Let’s define the concepts: is workwear PPE or not?
Special clothing is needed not only for representatives of dangerous professions, but also to maintain the appearance of the organization. By definition, workwear is a custom-made uniform that is worn over regular clothing and sometimes over the naked body. Protective equipment helps protect workers from exposure to harmful factors and mechanical shocks. For some specialists, reflective stripes are applied to the workwear, which help the worker to be seen in the dark.
Labor protection, workwear
Note ! Any protective clothing is workwear, but not every workwear can be considered PPE. This includes the uniform that employees wear to maintain the appearance of the company: cleaners in hotels, restaurants, flight attendants, and the like.
Manufacturing materials
In the Russian System of Safety Standards, classic PPE fabric is called fabric “for protection against general industrial pollution”: it is a twill weave fabric made either from 100% cotton or from a blend of cotton with synthetic threads. Lighter and more pleasant material for sewing workwear for personnel in the service sector - usually these are classic fabrics for making shirts and shirts, cotton or mixed, with elements of nylon and polyester, increasing the strength and practicality of the fabric.
If special clothing is intended for specific working conditions, for example, for extinguishing fires, specialized materials can be used for its production - resistant to fire, oil, water, ticks and mosquitoes, and insulated in a special way. Typically, the scope of application of a particular kit is read from the markings affixed to all special clothing and shoes, and to all personal protective equipment.
Primary requirements
Issuance of PPE: what guides the employer
Legislation puts forward its own requirements for workwear, safety shoes and personal protective equipment for working on construction sites, with electrical installations, in the chemical industry, etc. First of all, it should be useful, and the employee should feel comfortable in it.
To personal protective equipment
PPE should not interfere with the performance of work, nor should it negatively affect the quality of work. If PPE is divided into several parts (separately for the torso and the area below the waist, for example), then their joint use should not interfere with each other. When workers are issued personal protective equipment, they must be given instructions on use, maintenance and storage. Tests and special inspections are regularly carried out to determine suitability for further use. If overalls, for example, are worn out or torn, they must be replaced with new ones.
To workwear
Some of the requirements duplicate the requirements for personal protective equipment: convenience, unhindered use, quality. Workers are subject to storage and care requirements for protective clothing. The employee is required to perform laundry, cleaning and disinfection. If clothing belongs to PPE, then additional requirements may be imposed on it (additional cleaning of hazardous substances). In addition, staff must be able to properly handle clothing.

Medical staff in clothes
Note! Extension of the wearing period of workwear according to the Order of the Ministry of Labor allows for an extension of the operational life if the PPE and workwear maintain their quality condition.
For safety shoes
Requirements for footwear for labor protection:
- Firstly, safety shoes must be the right size;
- Secondly, match the working environment: adhesion of the sole to the coating on the working terrain (concrete, sand, earth, tiled areas);
- Thirdly, comply with hygiene standards and be environmentally friendly;
Workers can buy their own shoes in specialized shoe stores. Honest manufacturers conduct tests before releasing models for sale. Large enterprises provide regular cleaning and bulk orders for employees.
Examples of special clothing
- Overalls - a set of jacket and pants or overalls, supplemented with protective equipment depending on the field of activity, the most common type of workwear of all. The term “overalls” can mean a whole range of types of protective equipment.
- Waterproof sets, represented by suits and overalls, made of hydrophobic fabric or treated with hydrophobic impregnations: instead of absorbing drops of moisture, the material repels them, and they simply slide off. A hood is required, the seams are treated with polyurethane to prevent leaks.
- Kits for protection against aggressive environments. Requires glasses or a full-face mask, respirators, and durable gloves. Clothing covers the entire body, leaving no gaps or gaps with exposed areas of the body.
- Insulated workwear - winter clothes for workers who work in cold conditions in the open air. There must be an insulated jacket, warm pants or overalls, as well as a hat, socks, safety shoes, and thermal underwear.
- For protection against high temperatures. The fabric is treated with impregnations that increase the fire resistance of the material: as a result, it becomes heat-resistant and “immune” to the creation of static electricity. In such clothes it is impossible to accidentally “spark” and cause a fire.
