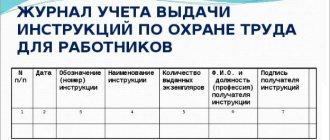
What is a labor protection agreement?
An occupational safety and health agreement is a legal form for planning and carrying out occupational safety and health measures in an organization, indicating deadlines for implementation, sources of financing and responsible persons.
In other words, this is a document that takes into account the timing, responsibility and amount of costs for implementing labor protection measures.
For educational organizations, there is a document that explains the basic concepts in detail.
How to draw up an agreement correctly
Outsourcing of labor protection: contract, engineer
The agreement must contain the necessary clauses defining the responsibilities of responsible persons, as well as a description of all planned measures to ensure labor safety, namely:
- Organizational measures mean that each staff member has undergone the necessary training and will be able to provide themselves with safe working conditions.
- A list of technical measures taken by management to ensure safety in the workplace.
- All employees involved in work associated with increased danger to life and health must be provided with PPE (personal protective equipment), which they must use for their intended purpose under the control of responsible persons, and the list of these devices is specified in the text of the contract.
- A set of treatment and preventive measures, which include the possibility of providing emergency medical care within the organization’s walls, as well as conducting an examination of all specialists before starting work associated with health risks.
- Measures to ensure comfortable sanitary conditions at the enterprise - the organization of canteens, places for recreation, as well as regulations for the stay of personnel in such places in strict accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and current Sanitary Regulations.
- Fire safety measures, including personnel training. Designation of persons responsible for TB and description of all primary fire extinguishing means.
Attention! In addition to the activities described in the list, the document contains links to regulations governing the employer’s requirements, the validity period of the document and a list of persons who are entrusted with monitoring the implementation of all requirements.
In order for the document to have legal force in the event of an emergency or other emergency circumstances, its form and content must comply with Articles 92, 117, 147 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which oblige each employer to provide employees with comfortable and safe working conditions.
Information about labor protection at the enterprise must be conveyed in an understandable form
Is the occupational safety and health agreement mandatory for everyone?
No, the labor protection agreement is not a mandatory document. However, it is an integral part of the collective agreement.
This leads to the question: “Is a collective agreement mandatory?”
No, if neither the employer nor the employees expressed a desire to enter into it. But if you have a concluded collective agreement, then there must be such a document.
Reason: Art. 40 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Download an example of a collective agreement
You may need other labor protection documents
How is compliance with the terms of the agreement verified?
Any internal act issued at the enterprise, after it comes into force, must be immediately accepted by an authorized employee, who, for the period of validity of the agreement, is obliged to monitor compliance with its requirements. The list of his actions includes the following important criteria to ensure the necessary checks:
- Delegation of authority to other company employees to comply with all requirements of the agreement.
- Periodic inspection of all technical systems by the engineering staff of the enterprise - fire alarms, signal panels, quality of electrical wiring and other equipment requiring special assessment.
- Each immediate manager of the department must provide instructions before the start of the working day of his team, or a corresponding work permit is drawn up for a particular type of work activity, followed by providing a copy of it to the person responsible for labor protection.
- If necessary, a working commission is created from employees of different departments to check working conditions and compliance with safety regulations during a certain period, most often once every quarter.
Attention! Each employee authorized for his area reports to the person who controls the execution of management’s orders on the results of his work, on the basis of which a general report is generated at the end of the year.
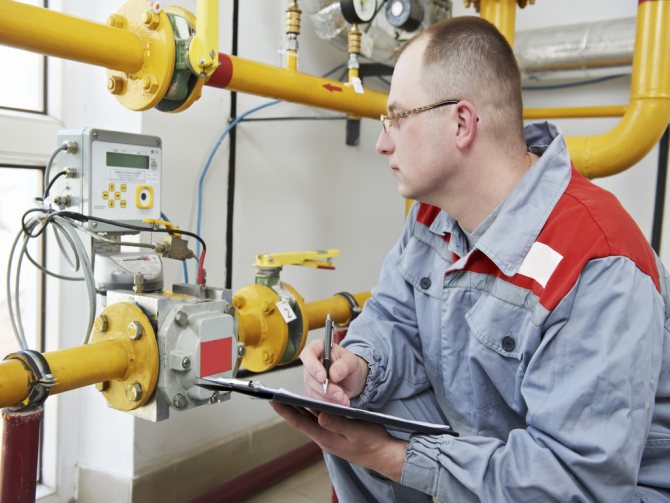

An authorized employee checks the serviceability of the equipment
How does an action plan differ from an occupational safety and health agreement?
- Firstly
, there are more questions in the standard agreement for organizing the education sector than the list of activities that
ORDER
, 2012 offers us. - Secondly,
the agreement indicates the amount, timing and responsibility, which allows for more accurate budget planning, as opposed to an action plan.
