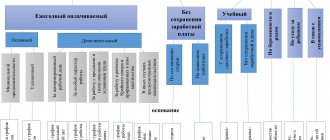
- Application of disciplinary action
- Time limits for imposing disciplinary sanctions
- Types of disciplinary measures
- Are not punitive measures
- Choosing a disciplinary measure
Documenting:
- Registration of the fact of disciplinary offense
- Request for a written explanation
- Conducting an inspection of violations
- Issuance of an order
- Announcement of the order
Disciplinary liability for an employee for misconduct occurs in the form of a disciplinary sanction, which is applied to the employee by the employer. A disciplinary offense is understood as an unlawful, culpable failure or improper performance by an employee of his labor duties (i.e., the employee violated or did not fulfill his labor duty, which is written down somewhere, and this is also the employee’s fault).
Rules for applying disciplinary sanctions
- before punishing an employee by applying a disciplinary sanction to him, the employer must at least request a written explanation from the employee himself regarding the case in question (the ideal situation is when the employee confesses in writing to what he did and admits his guilt);
- the rule “1 disciplinary offense = 1 disciplinary sanction.” Only one disciplinary sanction can be applied for one disciplinary offense (several disciplinary sanctions cannot be applied for the same thing);
- a disciplinary sanction is always formalized in writing (most often in the form of an order, less common options are in the form of an order or resolution);
- An order (or order or resolution) on disciplinary action indicating the reasons must be announced to the employee against signature within 5 days (during this period we may not count the time the employee is ill, as well as the employee being on vacation). An employee who is not familiar with the order (instruction or resolution) on a disciplinary sanction is considered to have no disciplinary sanction (the employee was not familiarized with the order - consider “there is no order”).
Return to contents
Time limits for imposing disciplinary sanctions
- A disciplinary sanction must be applied no later than 1 month from the date of discovery of the disciplinary offense (not counting the time the employee was ill and (or) on vacation). Moreover, the day of discovery of a disciplinary offense is considered the day when the offense became known to the person to whom the employee is directly subordinate (i.e., the period of 1 month for applying a disciplinary sanction is not tied specifically to the day the employee committed the disciplinary offense, because the offense may not be detected immediately) .
Exception: if materials about a disciplinary offense were considered by law enforcement agencies, a disciplinary sanction is applied no later than 1 month from the date of refusal to initiate or terminate the criminal case.
- A disciplinary sanction cannot be applied later than 6 months from the date of commission of the offense.
Exception: based on the results of an audit or inspection conducted by competent government bodies or organizations - later than 2 years from the date of the disciplinary offense. The specified time limits do not include the time of criminal proceedings.
Return to contents
Types of disciplinary measures
The list of disciplinary measures that an employer can apply to its employees is closed and clearly provided for by law:
- remark;
- reprimand;
— deprivation, in whole or in part, of additional incentive payments for a period of up to 12 months;
— dismissal (for example, for being intoxicated at the workplace and violating labor safety rules, resulting in death or serious injury to others by the employee).
The measures are listed in order of increasing severity (i.e. reprimand is the most harmless, dismissal is the last resort).
The employer cannot apply any additional measures (other than those provided for by law).
Exception: for certain categories of employees with a special nature of work, the legislation provides for other disciplinary measures (for example, for civil servants the following may be additionally applied: a warning about incomplete official compliance; demotion in the class of a civil servant for up to 6 months).
Return to contents
When can you not be fired for absenteeism?
It is impossible to fire a pregnant woman, even if she often does not consider it necessary to come to work. She may be subject to other disciplinary measures.
It cannot be recognized as absence from work without a valid reason if the employee refused to leave the vacation early. A day of rest after donating blood or its components is not considered absenteeism, even if the employer refused to provide it.
Are not disciplinary measures
In practice, the employer may additionally apply to employees who have committed a disciplinary offense:
- deprivation of bonuses;
— change in the time of granting labor leave
- and other measures.
