The requirements for the availability of these documents and their standard forms are provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws:
- Federal Law of December 28, 2013 N 426-FZ “On special assessment of working conditions”
- Federal Law of March 30, 1999 No. 52-FZ “On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population”
- Federal Law No. 125-FZ of July 24, 1998 “On compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases.”
- Federal Law of June 21, 1997 No. 116-FZ “On Industrial Safety of Hazardous Production Facilities”
- Federal Law of November 24, 1995 N 181-FZ “On social protection of disabled people in the Russian Federation”
- Code of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2001 No. 195-FZ “On Administrative Offences”.
- Federal Law No. 294-FZ dated December 26, 2008 “On the protection of the rights of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs during state control (supervision) and municipal control”
The other part of the document flow is created by a legal entity in the course of its activities to implement labor protection standards and rules on its own initiative, taking into account the specifics of production activities and current safety issues at work. There are two main requirements for such documents - they must comply with the requirements of current legislation and must not worsen the rights of employees in comparison with those established by law.
Documentation support for labor protection, among other things, has several goals:
- compliance of the company’s labor protection system with the current legislation of the Russian Federation
- continuity of the process of implementing labor protection measures at all stages of a legal entity’s work
- documentary evidence of compliance with legal requirements by a legal entity
- streamlining the company's labor protection system
- control over the implementation of labor protection measures, planning activities for the implementation of procedures, identifying persons responsible for the development and approval of labor protection documents.
The availability of documents, their proper execution, and relevance are the first things that are checked by representatives of government agencies when conducting an inspection of a legal entity.
Basic documents
So, the following documents must be completed by each legal entity in order to comply with current regulatory labor protection requirements:
Internal Labor Regulations (ILR)
The standard PVTR establishes the basic rights and obligations of the employee and the employer:
- the employee’s right to be provided with a workplace that meets state regulatory requirements for labor protection and the conditions provided for by the collective agreement (if any);
- the employer's right to demand that employees comply with labor protection and fire safety rules.
- The employer's responsibility to ensure safe conditions and labor protection rests with the employer (Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Employee employment contract
An employee's employment contract contains the rights and obligations of the parties to the contract.
By virtue of the direct instructions of the law - the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the contract must necessarily contain:
- guarantees and compensation for work under harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, if the employee is hired under appropriate conditions, indicating the characteristics of working conditions at the workplace; working conditions in the workplace (paragraphs 12 and 14 of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- working conditions stipulated by the employment contract must comply with labor protection requirements (Article 220 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
It was for the purpose of providing the employee with objective information about working conditions in the workplace that workplace certification was carried out, and from January 1, 2014, it was replaced by a special assessment of working conditions (Federal Law of December 28, 2013 N 426-FZ “On Special Assessment of Working Conditions” ).
New!
From 01/01/2017, according to Article 309.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employment contract for companies classified as micro-enterprises can be concluded in accordance with the standard form.
Thus, the employer has the right to fully or partially refuse to adopt local regulations containing labor safety standards.
These standards are enshrined directly in the text of the employment contract (in a standard form - Section VI Occupational Safety and Health): the following working conditions are established at the employee’s workplace. In particular, the working conditions (class and/or subclass) of working conditions at the workplace must be indicated, the number of the card for special assessment of working conditions, whether the employee is given initial training and its reasons, whether medical examinations are provided for this workplace, their type, what means personal protection are issued, the grounds for their issuance.
This is a right, and not an obligation, of a micro-enterprise; the decision is made by the manager independently - depending on the characteristics of the micro-enterprise’s production activities.
Regulations on the occupational safety and health management system (OSMS)
The regulations are developed by the employer on the basis of a standard form, independently or with the involvement of organizations and specialists from outside, and approved by order of the employer.
The Regulations reflect the specifics of the company's activities, determine the organization of management of the labor protection system (distribution of responsibilities of officials), the procedure and procedure for the functioning of the OSMS, establish a system of local regulations, recording (magazines, acts, records) documentation (Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated August 19, 2016 N 438n “On approval of the Model Regulations on the Occupational Safety and Health Management System”).
Job descriptions of specialized specialists
The job description of an occupational safety specialist, job descriptions for occupational safety of managers and specialists, as well as the Regulations on the occupational safety service directly establish the rights and obligations, responsibilities of managers and specialists of the company, the position is developed on the basis of the Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated 02/08/2000 No. 14 and Article 217 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (depending on how labor protection responsibilities are distributed in the organization).
