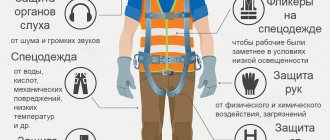
Flushing and neutralizing agents for workers - list
Washing, protecting and regenerating products that should be provided to employees include:
- soaps and detergents for face and body;
- cleansing gels and pastes;
- substances that absorb moisture and moisturize the skin;
- substances that repel moisture;
Flushing and protective agents
- combination agents;
- gels and creams against irritations due to environmental conditions;
- disinfectant solutions and gels;
- means protecting against insect bites;
- regenerating restorative creams and emulsions for workers.
Each tool is issued for specific types of work. It is legally required that work without them is not permitted, as the worker’s health may be at risk.
Standard for issuing soap to employees: what's new
It would seem that soap and various disinfectants are a trifle in comparison with other issues of conducting the economic activities of an enterprise. However, the labor inspectorate may impose a fine on the company's management if the personnel documents do not mention the standard for issuing soap to employees. This year, it has become easier to understand the procedure for issuing soap due to the fact that regulations have appeared regulating the procedure for providing soap to employees. We invite you to understand the innovations and also consider the issues of justifying the issuance of soap, reflecting the costs of its purchase, as well as the right of certain categories of workers to receive skin protection products.
Issuance of flushing and neutralizing agents by profession - standard
Standard standards for issuing personal protective equipment
In accordance with established standards, funds must be issued for certain categories of employees. This is how protection is used when working with various hazardous substances. Moisture-absorbing creams and gels protect workers when working with insoluble substances, such as varnishes, lubricants when working on cars, petroleum products, etc. Hydrophobic agents, on the contrary, are used to protect against water-based substances: they are issued when working with acids and alkalis and salts.
Attention! If it is difficult to determine exactly which specific substance will have to be worked with, combined mixtures are used.
Anti-irritation substances are useful for welding work, activities under increased ultraviolet radiation and when exposed to temperature and wind.
Work with possible bacteriological contamination should not be carried out without disinfectants, which should be applied to all exposed areas of skin or clothing. They will disinfect, protect and maintain the health of the worker.
During seasonal work, protection from blood-sucking insects or the bites of poisonous arthropods is especially important. In this case, protective substances of a biological nature must be provided.
Soap and detergents are useful for work with possible contamination. Moreover, these substances are also divided into several levels, depending on the difficulties that arise during rinsing.
Restorative creams and gels can be useful in all of the above cases, if, despite increased attention to protection, it was not possible to avoid the negative impact of the environment on humans.
What happens if you break the law
Violations in the area we are considering are regulated by the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, in particular, Art. 5.27. If neither the employment contract, nor its additional agreement, nor the internal documents of the organization reflect the standards for issuing personal protective equipment or there is no evidence that the employee is familiar with them, then, according to Part 1, the following fines may be applied:
- for the head of an organization - 1-5 thousand rubles;
- for an organization - 30-50 thousand rubles.
An entrepreneur in this case is equivalent to a manager.
An actual violation of Order No. 1122n, non-issuance or incomplete issuance of personal protective equipment may be regarded by regulatory authorities as a violation of contractual labor relations with the employee, and in this case, according to Part 4 of the article, the fine will be higher:
- for a manager - 10-20 thousand rubles;
- for an organization - 50-100 thousand rubles;
- for an entrepreneur - 5-10 thousand rubles.
Note that the vagueness of the wording of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation makes it possible for a broad interpretation of Art. 5.27 by regulatory authorities, with the accrual of appropriate fines.
The conclusion is obvious: it is better to issue personal protective equipment than to ignore this duty to employees, and the issuance procedure should not be neglected.
Main
The amended rules for accounting for personal protective equipment, which came into force this year, contain two important points:
- means for removing easily washable contaminants can now be issued without the recipient having to sign on his personal card;
- there is no obligation to reflect the standards for issuing personal protective equipment in the contract with the employee when hiring him.
