Arranging for a business trip begins with preparing the assignment and determining the deadline. After checking the possibility of sending an employee, an order is issued, an estimate is drawn up, and an advance is issued for the report. The entire period of absence from the work place of the traveler is noted in the report card in a special way. After the return, the advance report is approved and recalculation is performed.
What has changed in travel arrangements?
Changes in legislation regarding the preparation of documents when sending specialists affected the completion of:
- travel certificate;
- travel log;
- official assignment;
- trip report.
Now the requirements to fill them out have been canceled. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Regulations on Business Travel do not say anything about these documents, which were previously considered mandatory.
However, if the head of the company considers it necessary to maintain such documentation and introduces such a rule into the internal regulations on business trips, then the following must be prepared:
- travel certificate;
- official assignment;
- business trip registration log (a record is made about the traveler).
After returning, the employee submits a trip report.
The following must be completed:
- order to go on a business trip;
- advance travel report.
The order is issued by the manager, the document is signed by an official authorized to send employees on a business trip. And the traveler prepares an advance report after his return. An important point: if the duration of the trip changes, an additional order is issued to extend the duration of the trip or cancel it.
There is no longer any need to obtain a travel permit
The employee is familiarized with orders to be sent on a business trip, to extend its duration, or to be recalled from a business trip against signature. Before issuing the order, the employee is notified of the change in the duration of the assignment.
Travel expenses in 2021 per diem in Russia
During a business trip, an employee has the right to expect not only that his work will be paid, but that all expenses will be reimbursed, as stated in Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. We are talking about the cost of travel, daily allowances, housing, and so on.
A collective agreement is drawn up in advance, in which all of the above is stated.
As a rule, few managers include expenses such as a bar or restaurant, hotel services, such as a swimming pool, solarium, fitness club, services of other organizations, and everything in a similar spirit in their travel allowances.
As for daily allowances, there is no need to indicate them anywhere, since all this is negotiated between the boss and the posted employee.
Stage 1: preparing for the trip
Preparation for going on a business trip begins with checking the possibility of entrusting such a task to a specific official. There is a whole list of prohibitions and restrictions. In particular, it is prohibited to send employees under 18 years of age and pregnant women on business trips. Even if they agree, there is no way to send them on business.
Further, there are categories of employees who can be sent, but it is necessary to obtain from them written confirmation of consent to the secondment. Here is the list:
- women with children under 3 years of age;
- women with medical travel restrictions;
- a parent raising a child under 5 years of age alone (this also applies to guardians);
- parents raising a disabled child;
- an employee caring for a sick family member;
- foreign employee;
- highly qualified specialist;
- an employee with a disability;
- an employee working under an apprenticeship contract (for the duration of the agreement, unless the trip is related to the apprenticeship).
Consequently, the secondment of a specialist from the specified list begins with a request for his consent to be sent. When addressing a question about a trip, it is necessary to notify the sender of his right to refuse a business trip (Part 2 of Article 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It is prohibited to forcibly send the listed persons, as this entails administrative liability.
Video: how to send an employee on a business trip
Duration of the trip
The duration of a business trip consists of the time required to travel to the destination and back, and the duration of the work assignment. The duration of execution of orders is determined based on the assigned tasks, and travel time is calculated using travel documents. Most often, the duration of the trip is fixed according to the departure and arrival dates indicated on the tickets.
If there are no tickets, then a confirmation document may be a hotel stamp, as well as a rental agreement.
If the employee traveled by his own transport, then the period is determined by the memo, which he draws up after returning. All documents confirming the trip are attached to it. In this case, it is important that the travel period is no longer than the period specified in the business trip order.
Regulations on the specifics of sending employees on business trips
Regulation No. 749 on business trips was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 749 of October 13, 2008, it addresses the main issues governing the sending of employees on business trips. Thus, the regulation determines that the employee’s place of work is considered to be the location of the company where he works, and if the employee is sent to a separate division of the company, which is located in a place other than the location of the company, this trip is considered a business trip. But if the work of a company employee is of a traveling nature, then the business trip is not recognized as a business trip.
The duration of the business trip is determined by the employer, guided by the volume and complexity of the work to be done by the employee. The period when the employee is actually on a business trip is determined by the tickets that the employee provides upon return. Thus, the day of departure on a business trip is considered the day of departure of the vehicle (train, plane, etc.) that the employee travels to the destination, and the day of the employee’s return is determined in the same way.
