Almost every position and profession requires compliance with certain safety measures. The employer undertakes to train its employees in the rules.
For this purpose, a large volume of instructions is being developed. The Labor Code determines that the employer must be involved in the process of drawing up safety rules. But not all companies have taken such measures.
Often, instructions that are used in an organization become invalid because they were adopted too long ago.
Instructions in an organization or institution should be developed:
- for workers of certain professions and positions (teachers, educators, laboratory assistants, mechanics, etc.);
- for certain types of work (when conducting classes in classrooms, gyms, workshops, using technical teaching aids, during repair work, etc.).
The development of instructions on labor protection is ensured by the head of the organization, institution after preliminary consultations with the elected trade union body or representative body of workers, the labor protection service, the labor protection specialist (if any), and, if necessary, with other services and officials, in including SES, Rostechnadzor, Gospozhnadzor, etc.
Carrying out approvals
Instructions for workers are developed jointly with specialists involved in equipping workplaces, operating production equipment without harm to health, and preventing occupational injuries. Technologists, engineers, and labor protection specialists check the contents of the document and put their signature on the last page.
Important! If the enterprise has an elected trade union organization that unites at least 50% of employees, its opinion must be taken into account when drawing up instructions. The obligation to coordinate instructions with the trade union must be reflected when adopting a collective agreement.
Draft documents must be sent to the trade union committee with a covering letter attached. The response of the trade union organization must also be in writing. If there is no trade union body at the enterprise, you need to obtain the approval of the labor council. After signing by all involved persons, the document is approved by the manager. For this purpose, a separate order is drawn up for the enterprise, to which an extract from the minutes of the meeting of the trade union committee is attached. The validity period of the instructions begins from the date the order is issued and lasts five years. If there is a need to make additions, the procedure for registration will be the same as for the initial creation of documents. After five years of use, the document can be re-approved in the same form. Professions and safety requirements remain unchanged, so adjustments to instructions are not necessary. The developer draws up a validity extension sheet and attaches it to the original.
When issuing instructions for individual professions, the approval of specialists from other departments may be required. So for an employee whose work involves hazardous chemicals, the instructions must be agreed upon with sanitary services. To carry out work with flammable substances, the approval of the fire department is required.
Development of occupational safety instructions: should an occupational safety specialist do this?
The question is often asked in class: Which employee of the organization can the employer entrust with developing instructions? Should an occupational safety specialist do this?
According to Part 2 of Art. 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer must ensure the development and approval of labor protection instructions. But no recommendations are given regarding who exactly the employer should assign this job function to. Many people believe that this should be the responsibility of an occupational safety specialist.
However, in accordance with the Professional Standard “Specialist in the field of labor protection”, approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated 08/04/2014 No. 524n, the labor function of such a specialist, in particular, includes:
- interaction with representative bodies of workers on issues of labor conditions and safety and coordination of local documentation on labor safety issues;
- revision of local regulations on labor protection issues in the event of new ones entering into force or amendments to existing acts containing labor law standards;
- providing methodological assistance to heads of structural divisions in the development of training programs for workers in safe labor methods and techniques, and instructions on labor protection.
If we are guided by this Professional Standard, the development of labor protection instructions for positions and types of work should be entrusted to the heads of departments (divisions), since they are the ones who have complete information about the labor functions of their subordinates, and the labor protection inspector provides assistance in such development. You can also connect the legal department and human resources department to it. In addition, as a rule, official approval of the already developed draft instructions is carried out with the labor safety inspector.
Legislative regulation
The employer must organize a healthy environment at his enterprise that contributes to maintaining the efficiency of personnel (Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 212). Ensure the creation of a clearly functioning labor protection system, develop and approve effective directives for workers (Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 421).

Labor Code of the Russian Federation Article 212. The employer’s duty is to respect the human right to safe work
The procedure for the development and approval of labor protection instructions, their execution, recording and storage are carried out on the basis of:
- Occupation safety standards system;
- set of standards “Unified System of Technological Documentation” (USTD);
- industry and inter-industry standards and standard directives, which are drawn up on the basis of “Methodological recommendations for the development of regulatory requirements for occupational safety and health” (Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation No. 80 of December 17, 2002);
- technical documentation of the enterprise, manufacturer of equipment used in carrying out work, taking into account current production conditions.
What does the labor safety instruction include?