The types and procedure for applying such measures may be determined by internal labor regulations, collective agreements, agreements, and other local regulatory legal acts.
BUT!
All of the above are essentially additional measures of influence on the employee, but not disciplinary measures.
Deprivation of a bonus or reduction in the duration of labor leave to that established by law (possibly in the case where the employer provides the employee with leave of a duration exceeding that established by law) are not disciplinary measures because in this case the employer, for educational purposes, deprives his employee of the “goodies” that he the employee himself and provided in excess of the level established by law.
Example: the minimum vacation per year is 24 days. The employer set the employee's vacation to 28 days. But for absenteeism committed by an employee, the employer has the right to reduce the employee’s vacation by the number of days of absenteeism (but the vacation cannot be less than 24 days).
Return to contents
Reprimand as a disciplinary sanction
When hiring a new employee, the employer discusses with him the specifics of his job functions, introduces him to the job description against his signature, and conducts safety training at the enterprise. If the established rules are strictly followed, a person should not have problems in his work. But, nevertheless, there are often situations when a worker violates these requirements, and his actions do not have the best effect on the work of the entire enterprise.
In this case, the employer is obliged to respond to the current circumstances, and sometimes it is necessary to punish the offender.
The main types of disciplinary sanctions that an employer can apply to an employee are specified in Art. 192 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. One of them is reprimand. An employee can receive a reprimand for various offenses. But the most common reasons for issuing it are:
- improper performance of labor duties;
- violation of labor discipline;
- neglect of safety precautions, etc.
We will discuss below how an employer should act if he has chosen this measure of influence on a worker.
Choosing a disciplinary measure
The choice of disciplinary action, as well as the answer to the question “to punish or forgive” lies entirely with the employer.
However, when choosing a measure, the severity of the disciplinary offense, the circumstances in which it was committed, previous work and the employee’s behavior at work must be taken into account. In general, “the severity of the offense must correspond to the severity of the punishment.”
But in practice, employers often forget (unintentionally or intentionally) about the need to take into account all the circumstances when choosing a disciplinary measure. But this should not be done, if only because in the event of an unfair punishment, the employee can always go to court to “seek the truth,” and there the court will evaluate all the circumstances that the employer “forgot” about.
So, for example, often when considering claims for the reinstatement of persons whose employment contract was terminated, say, for violation of labor discipline, the court finds that although a disciplinary offense actually took place, the dismissal was made without taking into account the degree of guilt of the workers, the gravity misconduct, the circumstances under which they were committed, as well as the previous behavior of employees and their attitude towards work. In this case, the court satisfies the claim filed by the dismissed employee, while canceling the disciplinary sanction previously imposed on the employee in the form of dismissal.
Again, like a ladder, it is not necessary to apply disciplinary measures to an employee sequentially according to severity (first a reprimand, then a reprimand, then dismissal). As they say, you can immediately fire an employee if he “deserves it” and this is permitted by law.
But the employer may decide not to bring the employee to disciplinary action at all. But there is one “but” (or rather, there are two of them) when this cannot be done (even if the employer does not want to punish the employee):
- appearing at work in a state of alcohol, drug or toxic intoxication, as well as drinking alcoholic beverages, using narcotic drugs, psychotropic substances, their analogues, toxic substances during working hours or at the place of work;
- violation of labor safety requirements resulting in injury or death of other workers.
For these offenses, the employer is obliged to ensure that the employee who committed the offense is unconditionally brought to disciplinary liability, up to and including dismissal. If a decision is made to dismiss on these grounds, then it must be documented in the manner prescribed by the instructions on dismissal for a system of violations, even though the employee has not previously been subject to disciplinary liability.
Now about specific disciplinary measures. There is no significant difference between a reprimand and a reprimand (the consequences for the employee are the same). Formally, a reprimand is worse than a reprimand.
Return to contents
Sample reprimand for violation of labor discipline
Order of disciplinary action
In order to issue an order for disciplinary action, the manager must first receive written explanations from the employee and consider them.
