Few people know that if there is a delay in payment of wages, an employee can stop performing work duties, but at the same time keep his job. The basis for such actions is a statement issued by the employee to the employer. Today we will talk about the specifics of drawing up this document: in what cases an employee has the right to submit an application for termination of work, which categories of employees cannot submit an application to the employer, what mandatory details are provided in the document, how to draw up an application step by step and submit it to the employer.
Application for termination of work: when is it issued?
Unfortunately, the systematic delay and non-payment of wages and other benefits to employees at many enterprises is not the exception, but the sad norm. Employers explain this state of affairs by various factors: a decline in production, a decrease in the number of orders, a financial crisis, etc. Employees of such companies become hostages of this state of affairs and are forced unwillingly to put up with an unpleasant situation.
But what if the employer accumulates debt to employees without paying wages for months? Should employees work “on credit” in this case?
conclusions
For each month worked, the employee is paid a certain amount of money - salary. The procedure and timing of its payment must be reflected in the internal documentation of the institution.
If wages are delayed for more than 15 days, the employee has the right to prepare a special application for suspension of work and not go to the workplace until the situation is resolved.
If the employer does not accept or does not respond to the document, the citizen can file a complaint with higher authorities.
The management of the company cannot dismiss an employee who has submitted an application for suspension of activities. Ultimately, the working citizen is entitled to payment of wages and compensation for each day of delay.
Who cannot stop working upon application
It should be understood that not all employees suffering from dishonesty of employers can submit an application and stop performing their work duties.
The law provides for situations in which certain categories of employees do not have the right to leave the workplace even if there is a long delay in wages. Here are the main such situations:
- Regardless of the period and extent of the salary delay, employees cannot stop performing their official duties if there is a period of emergency or martial law in the territory of the municipality. This rule applies to employees of all categories and positions.
- Employees holding positions of state and local government, as well as other civil servants, are obliged to fulfill work duties within the framework of the employment contract, even in the event of a delay in salary.
- Military personnel of all types of units, as well as rescuers of the Ministry of Emergency Situations and employees of state defense and security agencies cannot stop performing their official duties.
- If an organization has hazardous production units, then employees of such units cannot leave the workplace in accordance with Art. 142 TK.
- Employees of public utility services, whose responsibilities include ensuring the livelihoods of the population, do not have the right to leave work, including if they owe wages to their employer. This rule applies to workers in the water, heat and energy supply sectors.
- Health workers of all categories and positions who have salary arrears cannot suspend work in accordance with Art. 142 TK.
Algorithm of actions for an employee in case of delay in salary
Additionally
There are certain cases when stopping work is unacceptable:
- workers of rescue and emergency services, military, firefighters;
- in a state of emergency;
- civil servants;
- workers who service particularly hazardous types of production and equipment;
- workers who ensure the livelihoods of the population (ambulance, water supply, gas supply, energy supply, heating, communications).
Based on legal norms, if wages are delayed for more than 15 days, the employee can take the following actions:
- write a notice to the employer stating that due to a delay in payments of more than 15 days, he ceases to perform his official duties. This document must be drawn up in 2 copies, one remains with the employer, and on the other the responsible person who accepted the notification must sign for acceptance. This is necessary to ensure that the employee does not have to register absenteeism, and to prove the legality of the actions in court (if necessary). It should also be taken into account that the employer will have to pay for the period of suspended work;
- do not go to work until written notification from the employer of the intention to issue wages;
- file a claim in court for violation of civil rights.
If the period of delay in wages exceeds 3 calendar months, then the employee, in addition to the actions listed above, can file an application with the arbitration court to declare the company in which he works bankrupt. The court will accept the case for consideration if the employer’s debt to employees is at least 300 thousand rubles.
In addition to the actions listed above, the employee has the right to report a violation of his rights to the following authorities:
- to the Federal Labor Inspectorate;
- to the prosecutor's office at the location of the company where the employee works;
- to court (a sample statement of claim for non-payment of wages can be found).
If at an enterprise or organization the salaries of several employees are delayed, then it is better to defend your rights together. Collective applications to government agencies will be processed faster than individual ones, and they will also have a greater chance of a positive result.
When contacting all government agencies, you must submit a written application indicating the fact of the delay in wages, the timing of the delay, the exact details of the company and your personal data. If available, provide supporting documents.
Watch the video for expert advice on how to collect your salary if you are delayed.