Stage 2: preparation of travel documents
After determining the candidacy for dispatch and calculating the duration of the trip, an internal order is issued in writing - an order or instruction on sending on a business trip.
The order can be issued arbitrarily; it is important that the text makes it clear who the head of the organization is, who exactly is being sent, where and for how long. To issue an order, the unified form No. T-9 can also be used (if several employees are sent on business, form No. T-9a).
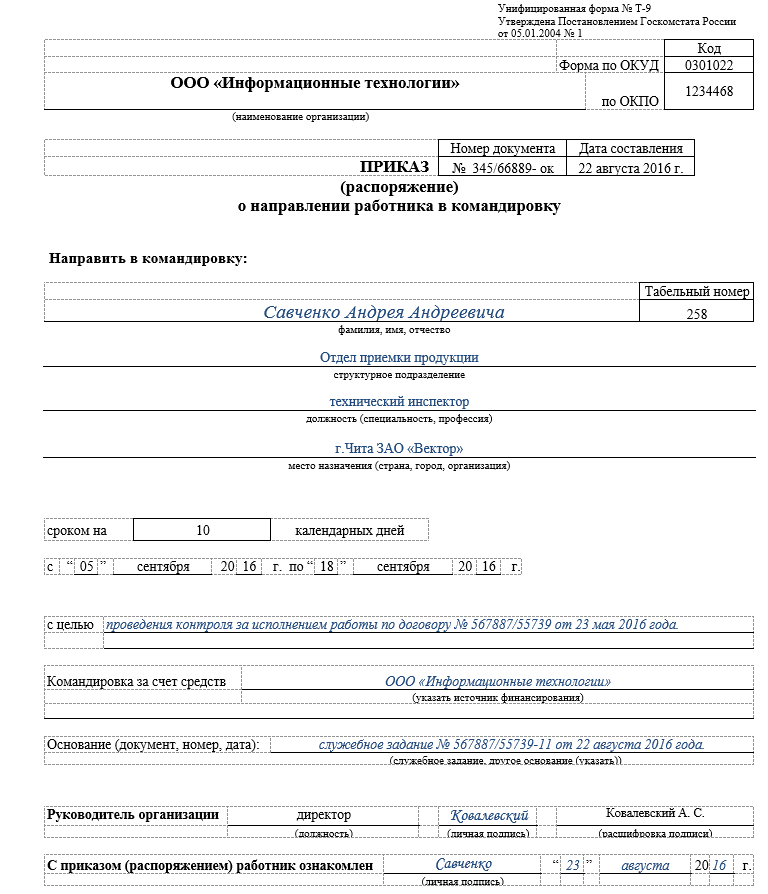
The text of the order specifies the duration of the business trip.
The purpose and objectives of the trip can be stated in the text. The person who has the authority to send employees on a business trip has the right to sign the order. It is also necessary for the traveler to familiarize himself with the order against signature - it is very useful, especially if the employee has low executive discipline.
If the internal company travel regulations require the execution of an official assignment, then it can be filled out in free form or according to the unified form No. T-10a. The job assignment specifies:
- last name, first name, patronymic of the seconded employee;
- place and duration of the trip;
- the purpose and tasks to be completed;
- contents of the report based on its results.
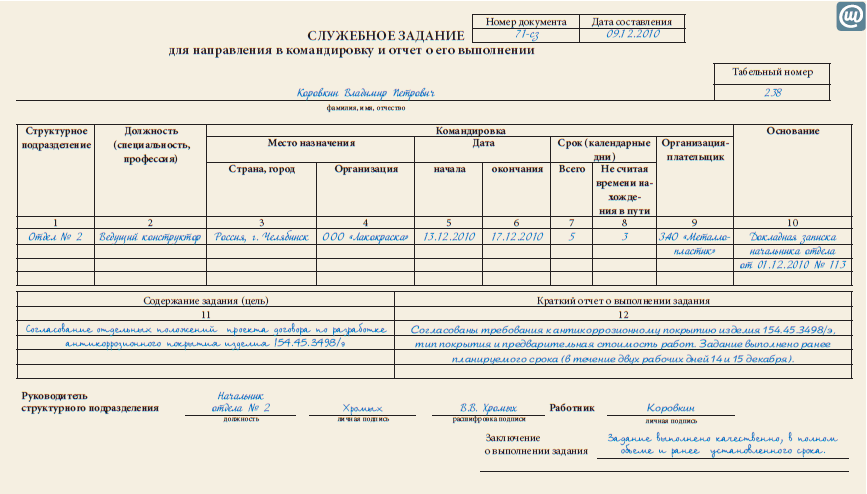
The assignment indicates the purpose and objectives of the business trip
The travel certificate is issued in form No. T-10, the following entries are made in it:
- about an employee sent on a business trip;
- about the duration of the business trip;
- about the place and purpose of the trip.