The outcome of the consideration is reflected in a report or resolution superimposed on the explanatory note. The employee may refuse to provide a written explanation. In this case, the manager draws up a corresponding act.
If the violation of discipline is complex, an internal investigation is carried out by a special commission to objectively assess the severity of the violation and the consequences. It should be carried out, first of all, in case of accidents, the cause of which was precisely a violation of labor discipline.
The investigation report must record the circumstances under which the violation was committed and preliminary conclusions about the severity of the violation. Options for punishing the violator (type of penalty) are also discussed here. In some cases, an independent examination also takes place. If there are serious reasons, the manager may transfer the results of the examination to law enforcement agencies.
The order to impose a disciplinary sanction is drawn up by the head of the enterprise, based on the explanations of the offender. The manager can also hold department heads and deputies accountable, but to do this, the application of the employees' representative body must be considered.
Sample
To order, you will need a general company form. According to the law, there is no unified form for this document. On the same form, you can draw up orders for incentives, penalties or their withdrawal. The sample document must contain information about the type of violation, the time when the offense was committed, the documents on the basis of which the order is issued, and the type of penalty.
The document on punishment is signed by the manager, then announced to the employee personally, and the employee, in turn, puts his signature. In addition to one original copy of the order, there must be 2 more copies. One must be filed in a personal file, and the other must be handed over to the employee who committed the offense.
As a rule, a note about the penalty is not made in the work book. This happens only with rare exceptions, when the type of punishment is dismissal.
For one offense, only one penalty can be imposed on an employee, and it is valid for a month.
An enterprise employee is responsible for any violation, be it internal rules or management orders. For all violations he may be subject to disciplinary action. If an employee does not fulfill job descriptions or other obligations for reasons beyond his control, he should not be held responsible. In this case, he is considered innocent.
In the Labor Code you can learn about all types of penalties. As a rule, there are three of them: reprimand, reprimand, dismissal. Sometimes the manager specifies other types of penalties in internal regulations.
Download
Sample order for disciplinary action: prikaz-o-disciplinarnom-vzyskanii.doc [30.53 Kb]
Act on the employee’s refusal to sign familiarization with the order: akt-ob-otkaze-ot-podpisi.doc [53.86 Kb]
Order to reprimand an employee
An employee who, in the course of work, performed his duties improperly or committed a disciplinary violation is subject to a sanction - a reprimand. This type of impact on employees is documented in writing.
When starting a job, each employee must undergo a procedure of becoming familiar with their job responsibilities, which are reflected in the instructions. Violation of labor activity, internal regulations, as well as other norms and working conditions, entails the application of disciplinary sanctions by the administration of the enterprise. A reprimand to an employee is one of the punishment options. All grounds for its issuance are indicated in the employment (collective) agreement, job descriptions, and other approved work rules that comply with legal norms.
Sample of filling out an order to reprimand an employee
An employee who has committed an offense is obliged to provide an explanation of the circumstances under which it occurred. The explanatory note sets out in detail the essence of the violation or improper performance of official duties, as well as the reasons why the incident occurred. The administration of the enterprise reviews the application submitted by the employee, and the manager makes a decision on the disciplinary measure, since only he has these powers. The document is drawn up in writing, indicating the reasons for the reprimand, the date, place and time of its issuance.
Information about single disciplinary sanctions is not entered into the work record book. If an employee committed several violations for which reprimands were issued followed by dismissal, then the data of the order listing disciplinary sanctions are entered into the work record book.
An employee is reprimanded only in cases where a violation of work process or discipline was committed directly through his fault. An employee has the right to challenge a reprimand if there is every reason to assert that the misconduct was related to independent external factors.
These include force majeure circumstances arising in connection with accidents, natural disasters, fires, government decrees, as well as other events that the employee had no opportunity to influence. When drawing up an explanatory note and justifying the factors that led to the violation, it is necessary to submit supporting documents (acts of the fire department, road transport services, certificates from housing and communal services, etc.), which must be attached to the application within 30 calendar days.