Order of the manager on the appointment of persons responsible for labor protection at the enterprise
The signature of the responsible person to familiarize himself with this order is required; appointment is possible only after completing training and receiving a certificate (Article 217 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Labor safety induction program
The program is developed by an occupational safety specialist; as a rule, it is common to all categories of workers, contractors, and company guests. Introductory training is carried out for absolutely all new employees of the company, regardless of their experience, qualifications, or position. The introductory briefing is for informational purposes and contains a description of the main corporate provisions of labor protection and links to local regulations. Instruction is carried out in person, upon entry to work, orally or by demonstrating video materials (Resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Social Development of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation No. 1/29 of January 13, 2003 “On approval of the procedure for training in labor protection and testing knowledge of safety requirements labor of the organization's employees").
Programs for conducting initial training on labor protection in the workplace
The program is developed by a labor protection specialist and the heads of relevant departments. The purpose of the initial briefing is to familiarize yourself with safe working methods directly at the workplace (PPE used, rules, requirements, instructions). Programs are developed on the basis of GOST 12.0.004-90 “SSBT. Organization of occupational safety training”, Resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Social Development of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation No. 1/29 dated January 13, 2003 “On approval of the procedure for training in occupational safety and testing knowledge of occupational safety requirements for employees of the organization.”
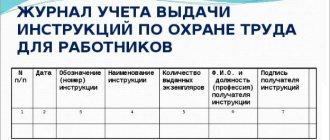
Briefing logs
Logbooks for registration of induction training, registration of initial briefing on labor protection in the workplace, registration of accidents (Article 230.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) can be purchased printed or printed independently. Their pages are numbered, laced, the bindings are signed by the responsible person, and certified by the seal of a legal entity. The employee’s signature in the log is the main evidence of properly conducted instruction (GOST 12.0.004-90. “SSBT. Organization of occupational safety training”).
Order on approval of the List of professions and positions of workers exempt from initial training at the workplace
The law provides for the possibility that employees may not undergo initial training at the workplace if such a list is approved by the employer (Resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Social Development of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation No. 1/29 of January 13, 2003 “On approval of the procedure for training in labor safety and testing knowledge of the labor protection requirements of the organization’s employees”).
Order on approval of the List of instructions on labor protection and Instructions on labor protection for all professions and workplaces of the company
The procedure for developing instructions is determined by the legal entity independently; inter-industry or industry-specific requirements for safe working conditions and standard instructions are used to create instructions. It is necessary to maintain logs of records and issuance of instructions.
Results of workplace certification and special assessment of working conditions
The results of a special assessment of working conditions must be presented in the form of a report (Appendix No. 3 to the Methodology for Conducting Special Labor Conditions, which was approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor No. 33n dated January 24, 2014) in strict accordance with Article 15 of Law 426-FZ. The report is drawn up by the organization that conducted the special assessment, must be signed by all members of the commission and approved by the chairman of the commission.
Determining which documents are missing
The first way to check the availability of documents was indicated above - by compiling a list. There is another way.
It is necessary to select a process from the occupational safety management system and determine the legislative framework that governs it. Then you need to determine the list of documents to compile and maintain.
If we touch on a more complex topic - psychiatric examination, then we consider either the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 23, 2002 No. 695 “On undergoing mandatory psychiatric examination by workers engaged in certain types of activities, including activities associated with sources of increased danger (with the influence of harmful substances and unfavorable production factors), as well as those working in conditions of increased danger,” or Resolution of the Council of Ministers - Government of the Russian Federation dated April 28, 1993 No. 377 “On the implementation of the Law of the Russian Federation “On psychiatric care and guarantees of the rights of citizens during its provision.”
We study this legislation and identify what documents need to be developed and maintained. If we are talking about a medical examination, then, accordingly, we need a contingent, a list of names, a log of the issuance of referrals.
For simplicity, you can download our inspection checklist and “run through” the list, as well as apply the procedures specified in Order No. 438n “On approval of the Standard Regulations on the Occupational Safety and Health Management System.”
Additional documents
In parallel with the development and approval of documents in accordance with the list above, it is necessary to systematize or develop documents in the following thematic sections:
Training and testing of knowledge on labor protection
- Labor protection training program for workers. The program is drawn up in any form, a list of employees who need to be trained, the subject of training, the timing of existing certificates, protocols, a schedule for sending to training, an annual plan for repeated and periodic briefings are approved).