Source
The procedure for issuing flushing and neutralizing agents to employees
Standards for issuing workwear by profession
Regulatory acts strictly regulate the procedure for issuing flushing and neutralizing agents. They establish that procurement and issuance should be handled by the management of the enterprise. All funds are issued to workers in accordance with standard standards established by law. Issue is carried out if there is a need to carry out special work specified in regulatory documents.
Important! Enterprise managers have the right to change the procedure for issuing flushing and neutralizing agents, but only in the direction of increasing the level of employee protection. If a decision was made to increase the standards, no problems with documents will arise after that. But no one is allowed to lower the standards.
All funds are purchased for a period of one reporting period (month). If at the end of the month there are any protective equipment left, they are allowed to be used in the next month, provided that the expiration dates are observed.
It is worth noting that all funds issued to employees must have official confirmation of compliance with certain standards. It is strictly prohibited to issue uncertified products. Occupational safety and health inspection organizations even request a certificate for toilet soap.

Issuance procedure
Approval of a complete list of selected flushing and protective agents is carried out after a detailed special assessment of working conditions.
How to keep records of personal protective equipment
Enterprises have the right to independently organize such accounting in accordance with the requirements of current legislation. In this case, it is advisable to take into account a number of circumstances:
- In accounting, soap and similar DSPIs are classified as inventories and are accounted for according to established inventory accounting standards, without any special features.
- The enterprise must have a list of professions whose employees must receive personal protective equipment, approved on the basis of the above regulations. As a rule, it is issued in the form of an order, an appendix to the collective agreement.
- It is advisable to develop standards for issuing personal protective equipment for production sites and approve them to control consumption in departments. On the reverse side of such a document there is usually a statement of the actual issuance of personal protective equipment to the site with the signature of the responsible person
- A sample of a personal DSHI registration card is contained in the text of the appendix to order No. 1122n; when working, you must use the approved form.
- If personal protective equipment is issued not individually to an employee, but for collective use, it is necessary to appoint a person financially responsible for this. For example, this could be a foreman who receives personal protective equipment for all his workers and monitors. To ensure that they are available in sufficient quantities, if necessary, notes the fact of issue in the personal cards of employees and takes care of their certification with signatures.
Order for issuing detergents: sample
Sample order for standards for issuing workwear
Each employer must keep records of the distribution of flushing and protective equipment. Such accounting is carried out using personal cards of workers. They indicate the employee’s name, position, as well as a list of items issued. In most cases, such cards are quite enough. There is no need to draw up a special order for extradition.
However, if necessary, such an order can be drawn up. It indicates the list of employees to whom the issuance is carried out, as well as all funds. The order is signed by the manager or responsible person. The employees themselves do not have to sign for it.
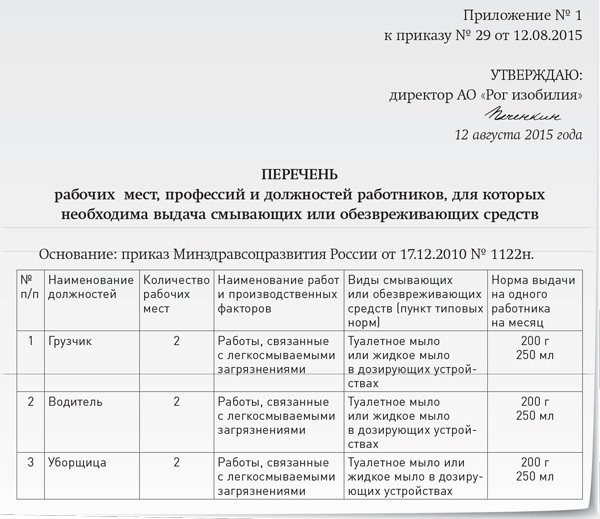
Sample order for extradition
What regulatory documents regulate the provision of flushing agents to employees?