In some cases, the head of an enterprise can cancel a disciplinary sanction in force against an employee of the enterprise, with reasoned arguments in favor of his innocence. To do this, an order is issued that cancels the reprimand.
Download the order form to reprimand an employee (Size: 32.0 KiB | Downloads: 3,852)
Is the form or article out of date? Please click!
Violations of labor discipline - we punish the employee
Labor legislation provides for the creation of each organization's own rules of procedure. It is this document that employees are guided by, because it describes all labor issues and issues that arise at the enterprise: the start and end times of the working day, the procedure for calculating wages and even the specifics of trade secrets.
Even a slight delay or leaving the workplace for 5 minutes can be considered a violation of labor discipline. Such seemingly harmless offenses can result in heavy penalties. Therefore, it is very important to learn to identify those actions that are violations, as well as assess the possible punishment for them.
Violation of labor discipline - definition and types
First you need to understand the basic concepts. Labor discipline is a set of rules that apply to an enterprise and are mandatory for all its employees. These include work rules, corporate ethics, labor protection rules, etc. The employer himself, in addition to creating these rules, must ensure the possibility of their implementation, because if he does not do this, then any violation by the employee of any rule will be recognized as the fault of his superiors.
To understand why various penalties can be applied to employees, you need to clearly understand those actions that constitute a violation of discipline and what it is.
Responsibilities of the employee
The Labor Code defines a number of responsibilities that are inherent to an employee, namely:
- Compliance with all fixed rules and labor standards.
- High-quality and conscientious performance of official duties.
- Compliance with work rules, labor protection and various regulations and requirements that are present in the workplace.
- Take care of the material property that the enterprise has.
- Notify your management if any hazards arise that could harm other employees.
It is believed that if an employee has violated at least one of these points, he has violated labor discipline.
Types of labor discipline violations
There are three groups of violations that an employee can commit, depending on the characteristics of the work process itself:
- a) technological, which combine all violations of various technological standards
- b) violations of coordination of the management process and subordination, if management procedures in the organization are violated
- c) regime violations (rest and work time).
- visiting the workplace under the influence of alcohol, drugs or any other intoxication
- misconduct that is related to labor protection and led to any accident
- lateness (to the start of work or even to the end of the lunch break), as well as absenteeism
- leaving a certain workplace too early (during work or at the end of the day)
- work in an incomplete volume, which is fixed in advance
- embezzlement, theft or damage to property that belongs to the employer
- disclosure of any trade secrets
- refusing a medical examination or training required for the job
- illegal acts
- violation of subordination and management orders
- special failure to comply with the requirements that are written in orders and instructions
- active participation in activities that may reduce the authority of management.
- a) by time and deadlines
- b) at the place of execution
- c) by volume
- d) according to the method of execution
- d) according to form
- e) by performer.
- a) remark
- b) reprimand
- c) dismissal.
- Application for student leave sample for work
- Sample act of acceptance of transfer of material assets to an employee
So, if an employee contributes to the damage of products, then he will commit a technological offense, and if he is late for the workplace, then he will commit a security offense.
Each violation entails the collection of supporting documents and an investigation.
List of labor discipline violations
Among the most common offenses that are associated with violation of labor discipline are:
From this entire list, gross violations include constant absenteeism, forgery of documents, theft, attending work while drunk, or committing some illegal act.
All types of failure to fulfill their work duties are divided according to the following criteria:
Disciplinary offenses are acts of violation of discipline during the performance of official duties.
Also, every employer must be able to distinguish between misconduct and financial liability, because if an employee has caused some kind of material damage, then the liability for this may continue after the end of the employment relationship.
Penalties for violations of labor discipline
Article 192 of the Labor Code defines several penalties that apply to employees in the Russian Federation:
If one of the local documents indicates the possibility of depriving a bonus for misconduct, then the employer can take advantage of it.