Notes are also made here about arrival and departure to destinations.
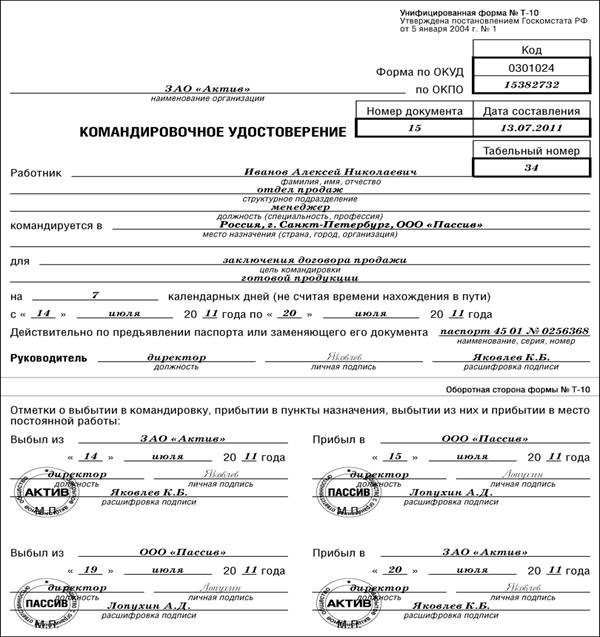
The certificate contains marks indicating arrival (departure) at the destination
The final stage is to prepare an estimate for the trip, this paper is signed by the chief accountant and manager. A cash order is issued using it and the amount required to purchase a ticket, pay for housing and stay during the entire trip is issued in advance. An advance is issued before the trip; failure to issue money before departure is considered a violation of the law.
On the day of departure, an entry is made in the business trip log about the employee being sent. The date of departure and arrival are counted towards the duration of the business trip, so presence at the workplace on these days is determined by the decision of management.
During all days of a business trip, a mark (K) or a digital code (06) is entered in the work time sheet in form No. T-13; the hours worked are not entered. The time sheet for the posted employee is filled out on the basis of the travel order. Non-working days and holidays falling on business trip dates are marked with the code РВ (or 03). This is necessary when calculating wages on weekends and holidays.

Working days of the traveler are marked with code (K), weekends and holidays (RV)
Registration of a business trip in 2021: documents
The basis for sending an employee on a business trip is the order of the manager in the T-9 form. The form of this form is unified and approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee No. 1 of 01/05/04. (OKUD form 0301022). However, the law does not prohibit the use of your own form of this document if it is approved by the organization. Due to the fact that currently the accountant does not draw up the large package of documents for the posted employee that was previously required (travel certificates and official assignments were canceled by Government Decree No. 1595 of December 29, 2014), drawing up an order is essential for the company’s document flow.
When answering the question of how to arrange a business trip for an employee in 2017, it is important to consider that the manager’s order is not the only document the preparation of which is a mandatory requirement when arranging a business trip.
How to arrange a business trip and justify the expenses incurred to the tax authorities? The need to confirm business trip expenses is determined by tax law, in particular Articles 252, 264, 313, 314 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If, at the stage of sending an employee on a business trip, the employer undertakes to formalize his order in the form of an order, then the employee, upon returning to his employer, must report on the expenses incurred through a completed advance report.
The form of this document AO-1 is also unified - approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee No. 55 of 01.08.01. (OKUD code 0302001). An organization has the right to use a document of a different format in its activities if it contains all the information required for disclosure.
Based on the advance report submitted to the accounting department, the company has the opportunity to justify the expenses incurred before the inspection. The Government Decree defines specific deadlines within which the employee must submit to the organization an advance report and the originals of all supporting documents (cheques, tickets, receipts). So, in accordance with Government Decree No. 749 of October 13, 2008. The employee must submit an advance report within 3 working days after returning from a business trip.
