The obligation to conduct labor safety briefings is established at the legislative level. The main reason for unscheduled training is frequent changes in regulations relating to occupational safety. The requirement for its organization is enshrined in labor legislation in Article 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The obligation to pass falls on all employees, including those holding managerial positions.
Specialists responsible for labor protection fill out a large number of document forms, which include logs for recording unscheduled briefings, the completion of which must meet established requirements.
Is registration required?
In order to conduct an unscheduled briefing outside the program approved by the head of the enterprise, a reason is required in accordance with labor legislation.
Training colleagues in labor safety is a must. Unscheduled events (as well as initial briefing) are important actions in the special training of workers that help avoid injuries and accidents in the workplace.
If, during an inspection by regulatory authorities, no evidence is found confirming the completion of unscheduled training (entry in the journal), then the institution faces a fine of 130 thousand rubles.
Who passes
Unscheduled briefing is both a group and individual procedure. The head of the organization, by local act, determines the list of employees who need to be trained in labor protection.
Such employees may be:
- those who have violated safety rules during their work activities or had an unsatisfactory assessment based on the results of a previous occupational safety inspection;
- employees of the unit where the accident occurred;
- all employees of the enterprise.
The procedure for conducting extraordinary instructions
First, you should identify the reason for conducting an unscheduled briefing. They can serve as:
- the occurrence of an emergency situation;
- changes in working conditions (technology, equipment) requiring personnel training.
More detailed reasons may include:
- introduction of new standards, norms, regulations related to labor protection in the company;
- amendments to the existing labor protection procedure;
- introduction of innovations into production (new equipment, change of technology, replacement of raw materials);
- an order from supervisory authorities that requires the elimination of inconsistencies with the norms of current legislation;
- identification of violation of rules (by an employee or student) that caused harm to health or damage to equipment;
- obtaining information about the accident from similar organizations;
- the presence of a large interval (2 months or more) between permission to work, and when working with increased danger - 1 month or more;
- issuing a special order from the head of the enterprise.
An individual program is prepared for each individual case that caused it.
The general requirements for the program are:
- delivering information to students about harmful and dangerous production factors;
- studying labor safety standards in the company, technical documentation for machines and tools;
- specifying methods for performing work safely.
The place for unscheduled training is the specialist’s specific workplace . The training material can be presented to one employee or a group of people of the same profession.
After instruction, registration in the journal is required.
Filling rules
The cover of the magazine contains the name of the enterprise, as well as the name of the organization. Next, the start and end days of logging are recorded.
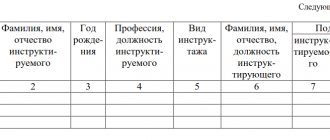
The following pages of the book are presented in the form of a table into which information is entered:
- the day of the unscheduled briefing;
- personal data (full name) of the instructed specialist, year of birth;
- employee position;
- type of briefing (unscheduled);
- the reason for conducting worker training;
- personal information about the instructor and his position;
- personal signature of the instructor and student.
How it is carried out for employees - step by step procedure
The training is carried out in several stages, each of them involves certain actions:
- Step 1. Issuing an order to conduct an unscheduled briefing indicating the reasons;
- Step 2. Determining the circle of persons responsible for carrying out this type of event and having the appropriate clearance;
- Step 3. Selecting a program or instruction to carry out in compliance with all specified requirements: coordination, approval, additions;
- Step 4. Determining the employees with whom unscheduled training should be carried out;
- Step 5. Testing the acquired knowledge;
- Step 6. Recording the fact of the event in the appropriate journal in compliance with all details: date, time, place. The signatures of the person being instructed and the person instructing are required.
Failure to comply with the last point entails the invalidity of the unscheduled briefing with all the ensuing consequences: the employee receives new information a second time, and the responsible person is subject to punishment, the severity of which is determined by the consequences that occur.
Administrative punishment includes a fine, and if a violation of occupational safety rules leads to harm to an employee or his death, then a case is initiated under an article of the criminal code, which provides for liability up to imprisonment.
What documents need to be completed?
Each action to conduct extraordinary employee training is documented:
- an order is issued to conduct an unscheduled briefing, which includes several points regarding the reasons for the conduct, the circle of persons responsible for the conduct and the employees to whom new information needs to be conveyed;
- familiarization with the order is mandatory for all persons participating in an unscheduled event;
- the fact of unscheduled training, regardless of the reason, is entered in a special journal developed on the basis of existing standards: date of conduct, time, reason, information about the place of work of the trainee, his identification data.