In the event that there are Federal laws describing special methods of punishment, then they can also be applied.
Reprimand for violation of labor discipline
In case of violation of discipline, a report is created about this with a detailed description of the offense, the chosen punishment and the explanation of the employee himself. Although the remark does not cause much harm, it can stop the employee from systematic violations that are caused by repetition of misconduct.
Reprimand for violation of labor discipline
The reprimand that is issued when a disciplinary offense is committed is of two types: ordinary and strict. It must be written down in the order, but is not indicated in the work book. It can only note the dismissal, which was due to constant violations and failure to perform one’s work.
Dismissal for violation of labor discipline
It is believed that dismissal is the last resort of all possible penalties. It is assigned if a person has committed a very serious violation or stopped working. So, in banking institutions, for example, they can safely fire you if an employee has committed theft of property.
Responsibility for violation of labor discipline
Labor legislation states that all employees are responsible for their actions and are required to familiarize themselves with the labor protection rules, procedures and other requirements upon signature. The employer retains the right to impose penalties if the employee violates something. At the same time, they are compared with the complexity of the offense.
The procedure for punishment for a disciplinary offense
The authorities independently choose the punishment, which should be based on existing information and legislative norms.
Act on committing a disciplinary offense
Each violation must be recorded using an act. This paper is created by the employee’s superiors together with witnesses. Then the document, after signing, is sent to the employee, and a second copy is sent to higher management so that they can take any action. Those people who will be responsible for drawing up this act must be indicated in advance in local documents.
Employee's explanations
The employee must provide an explanation of what happened. It is advisable to require it in writing to protect yourself from unnecessary problems. Sometimes an act can be created, but only if the person refuses to explain any nuances. At the same time, it is worth knowing that such a reluctance to comment on the situation cannot exempt you from punishment, so it is advisable to still issue a note within 2 days.
The act of misconduct, the report and explanatory note of the employee himself are sent to senior management, who already determine the specifics of imposing a penalty in a given situation.
Order to impose a penalty
Management must analyze all the information and papers present in order to subsequently issue an order stating the employee’s misconduct.
Although there is no fixed example of such a document (ready-made forms exist for creating dismissal orders), the act describes the violation itself, the time it was committed and the punishment that was chosen. The documents that regulate all this are also indicated. The completed order must be endorsed by the employer, the violator’s immediate superior and the head of the human resources department.
The order is not noted in any way in the work book unless it led to dismissal, although a copy of it can be filed in the employee’s personal file after the violator has familiarized himself with it. No more than three days are given for this. It is very important to compare the size of the penalty and the complexity of the offense, and also to impose it reasonably so that the person cannot challenge it in any way.
Order to lift a disciplinary sanction
If the authorities decide to cancel the punishment, they can do this within a year after the offense occurred. To do this, you need to draw up a new order, where you must describe the reasons that prompted you to remove the penalty. After its publication, the employee must familiarize himself with the document in the general manner (as after a violation).
The punishment can be canceled on its own (as if it never happened) if no further violations were committed by the employee during the calendar year.
Time limits for imposing penalties
Any punishment can only be used within a month after the punishment. If more than six months have passed, then the employer is no longer able to influence his employee. In the event that the offense was discovered only after the next audit, the possible sentence is increased to 2 years.
It should be understood that a fine cannot be applied in case of violation of labor discipline at the enterprise, but deprivation of incentives (for example, bonuses) can be used by decision of management. If an employer punishes his employee more than once for the same offense, this will be a violation of current legislation.
Examples of violations of labor discipline
Among all the misconduct, the most popular is absenteeism, which consists of the absence from work of an employee who did not warn his management in any way and did not provide a normal and confirmed reason. If some kind of emergency situation occurs (fire, attack, accident), then the possibility is considered that the person did not have the opportunity to explain something. Based on this, for the sake of their own safety, employers are not advised to immediately punish an employee in any way, because if his reason was valid, then he can calmly complain to his management in court with a request to restore justice.