Each instruction must be assigned a name and its registration number. The name should briefly indicate what profession, position or type of work it is intended for.
The instructions are drawn up, as a rule, in triplicate and are issued against signature to the performer and his immediate supervisor. The original instructions are kept by the head of the organization or institution.
Instructions should not include requirements that contradict laws and other regulations in force in the education system.
The development of labor protection instructions for workers in certain professions, positions and for certain types of work should contain 5 sections:
1. General labor protection requirements
2. Labor protection requirements before starting work
3. Labor protection requirements during work
4. Occupational safety requirements in emergency situations
5. Labor protection requirements upon completion of work
Who is required to draw up occupational safety instructions?
List of labor protection instructions for workers
OSH directives for workers are internal regulations. Responsibility for their development lies with the employer. The manager, as a representative of the employer, involves the heads of structural units in the development. The immediate manager is better informed than others about the working conditions of his subordinates, understands the existing risks and the specifics of the work.

Development of instructions is the direct responsibility of the employer
These issues are resolved by the Occupational Safety and Health Commission. If necessary, third-party services are involved. Individual specialists providing licensed services in the field of occupational safety may be included in the work, which is formalized by an appropriate order.
Organizational and control activities can be carried out by a deputy manager, whose professional responsibilities include the tasks of the labor protection organization.
Important! General management remains with the employer, since the main responsibility lies with him.
In the section “General labor protection requirements” it is recommended to reflect:
- conditions for the admission of persons to independent work in their profession or performance of relevant work (age, gender, health status, medical examinations, instructions, etc.);
- instructions on the need to comply with internal labor regulations;
- workplace safety requirements;
- requirements for compliance with work and rest schedules;
- characteristics of dangerous and harmful production factors affecting the employee;
- provision of special clothing, safety footwear and other personal protective equipment for this profession;
- fire safety requirements;
- the procedure for notifying the administration about cases of injury to workers and malfunction of equipment, devices and tools;
- instructions for providing first (pre-medical) aid;
- personal hygiene rules mandatory for workers when performing work;
- employee liability for violation of instructions.
In the “General Provisions” section, it is especially necessary to pay attention to the characteristics of dangerous and harmful production factors affecting the worker and to informing workers about the provision of personal protective equipment to them.
Procedure for development and content of instructions
The employer’s duty, regardless of the type of activity and form of ownership, is to ensure the safety of workplaces, production premises, enterprise territory, construction or other sites where work is carried out on his behalf.
Fire safety measures: development procedure at the enterprise
Including:
- when operating equipment;
- execution of the technical process;
- use of tools, materials, raw materials.
The normative act establishing occupational safety requirements when performing all types of work is the labor protection instruction. The document, which takes into account the typical causes of accidents and occupational diseases, defines safe methods and techniques. Its adoption is a critical step in creating healthy and safe production.
Note! Regulatory instructions are developed for all professions included in the staffing table and for all types of work that are carried out in production, construction and installation, trade, warehouse and transport enterprises, in research and design institutes, in design bureaus, repair and restoration workshops, in medical and children's institutions.
General requirements
A short list of general OT requirements that must be included in the instructions:
- inner order rules;
- work schedule and rest;
- dangerous and harmful factors, they are determined for specific professions and types of work;
- sanitary standards that must be observed when performing work;
- a list of work clothes, shoes, and protective equipment that a person is provided with according to established rules and regulations;
- the procedure for reporting to a superior about cases of injury or malfunction of technical equipment.

Safety instructions are drawn up for each profession or type of work
The instructions regulate a certain procedure for action in different situations.
Before starting work
Describes the specifics of preparing the workplace and means of ind. protection. Equipment, instrumentation, starting, braking, protective, blocking devices, alarms, grounding, and primary fire extinguishing equipment are checked. The procedure for checking the materials needed to begin work is indicated. The process of receiving and transferring a shift during a continuous work process, in the event of equipment malfunction or technological process failure, is described.
During work
The sequence of actions and safe methods of operating the equipment are regulated. The procedure for using raw materials, tools, devices, vehicles, lifts, mechanisms, and containers is described. The procedure for maintaining the workplace is separately mentioned. The conditions and factors under which work must be stopped immediately, as well as actions to prevent emergency situations, are listed.
In emergency situations
Actions in case of emergency, principles of first aid for injuries, poisoning, and other health damage are indicated.
