Reasons for leaving a job can be both objective and subjective. Objective, specified in the norms of the current labor legislation, as general legal grounds. Subjective reasons for voluntary dismissal relate, rather, to the interpersonal relationships that were formed in the process of work between the employee and his colleagues, or between him and his immediate superiors. In addition, the employee may want to change his qualifications, place of residence, etc.
But the law gives us clear instructions specifically about the legal grounds for terminating an employment contract. And, regardless of personal issues, when dismissing, you should choose the wording for the reason for dismissal, in accordance with the Labor Code. There are both reasons to fire a negligent employee from the company where he works, and the employee’s desire to leave his position. Let's consider the legal grounds for terminating an employment contract.
How are grounds and causes classified?
To terminate an employment contract there must be at least one of the legal grounds, which can be classified as:
- basic;
- additional;
- due to current circumstances;
- legally justified.
1. In Art. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides a list of general grounds when an employment contract ceases to be valid:
- Based on the agreement and agreement reached between the owner and the hired worker (Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Upon expiration of the contract or the scope of work provided for by its terms has been completed (Article 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- When an employee no longer wants, or due to current circumstances cannot continue to work in this organization and wants to resign of his own free will (Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- The employer does not want to continue to have any joint production relations with the employee in the future due to loss of trust or failure to fully fulfill official duties, violations of labor discipline, and other situations permissible in accordance with Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- In the event that, under a written guarantee of employment from another employer, a person is transferred to another organization or may be elected to an elective position.
- If the employee is not satisfied with the new owner of the enterprise or changes in jurisdiction that occurred in connection with the reorganization, the transition of a state institution to a municipal type (Article 75 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- If the employee does not agree to accept the changes made by the employer to the terms of the employment contract and refuses to continue working, fulfilling the new requirements (Part 4 of Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- If the employee does not want to transfer to a vacant position offered by the manager, where the working conditions are compatible with his state of health and medical report.
This may include cases when the employer does not have suitable workplaces where the employee can continue to work if medical indications do not allow him to perform previous duties (transfer to light work, according to Part 3 and Part 4 of Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- Change by the owner of the legal and actual address of the location of the enterprise and the employee’s refusal to move from his main place of residence in order to be able to continue working in his specialty for the previous owner (Part 1 of Article 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- Circumstances that do not depend on the wishes of either party to the contractual relationship (Article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- When the contract is concluded in violation of the rules established by labor legislation or other federal laws, which excludes the possibility of continuing to work further (Article 84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
2. Additional reasons when an employment contract may be terminated are also defined in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, these include:
- removal from his position of the head of an enterprise that is in the process of bankruptcy (Article 278 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- termination of contractual relations providing for combination of professions when hiring a person for a combined position for permanent work;
- For teachers involved in the upbringing and education of the younger generation, the following is fraught with dismissal: repeated violation of the charter of an educational institution;
- even a single use of unacceptable methods of education with the use of violence against a student of a physical or psychological nature;
- reaching the age when, according to Art. 332 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, certain positions cannot be filled;
- in the event of an emergency in the host country (the outbreak of hostilities, natural disasters, etc.);
- in case of disqualification for more than six months;
This is also important to know:
Dismissal of an employee due to loss of trust, article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Special requirements for compliance with the charter or regulations on discipline for civil servants, accordingly, expand the grounds giving the right to terminate the employment relationship if they are not fulfilled.
3. The legal grounds for termination of an employment contract are listed in Art. 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, when the decision to dismiss does not depend on the will of the parties:
- conscription into the Army to fulfill military duty to the Motherland, or for alternative civilian service in special cases determined by law;
- when by a court decision the dismissal of a previously held position in whose place a new employee is hired is declared illegal and the latter is restored to his rights to work;
- if an employee is found guilty of a crime by a court verdict and sent to places of serving the actual sentence, or is excluded from the possibility of further engaging in certain types of activities;
- due to the deterioration of a person’s health, the conclusion of a medical examination indicating complete disability;
- unexpected death of an employee or employer, equivalent to this situation, a court decision declaring an individual dead or missing;
- recognition by the Government of the country or a government body of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation of the onset of emergency situations when it is impossible to continue normal work activity (natural and man-made disasters, accidents, epidemics of viral diseases, the outbreak of hostilities, etc.);
- bringing to administrative responsibility up to and including disqualification of the employee and issuing a decision to remove him from his position for a specified period;
- in case of expiration of a possible two-month period of suspension of special licenses, if it is no longer possible for the employee to perform his job duties (for example, deprivation of a driver’s license, the right to store and carry weapons, etc.);
- in case of a ban on access to state secrets, when fulfillment of the terms of the employment contract is impossible without this permission;
- if a previously adopted court decision on reinstatement at work is canceled upon appeal by the employer;
- in other cases, when circumstances arise that, in accordance with the requirements of labor legislation and federal laws, exclude certain departments and sectors of the national economy from engaging in a certain type of activity.