- Order on the appointment of an internal commission to test knowledge of labor protection. A permanent commission, consisting of employees trained at the training center, authorized to test the knowledge of labor protection of company employees and draw up appropriate knowledge testing protocols.
- Orders on the appointment of responsible persons (mentors), under whose guidance new employees undergo training. All newly hired employees, after initial on-the-job training, must undergo on-the-job training during the first 2–14 shifts. In cases established by law, workers can be allowed to work independently only after passing it, testing theoretical knowledge and acquiring skills in safe ways of working, that is, if there is a protocol on successful completion of the test and an order for admission to independent work (GOST 12.0.004- 90 "SSBT. Organization of occupational safety training").
- Copies of valid certificates, protocols for testing knowledge of labor protection requirements for managers, specialists and engineers, working personnel
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
- The order on working with personal protective equipment in an organization streamlines the processes of procurement, issuance, maintenance of workwear and other personal protective equipment, responsible persons)
- The list of jobs and professions for which personal protective equipment should be issued is developed on the basis of the Standard Industry Standards for the free issuance of special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment and the Rules for providing workers with special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment (Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated 01.06 .2009 No. 290n, Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Personal cards for recording the issuance of personal protective equipment. The cards are maintained individually, the goal is to record the fact that PPE has been issued to the employee (Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated June 1, 2009 No. 290n “On approval of intersectoral rules for providing workers with special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment”).
- Copies of certificates (declarations) of conformity of personal protective equipment with the technical regulations of the Customs Union “On the safety of personal protective equipment” TR CU 019/2011, approved by the Decision of the Commission of the Customs Union dated 09.12.2011 and certificates (declarations) of conformity of fabrics, knitted fabrics and non-woven materials used for the manufacture of special clothing, the technical regulations of the Customs Union “On the safety of light industry products” (TR CU 017/2011), approved by the Decision of the Customs Union Commission dated December 9, 2011 No. 876. The certificates (declarations) indicate the address of the location of production, which is crucial for cost recovery through the Social Insurance Fund.
Medical examinations, first aid, first aid kits
- An order appointing a person responsible for providing first aid to victims of an industrial accident and storing a first aid kit. Attachments to the order are a schedule for auditing first aid kits, monitoring the expiration dates of medical products, and instructions. Activities are carried out with the aim of providing medical and preventive services to workers (Article 223 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated 03/05/2011 N169n “On approval of the requirements for equipping first aid kits with medical products to provide first aid to workers”).
- Copies of certificates of persons who have been trained in first aid in case of accidents at work, first aid kit inspection logs (in free form with notes on the audit, on the use of its contents).
- List of employees subject to periodic medical examinations. It is being developed on the basis of order No. 90 dated March 14, 1996 “On the procedure for conducting preliminary and periodic medical examinations of workers and medical regulations for admission to the profession” and order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated August 16, 2004 No. 83 “On approval of lists of harmful and (or) hazardous production factors and work during which preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) are carried out, and the procedure for conducting these examinations (examinations).” Other documents, depending on the specifics of the company’s work: regulations on the organization of pre-trip and post-trip examinations of car drivers, a list of professions and jobs for which an employee must undergo a preliminary medical examination upon entry.
- Production control program (developed on the basis of the Federal Law “On the Sanitary and Epidemiological Welfare of the Population” dated March 30, 1999 N 52-FZ, standard production control programs in accordance with the letter of Rospotrebnadzor dated April 13, 2009 N 01/4801-9-32)
Typical errors that occur during checks
In addition to the fact that chaos in documents may accompany us, there are also errors.
- For example, the lack of an action plan to improve working conditions and safety, as well as when it is not clear who is responsible for the development. If such a situation happens to you, then by order appoint someone responsible for the development of documents, instructions, regulations, etc., if, for example, you do not have a labor safety specialist on staff.
- All materials are available and maintained on the computer, but they are not approved as documents. A local regulatory act must be approved and certified by the signature of the manager or the person who approved it.
- There is no Regulation on OSH, but this is the most important thing. Often when checking it turns out that it is not there.
