What payments are due to a business traveler?
The definition of a business trip is given in Art. 166 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It is indicated that this is a trip to a remote area for a specific period, necessary to resolve a range of issues identified by the hiring company. A specialist goes to another city not of his own free will, so the costs associated with a business trip are borne by the employer.
In Art. 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation indicates what the payment for a business trip made in Russia or abroad consists of. It includes:
- reimbursement of expenses associated with travel to the destination and back (cost of transport tickets);
- compensation for the cost of a booked room, rented room or apartment;
- reimbursement of additional expenses associated with living away from home - daily allowance;
- compensation for other expenses related to the trip and incurred with the consent of the hiring company.
The last category includes expenses for visa support, purchasing an Aeroexpress ticket, taxi or car rental in a foreign city, insurance, communications, etc. These expenses must be confirmed by checks, receipts or BSO.
How travel allowances are paid is determined by the employer in local regulations. He prescribes what amount of daily allowance is due to a specialist sent on a business trip. The law sets the following limits:
- 700 rub. per day – for business trips in Russia;
- 2.5 thousand rubles. – for overseas business trips.
Amounts established within these limits are not subject to personal income tax and insurance premiums are not charged. Income tax is paid on the excess amount and deductions are made to extra-budgetary funds.
The law does not prohibit a company from setting daily allowances below the specified values or making them differentiated depending on the position held by the employee. It all depends on the financial capabilities of the commercial structure and its attitude towards its own staff.
Accrual of travel allowances in 2021
What is daily allowance and what is its limit for business trips within the country and abroad
Per diem is usually called the additional expenses of a posted worker, which he incurs as a result of staying for official reasons outside the area where he lives.
Daily allowance is paid for each day you are on a business trip, including those spent en route
This is exactly how they are interpreted in the wording of paragraph. 3 hours 1 tbsp. 168 of the Labor Code (LC) of the Russian Federation, obliging the employer to reimburse the employee for this type of travel expenses.
At the end of 2021, information appeared that from 2021 daily allowances would be cancelled. However, she found no confirmation. The relevant provisions of the law have not changed, which means that daily allowances must still be paid in 2021.
Maximum amount of daily allowance for trips in Russia and abroad
The maximum amount of daily allowance is legally defined in the Tax Code (TC) of the Russian Federation. They are indicated in paragraph. 12 clause 3 art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and are:
- 700 rubles per day when traveling around Russia;
- 2.5 thousand rubles per day for business trips abroad.
The employer has the right to set the daily allowance for its employees either less or more than these limits. However, if they are exceeded, he condemns himself to additional bureaucratic costs associated with taxation of these amounts.
The amount of daily allowance is determined by the financial capabilities of the employer. Although in some cases, to be honest, his greed and disregard for the staff may be of key importance. But from the point of view of the law, there will be nothing to complain about.
I worked for a large company and was in the process of obtaining travel certificates in accordance with all the frameworks of the legislation of the Russian Federation. And on the basis of them [the employees] in the accounting department they issued payments. Each company has its own.
In my company, business travelers traveled around the region - on average 100 - 200 km from the city. 1000 rubles per day for housing and 300 for food. You had to report for renting an apartment and bring a receipt from the hotel; you couldn’t do it without it.
olga-koshka2
https://www.bolshoyvopros.ru/questions/2177592-na-kakie-traty-vydajutsja-sutochnye-dengi-komandirovannym.html
To determine the amount of daily allowance for its employees, the employer must draw up a local act where it should be registered. The easiest way to do this is to include the corresponding clause in the Business Travel Regulations (). But you can also issue a separate order ().

Sample order to determine the amount of daily allowance
What can you spend your daily allowance on and do you need to document it?
All questions regarding per diem arise because this is the only item of travel expenses that is not subject to documentary evidence. If the cost of travel and accommodation on a business trip is compensated based on the amounts indicated in tickets and invoices, then no documents are needed for daily allowance: it is enough to reflect this expense item in the advance report and correctly calculate the amount in accordance with the local act and the current general rules, and accounting compensates for it by default.