4. From a legal point of view, termination of an employment contract is regulated by law and must be carried out in compliance with the established rules:
- the validity of the decision to dismiss the employee;
- fulfillment of all procedural requirements;
- documentary evidence of the legal basis for termination of industrial relations.
How to determine legality and illegality
Grounds for dismissal can be considered legal if they are documented and comply with current legislation. The documents indicate the rules of law that the employer is guided by and the reasons.
Reference! All types of dismissal, excluding voluntary dismissal, are accompanied by documents confirming the grounds.
Dismissal may be considered illegal if:
- there are no legal grounds;
- they are not true;
- the rules of law and reason are incorrectly applied.
When dismissing an employer, he must be guided not only by the Labor Code, but also by other federal laws that relate to this issue .
What laws govern the legal relationship between employer and employee?
The relationship between an employee and his employer is regulated by labor law.
Its main source is the Labor Code of the Russian Federation of December 30, 2001, 197-FZ, regulations.
This is also important to know:
Dismissal of one’s own free will during sick leave: procedure
On their basis, an employment contract is developed between the employer and the employee.
According to Art. 6 of the Labor Code, the procedure for dismissal is established by federal authorities.
The general grounds for dismissal are given in Art. 77 TK.
Also, the document (Articles 278, 288, 307, 312, 336) provides additional grounds on which an employee can be dismissed.
Dismissal occurs:
- at the initiative of an employee or employer;
- by agreement of the parties;
- due to circumstances (not at the will of the employer and employee);
- when does a fixed-term employment contract end?
- if the employee is to be transferred to another employer or to another position (job);
- if the employee does not agree to work due to a change in the owner of the organization;
- if the employee refused to work due to a critical change in the terms of the employment contract;
- when an employee refuses to be transferred when the employer moves to another location;
- when an employee refuses to be transferred to another job due to changes in his health status;
- when the rules for concluding an employment contract are violated, if this makes it impossible to continue working.
The first five types of dismissal are the most common.
General grounds for dismissing an employee
Any employee can terminate cooperation with a specific employer. But for this you will need to go through the procedure prescribed by law. Here are the key points to highlight:
- In order to resign or be dismissed, you must have a clearly established basis by law. This may be the desire of the employee, the employer, reasons that do not depend on the parties;
- To start the dismissal procedure, an initiative document (or a document confirming the fact of the event) is required. Usually this is a statement, a memorandum, minutes of an operational meeting, a summons from the military registration and enlistment office, a death certificate and others;
- the legal fact of termination of an employment contract is confirmed by an order (instruction) of the head of the company. The employee gets acquainted with such an act personally, against his signature;
- The day of dismissal is always the last working day. This means that during this time wages will be accrued and paid;
- upon dismissal, the HR department enters information into the work book, and the accounting department makes a full settlement with the employee. The work book must be issued to the employee personally. If not picked up, it is sent by mail with delivery notification;
- upon application of the worker, he is given all copies of documents related to his dismissal and payment. They have no right to refuse this request.
Remember, the dismissal procedure differs depending on the initiative (the employee or his employer). Here it is necessary to consider each specific case separately.
Dismissal at the initiative of an employee
In most cases, an employee quits on his own initiative under clause 3, part 1, article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
He notifies the employer of his intention no later than two weeks in advance, unless a different period is established in the employment contract or federal legislation.
Two weeks are counted from the day after the application is submitted.
In a number of situations, the employer must carry out the dismissal within the period specified in the submitted application.
These include the following circumstances:
- impossibility of continuing to perform work duties due to retirement or enrollment in an educational institution;
- failure by the employer to fulfill obligations under the employment contract.