The report must be compiled in one copy, which is intended for accounting employees. In addition, original documents confirming all expenses incurred during the business trip, except for daily allowances (which employees can spend at their own discretion), are attached to it.
The advance report submitted to the accounting department is subject to verification by a specialist and subsequent transmission to the head of the organization for signature. After this, the employee either returns the unspent funds to the cash desk or applies for a refund.
Stage 3: extension of the secondment period
The procedure for extending a business trip is as follows:
- the employee is notified of the extension of the business trip;
- issue an order;
- calculate daily allowances;
- pay the employee the amount necessary for the additional period.
It is necessary to obtain written consent from those employees who are sent on business trips with their written consent.

The employee is notified of the extension of the business trip by any available means.
Who can be sent on a business trip
It would seem that the employer has the right to send any of his officially employed employees on a business trip. In reality, he can only send those workers who are regularly in the same place, office, city, and so on. If we are talking about a courier or driver, the employer does not have the right to send such employees on business.
According to Article 310 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employer can send a freelancer on a business trip, that is, a person working officially outside the office, at home. A freelancer is sent on a business trip on general terms and conditions.
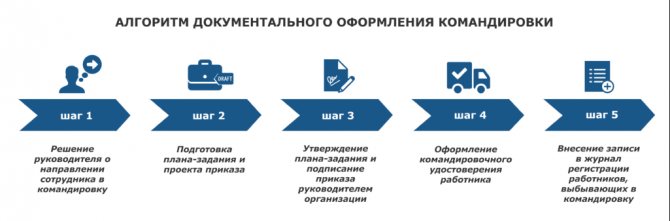
Step 4: Reimbursement
Within three days after returning, the employee submits an advance travel report. This document can be prepared in free form or use the unified form No. OA-1. It should be accompanied by all documents confirming expenses - checks, payment receipts, tickets.
Since the employer compensates for travel to the place of business trip, payment for housing and accommodation, documents confirming payment for these services must be attached to the report.
It is possible that the company also accepts compensation for additional expenses - for purchasing travel documents, obtaining a foreign passport, obtaining a visa, paying for communication services. It is useful to inquire about the possibility of compensation for these expenses before the trip, and if this is permissible, obtain permission from your superiors.
If, according to supporting documents, it turns out that an amount greater than the advance payment was spent, the company will issue the unpaid money. If, on the contrary, more was given in advance than was spent, then the employee must hand over the unused funds to the cashier.

The employee reports on the results of the business trip in free form
Business trip in your own car
If an employee goes on a business trip using personal transport, an additional agreement is concluded with him, which fixes the amount of compensation for the use of the car, the amount of depreciation and other expenses reimbursed by the company. At the same time, the procedure for compensating expenses when traveling on a business trip using personal transport is indicated. Since the manager’s decision on such a business trip must be written, this point can be indicated in the order.
At the end of the trip, a memo is submitted in which the duration of the trip should be indicated. This reporting document is accompanied by a route sheet (waybill), cash receipts, invoices, and receipts confirming the route of the vehicle. Also, the duration of the trip can be determined by documents from the hotel or rental agreement.
Foreign business trip
Registration of a foreign business trip occurs in the same way as a domestic Russian one, with the only addition that the money is paid in foreign currency. Here it is important to correctly determine how many days are paid in foreign currency and how many in rubles. Time spent on the territory of a foreign state and travel outside Russia is paid in foreign currency, travel through Russian territory is paid in rubles. The date of crossing the state border is paid in different ways: the day of departure from Russia - in foreign currency, the day of entry into our country - in rubles. Travel allowances can be issued through a cash desk or credited to a bank card.
Registration of a business trip: changes in labor legislation
In 2021, the main transformations in terms of accounting for accountable funds affected budgetary institutions. In connection with the adoption of amendments to the instruction on budget classification, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 1, 2013 No. 65n, some KOSGU codes have changed, as a result of which the analytical accounts for accounting for accountable amounts have also changed.
For the procedure for accounting for accountable amounts in budgetary institutions, see the article “Settlements with accountable persons in budgetary institutions.”