Standards for issuing flushing agents to employees
The employer is obliged to provide its employees with means for degreasing and washing off dirt. This determines labor legislation in the area of labor protection. But it is worth considering that these funds are issued not only to those categories of workers who work in harmful conditions, but also in optimal or acceptable ones.
The organization of hygiene at the enterprise must be ensured for all employees without exception. The employer must provide everyone with soap, both bar soap and in a dispenser.
In addition to labor legislation regarding the issuance of cleaning and degreasing products, organizations are developing regulatory documents regulating the issuance.
Enterprises have internal documents regulating the process of issuing products to employees for skin regeneration and washing away impurities. As a rule, these are enterprise standards or provisions approved by regulatory documents.
They reflect the following information:
- a list of all regulatory documents on the basis of which employees must be provided with these funds (labor legislation, issuance standards, as well as the results of a special assessment of the conditions of the labor process);
- sequence of receipt, procedure and form of application;
- the procedure for issuing funds to employees and the form of the issuance card.
After preparing the draft document, it is sent to the legal department for examination. If there are no comments from lawyers, then the local act can be signed. We must not forget that a motivated opinion is required from the trade union.
After the act comes into force, it is necessary to familiarize all employees with this document, from blue-collar workers to deputy managers. This function should be assigned to one employee so as not to miss a single employee and collect all signatures.
How to familiarize employees with soap dispensing standards
All employees of the enterprise must be promptly notified of the organization’s standards for issuing soap and other protective or flushing agents. This can be done in several ways. The simplest thing is to include the relevant clauses in the employment contract.
If you were not familiarized with the standards when you were hired, this must be done as soon as possible by mail or in person. The main condition is the ability to confirm that the employee has been familiarized with the standards. Therefore, his signature must be affixed to all relevant documents.
When issuing funds, all employees must be familiarized with the rules for their use.
Flushing and neutralizing agents in an employment contract
In order to comply with all established labor safety standards, it is advisable for the employer to include information about the standards for issuing flushing agents already at the stage of developing the employment contract.
In this case, a simple reference to the organization's normative act may not be enough. It is necessary to familiarize the employee with a specific list of everything that will be provided to him to ensure normal working conditions. This is especially true for activities associated with increased pollution and health risks.
Important! It is in the interests of the enterprise to prescribe the standards for issuing hygiene products in the employment contract - already at the stage of familiarization with the vacancy, the employee will see that they are worried about him.
Professions and DSPE standards
Rinsing and similar substances applied to the skin (dermatological) are classified by the occupational safety service as personal protective equipment for workers - PPE. Order No. 1122n contains a list of personal protective equipment by category, indicating fixed issuance rates calculated per month of consumption.
Protective in nature
Moisturizing skin - for persons in contact with oils, greases, soot, solvents, petroleum products, industrial dust and similar media that are not soluble in water (100 ml).
Water-repellent, drying the skin to a natural state, for persons in contact with water, soap-water solutions, cement solutions containing salt, acid, alkali, etc.; working in gloves without lining, made of ordinary rubber (100 ml).
Labor experts know cases where large fines have been imposed on an employer, for example, for failure to specify the standards for dispensing soap in an employment contract. See what responsibility
Combining the above characteristics, combined. If you have to work with substances that change the condition of the skin, then dry the skin or moisturize it (100 ml).
Prevents irritation and damage to the skin - when welding, working in windy, cold conditions (100 ml).
Documents on the basis of which flushing and neutralizing agents are issued
The issuance of flushing and neutralizing agents is carried out on the basis of several basic documents. The main order is considered to be the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development 1122n. At the legislative level, it stipulates the employer’s obligations to ensure comfortable and safe activities for employees.

Regulations governing the provision of protection
At the organizational level, the defining document is the employee’s personal card. It is a special document that indicates basic information about the employee and where all issued substances are entered.
Briefly about the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of December 17, 2010 N 1122n
Order 1122n includes all the main aspects to ensure safe work with various contaminants. It specifies all the substances that need to be given to employees and lists the types of work for which they will be needed.