Also, if the employer signs this document, then he is obliged to carry out the activities specified in it. And an employee or employee representative can write a collective complaint to the inspectorate regarding non-compliance with the agreement
.
2.4.4. Planning occupational safety measures and developing programs to improve working conditions and safety in the organizationPlanning of work on labor protection is an organizational management process carried out with the aim of ensuring safe working conditions for workers based on the effective use of funds allocated to improve working conditions and safety. Planning of work on labor protection is carried out on the basis of: - long-term comprehensive plans (programs) for improving labor protection conditions and sanitary and health measures that are an integral part of the enterprise development programs (if any); — current (annual) labor protection action plans included in the labor protection agreements of the collective agreement; — operational (quarterly, monthly) plans for departments (for example, for workshops and sections). In addition to the labor protection measures of the collective agreement and labor protection agreements, the following are developed: - monthly work plans for labor protection in the department; — employer action plans to reduce industrial injuries and occupational diseases at work. Current planning for improving and improving working conditions, reducing occupational injuries and occupational diseases involves the development of annual work plans or activities. This plan includes organizational, technical, sanitary and hygienic, treatment and preventive, socio-economic and other activities carried out in accordance with regulatory legal acts on industrial safety and labor protection. Current (annual) plans are formalized by annual order No. 1 for the enterprise and agreements on labor protection of divisions, indicating deadlines and responsible persons. The agreements include the most important activities, supported (confirmed by relevant planning and economic documents) with the material and financial resources necessary for their implementation. Activities included in the plans mentioned above must have appropriate design and technological documentation, as well as be provided with material and technical resources. The annual action plan to improve and improve the working conditions of the unit and structural unit is drawn up by the head of the unit and submitted to the labor protection department by December 1 of the year preceding the plan. The annual plan for improving and improving working conditions, reducing injuries at the enterprise level is formed by the labor protection department on the basis of draft annual plans of departments and structural units sent to it. The labor protection department, before December 25 of the year preceding the planned one, forms and submits for approval to the chief engineer/technical director a draft annual plan for improving and improving working conditions, reducing injuries throughout the enterprise, breaking down this plan into quarters and indicating responsible executors. The adjusted and agreed annual plan for improving and improving working conditions and reducing injuries is approved by the General Director in annual order No. 1. Operational (quarterly) plans are developed to solve newly emerging problems in ensuring labor safety based on the results of ongoing monitoring of the state of conditions and labor protection at the department level and structural divisions, instructions from state supervisory authorities and public control over compliance with labor protection requirements and other measures to create safe working conditions, materials from the investigation of industrial accidents, accidents, etc. Operational planning is a continuation and development of current planning. Planning work on industrial safety and labor protection at the enterprise includes: - work on construction, reconstruction, technical re-equipment and scheduled maintenance of existing production facilities and equipment in order to increase their safety and emergency resistance, improve working conditions; — inspection and testing of pressure vessels, lifting machines and mechanisms, accessories for lifting mechanisms, dielectric protective equipment, etc.; — timely fulfillment of conditions relating to labor protection, validity of licenses for the types of activities carried out; — timely implementation of measures provided for by target programs and agreement on labor protection; — carrying out checks of compliance with the rules for performing high-risk work (availability of work permit, permit); — timely and high-quality training (including advanced training of employees), conducting knowledge tests; — organizing testing of knowledge on labor protection among chairmen and members of permanent examination commissions; — timely receipt and delivery of personal protective equipment; — timely conduct of preliminary (upon hiring) and periodic medical examinations of employees; — implementation of measures to prevent accidents and incidents, to localize and eliminate the consequences of accidents at a hazardous production facility; — insurance of employees against industrial accidents and occupational diseases; — insurance of liability for causing harm to third parties during the operation of a hazardous production facility; — holding meetings on the prevention of injuries, illnesses and emergencies with reports from managers and specialists on the state of labor protection, as well as on the implementation of activities planned for this period; — organizing the work of permanent commissions on labor protection and planning the timing of inspections of compliance in departments and structural units with instructions from state supervision and control bodies, public control, orders and regulations for the enterprise; — carrying out targeted and comprehensive inspections of the state of labor protection in divisions and structural units, organizing work on accounting, analysis and assessment of the state of labor protection (at the workplace, on the site, in the workshop, in the department); — development and implementation of measures based on the results of certification of workplaces according to working conditions; — timely execution of established reporting on labor protection, preparation of statistical reports and analytical notes on the state of working conditions in departments and structural units, preparation of a consolidated annual report on the results of work on labor protection; — timely provision of all departments and structural units with regulatory documents, reference and teaching aids, posters, safety signs, etc.; — organizing and conducting events to promote labor safety, incl. lectures, seminars, conversations, etc.; — exchange of experience in labor protection, planning work to introduce best practices in labor protection. When planning the costs of ensuring labor safety work, as part of quarterly and annual financial plans for departments and structural units, it is necessary to provide for: - carrying out scheduled preventive maintenance of equipment; — carrying out current and major repairs of buildings and structures; — prevention and testing of lifting machines and mechanisms, accessories for lifting mechanisms, pressure vessels, and other objects of Gosgortekhnadzor (in accordance with the current regulations and inspection periods); — testing of dielectric protective equipment; — training of department employees on labor protection issues (conducting all types of briefings in the workplace, training and testing knowledge on labor protection, advanced training, etc.), regular and extraordinary knowledge tests; — providing workers with personal protective equipment, milk, special food, soap and detergents; — conducting periodic medical examinations of workers; — participation in workplace certification; — revision and development of regulations, instructions on labor protection by profession and type of work and other administrative documents on industrial safety and labor protection; — organization and participation in the commission of the appropriate level of control over the state of labor protection; — quarterly verification of the progress of implementation of the agreement on labor protection, materials from the investigation of industrial accidents, materials from inspections and surveys of the enterprise to ensure labor protection, instructions from regulatory authorities. When planning work on labor protection and industrial safety, it is necessary to take into account the recommended list of typical measures for industrial safety and labor protection. At the discretion of the employer and representative bodies (trade union) authorized by employees, labor protection measures may include other work aimed at improving the health of workers and improving their working conditions.