Mandatory details and recommendations for the document
The current legislative acts do not establish an application form according to which the employee notifies the employer of termination of work duties due to non-payment of wages. Thus, in the event of a violation of your labor rights, you can draw up and submit an application in free form. It is important to indicate the required details:
- applicant's details (full name, position, structural unit);
- information about the company (name, address, full name, position of manager);
- date of application;
- the applicant's handwritten signature.
The text of the document must indicate the following basic provisions:
- the established date for payment of wages under the employment/collective agreement;
- the fact of delayed wages as of the date of the application;
- link to article 142 of the Labor Code, which allows you to stop working in the current situation;
- direct notification to the employer of termination of employment duties from the specified date.
For completeness and correctness of the information described in the text of the document, it is recommended to refer to specific regulatory documents. In other words, when mentioning the dates set for payment of wages, you must indicate the number and date of the collective/employment agreement, as well as a point confirming the fact you described.
Compensation for delayed wages
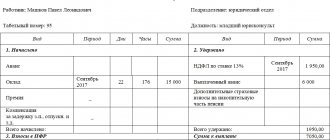
Important! The key rate is taken equal to the period of time for which compensation is calculated.
According to labor legislation (236 Labor Code of the Russian Federation), there is a minimum amount of compensation to be paid to employees. This amount can be set higher and approved in company documents such as labor, collective agreement or local regulations. Compensation is paid simultaneously with the payment of arrears of wages.
Drawing up a notice of termination of work
In order to stop working if wages are not paid, we suggest following the following algorithm.
Step 1. Completing an application.
In case of delay in salary, make a statement in free form, but taking into account the above recommendations. The application should be submitted on the 16th day following the established salary payment day if, at the time of drawing up the documents, the employer has not made payment. You have the right to submit an application either in printed form or by writing it by hand. In any case, your handwritten signature is required. The document should be prepared in 2 copies.
Step 2. Submitting an application to the employer.
Immediately after drawing up the document, submit it for registration at the office. The office employee must mark the acceptance of the document, indicating the date and signature on behalf of the employer. Keep one of the copies (with a mark) as documentary evidence. Since the document is of a notification nature and is based on the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, approval of the application from the head of the organization is not required.
Step 3. Termination of work duties.
The fact that the notice was sent to the employer and the presence of the corresponding office mark is the basis for your termination of official duties. Let's consider an example: on 07/05/17 the employer "Sigma" was obliged to pay you for your salary. As of July 20, 2017, no calculation was made. 07/21/17 You submitted notices of absence from work. 07/22/17 You have every right to stop performing your official duties.
How to write the text of an application for suspension of work if there is a delay of more than 15 days?
In the header of the application, the addressee is indicated - the head of the enterprise, indicating his last name, first name, patronymic and position. Next, write down the position and personal information of the notifier. It would be more appropriate to call the form not an application, but a “notification”, since the employee does not ask to agree on anything, but states the fact of absence from work due to non-payment of wages.
In the preamble of the application, the reason for the suspension of work is indicated, indicating the exact dates on which the violation occurred in the form of a delay in payment, and it must be ensured that this violation lasts more than 15 days. It is important to understand that this counting should be made not from the date of the last payment, but from the day following the day of non-payment on time. are established by the employer independently.
The informative part of the application contains the actual notification that the employee is suspending the work process due to non-payment of wages. In this case, it is worth not only informing about the suspension of work, but also about the presence of the right not to appear at work. In conclusion, it must be added that if the debt is repaid, the employee will be ready to resume work the next day.
Example:
A well-drafted notice might look like this:
“Due to the fact that the payment of wages for March was delayed for more than 15 days, on the basis of Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, I notify you of my intention to suspend work from May 15, 2021. Ready to begin performing official duties from the moment the debt is repaid. During the period of suspension, I reserve the right not to be present at the workplace.
- Through the secretariat or personnel department of the enterprise. In this case, the employee has the opportunity to request a record of receipt of the application in the Book of Incoming Messages indicating the date and signature of the person who accepted the notification.
- Sending the form by mail to the legal address of the employer. In this case, you must send the application by registered mail with notification. After the employer receives the letter, the notice with his signature will be returned to the employee who sent it, and, if necessary, will become evidence of the warning in due time in court.
Who does not have the right to suspend activities?
Important
: employees of the following categories do not have the right to suspend work even if wages are not paid for more than 15 days:
- Persons working in the civil service
- Workers whose activities are related to providing citizens with electricity, gas, heating, water supply, and medical services.
- Military personnel, employees of the Ministry of Emergency Situations, law enforcement agencies and correctional officers.