- entering information about unscheduled training into the employee’s personal card.
Thus, documentation can be divided into two types. The first of them records the preparatory work regarding the reasons, the amount of information, the order of implementation, training in safe work practices, and the second is the final one: the acquired knowledge is checked by the supervisor through an oral questioning.
Only those employees who have learned new information and passed an oral exam are given permission to work.
Making an order
The basis for unplanned instructions is the order of the manager, without which the training process cannot be carried out.
In addition to the basic general design attributes, the order must include the following items:
- the reason for holding the employee training event;
- place and time;
- appointment of a person responsible for recording the results in the appropriate journal with the obligatory signatures of the instructed person(s) and the instructor;
- identification data of the instructing employee;
- assigning individual responsibility for monitoring the execution of an order to a specific person.
An addition is attached to the order in the form of a separate sheet, on which everyone who has read the document signs.
order to conduct unscheduled briefing:
→ with the introduction of new labor protection rules from January 1, 2021;
→ in case of an accident;
→ when updating equipment.
What programs and instructions should I use?
It is impossible to foresee the reason for unscheduled training in advance, therefore, in each production there are standard programs developed in advance by the Ministry of Labor, which are subsequently supplemented with specific reasons for training, rules and the order of delivery of information.
The volume of unplanned instructions and their content are determined by motivating reasons. For example, a workshop received new equipment that is serviced by two employees. An order is issued on the need to conduct unscheduled training only with these two employees, indicating the amount of information that they must receive in order to ensure safe working conditions on the improved equipment.
Each program is coordinated with the labor protection department or trade union committee, which is confirmed by the signature of the responsible persons.
You can use labor protection instructions that regulate this or that work. The right to choose belongs to the administration.
If an unscheduled briefing is due to a change in the legislative framework regarding a specific area of work, then the texts of such documents must be used. On this basis, the responsible person makes changes to the instructions, which are subsequently conveyed to the employee, but after approval and agreement with the manager.
Off-plan instruction follows the same instructions and programs as initial training. They are developed by the manager of the employee(s). It is based on the regulatory framework that has legal force at the time of training and relates to the specifics of a particular job.
Maintaining a log book
The work of the labor protection department at each enterprise is aimed at increasing the labor safety of each employee, therefore each of their actions is documented and serves as an evidence base if necessary. One of these important documents is the logbook for registering unscheduled employee training.
Basic requirements for the journal:
- each page must be numbered;
- lacing is required, the ends of which are displayed on the last page, fixed with a sticker, sealed with the seal of the organization and the signature of the person responsible for maintaining the journal;
- When filling out, errors are not allowed, as well as unfilled lines;
- the journal form and columns are developed on the basis of regulatory documents that are advisory in nature, and therefore can be supplemented and changed in accordance with actual circumstances;
- The journal must be kept at the enterprise for 10 years, unless otherwise established by other regulations relating to certain specifics of labor. For example, recording unscheduled training in particularly difficult areas (mine, metro construction, etc.) requires long-term storage, up to 45 years.
The journal is maintained and filled out by the responsible person appointed by order of the manager.
.
Unscheduled briefing on labor protection
Instructions, including unscheduled ones, are part of the occupational safety and health (OHS) training process. It is important to develop programs correctly and adhere to their deadlines. The rules for its conduct and training in occupational safety are established in a special Procedure (Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation, Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/29).
According to the Procedure, there are the following occupational safety instructions:
- introductory: mandatory for all employees. It is carried out by a specialist in occupational health and safety (OHS) or a responsible employee (based on the Order of the manager);
- initial instruction (at the workplace) on labor protection. Employees whose duties are not related to equipment, any tools, storage and use of raw materials and materials may be exempt from it. The professions and positions of those released are approved by the employer. In accordance with Letter of the Ministry of Labor No. 15-2/OOG-1551, such employees do not undergo re-training;
- repeated instruction is carried out twice a year according to primary programs;
- unscheduled or extraordinary is organized based on the decision of the employer;
- the target is carried out in the cases specified in clause 2.1.7 of the Procedure.
Peculiarities
The peculiarity of unscheduled briefings is the absence of a pre-developed and approved program for conducting labor safety briefings of this type. In order to prepare for it as much as possible, the person responsible for labor protection in the organization should draw up a procedure for developing and approving a program for typical cases. Typical cases include changes in the requirements of regulatory documentation, accidents, identification of employees with gaps or erroneous knowledge of occupational safety.