- Signal clothing is intended for work in conditions of poor visibility, for example, on roads, at airports, and it is recommended to wear it when hunting. The light is usually reflected by individual elements of the set.
- Uniform - it is worn by service personnel, employees of some companies, animators, and athletes. In addition to the protective and hygienic function, it also plays a brand-building role, helping to distinguish an employee of a particular company or team player from others. The same uniform promotes team spirit among staff.
Workwear can be made to order, or it can be purchased ready-made in a store. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer must provide the employee with special clothing for protection from the environment, along with other personal protective equipment.
See an unfamiliar term? Look up its meaning in the dictionary.
Source
Providing workers with special clothing
Employers, concluding an agreement with applicants, undertake to provide them with a uniform, if required. You can discuss the availability and form of workwear before drawing up a contract. If the organization’s charter stipulates the need for special clothing, then the employee undertakes to perform work in personal protective equipment. Failure to comply can result in a reprimand, fine and suspension from work.
Who should
Rules for the use of personal protective equipment
Firms can be divided into 2 groups: some are obliged to supply workers with special clothing, while others do this at their own discretion. What are the requirements for workwear regarding the provision of:
- Signal clothing: road workers, traffic police, police, janitors and other representatives of uniforms with reflectors.
- Warm uniform: builders, installers, traffic police, welders, electricians and the like.
- Pass-through protective clothing: for workers in hazardous and food production facilities and unfavorable temperatures.
Note! Sometimes different types of workwear can be used together. For example, to do metalworking or carry out construction work outdoors in winter, wear a warning light over warm clothing.

Hotel uniform
Also, uniforms are required for a number of civil servants, as well as for medical workers in order to protect hygiene. There is a difference between branded clothing and workwear. The brand name is issued by representatives of the enterprise; individual ordering of tailoring and design development is carried out through a contract with a tailoring organization. Workwear can be bought online and in specialized stores.
Issue norms
The procedure and norms that are intended to be responsible for issuance are developed and approved within the organization with the help of an order from the chief executive. In the rules, managers indicate hygiene requirements for issued clothing. It is allowed to deduct part of the salary for branded clothing. Free PPE, designed to protect the body, is issued without charging the employee, since performing work without it is contrary to GOSTs and SNIPs.
Working clothes and personal protective equipment
Classification of PPE
The classification of PPE in Russia is established by GOST 12.4.011-89, where, depending on the purpose, they are divided into 11 classes, which, in turn, depending on the design, are divided into types:
§ Isolating suits (pneumatic suits, waterproof suits, spacesuits)
§ Respiratory protection equipment (gas masks, respirators, self-rescuers, pneumatic helmets, pneumatic masks, pneumatic jackets)
§ Special protective clothing (sheep coats, coats, short coats, short fur coats, capes, raincoats, half-coats, dressing gowns, suits, jackets, shirts, trousers, shorts, overalls, bib overalls, vests, dresses, sundresses, blouses, skirts, aprons, shoulder pads)
§ Foot protection (boots, boots with an extended top, boots with a short top, ankle boots, shoes, low shoes, shoes, shoe covers, galoshes, boots, slippers (sandals), high boots, boots, shin guards, over the knee boots, foot wraps,
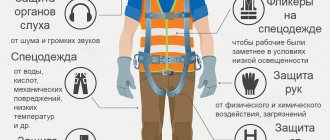
§ Hand protection (mittens, gloves, semi-gloves, finger pads, palm pads, wrist pads, sleeve pads, elbow pads)
§ Head protection (hard hats, helmets, balaclavas, caps, berets, hats, caps, headscarves, mosquito nets)
§ Eye protection (safety glasses)
§ Face protection (face shields)
§ Hearing protection (anti-noise helmets, anti-noise earplugs, anti-noise headphones,
§ Fall protection equipment and other safety equipment (safety belts, cables, hand grips, manipulators, knee pads, elbow pads, shoulder pads)
§ Dermatological protective products (protective creams, skin cleansers, reparative agents)
§ Comprehensive protective equipment
What is PPE?
Personal protective equipment is devices, products, equipment and systems that a worker wears or otherwise uses at work to ensure his safety and protect his health from the influence of one or more risk factors in the work environment.