The advantage of this method of dismissal is that the employee has the right to withdraw his own application if another person has not been invited to take his place until this moment, and who cannot be denied employment according to the norms of current legislation.
Such an invitation is drawn up in writing.
After the expiration of the period, the applicant has the right not to go to work.
If the two-week period has expired, but the contract has not been terminated and the employee does not demand dismissal based on the previously given application, then its validity does not terminate.
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
This method of dismissal is beneficial to both the employer and the employee. The first one has time to either persuade the employee or find a new specialist to fill the vacant position, and the second one does not close the door on himself if he is not sure of his future.
Reason for dismissal No. 2 – lack of prospects

Some workers quit simply because there are no real prospects in their workplace. Working for a long time with the same salary and in the same position without visible progress will definitely force an employee to think about looking for a more promising job. Even a small salary with ample opportunities for career growth in the future may not become a hindrance in this case for tired workers to remain at the same level.
At the same time, it is logical that not every employee is truly worthy of an effective promotion or promotion up the career ladder - in any case, there are not enough vacant management positions for everyone. However, it should be remembered that at any enterprise it is possible for employees to occupy additional positions. Thus, an employee who does not demonstrate leadership talent, but conscientiously performs his duties, can be increased in salary and offered the role of an instructor for novice applicants, or simply provided with additional income by giving him the position of someone responsible for fire safety or other labor standards.
In some professions there is also a certain ceiling for career growth, above which the employee simply cannot rise. In this case, the employee is unlikely to quit for this reason, but may begin to think about changing his specialty. If the employer values such an employee in this capacity, a good option may be to offer him a part-time job with another position that provides for his own, separate career growth, if possible. Even the very fact of even minimal prospects for the future, when reaching the “ceiling” in a busy specialty, can easily convince an employee to quit.
Dismissal initiated by the employer
At the initiative of the employer, the employee is dismissed in the following cases:
- liquidation of the organization is expected;
- the owner of the organization’s property changes (the situation applies to the manager, his deputies, and the chief accountant);
- the number or staff of employees is reduced;
- the employee is not suitable for the position he occupies or is unable to fulfill the obligations assigned to him;
- the employee constantly evades fulfillment of contractual duties without good reason, if he has previously received a disciplinary sanction;
- the employee grossly failed to fulfill his job duties one time (he skipped work, showed up at work drunk, divulged a secret protected by law, committed theft of work property, violated labor safety requirements, which led to grave consequences);
- the commission by an employee who services commodity-monetary assets of actions that led to a loss of confidence in him;
- the employee committed an immoral act that was incompatible with his position, which involved edifying functions (kindergarten teacher, teacher, etc.);
- the manager, his deputies or the chief accountant made an unreasonable decision, and it led to a violation of the safety of property, its misuse, and other damage to the organization;
- the employee submitted false documents when applying for a job;
- the employee violated other terms of the employment contract;
- other cases established by current legislation.
It is worth noting that it is prohibited to dismiss an employee if he is temporarily disabled (illness, pregnancy) or is on leave, including for child care.
The exception is the upcoming liquidation of the enterprise.
Who cannot be fired if there is a legal basis
The law defines the circle of people who cannot be dismissed, even if there are justified reasons. This category is established in particular in the Labor Code in Article 261. Such persons include:
- pregnant women;
- single mothers or fathers;
- the only breadwinner in the family (a disabled child or a large family, one of the children under 3 years old);
- an employee on sick leave or on vacation;
- a person of pre-retirement age;
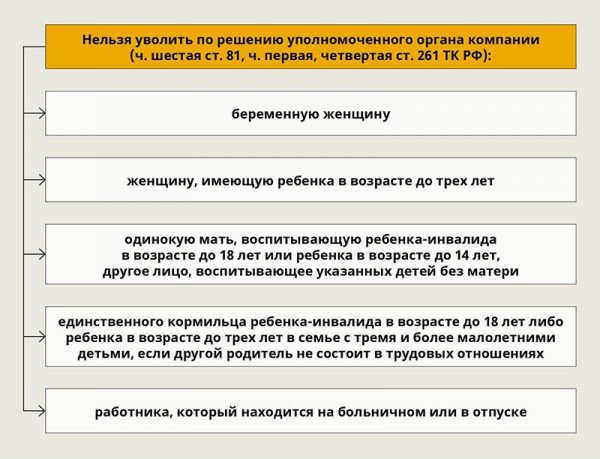
And a number of other citizens, for example, a single father.