When unscheduled instruction on labor protection is carried out due to changes or the introduction of new rules, codes, GOSTs and other regulatory documentation of state significance, a state inspector or employees of a specialized training center can be invited to conduct it. One such organization is EcoStandard group. It includes a Training and Methodological Center, which develops training programs taking into account the latest changes in legislation and current cases from the practice of Russian companies.
When is it carried out?
Let's take a closer look at the unscheduled safety briefing, which is carried out by the work manager (foreman, foreman, teacher, etc.) or by a commission (commission: head of the organization and structural divisions, specialists from the safety and safety services, chief specialists (technologist, mechanic, power engineer, etc.) .d.)).
Unscheduled briefing is carried out in the following cases:
- a special decision of the manager was issued;
- new legislative acts on occupational safety have appeared or have changed;
- production methods and processes have changed, equipment is being replaced or improved, and other changes related to labor safety are taking place;
- there was a violation of occupational safety requirements with serious consequences, including an industrial accident, accident, etc.;
- government agencies require unscheduled briefing;
- workers had breaks from work (for work with harmful and (or) dangerous conditions - more than 30 calendar days, and for other work - more than 2 months).
How is it drawn up and recorded?
To conduct extraordinary training for employees, the employer issues an administrative act on the need for it.
The order must include main sections informing:
- about the reasons why extraordinary training is carried out, including with references to changes in legislation, instructions, regulations;
- established date, place and time of study;
- the employee-instructor assigned to conduct the training;
- a list of employees who must undergo training (or a list of those who are exempt from such training).
All employees mentioned in it are familiarized with the document.
The result of the training is entered into the registration log, the form of which is established by the relevant GOST.
The log contains information about the employee who is being instructed, indicating his full name, date of birth, position, type of training and the reason for its implementation, date of conduct.
Registration takes place in accordance with the following rules:
- mandatory presence of the date of entry in the journal;
- mandatory completion of the column about the reasons for conducting training with a brief description of the reasons for conducting it;
- the established form requires the signatures of both parties: the signatures of the instructor and the instructed are required.

The procedure for conducting unscheduled training
The volume, order and timing of activities are determined by the employer. The program is developed for each unscheduled workplace safety briefing and depends on the reasons that necessitated its implementation. General requirements for the program:
- informing about existing dangerous, harmful production factors;
- study of occupational safety requirements in the organization, technical and operational documentation for equipment and tools;
- application of safe methods and techniques for performing work.
The location of training events is a specific workplace. Training is carried out individually or with a group of workers of the same profession.
conclusions
There are several main points on this topic:
- After an accident, an unscheduled briefing is carried out in the structural unit where it occurred.
- To carry it out, an order must be issued for the enterprise.
- Training of employees is carried out by a manager who has the necessary knowledge and has the right to do so.
- At the end of the lecture, employees are tested and it is determined whether they have learned the information or not.
- Employees who have not completed training and testing are not allowed to work.
- Personnel are instructed directly at the place of work.
Registration of results
Upon completion, an oral test of the acquired knowledge is carried out. Those who do not pass the test are not allowed to work (Article 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), about which a corresponding order is drawn up.
Those who successfully pass the verification receive a certificate in the form according to Appendix 2 to the Procedure.
The results of the inspection are documented in a protocol (the form is established in Appendix 1 to the Procedure). A note is made in the appropriate journal according to the forms established by GOST 12.0.004-2015 (Gosstandart Order No. 600-st).
Sep 10, 2019adminlawsexp
vote
Article rating
What will happen if you don’t
Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in Art. 5.27.1 defines the penalties applied for violation of occupational safety requirements. The employer must provide not only for the provision of labor safety training, which is mandatory, but also for the organization to have documents confirming the training (magazine).
Otherwise, the following penalties will apply:
- for a legal entity - in the amount of 100,000 rubles to 130,000 rubles;
- for an official - in the amount of 15,000 rubles to 25,000 rubles.
Such significant numbers are a convincing argument in favor of both training and its correct recording.
However, violation of established occupational safety requirements may result in criminal liability. In accordance with Art. 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, if a violation of occupational safety caused serious harm to health or the death of a person, not only fines, but also disqualification, forced labor, and, in the most serious cases, imprisonment are provided as penalties.