Consumers of PPE
Consumers of PPE are mostly legal entities, namely employers, who, at the expense of the enterprise (this is established in the legislation of the Russian Federation), provide workers with the necessary protective equipment. Employers can entrust the assessment and purchase of PPE to specialists of the enterprise (institution). At the same time, a small part of consumers uses PPE for personal needs, for example, peasants, artisans, and householders.
Working clothes and personal protective equipment
Overalls are one part of all personal protective equipment. Workwear, like other personal protective equipment , is in demand and is applicable in many areas of production. Such professional activities include the activities of builders, installers, chemical production, heavy engineering, pharmaceutical production, metallurgy, food industry and others.
The main function of workwear is to ensure a sufficient level of labor safety, including protection from various mechanical damage. However, in addition to the main function, workwear also performs several additional ones. These include the advertising or marketing function, which is important for the operation of an enterprise. Workwear plays an important role in the prosperity of an enterprise and a certain psychological mood, in uniting the team and increasing labor productivity. That is why work shoes and work suits, as well as other types of workwear, should be selected not only based on practicality and safety, but also from the point of view of branding. As a rule, the company logo and often a slogan are applied to the workwear. For example, in the city of Lipetsk, in an auto parts store, the managers have a T-shirt that says “I know everything, ask me”
Workwear is clothing developed using special technology that is designed to protect a worker from the negative impacts of the production process or the environment. Workwear includes a work suit and special shoes, work gloves and a respirator, gloves or hats. Overalls must provide a certain level of protection, for example, be water-repellent, heat-resistant, hygienic (for medical staff), antistatic, etc.
Types of workwear
At the moment, there are a sufficient number of types of workwear. These include not only work suits, but also clothes for service sector workers, uniforms for medical staff, corporate accounting clothes, workwear for pharmacy and pharmacy store workers, robes for judges and clergy. The presence of simply a huge variety of workwear aroused genuine interest in it among modern designers, company managers and directors, who have already “tried it on”, albeit in absentia, to their employees. The purchase of corporate workwear has even become an element of a certain prestige for the company and a way to advance in the thematic market.
Accounting for the issuance of workwear at the enterprise
Standards for issuing workwear by profession
There is an average amount that an organization allocates for each employee for PPE. For ordinary industrial production it is 7 thousand per year, for others it can reach 24 and even 50 thousand.
Note! Since the amounts for enterprises are quite large (especially if there are many employees), records are kept of the uniforms issued and the minimum and maximum acceptable periods of wear are established.
A special responsible employee is appointed for control. In case of premature loss due to the fault of the employee (lost, torn), the company has the right to recover the cost of the new uniform from the employee. Poor calculation of the terms of use threatens unnecessary costs for clothing, or, conversely, a shortage of personal protective equipment and stagnation of the production or construction process.
Types of fabrics for work clothes
Most often, twill weave fabrics made from pure cotton or mixed with polyester fiber are used for workwear. For clothing for service industry employees, lighter plain weave materials are used. There are also special materials for protection from wind and rain, mosquitoes and ticks, sparks and metal splashes. Here are some types of fabrics for workwear:
- Moleskin is a thick cotton fabric with a brushed inside and a smooth surface on the outside, retains heat, does not allow moisture to pass through and protects from dust;
- ripstop - nylon or polyester fabric with reinforced thread, characterized by increased strength;
- cordura - thick nylon fabric with water-repellent impregnation and polyurethane coating;
- lyocell is a textile fiber made from cellulose, prevents the growth of bacteria, allows air to pass through, does not pill or lose shape after washing, and is highly wear-resistant (car cables are made from it).
To create our collections, we use lightweight and breathable fabrics, but durable. For example, ProTencel – 50% lyocell/50% polyester (CarePro and HoReCaPro lines) and polyester and cotton materials in different ratios:
- ProStretch – 64% PE/32% cotton, 4% elastane (HoReCaPro collection);
- ProTwill – 65/35 (WorkerPro, FoodInPro and CarePro collections);
- ProOutdoor – 70/30 (insulated WorkerPro line);
- ProChef – 67/32 cotton (clothing for chefs);
- Single Knit and Sweater knit – 50/50 (universal lines of T-shirts and jumpers).