Problem
Hello, my husband and his colleagues at work wrote a collective notice of suspension of work due to non-payment of wages to their superiors. The director signed it, but did not stamp it; he said that stamps are not placed on notifications. Question: if the notification was collective, then the response notification of readiness to pay salary should also be collective, that is, for all employees at once, or the director may not pay salary to all employees at once, but one at a time, for example. Colleagues are concerned about this issue. Please tell me how events usually develop after employees write such a notice. And what to prepare for.
Solution
Hello!
If the employer does not pay the salary, then it is worth suspending work, read our Algorithm:
The employer does not pay wages for a month, two, or even three months - suspend work
It’s unlikely that anyone will describe to you how events usually develop, because... it all depends on the financial condition of the employer.
Whether the employer will immediately pay the debt to the entire team or this will happen for each specific employee, this again depends on the financial condition of the employer. The employee must comply with the requirement of the law, Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
Worker
who was absent from the workplace during his working hours during the period of suspension of work, is obliged to return to work no later than the next working day after receiving written notification from the employer of readiness to pay the delayed wages on the day the employee returns to work.
Those. the law obliges the employer to send written notice to the employee, not the team, and obliges the employee to return to work no later than the next working day after receiving written notice from the employer.
So, expect written notice from the employer to each employee.
But there is also judicial practice that is worth focusing on:
1. The company has paid off its salary debts - those who have not resumed work can be fired for absenteeism
The employee suspended work because his salary was delayed by more than 15 days. He did not begin his duties even after he received all the money. In this case, dismissal for absenteeism is legal.
The employee had to resume work the next working day after receiving the money.
The entire amount was transferred to his bank card, so a written statement indicating the date of payment of the debt was not required from the employer.
Document: Appeal of
the Ulyanovsk Regional Court dated September 29, 2015 in case No. 33-4012/2015
2. If the salary debt is partially repaid, the employee is not obliged to resume work
Lasts until the entire delayed amount is paid.
This applies to both the debt due to which the work was suspended and the debt for the subsequent one. Since the delayed amount was not paid in full, the employee did not resume work.
The court indicated that the employer had no grounds to fire him for absenteeism. has already been encountered in judicial practice.
Document: Appeal of
the St. Petersburg City Court dated May 17, 2016 N 33-9739/2016
So,
that there must be a written notice, but there may not be one if the salary is paid to the current account, and when the entire amount is received in the current account, the employee is obliged to leave the next day.
Plus,
the employer is obliged to make payments for the period for which the debt arose, due to which the employee wrote a statement of suspension of work, but the period of suspension of work itself must also be paid according to average earnings:
During the period of suspension of work, the employee retains his average earnings.
And the calculation must be made with interest
, which the employee is not obliged to remind the employer about in the application, but I recommend doing so, because employers ignore Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
If the employer violates the established deadline for payment of wages, vacation pay, dismissal payments and (or) other payments due to the employee, the employer is obliged to pay them with interest (monetary compensation) in the amount of not less than one hundred and fiftieth of the key rate in force at that time of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation from amounts not paid on time for each day of delay starting from the next day after the established payment deadline until the day of actual settlement inclusive. In case of incomplete payment of wages and (or) other payments due to the employee on time, the amount of interest (monetary compensation) is calculated from the amounts actually not paid on time.
The obligation to pay the specified monetary compensation arises regardless of the employer’s fault.
Employer's responsibility - material from Consultant Plus:
Administrative liability (fine) for delays in wages, vacation pay and other payments
For non-payment or incomplete payment on time of wages and other payments made within the framework of labor relations (if these actions do not contain a criminal offense), liability is provided under Part 6 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in the form of a warning or a fine in the amount of:
From 10,000 to 20,000 rubles. - for officials;
From 1000 to 5000 rub. — for individual entrepreneurs;
From 30,000 to 50,000 rubles. - for legal entities.
A person who was previously subject to administrative punishment under Part 6 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation and has repeatedly committed a similar offense, may be prosecuted under Part 7 of Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (if the person’s actions do not contain a criminal offense). In this case, he faces punishment:
A fine of 20,000 to 30,000 rubles. or disqualification for a period of one to three years - for officials;
A fine of 10,000 to 30,000 rubles. — for individual entrepreneurs;
A fine of 50,000 to 100,000 rubles. - for legal entities.
Please note: if a legal entity has committed an administrative offense and the officials through whose fault it was committed are identified, both the legal entity and these officials can be held administratively liable under the same norm. This follows from Part 3 of Art. 2.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, para. 1 clause 15 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 24, 2005 No. 5.