Important! These legislative norms lose their force if the enterprise is liquidated or the employee repeatedly violates production discipline or evades fulfilling his duties.
Features of dismissal during liquidation of an enterprise
Dismissal upon liquidation of an enterprise is carried out in accordance with clause 1, part 1, art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In this case, the employee is warned about the upcoming dismissal at least two months in advance.
This is also important to know:
Certificates upon dismissal of an employee in 2021: what certificates does the employee receive?
In addition to salary and monetary compensation for unused vacation, the employer pays him severance pay - average monthly earnings, and also retains his average monthly earnings for the period until he finds a job, but this period should not exceed 2 months.
The specified period can be increased to three months, but provided that such a person contacted the employment service within two weeks after dismissal and during this time he was unable to find a job.
Such dismissal is carried out in accordance with Part 1 of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Upon dismissal due to liquidation, no additional guarantees are paid to union members and those on vacation or sick leave.
Quite often, management, not wanting to burden themselves with financial obligations, is cunning and persuades employees to leave of their own free will.
In this case, the dismissed person will not receive any compensation other than the basic calculation or the amount specified in such an agreement.
What is dismissal
Dismissal is a legal fact of termination of an employment relationship. Depending on the circumstances, dismissal may be initiated by different parties, or may occur as a result of some event. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation identifies the following main areas:
- Termination of labor cooperation on the initiative of the worker himself . Everything is simple here. An employee can pay off his job at any time and start looking for a new one. Of course, there are some nuances here, but the employer does not have the right to dismiss you.
- When the employer takes the initiative to quit . Quite often, situations arise in companies when it is necessary to reduce staff, get rid of violators, and bring the culprit to justice. The dismissal procedure in this case is clearly regulated at the legislative level. Violation of the sequence of actions, procedure and timing of dismissal may become the basis for the worker to be resumed in his previous position and the need to pay compensation for the entire period of forced absence.
- Mutual agreement . In practice, there are often situations when the parties, by their own mutual consent, stop further cooperation. For example, when an ongoing project was completed ahead of schedule.
- The severance of labor relations occurs due to reasons independent of the parties . In practice, situations may arise when it is necessary to terminate an employment relationship without anyone’s consent. For example, due to the death of a worker, conscription for military service, when an employee who was previously illegally dismissed was reinstated to his position. Here, the procedure for terminating an employment agreement is carried out upon the fact of the event.
Remember, an employment agreement provides for the obligations and responsibilities of both parties. In case of violation, each party may initiate a procedure for its early termination.
Dismissal for violating corporate rules
These include all the above-described violations of labor discipline.
However, proving that an employee actually violated corporate rules is not so easy.
For example, if a person is not at work for one day, this does not mean that he was absent.
He may appear in a few days with a sick leave certificate, but it is impossible to dismiss an employee who has temporarily lost his ability to work.
If a person is drunk, then to do this you need to force him to undergo a medical examination and receive an appropriate document that would confirm this fact.
It is even more difficult to prove professional unsuitability. For this purpose, certification of all company employees is assigned.
The employer must first comply with everything, and then prove that it was carried out in accordance with all the requirements of current legislation.
The reason for certification must be compelling, for example, a drop in product quality, a decrease in production volumes, consumer complaints about services or products.
The procedure for its implementation is established by labor legislation and other regulations, taking into account the opinion of the representative body of workers.
Dismissal in the event of a reduction in staff or if an employee is not suitable for the position held is carried out only if such an employee cannot, for various reasons, be transferred to another job, in the same organization or with the same individual entrepreneur.
The position is offered in the same location, unless a transfer to another within the same enterprise is provided for in the employment contract.
It is worth noting that the transfer is carried out with the written consent of the dismissed person.
Wrong reward system
Management can shout all they want about high bonuses, but if employees don’t see them because of a well-organized system of fines, people will quit. The eternal problem of “carrot and stick” motivation - there should be approximately equal numbers of pros and cons, or even better - a bias towards the pros. Otherwise, it’s much easier to leave and find something more loyal. In addition, you can encourage employees with uniform bonuses - stable increases, increased vacation pay, additional bonuses - all this serves as a good motivation for effective work. And it’s very bad if all this is missing.