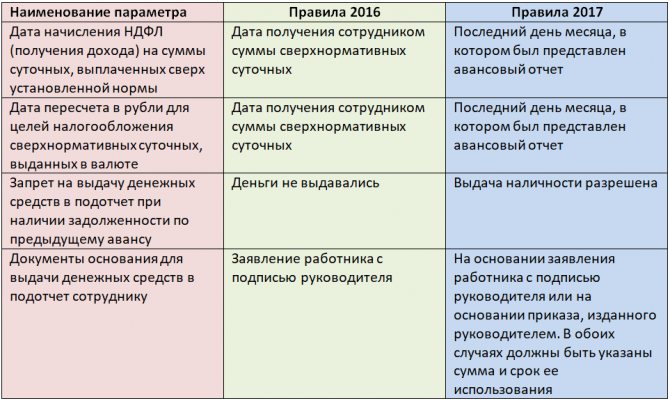
Also in 2021, amendments were made to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Now the date for personal income tax assessment of excess daily allowance paid is the last day of the month in which the employee submitted an advance report (subclause 6, clause 1, article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Previously, officials considered the date of receipt of income subject to taxation to be the moment of payment of excess funds to an employee (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated June 25, 2010 No. 03-04-06/6-135).
If excess daily allowances were paid in foreign currency, then they should be recalculated into rubles to determine income at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation valid on the last day of the month in which the advance report was approved (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 5, 2017 No. 03-04-06 /35510).
Let us recall that in tax accounting the daily allowance norms are approved by clause 3 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and amount to 700 rubles. per day for business trips in Russia and 2,500 rubles. - for trips abroad. Amounts of daily allowance paid to employees in excess of the specified norms are subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions.
In 2021, 2 important changes were made to settlements with accountables, and more specifically, to clause 6.3 of the instructions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U:
- Now, to issue funds, an employee’s application is not necessary - it is enough to issue an administrative document on behalf of the director of the enterprise or individual entrepreneur.
- Accountable amounts can be issued even if there are previously unreturned accountable funds.
The changes are based on the instructions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated June 19, 2017 No. 4416-U and came into force on August 19, 2017.
Otherwise, the procedure for settlements with accountants in 2021 remains the same. Let's look at it in more detail.
Please note that the main change for business travel in 2017 affected daily allowance rates, which were not previously established for insurance premiums.
From January 1, 2021, insurance premiums are not charged only for a certain fixed amount of daily allowance:
- 700 rubles – for business trips within the Russian Federation;
- 2500 rubles – for foreign business trips.
However, please note that the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain any restrictions on the employer’s right to set certain daily allowance rates when sending personnel on business trips to perform official assignments.
In 2021, an enterprise can independently determine the amount of daily allowance, which is also provided for in Art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (subparagraph 13, paragraph 1), and enshrine them in their internal acts. In this case, the organization deducts insurance premiums from the difference between the standard and the actual amount of daily allowances issued.
For more information about this, see “How per diem is assessed in insurance premiums from 2021.”
Share with friends on social networks
Changes in labor legislation in 2021 did not bring significant changes to the procedure for registering a business trip. They only affected the procedure for calculating insurance premiums from certain daily allowance amounts. The employer is prescribed a certain limit from which contributions are not deducted.
So, for example, for trips around Russia it is 700 rubles. If you travel abroad, the minimum daily allowance from which contributions are not calculated is set at 2,500 rubles. At the same time, the legislator does not limit companies in calculating daily allowances, but only charges an insurance premium for the difference between the funds issued and the established limit.
Including within the administrative territory in which the employer’s organization is registered. For more information about this, see “.” The simplified business trip procedure does not require extensive paperwork, however, changes introduced to the legislation require more thorough documentary evidence of the costs incurred.
This still includes: earnings calculated on the basis of the average daily salary for the entire period of the official trip; payment
Business trips and vacations: is this possible?
Vacation is an employee’s personal time, which he disposes of at his own discretion. And if such a need arises, then sending on a business trip can only be done with the written consent of the employee.
An important caveat is that only annual paid leave can be interrupted. In such an extreme case, the company formalizes the recall of the employee from vacation, then, with his written consent, issues a business trip order.

It will not be possible to combine vacation and business trip according to the documents: either the person is working or on vacation
Revocation from a business trip or its cancellation
The Labor Code does not provide clear instructions on actions to take when business trips are cancelled. Cancellation of a trip or recall ahead of schedule is carried out in several steps. Before issuing the order, the employee is notified of the extension of the business trip (or recall from it). Then an order is issued. Next, the employee is introduced to this order against signature; this can be done after returning to the workplace. If the money has already been issued, but the business trip is canceled or interrupted, the employee draws up an advance report and returns the previously issued and unspent funds.