If your company sends you on a trip, it pays for your travel and hotel accommodation, for which you must report upon return by depositing round-trip transport tickets and a check from the hotel into the accounting department. The daily allowance is your pocket money, i.e. This is for food, local transport, etc.
dydySacha
https://www.bolshoyvopros.ru/questions/2177592-na-kakie-traty-vydajutsja-sutochnye-dengi-komandirovannym.html
However, to say that daily allowances are not subject to documentary confirmation at all would be a sin against the truth. When issuing an advance before a trip, the length of stay on a business trip is calculated based on the dates in the corresponding order, and it is they that serve as the basis for calculating the total amount of daily allowance. When an employee reports upon return, the marks of departure and arrival in his travel certificate and the corresponding dates in travel documents (tickets) are taken as a basis.
...per diem is a certain amount sufficient for a person on a business trip to be able to buy food with it. Or go to the cafeteria. As far as I remember, accommodation was always a separate line in the advance report and at the hotel you always had to take checks and confirmation that you lived there. Separate money was allocated for this, for which it was necessary to account for after the business trip. And there was no need to report for daily allowance—just a note on the travel certificate was enough.
Andrey V.B.
https://www.bolshoyvopros.ru/questions/2177592-na-kakie-traty-vydajutsja-sutochnye-dengi-komandirovannym.html
By default, it is believed that this money should be spent on food for the employee during a business trip, travel by local public transport, etc. In practice, it turns out that if he ultimately has something left in his hands from the amount issued, this is his legal profit, and when he doesn’t fit into it, that’s his problem.
When an employee has actually spent money on some kind of entertainment, even on intimate services, but has saved money on food, for example, by stocking up on instant noodles, the employer has no right to make claims against him. And harm to one’s own health is a personal matter for such an employee.
...[daily allowance] for students was 50 rubles per day (one trip on the metro), and for my colleague and me - 100 rubles. You can't go wild with this money. In total, each of us (including students) spent 5,000 rubles. in four days. This money was spent on food, travel around Moscow and excursions. This is how our native university takes care of us.
Natalya Yu.
https://www.bolshoyvopros.ru/questions/2177592-na-kakie-traty-vydajutsja-sutochnye-dengi-komandirovannym.html
In the example, the author mentions excursions among expenses, which, to put it mildly, are difficult to classify as travel expenses. The employee has the right to make such expenses from his personal funds. And he cannot demand compensation from the employer. The situation is similar with trips to the bathhouse, gym, circus, zoo, theater, etc. - but you never know how an employee is used to spending his free time at home and on trips.
Another question is that for the 50–100 rubles per day mentioned in the example, you can’t really eat, not only in the capital, but also in cities where prices are not so high. However, if the local act of the employer provides for this exact amount, there may only be a reason to think about whether to look for another, more generous one. But there is no violation of the law.
Joke. Upon returning from a business trip, the employee draws up an advance report, among other expense items he indicates “a girl in the room - 2 thousand rubles.” The accountant calls him and asks him to refrain from such frank language. They agree that in the new report the employee writes “driving nails in the room.”
After some time, the same employee is sent on a new business trip, upon his return he again writes a report, where he indicates: “... driving nails in the room - 2 thousand rubles, repairing a hammer - 20 thousand rubles...”
How to calculate the amount of the advance before the trip?
The current legislation specifies how business trips are paid. It states that the employee is required to pay an advance before going on a trip. Its amount is calculated based on the following factors:
- approximate cost of travel there and back;
- the amount of daily allowance for the entire planned period of the trip;
- other expected expenses of the specialist.
The advance is paid on the basis of an estimate, which is drawn up by an authorized accounting employee and given to the chief accountant and the head of the company for signature. The issuance of travel allowances before departure can be made on the basis of an application drawn up by the employee himself and containing a calculation of expected expenses.
You can pay the advance in two ways:
- from the cash register in cash (in rubles or foreign currency depending on the country of destination);
- to a specialist’s bank card.