Staff reduction
In general, the algorithm for dismissing an employee looks like this.
This type of layoff is worth paying close attention to, especially during a financial crisis when companies are laying off staff en masse.
- Firstly, the reduction order must indicate its date. The notice period for employees depends on it.
- Secondly, notice of dismissal of employees subject to layoffs is issued no later than two months before the future dismissal. Such notices are issued to each employee individually against signature. It also lists the positions that can be provided, as required by Art. 180 TC, if such work is available. It should be noted that vacancies are offered as they become available, up to the date of termination. If the employee agrees to another job, a transfer is issued.
- Thirdly, if there is a trade union organization, it is notified of the reduction 2 months before the start of dismissal of employees, including those who are not members of the PS, which corresponds to the definition of the Constitutional Court of January 15, 2008 No. 201-O-P. If we are talking about mass dismissal, then this period is increased to three months (for example, during the liquidation of an organization).
When dismissing employees due to downsizing, a preemptive right applies if there is a choice between several specialists.
The following shall not be dismissed on this basis:
- pregnant women and mothers with children under 3 years of age;
- traditionally retain more productive and highly qualified employees;
- if it is impossible to choose the best, then preference is given to: family families who support two or more dependents;
- if the employee has no other working family members;
- employees who received work injuries or an occupational disease from this employer;
- combat disabled people;
- employees who improve their skills on-the-job at the direction of the employer.
Dismissal by agreement of the parties
This type of dismissal is considered the most peaceful.
This is also important to know:
How to draw up an employment contract with a remote worker
In fact, the law allows bilateral termination of an employment contract with the consent of both parties.
The initiative can belong to both the employee and the employer.
In this case, an agreement to terminate the contract is usually drawn up, which is drawn up in any form.
Such an agreement specifies the terms of dismissal and its conditions.
Some companies follow a simplified procedure: the manager simply imposes a resolution on the employee’s statement, in which he indicates the reason - an agreement of the parties.
In general, dismissal by agreement of the parties is interesting for both the employer and the employee:
- the employee can count on compensation, that is, additional payments upon termination of the contract, the amount of which is not limited in any way. However, such payments must be recorded, otherwise the calculation will be made in accordance with the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - the amounts will be minimal;
- the employer has a guarantee that the former employee will not change his mind, as happens when dismissing at his own request: in order to cancel the agreement, the good will of both parties is required. In addition, he can fire an employee, even if he is on vacation or sick leave.
Reason for dismissal No. 8 – low employee motivation

Lack of motivation to work can cause dismissal only in the most advanced cases. However, insufficient motivation in itself is an extremely serious problem, and dismissals for this reason are a serious marker of structural shortcomings in the personnel policy of the enterprise. First of all, bonuses should be the main tool for motivating employees.
Current labor legislation allows the use of a wide variety of bonus systems for employees. However, many employers still approach the issue of assigning and paying bonuses only formally - simply writing them out to workers as an additional 13th salary or issuing them regularly. Such bonuses almost completely destroy the very motivational essence of this procedure.
At the same time, promising bonus systems should focus on specific key performance indicators for each individual employee. In this case, when the employee has clearly set goals and the understanding that their achievement will be rewarded by the employer, he is unlikely to quit due to lack of motivation. Moreover, a high-quality motivational system can even outweigh many other factors in the employee’s value system that could push him to quit.
Dismissal due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties
Here, dismissal is regulated by Art. 83 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This article is rarely used.
The grounds for such dismissal may be:
- conscription for military or alternative service;
- reinstatement of an employee who previously occupied this position based on a court decision or labor inspectorate;
- failure to be elected to office;
- conviction to punishment in accordance with a court decision;
- a person’s inability to work according to a medical report;
- death of an employer (IP) or employee, recognition of one of them as missing;
- emergency circumstances recognized by the decision of the Government of the Russian Federation, a state authority, a subject of the Russian Federation (war, natural disaster, accident, etc.);
- disqualification or administrative punishment that excludes the possibility of performing duties in accordance with the employment contract;
- expiration, suspension for two or more months, deprivation of an employee’s license, the right to drive a vehicle and other special rights;
- termination of access to state secrets, if necessary;
- excess share of foreign workers;
- changes in labor legislation.