- In addition, labor safety instructions have not been revised. For example, it also happens that since 2005 no one has revised labor safety instructions. As a result, the statute of limitations for review has expired. Today, this topic is very pressing, because since the beginning of the year, more than 40 new labor protection rules have come into force. It is necessary to review all occupational safety instructions.
- Failure to familiarize employees with local regulations is also one of the typical mistakes. For example, you made some provision and did not familiarize all the key persons who are involved in these processes. Or there are outdated links to legal acts.
Other
There are different opinions regarding the inclusion of fire safety, electrical safety, and environmental work in the job responsibilities of an occupational safety specialist. Theoretically, each of these areas is a separate field of activity requiring special knowledge and qualifications. However, in practice, due to cost optimization, crisis phenomena in the economy, and the peculiarities of the company’s production activities, nevertheless, work in the areas listed above is also assigned to a labor protection specialist (department).
Documentation flow on labor protection may contain specific provisions, orders, instructions depending on the characteristics of the company’s production activities; we are talking about work with cranes, thermal power plants, boilers, pressure vessels, chemicals, and so on.
A separate area of labor protection is activities for the safe performance of work by contractors; instructions are also developed for them; rules and requirements are included in the text of the contract for the performance of work and provision of services. There is a system for issuing permits for fire, welding, and high-risk work. A special place in the document flow system for labor protection is occupied by work on anti-terrorism protection, documents on civil defense and emergencies.
Thus, the workflow for labor protection is a complex system; the full list of documents will always differ depending on the characteristics of the production activities of different companies. Corporate documents on labor protection establish the norms and rules of labor protection that are mandatory for all employees of the company, record events and facts regarding labor protection that have developed at a certain point in time.
Making a basis
The main list of required labor protection documentation includes:
- orders (organizational and administrative, on responsibility);
- instructions (on labor protection, fire safety, production);
- regulations (commission on labor protection, knowledge testing);
- programs (training, introductory (primary) briefing);
- protocols (knowledge tests, occupational safety meetings, measurement results);
- journals (accounting for briefings, testing knowledge, recording instructions, etc.);
- rules (internal labor regulations, safety rules for being on site);
- standards (corporate, compliance with international safety requirements);
- registration cards (issue of personal protective equipment, cleaning agents).
Depending on the production specifics of the facility, the above list can be supplemented or, conversely, reduced. But the basic basis is this.
Lifehack. For convenience, we recommend that you make a list of the required package of documents on labor protection, indicating links to regulatory legal acts. This same list can be used in the future as an internal checklist for checking your structural divisions.
Fire safety documents:
– fire safety instructions;
– evacuation plans;
– instructions for ensuring safe and quick evacuation of people;0:55:53 PM
– briefing log;
– briefing schedules;
– register of industrial premises of classes according to PUE, NPB;
– logbook for maintenance and performance checks (APS, water supply, fire equipment);
– fire extinguisher maintenance log;
– fire extinguisher log book;
Industrial safety documents:
– production control program;
– protocols for certification of specialists;
– personnel certification protocols;
– book of registration and inspection of the vessel;
– log of control checks of pressure gauges;
– logbook for testing the knowledge of elevator operators and operators;
– a logbook for checking pressure vessels in working condition;
– journal for testing knowledge of the rules of technical operation of thermal power plants;
Functional responsibilities of the OSMS
They must be specified in the Regulations themselves, or they must provide links to an internal regulatory act where they can be reflected, for example:
They must be specified in the Regulations themselves, or they must provide links to an internal regulatory act where they can be reflected, for example:
- in a separate provision on the distribution of functional responsibilities;
- in action plans for the implementation of procedures (indicating information about who is responsible for what);
- in employment contracts;
- in the job descriptions of persons involved in labor safety management (for example, in the paragraph “Occupational Safety and Health Responsibilities”).
Also, do not forget to familiarize all responsible persons with local regulations.
Lifehack. If there is a huge amount of documents, you can reflect all functional responsibilities in an employment contract or make a register with a list of documents for it. When hired, the employee signs that he has read all the requirements.
Individual local regulations mean:
- orders;
- orders;
- documents on the distribution of duties and responsibilities in the field of labor protection, which are signed by the employer (orders, instructions, instructions).
For example, in our Regulations on the functional responsibilities for labor protection of the manager, everything is spelled out: that he organizes resource provision, ensures compliance with the work and rest regime, etc.

The duties of the deputy manager indicate that he organizes medical examinations, etc.