Order of reprimand
Class365 - fast and convenient filling out all primary documents
Connect to Class365. 0 rub/month!
Failure to perform or improper performance of job duties by an employee may lead to disciplinary action, i.e. to a reprimand.
How to simplify your work with documents and keep records easily and effortlessly more>>
See how Class365 works
Login to demo version
How is a reprimand order drawn up?
Although a reprimand is not entered into the employee’s work book, if the violation of labor discipline was systematic and the employee was fired for this, the order of reprimand is mentioned in this dismissal order in the same way as all other cases of violation of labor discipline.
A prerequisite for hiring an employee is to familiarize him with the rules of discipline in the work team, with his responsibilities and with what will be the basis for reprimanding the employee. All this happens when he signs an employment contract.
If all these conditions were not met when the reprimand was issued, the employee has every right to challenge this penalty. You can also challenge a reprimand if the violation of labor discipline or official duties occurred not through the fault of the employee, but due to some circumstances that prevented him from fulfilling his official duty.
For example, a person who was involved in an accident urgently needed medical assistance, and an employee drove him to the hospital, but was late for work. Or the employee himself got into an accident or a serious traffic jam. In order to challenge the order of reprimand, certificates from the traffic police and medical institutions, which will be attached to the explanatory note written by the employee, will be sufficient. In the event of a fire, a certificate is issued by the fire department. In case of other extreme situations - the Ministry of Emergency Situations. If, let’s say, some serious accident occurred at home (for example, a water pipe burst or there were problems with the sewer system), the housing office issues a certificate.
30 working days is the deadline for providing these documents. Moreover, it is better - by mail, with subsequent registration. To ensure that documents confirming the employee’s innocence are not lost if they are handed over personally to the head of the enterprise, they must first be passed through the office or personnel department.
So, if the order of reprimand has been challenged, an order to cancel the penalty is drawn up.
Get started with the Class365 program today!
Order to impose a disciplinary sanction on an employee
An order for disciplinary action is prepared on the basis of the employee’s written explanations, reviewed by the head of the relevant structural unit. The results of the review may be reflected in a memorandum or resolution on the employee’s explanatory note.
reprimand order
employee
If the violator of labor discipline refuses to provide written explanations, a corresponding act is drawn up.
In the most difficult cases, to objectively assess the severity of the disciplinary offense, as well as its consequences, the head of the enterprise may order an internal investigation. Such an investigation, in particular, should be carried out in case of accidents resulting from the indiscipline of an employee. As a rule, the investigation is carried out by a specially appointed commission.
The results of the investigation are recorded in the report. Such an act usually not only sets out the circumstances of the disciplinary offense committed by the employee, but also makes preliminary conclusions about its severity, and also makes proposals for applying adequate penalties (disciplinary sanctions) to the violator.
The head of the enterprise makes a decision to apply disciplinary punishment against the employee based on the content of his explanations (act of investigation of the misconduct). The decision to bring heads of structural divisions and their deputies to disciplinary liability can be made by the head of the enterprise based on the results of consideration of a written application from the representative body of employees.
reprimanding
In necessary cases, an independent examination may be additionally carried out to objectively assess the severity of the offense committed and its consequences. If there are appropriate grounds, the head of the enterprise has the right to transfer the materials of the investigation (examination) to the competent authorities to initiate a criminal case against the violator of labor discipline.
An order for a disciplinary sanction is drawn up on the general form of the organization, since a unified form is not provided for by law (an order of encouragement and an order of removal of a penalty can also be drawn up on the appropriate form of the organization, if necessary). The order of punishment signed by the head of the enterprise is announced to the employee against signature. Information about penalties is not entered into the work book (except for the case in which the penalty is the dismissal of an employee).
Sources: forms-blanks.ru, mirblankov.ru, ipgid.ru, class365.ru, blankiroom.ru