Upon completion of work
The algorithm for shutting down, disassembling, cleaning and lubricating machines, equipment, and mechanisms is regulated. The need for waste collection is mentioned. Specifies the procedure for notifying the work manager of safety problems discovered during the production process.
Important! The content can be supplemented by the employer taking into account production features; the document may include additional sections.
In the section “Occupational safety requirements during work” it is recommended to provide:
- methods and techniques for performing work safely, rules for using technological equipment, devices and tools;
- requirements for safe handling of starting materials (raw materials, blanks, semi-finished products);
- rules for the safe operation of vehicles, containers and lifting mechanisms;
- instructions for maintaining a safe workplace;
- main types of deviations from the standard technological regime and methods for their elimination;
- actions aimed at preventing emergency situations;
- requirements for the use of protective equipment for workers.
In the section “Occupational safety requirements upon completion of work” it is recommended to reflect:
- procedure for safe shutdown, shutdown, disassembly, cleaning and lubrication of equipment, devices, machines, mechanisms and equipment,
- procedure for handing over a workplace;
- requirement of personal hygiene;
- procedure for notifying the manager of all deficiencies discovered during work
The text of the instructions should be concise, clear and not subject to different interpretations.
The terms used in the instructions must correspond to the terminology adopted in the relevant legislative acts, GOSTs, technical regulations, and other documents on labor protection.
The revision of instructions for employees is organized by the employer (head of the institution, organization)
The instructions must be reviewed at least once every 5 years.
Document structure

Standard instructions developed by state labor protection authorities consist of five main sections. They set rules at different stages of work:
- General safety rules;
- Requirements before starting work;
- Security on the main part of operations;
- Compliance with requirements at the end of the process;
- Actions in case of emergencies.
The same structure should be followed in the document that is developed at the enterprise. If there are production features that need to be included in the document and highlighted as a separate section, they can be added to the instructions.
Instructions may be revised ahead of schedule:
- when revising intersectoral and sectoral rules and standard instructions on labor protection;
- when the working conditions of employees change;
- when introducing new technology;
- based on the results of the analysis of materials from the investigation of accidents, industrial accidents and occupational diseases;
- at the request of representatives of labor authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation or the federal labor inspectorate.
If during the period of validity of the instruction the working conditions of the employee have not changed, then by order (instruction) on the organization, establishment and decision of the trade union committee, the validity of the instruction is extended for the next period, about which an entry is made on the first page of the instruction (the “Revised” stamp is placed, date and signature person responsible for revising the instructions).
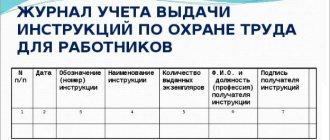
Approved instructions of an organization or institution are registered in the journal of instructions for the organization or institution in accordance with the procedure established by the Ministry of Labor of Russia.
The head of an organization or institution must constantly keep a set of current instructions, as well as a list of these instructions approved by him.
One set of instructions may be provided by a trade union committee of an organization, an institution or a representative body of workers, a labor protection commissioner, or a labor protection committee (commission).
All employees, heads of offices, workshops and other departments must be provided with instructions.
The location of instructions for employees, a list of them and a log of the issuance of instructions is determined by the head of the organization or institution, taking into account the availability of ease of familiarization with them.
Instructions can be handed out to employees or posted at their workplaces, taking into account the need to ensure simplicity and ease of familiarization with them.
If the information was useful, leave comments and share the link to this article on your social networks. Thank you!
Approval and storage of instructions
The instructions are coordinated with the trade union and other services (for example, with the legal department, labor protection service, heads of structural divisions, etc.). After which, labor safety instructions are approved and put into effect by order of the employer.
Note: The title page must contain the “I approve” glyph, the date and the employer’s signature. As well as notes on agreement with the primary trade union organization, and in its absence, with the labor protection commissioner.
Labor protection instructions are recorded in a special journal by an authorized employee of the labor protection service.
A control copy of the instructions is stored in the labor protection service, and the required number of copies is issued to structural units.
The fact of issuing instructions must be recorded in a special journal.
All employees instructed according to the instructions must be familiar with it and signed it.
It is recommended to record notes about familiarization with the instructions on a copy of the person conducting the instructions, or in a special journal.
It is also recommended to post copies of the instructions at workplaces (for example, on a special stand).