The occupational safety standard specifies that workers must be provided with flushing agents. Who is responsible and how can this be regulated. There is also a list of actions that are prohibited:
- It is forbidden to use preparations with a high alkali content to wash off light stains;
- soap should not be replaced with powder or any abrasives;
- Do not use regular soap or gels to wash away stubborn stains.
Important! All employers without exception should follow this order. Changes can be made to the regulations that do not contradict the basic norms.
Standards for issuing personal protective equipment by profession
They operate on the basis of Appendix No. 1 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated December 17, 2010 No. 1122n.
| No. | Type of activity, profession | Type of DSPE | Issue rate per 1 person |
| 1 | Professions that use components that have a negative effect on the skin:
| Moisturizers and moisture-absorbing products | 100 ml |
| 2 | Works where it is necessary to interact with water and/or aqueous solutions:
Professions where it is necessary to operate in rubber or polymer gloves, as well as closed special shoes. | Skin-drying and moisture-repellent products | 100 ml |
| 3 | Works of alternating exposure to water-soluble and insoluble pollutants | Hydrophilic-hydrophobic agents (combined) | 100 ml |
| 4 | Professions where you have to work with bacterially hazardous substances (environments). Work carried out away from stationary sanitary facilities. Professions where hand sterility is required. | Disinfectants | 100 ml |
| 5 | Seasonal work outdoors in the warm season | Repellents | 200 ml |
| 6 | Work during which a person receives easily washable contaminants (which can be removed with water and soap) | Solid or liquid soap, for item 7 – cleansing gels, pastes, creams | 200 g solid or 250 ml liquid hand soap, 300 g solid soap or 500 ml liquid body soap |
| 7 | Work associated with difficult to wash off, persistent stains (see clause 1) | 300 g of solid or 500 ml of liquid soap, 200 ml of paste (cream, gel) | |
| 8 | Coal industry works | 800 ml solid or 750 ml liquid soap | |
| 9 | Work during which the skin is exposed to aggressive influences (see clause 1, clause 2, clause 4) | Regenerating emulsions, regenerating agents | 100 ml |
Differences between old and new rules regarding PPE
In the latest edition, Order 1122 on the issuance and provision of protective equipment to workers has some fundamental changes compared to the previous version:
- Most funds must be entered into the employee’s personal card when issued. But now it is not necessary to record the dispensing of substances for easily washed off dirt on the card.
- Now, in addition to fixing the norms for the distribution of substances in the employment contract, the employee can be informed using a special act. Information must be provided in writing so that it can be confirmed.
Why Russian workers turned out to be the greatest individualists on the planet
2440
Anastasia Zhigach
The largest fines, says Elena Mikhalevich, lawyer at the Barshchevsky and Partners Bar Association of Moscow, are established for evasion or improper execution of an employment contract or the conclusion of a civil contract that actually regulates labor relations between the employee and the employer - from 50 thousand. up to 100 thousand rubles for legal entities; for non-payment or incomplete payment of salaries on time - a fine of 30 thousand to 50 thousand rubles.
In the area of violation of state regulatory requirements for labor protection, for example, for failure to provide workers with personal protective equipment, the fine for legal entities ranges from 130 thousand to 150 thousand rubles. “It should be emphasized that the legislator prudently increases the amount of the fine for a repeated violation,” reminds Alina Pavlova, legal adviser at Bridge Group. In some cases it grows 2 times.
However, the general director of the insurance company Pomoshch, Alexander Loktaev, says that in general the system of penalties in 2017 was revised and softened. “Starting from 2021, the state labor inspectorate is proposed to issue fines only to the most negligent employers. After the first violation, the employer will receive a warning order, and only if it is not complied with, inspectors will be able to issue a fine. It is proposed to impose penalties only on employers who have repeatedly violated labor laws,” says the expert.
