionally divided into three parts: basic piecework + progressive (subject to exceeding the norm) + time-based payment for those periods when the employee was not able to perform his duties for reasons beyond his control.
- Indirect: an excellent option for calculating wages for employees of support departments (for example, a repair team) or management. Their payments will directly depend on the amounts that will be accrued to the main production. Thus, repairmen will be interested in ensuring that there are as few breakdowns as possible.
- Chord: used for teams performing one-time work: construction or harvesting. If the work is completed ahead of schedule or in excess, the employer issues a bonus to the entire team, and then this bonus is distributed among the employees depending on the contribution of each of them.

How is salary calculated if the norm is not met?
There are often situations when workers simply cannot fulfill the standard norm that is set for them for the day, work week or month. In this case, the managers of the enterprise should refer to the information contained in Art. 155 TK. It states:
- if the reason for such a low level of labor productivity is the employer, for example, there is downtime or equipment does not work that has not been repaired by the business owner for a long time, then it is not allowed to reduce the average monthly salary of the employee;
- if events arise that neither the employer nor the employee could influence, then the employee receives 2/3 or most of his tariff rate, for which the time he worked is taken into account;
- if the employee himself is to blame for such poor performance, then his salary is calculated based on actual results.
Finding the culprit often requires an analysis by a special commission.

Main features of the system
Progressive wages under socialism were used quite often at various large enterprises specializing in the production of similar products. Its use was effective, as it set workers up for productive activity, since they realized the dependence of their wages on the labor invested.

Even now, many businesses use this payroll scheme permanently or for a certain period of time. But some features are taken into account:
- before use, it is necessary to evaluate the possible economic effect of the system;
- all employees should be notified of such an innovation, as this will motivate them to work productively;
- it is preliminarily decided how the earnings of each employee will be calculated;
- The process of checking the quality of products must be established, since the haste of workers can lead to the constant appearance of defects.
Therefore, before implementing such a payroll scheme, it is necessary to evaluate all its features and negative parameters.
Let's complicate the task
There is also a more complex (and interesting) piece-rate progressive form of remuneration. In this case, the increased percentage is calculated not only from additional revenue, but also from the main one. That is: let’s take the same rate of 10% and a surcharge of 2, 3, 4%, etc. for each additional 100 thousand, but this surcharge will already work for the entire amount:
— Sales 300 thousand rubles. = 30 thousand salary (10%).
— Sales 400 thousand rubles. = 48 thousand salary (12% of the total amount).
— Sales 500 thousand rubles. = 65 thousand salary (13% of the total amount);
Of course, in a large enterprise, calculating piece-rate progressive wages will not be easy, and this is the main reason why such a scheme is used mainly in sales of goods and services. Below we will look at a formula that can be used in a manufacturing plant.