Typical measures for planning work on labor protection
No.
| Event name | |
| Organizational events | |
| 1 | Organization of training, instruction, testing of knowledge on labor protection of enterprise employees - in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.0.004-90. |
| 2 | Activities related to the provision of workers engaged in work with harmful or dangerous working conditions, as well as in work performed in special temperature and climatic conditions or associated with pollution, special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment, flushing and neutralizing agents in in accordance with established standards. |
| 3. | Organization of offices, occupational safety corners, mobile laboratories, acquisition of necessary equipment for them, visual aids, demonstration equipment, etc., holding occupational safety exhibitions. |
| 4. | Development, publication (reproduction) of instructions on labor protection, as well as the acquisition of other regulatory legal acts and literature in the field of labor protection. |
| 5. | Organization of certification of labor protection work based on the results of certification of workplaces according to working conditions. |
| Technical events | |
| 6. | Modernization of technological, handling and other production equipment in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.2.003-91, GOST 12.2.009-99, GOST 12.2.049-80, GOST 12.2.061-81. |
| 7. | Introduction of systems (devices) for automatic and remote control and regulation of production equipment, technological processes, lifting and transport devices, the use of industrial robots in hazardous and hazardous industries to ensure the safety of workers in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.2.049-80, GOST 12.2.061 -81, GOST 12.2.062-81, GOST 12.2.064-81, GOST 12.2.072-98, GOST 12.3.002-75, GOST 12.4.026-01 |
| 8. | Improvement of technological processes in order to eliminate the impact on workers of hazardous and harmful production factors in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.2.003-91, GOST 12.1.007-76, GOST 12.3.002-75. |
| 9. | Implementation of automatic control and alarm systems for the presence and occurrence of dangerous and harmful production factors, as well as interlocking devices that provide emergency deflection of process and power equipment in cases of malfunction in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.1.001-89, GOST 12.1.002-84, GOST 12.1.003-83, GOST 12.1.006-84, GOST 12.1.008-76, GOST 12.1.012-90, GOST 12.1.019-79, GOST 12.1.031-81, GOST 12.1.045-84, GOST 12.1.047-85, GOST 12.1.048-85, GOST 12.4.012-83. |
| 10. | Introduction of technical devices that provide protection for workers from electric shock, in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.1.018-93, GOST 12.1.019-79, GOST 12.1.030-81, GOST 12.1.038-82, GOST 12.1.045-84 , GOST 12.2.007.0-75, GOST 12.2.007.14-75, RD 153-34.0-03.150-00. |
| 11. | Installation of safety, protective and signaling devices (devices) in order to ensure safe operation and emergency protection of steam, water, gas, acid and other industrial communications and structures in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.2.016-81, GOST 12.2.052-81, GOST 12.2.063-81, GOST 12.2.085-82, GOST 12.3.001-85. |
| 12. | Mechanization and automation of technological operations (processes) associated with storage, movement (transportation), filling and emptying of mobile and stationary tanks (vessels) with toxic, aggressive, flammable and combustible liquids used in production, in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.1.004- 91, GOST 12.1.007-76, GOST 12.1.010-76, GOST 12.2.022-80, GOST 12.3.020-80, GOST 12.4.026-01, SNiP 2.05.07-91 (1996). |
| 13. | Reduction to regulated levels of harmful substances in the air of the working area, adverse mechanical vibrations (noise, vibration, ultrasound, etc.) and radiation (ionizing, electromagnetic, laser, ultraviolet, etc.) at workplaces in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.1.001 -89, GOST 12.1.003-83, GOST 12.1.005-88, GOST 12.1.006-84, GOST 12.1.012-90, GOST 12.1.040-83, GOST 12.1.045-84. |
| 14. | Installation of new and improvement of existing means of collective protection of workers from the effects of hazardous and harmful production factors in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.4.011-89, GOST 12.4.120-83, GOST 12.4.125-83. |
| 15. | Installation of new and reconstruction of existing heating and ventilation systems in industrial and service premises, thermal and air curtains, aspiration and dust and gas collection systems in order to ensure normal thermal conditions and microclimate, clean air in the working and serviced areas of the premises in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.1.005 -88, GOST 12.2.028-84, SNiP 2.04.05-91 (2000). |