Employers are often held accountable for violating laws on personal data, but the fines are currently insignificant, notes Elena Mikhalevich. Thus, violation of the procedure established by law for the collection, storage, use or dissemination of information about citizens (personal data) entails a warning or the imposition of an administrative fine on officials - from 500 to 1 thousand rubles, on legal entities - from 5 thousand to 10 thousand. rubles
In the near future, in connection with the adoption of Federal Law No. 13-FZ “On Amendments to the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses,” the situation will change: from July 1, 2017, the employer’s liability for violating the law in the field of personal data will increase. The maximum fine (when processing personal data without written consent of the subject of personal data, when such consent must be obtained, or in case of violation of the requirements for the composition of information included in written consent) will be 75 thousand rubles.
New standard standards for issuing PPE in certain industries
The Ministry of Labor also approved several orders that contain standard standards for the free distribution of work clothes, safety shoes and other personal protective equipment to workers. Some HR professionals may need:
- Order of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation dated December 22, 2017 No. 863n “On approval of the Standard Standards for the free issuance of special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment to workers in the elevator, flour-grinding and feed milling industries engaged in work with hazardous and/or dangerous working conditions, as well as work performed in special temperature conditions or associated with pollution.” Effective mid-April 2021;
- Order of the Ministry of Labor dated December 28, 2017 No. 883n “On approval of the Standard Standards for the free issuance of special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment to workers engaged in geological, topographic and geodetic, survey, land management work and in cartographic production (employed in work with hazardous and (or) hazardous working conditions, as well as work performed in special temperature conditions or associated with pollution).” Effective 06/03/2018;
- Order of the Ministry of Labor dated December 27, 2017 No. 882n “On approval of the Standard Standards for the free issuance of special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment to workers in the construction materials industry, glass and porcelain-faience industries engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, as well as work performed in special temperature conditions or associated with pollution.” Will come into effect early June 2021.
Let us remind you that, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, when performing work in industries with harmful or dangerous working conditions, as well as in special temperature conditions or associated with pollution, workers must be provided with special protective equipment, including shoes and clothing. The standards for free issuance in various industries are established by specific orders of the Ministry of Labor.
The employer has the opportunity to reimburse expenses incurred for the purchase of PPE. But purchased clothing, shoes and products must be certified or declared for compliance with TR CU 019/2011 “On the safety of personal protective equipment.”
Answers to common questions about what is the standard for issuing soap to employees
Question #1:
Can the standard for issuing soap to employees be approved by the employer at his own discretion?
Answer:
Yes, the standard for issuing soap to employees can be approved by the management of the enterprise. However, the established standards for the free issuance of funds should increase the protection of personnel, and not worsen the situation of workers in comparison with the Standard Standards.
Question #2:
An employee who handles contaminants while performing his or her job is not employed full-time. How should the rate of soap distribution to employees be calculated in this case?
Answer:
It is necessary to provide soap and disinfectants in proportion to the employee’s time of employment. If, for example, a full-time employee (performing similar job functions) is supposed to be given 500 grams of free soap per month, then a part-time employee should be given 250 grams of soap. See Letter of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated September 29, 2016 No. 15-2/OOG-3452.
Source
Common mistakes
Error:
The company did not conduct a special assessment of working conditions, and therefore the standard for issuing soap to employees was not approved by management. Therefore, employees do not receive cleaning agents and disinfectants at the enterprise, although the type of activity is listed in the text of the Standard Standards of Order of the Ministry of Labor dated December 17, 2010 No. 1122.
A comment:
Even if a specific workplace assessment has not been carried out, it is necessary to provide employees with soap and other supplies if they are performing work that requires the provision of flushing and disinfecting protective equipment.
Error:
The accountant and HR staff were not provided with free soap at the employer's premises.
A comment:
Despite the fact that accountants and personnel employees do not encounter pollution when performing their work duties, in the Letter of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated August 30, 2016 No. 15-2/ОOG-3095 and in the Letter of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 2016 No. 15-2/ОГ -1752 states the need to provide them with soap for hygienic purposes (solid soap or a dispenser with liquid soap in sanitary facilities will be sufficient).