Criminal liability (including fine) for non-payment of wages and other amounts due to the employee
Currently, criminal law provides for liability for non-payment of wages, pensions, scholarships, benefits and other payments. Responsibility can be assigned not only to the head of the organization, but also to the head of a branch, representative office, or other separate structural unit of the organization (Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
In case of partial non-payment of wages, pensions, scholarships, allowances and other statutory payments for more than three months, the specified managers face (Part 1 of Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation):
A fine of up to RUB 120,000. or in the amount of wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of up to one year;
Deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or carry out certain activities for a period of up to one year;
Forced labor for up to two years;
Imprisonment for up to one year.
Partial non-payment means making a payment in the amount of less than half of the amount payable (Note to Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
In case of complete non-payment of wages, pensions, scholarships, allowances and other payments established by law for more than two months or payment of wages for more than two months in an amount below the minimum wage established by federal law, the specified managers face (Part 2 of Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation):
Fine in the amount of 100,000 to 500,000 rubles. or in the amount of wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of up to three years;
Forced labor for a period of up to three years with or without deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities for a period of up to three years;
Imprisonment for a term of up to three years with or without deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or carry out certain activities for a term of up to three years.
If non-payment (partial or complete) has resulted in grave consequences, the head of the organization (branch, representative office, separate structural unit) may be held liable in the form (Part 3 of Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation):
A fine of from 200,000 to 500,000 rubles. or in the amount of wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of one to three years;
Imprisonment for a term of two to five years with or without deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or carry out certain activities for a term of up to five years.
It should be noted that both administrative and criminal liability can occur only in the presence of guilt (Article 2.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, Article 14 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). Non-payment of wages entails criminal liability only if the enterprise, institution or organization has funds and the non-payment is due to self-interest or other personal interest of the head of the organization (branch, representative office, separate structural unit).
This is for you to contact the State Tax Inspectorate and the police so that the employer can be checked why he is not paying the salary.
You can submit an application to the authority via the Internet on the website of these organizations (except the court), the response in this case is within 30 days.
And of course, your right to go to court with a Statement of Claim.
Clarification: if the employer pays the salary arrears, but does not pay interest under Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then the employee is obliged to go to work, because the employee suspends work due to non-payment of salary, and interest under Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is not wages.
And then the payment of interest under Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation will be decided through the inspection authorities or the court.
Is it necessary to submit a Notice of Work Suspension due to non-payment of wages under the contract? Is there a unified form for such notification? When must it be submitted to the employer? We will answer these and other questions and provide a sample.
What to do after submitting your application
Having stopped working on the basis of an application, you can return to it only after the employer has fully repaid the debt. It is important to understand the following: at the time of your absence from work, you retain not only your position and length of service, but also your average earnings. In other words, during the period of absence the employer is obliged to pay you a salary based on your average earnings. That is, for you to return to work, the company must not only repay the existing debt, but also pay the amount accrued during the period of your absence.
Average earnings during work suspension
Having received a notice from the employer indicating readiness to pay wages, the employee is obliged to go to work the next day. If an employee ignores the employer’s message and does not go to work, then he can be fired for absenteeism on legal grounds - paragraphs. “a”, clause 6, part 1 article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The procedure for calculating average earnings for this period of time is as follows. Initially, the billing period is determined and then the amount of payments for this period that will be included in the calculation.
The billing period in this case is 12 months. Months are taken as calendar months, starting with the month preceding the month for which the calculation is made. For example, if the suspension of work was in December 2021, then the billing period will be from December 2021 to November 2021. The employer has the right to change it to another period. In this case, it is important to consider the following conditions:
- The amount received in the calculation taking into account a different period should not be lower than the amount received in the calculation in the usual way;
- A different billing period must be fixed in one of the following documents: a local regulation or a collective agreement.
Average earnings for the period of suspension will be calculated as follows: average daily earnings multiplied by the days of suspension.
Average daily earnings will be equal to the accrued amounts for the billing period, divided by the number of days actually worked by the employee.
Reasons for registration
Before ceasing to work, a specialist must inform the employer in writing of his intention not to go to work. To do this, you need to draw up an application for suspension of work due to a delay in payment of more than 15 days.
The application must be filled out; you cannot simply stay at home 15 days after the salary delay.
This action will be regarded as a violation of labor discipline (absenteeism), for which the employer can unilaterally terminate the employment relationship with the employee. This should not be allowed.
It is imperative to notify the employer in writing.
In this case, 1 copy of the form with an acceptance note from the employer’s representative will be evidence of notification to the organization of the subordinate’s desire to stop working.
You can also file a claim with the employer about the presence of overdue wages and demand their payment.