What document should I fill out when issuing workwear to employees?
There are groups of documents within the organization that reflect receipt and issue. This is a card for issuing workwear, where the recipients sign, indicate the date of issue and the set.

Sheet MB-7
Another document is the issuance record sheet in form MB-7, which is maintained by an accountant. A more extensive document containing information about the list of issued protective clothing and costs, as well as accounting entries.
Reference! The accountant also records the issuance of workwear with postings.
How to organize the repair of work clothes
The employer organizes repairs and maintenance at his own expense. There are two options on how to do this: yourself at the enterprise or delegate it to a contractor. The first option will require additional hassle - the cost of equipment, organizing space for sewing machines and hiring qualified specialists. With the second approach, you save yourself from such a headache, since you transfer the care of work clothing to professionals who already have the equipment and experience. But you will have to spend time selecting and checking companies that provide industrial laundry services.
Order on write-off of workwear
Clothes are written off not simply through accounting. To write off, it is necessary to assemble an entire commission and approve property that is unsuitable for work. After this, an order is issued and the property is officially written off.
Reference! Only those items that are unsuitable for subsequent use and cannot be repaired are subject to write-off.
The reason for the write-off must be identified: damage to property due to someone else’s fault, wear and tear, and so on.
Who should repair workwear?
Work clothes get dirty, damaged and worn out. At the same time, it is prohibited to wear faulty or unrepaired work clothes in the workplace. It is the employer’s responsibility to monitor its condition. He is obliged to ensure the correct storage of the kits at the enterprise, organize washing and repairs himself or transfer them to the contractor.

You cannot delegate the care of workwear to employees
It is impossible to leave the care of textiles to the employee. Firstly, the Labor Code prohibits this. According to Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer provides special clothing to the employee at his own expense, and also organizes the storage, washing, repair and replacement of worn-out sets. Secondly, it will be difficult to organize quality control of washing and repairs carried out at home. Only 4 out of 10 workers monitor the condition of their workwear, according to a study by the European Enterprise Association.
A special commission should assess the condition of the workwear
To check the wear and tear of work clothing, the employer regularly assembles a commission that inspects the protective equipment and checks its functionality. The results of the inspection are entered into registration cards by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development N 290n. They indicate the percentage of wear of the set. This is important because some types of workwear are required to be issued to the employee before they are worn out. For example, dot-coated gloves for a gas welder.
Legislative regulation
The highest level of documents are federal laws, and the most important in the field of issuing workwear and personal protective equipment are the Labor Code (Article 221), Order No. 290n. They contain rules for the manufacture and issuance of special clothing.

Order to write off special clothing, sample
Some of the regulatory documents are necessary to list the list of mandatory professions that require PPE. Also, maintaining proper condition for the special uniform: washing, cleaning and storage. The employer is obliged to provide uniforms for each separate period of work. Otherwise, employees have the right to complain and supervisory authorities to impose penalties.
Working clothes and personal protective equipment are work attributes that most workers encounter in the process of building their working career. This does not include a dress code. Neglecting the rules for wearing protective clothing can cause damage to health, injury and disfigurement.
Responsibility for failure to use special clothing
If an employee has not received special clothing at the expense of the employer, he has every right to refuse to perform work functions without any sanctions from his superiors. Moreover, the employer will be obliged to pay for forced downtime for an employee unprotected by special clothing. In turn, if an employee does not wear protective clothing or uses it (as well as other personal protective equipment) incorrectly, management has the right to refuse permission to work and impose a disciplinary sanction.
Specific standards and terms for providing workwear - federal, regional, industry and private - are given in separate documents.
Frequency of washing workwear
But for cotton workwear, the speed should be 1-1.14 m/s.
In addition to ordinary washing, you can use special stain removers; this applies only to those organizations whose activities are associated with specific stains. Those workers who are involved in the operation of oil depots at gas stations before washing are required to ventilate their overalls in the open air for 2 hours and only then soak them in a 10% solution of laundry soap.
If all washing standards are followed, the workwear will retain its protective properties, which are established by regulatory documents, appearance and, of course, all its performance qualities such as strength, water resistance, elasticity.