Such dismissal sometimes requires a special procedure to be followed when another position must be offered in the same enterprise in the same area.
When dismissing an employee under this article, there is no preliminary deadline, that is, dismissal can occur on the same day.
But the employee must receive written notice of dismissal, which can be given even two hours before the event.
What to write on your resume if you were fired due to an article

If you were fired under an article - we sympathize
. Getting a job will not be easy and lying about it during an interview is useless.
The recruiter will still see the employment history and contact the previous employer.
Therefore your tactics
– clearly explain the reasons for parting with the employer, talking about this at the interview:
| think through and clearly explain what specifically led to the dismissal; find arguments in favor of mitigating guilt; try to convince the interviewer that you realized you were wrong (if you were wrong, of course) and repented of your wrongdoing, tell us what lesson you learned and how you will now behave in a similar situation. |
It’s clear that you can’t tell about this in two lines of your resume, but you have a cover letter...
If you are sincere
, you will gain the trust of the employer, even if you were fired under the article.
6
How to protect yourself from wrongful dismissal
Quite often, a fired person believes that he was deprived of his job unfairly.
According to statistics, 50% of workers face such a violation.
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Call: 8 800 511-39-66
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
One of the most difficult disputes is one that involves a statement of voluntary resignation, when the employee claims that he wrote it under pressure.
Here it is rarely possible to prove that rights were actually violated.
If an employee believes that he was fired illegally or with violations, then he can always apply to protect his rights:
- to the labor inspectorate at the place of work - complaints are considered within 30 days;
- to the court at the location of the organization - complaints are considered within 30 days as required by law, in fact this period is longer;
- to the prosecutor's office.
Non-existent "benefits"

Figuratively speaking, if an employee is sometimes “untied from the battery and given a cigarette at the company’s expense,” this is not an advantage or motivation to work better. Modern workers know what they are entitled to by right. And we are ready to demand it.
Why you can fire an employee under the Labor Code
The grounds for dismissal of an employee under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, initiated by the employer, are listed in Art. 81 of this normative act. At the same time, the list given in it is not exhaustive (special norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or special laws may provide for other grounds).
This is also important to know:
Work upon dismissal: in what cases is it necessary and in what cases can it be avoided?
Unlike the right of an employee, who can quit without giving any reason, the right of an employer to dismiss an employee is limited by law. The restriction is aimed at protecting the employee as the more vulnerable person in the relationship in question.
The grounds listed in this article, in turn, are also classified into 2 types:
- Grounds arising as a result of the employee committing illegal actions or other guilty behavior.
- Grounds that have an objective reason, in the absence of a relationship with the employee’s guilty behavior.
The grounds related to the first type are listed by the legislator in paragraphs. 5–11 st. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, among them:
- failure to fulfill duties in the absence of valid reasons, committed more than once;
- gross failure to comply with duties committed once;
- actions of the employee that caused a loss of confidence in him;
- committing an immoral act (for certain categories of workers);
- actions that caused damage to the employer (in relation to managers, their deputies and chief accountants);
- submission of false documents during the registration of labor relations.
All other grounds on which you can dismiss an employee, named in this article, belong to the second type.
Reasons why newbies don't work long
To understand why new employees quit, they look at the regulations for young people joining a little-known team.
At the right enterprise, introductory courses and trainings are carried out, mentors are assigned to monitor the actions of the new employee. There is a significant difference between an inexperienced specialist joining a team and a qualified employee who has experience in other organizations. In the latter case, the stereotypes that a person has developed often do not coincide with the routine that exists at the new enterprise. There are 3 possible scenarios:
- the experience of interacting with clients and co-workers does not contradict the norms and rules prevailing in production: adaptation is successful;
- a person is ready to change and adapt to changing conditions in order to continue working in a team;
- the newcomer takes the initiative, tries to change corporate foundations, and pushes his own line.
In the latter case, the employee should think about it, because the manager has a sufficient arsenal at his disposal to ensure the development of the enterprise and the team. The explanatory work of the HR department and the executive director helps the newcomer to comfortably join the organization and understand the specifics of the company’s activities.