| 16. | Bringing natural and artificial lighting in workplaces, workshops, domestic premises, places of mass passage of people, on the territory to the standards of SNiP 23-05-95. |
| 17. | Redevelopment of the placement of production equipment, organization of workplaces in order to ensure the safety of workers in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.3.002-75, SNiP 3.05.06-85, GOST 12.2.032-86, GOST 12.2.033-86. |
| 18. | Applying signal colors and safety signs to production equipment (control and monitoring controls, structural elements), communications and other objects in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.4.026-01, GOST 12.4.040-78, GOST 14202-69. |
| 19. | Mechanization of work during storage and transportation of raw materials, wholesale products and production waste in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.2.022-80, GOST 12.3.009-76, GOST 12.3.020-80. |
| 20. | Mechanization of cleaning of production premises, timely removal and neutralization of production waste, which are sources of hazardous and harmful production factors, cleaning of air ducts and ventilation units, lighting fixtures, windows, transoms, skylights in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.04.05-91 (2000), SNiP 05/23/95. |
| 21. | Bringing buildings (industrial, administrative, household, public, warehouse), structures, premises, construction and industrial sites to standards in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.08.02-89 (2001), SNiP 2.09.02-85, SNiP 2.09.04- 87 (1995), SNiP 12-03-2001. |
| 22. | Construction of sidewalks, passages, tunnels, galleries on the territory of an enterprise (workshop), construction site in order to ensure the safety of workers, implementation of a system of measures to prevent road traffic injuries. |
| 23. | Conducting an examination of working conditions in design and technological documentation during the construction of new and reconstruction of existing enterprises, buildings, structures, and production facilities. |
| Sanitary, medical and preventive measures | |
| 24. | Expansion, reconstruction and equipment of sanitary facilities (dressing rooms, showers, washrooms, latrines, places for half-showers, rooms for personal hygiene of women, rooms for heating or cooling, processing, storage and distribution of special clothing, etc.) in accordance with the requirements SNiP 2.09.04-87 (1995). |
| 25. | Purchase and installation of saturating units (automatic machines) for preparing carbonated water, arrangement of centralized supply of drinking and carbonated water, tea and other tonic drinks to workplaces in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.09.04-87 (1995). |
| 26. | Construction at existing facilities of new and reconstruction of existing places of organized recreation, rooms and rooms for relaxation, psychological relief, premises of paramedics and medical health centers, places for heating workers, as well as shelters from sunlight and precipitation when working outdoors - in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.09.04-87 (1995). |
| 27. | Equipping workshops for industrial gymnastics, purchasing the necessary sports equipment for these purposes, paying instructors and methodologists for industrial gymnastics and physical education and health work. |
| 28. | Equipment of houses and recreation centers, etc. |
| Socio-economic events | |
| 29. | Compulsory insurance of employees against temporary disability due to illness, as well as against industrial accidents and occupational diseases, etc. |
| 30. | Encouraging work without injury or safety violations. |
Note: In all points, in addition to the listed regulatory legal acts, other current legislative and intersectoral regulatory legal acts on labor protection can be used.
Activities that should be included in the plan
The main activities that are recommended to be included in the occupational safety plan:
- Automation of control systems.
- Identification of occupational risks through the implementation of special operating conditions.
- Implementation of activities necessary to improve the results of SOUT.
- Equipping premises with alarm systems or devices to control indicators of the negative impact of production factors.
- Introduction of modern means of collective protection.
- Updating obsolete equipment.
- Arrangement of fencing for moving elements.
- Mechanization of transportation of dangerous goods.
- Arranging a normal microclimate: installing heating and ventilation systems, ensuring cleanliness.
- Installation of additional lighting at workplaces.
- Providing employees with work clothes and protective equipment.
- Regular briefings on labor protection.
- Arrangement of premises with medical aid stations and first aid kits.
- Regular medical examinations.
The list of activities included in the plan depends on the specifics of the organization’s work.