The reason a new employee leaves a company is often a lack of recognition of personal success. And this is not necessarily expressed in material form - there are also free methods of encouragement.
Sometimes the unethical behavior of a manager with partners and clients pushes a principled newcomer to terminate the contract. Excessive bureaucratization of the decision-making process also affects the likelihood of dismissal of an employee with little experience.
What types of dismissal are the most profitable?
The most convenient from the point of view of material benefits is dismissal by agreement of the parties, when, roughly speaking, you can bargain with the employer for the so-called payout. Moreover, it is beneficial for both the employer and the employee.
The most advantageous from the point of view of freedom of action is dismissal at will, when there are two weeks left for maneuvers and making a final decision.
In the case where the employee is under pressure, the statement “at his own request” can be called one of the most disadvantageous, since it practically makes it impossible to challenge the dismissal.
Reason for dismissal No. 12 – divergence of principles
It is not so often now that people resign of their own free will due to ideological and fundamental disagreements with the employer. But sometimes situations arise in which dismissal for these reasons is possible. For example, when a company where a committed vegan worked begins to build a cattle farm as a side project. Or when the company expresses support for certain policies that may cause antipathy in the employee.
Such situations make up only a small fraction of the total number of independent dismissals of employees, but for many employers they are the most unpredictable. However, such a layoff can usually cause serious damage to a business only when there are a small number of employees. And in small enterprises, the employer always has the opportunity to prevent such events or at least be aware of the interests and principles of their employees.
In general, the head of the department, HR specialists or the employer himself are practically unable to influence such a situation. And such influence, even if possible, is unlikely to be justified - there is no point in sacrificing the interests of the business for the interests of one individual employee. However, if the company’s policies and actions cause massive dissatisfaction among employees, and such dismissals are not an isolated practice, you should seriously think about the chosen vectors of development.
Reasons for dismissing an employee that do not require prior sanctions
Clauses 5 and 6 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provide for the possibility of dismissing an employee if labor discipline is not observed. The difference between them is that dismissal under clause 5 is possible only if the employee already has an outstanding disciplinary sanction, and clause 6 does not require an existing punishment, but states that the offense must be gross.
The same article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides a list of gross violations of labor discipline, which make it possible to dismiss a person who has not previously had any penalties. Moreover, according to paragraph 38 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2, the presented list of violations is not subject to a broad interpretation and is exhaustive.
Reasons for dismissing an employee that do not require prior sanctions are as follows:
- absenteeism, which means absence from work for more than 4 hours;
- being at work in a state of intoxication;
- disclosure of commercial, official or other protected secrets;
- entry into force of a judicial act confirming the theft of property, embezzlement, or damage to property at work;
- non-compliance with labor safety requirements, resulting in serious consequences.
It turns out that all other violations of labor discipline cannot be grounds for dismissal if the employee has no outstanding penalties. Read about this in the article “How long does a disciplinary sanction last?”
Bad management
Moreover, we are not talking about the highest corporate echelons, which, as a rule, are excellent specialists and good leaders, but about lower levels. the work with his mere presence , even if the top people are actively pursuing a progressive and employee-friendly policy. Shitty managers who are unable to ensure normal interaction between departments and different levels of the company are also a problem. Because it’s difficult to get rid of them, and it’s almost impossible to interact productively.
Circumstances of termination of labor relations beyond the control of the parties
The grounds for dismissal under the Labor Code, related to the last, third, group, arise as a result of the actions not of the parties to the trade union, but of third parties, or as a result of events that neither the employee nor the employer can influence. Their list is presented in Art. 83 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Important points to pay attention to:
- When conscripted into service (military or alternative civilian), dismissal is made upon presentation of a summons and an order (clause 2 of article 14 of the law “On alternative civil service” dated July 25, 2002 No. 113-FZ, clauses 6, 7 of the regulation “On conscription for military service”, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 11, 2006 No. 663).
- Dismissal upon reinstatement of a previously employed citizen is carried out only on the basis of a decision of the State Labor Inspectorate or a judicial act.
- An employee can be recognized as incapable of work only on the basis of an ITU conclusion.
- Termination of TD in connection with an emergency circumstance is possible only when this circumstance is recognized as such by a decision of the Government of the Russian Federation or an authorized government agency of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation.