The organization has the right to pay individual employee expenses (for example, the cost of booking a room, plane tickets) from its current account. In this case, it deducts them from the advance amount. Failure to pay travel allowances before departure gives the specialist the legal right not to go anywhere.
Advance calculation example
The employee is sent on a business trip to Perm in the period from 16.06 to 20.06 (five calendar days). He has a hotel booked for 4 nights (room rate is 1,000 rubles per day), which must be paid on the spot. Previously, the organization bought train tickets. The company’s local regulations establish the amount of daily allowance for domestic Russian business trips – 700 rubles. in a day. How to pay for a business trip before the employee departs?
The cost of the hotel will be 1,000* 4 = 4,000 rubles.
The daily allowance will be 700 * 5 = 3,500 rubles.
Tickets have been paid for previously and are therefore not taken into account in the calculation. The amount to be issued before the employee’s departure will be: 4,000 + 3,500 = 7,500 rubles.
The influence of travel allowances on the amount of vacation pay
Business trips are not taken into account when calculating the amount of vacation pay - both by salary and by the number of days.
An example of calculating vacation pay taking into account a business trip
Senior Inspector P.E. Krivoruchko was on a business trip twice during the billing period (12 calendar months) - from May 10 to 24 and from June 15 to 18. He wants to take a vacation from September 1, which means both business trips will fall within the billing period. The standard vacation duration is 28 days. Salary P.E. Krivoruchko’s salary for the year, excluding travel expenses, amounted to 620 thousand rubles. Over the past year, the senior inspector has never been sick. The employee also received travel allowances based on average earnings of 33.5 thousand rubles.
We calculate the estimated number of days in May and August, since the business trip days fell in these months (fifteen in May and four in August). The average monthly number of calendar days is 29.3.
The estimated number of days in May will be (29.3/31)*(31–15)=(29.3/31)*16=15.1 days.
We calculate the estimated number of days in August (29.3/30)*(30–4)= (29.3/30)*26=25.4 days.
The number of days in the billing period will be 10*29.3+15.1+25.1=334.5 days.
And finally, we count vacation pay (620000/334.5)*28=1853.5*28=51898.4 rubles.
Final payment for business trip
To make final payments to the employer for a business trip, the employee draws up and submits an advance report to the accounting department. He is obliged to do this within three days after arriving back. The form of the document is established by local regulations of the company: it is possible to use the unified AO-1 form or your own sample.
From the report it becomes clear how travel allowances are paid upon the trip. There are two possible outcomes: the employee will be transferred funds for the amount spent in excess of the previously issued advance or they will receive the unspent surplus from him.
The report reflects:
- name of the employer;
- Full name and position of the employee;
- destination;
- the amount of the advance received;
- list of expenses made;
- the amount of surplus (overspend).
The information from the report is documented: the compiler attaches checks, receipts, contracts and other papers, from which the amount of his expenses becomes clear. The transfer of travel allowances to the salary card is made after the submitted form is checked by the accountant and approved by the manager.
If the specialist has not retained supporting documents regarding expenses of a certain type, the question of the possibility of compensation remains at the discretion of the employing company. If she decides to cover these expenses, they will be subject to personal income tax.
Confirmation of business trip expenses
All business travel expenses for which reimbursement is expected must be documented. These are tickets for all types of transport, receipts from gas stations, etc. Accommodation in a hotel is confirmed by an invoice and a receipt, in a rented apartment - by a rental agreement and a receipt for receipt of money.

Hotel form 3G replaces a cash receipt
Electronic travel documents are confirmed:
- for an airplane - a paper ticket receipt and boarding pass (or control coupon);
- for a train - a control coupon.
Taxi travel is confirmed by a cash receipt or a receipt in the form of a strict reporting form.
The traveler receives money for expenses before the trip, and after returning, within three working days, he submits an advance report, which describes how the advance was spent, and a final report. If there are unspent amounts, they must be returned to the company, and if there was a justified overspending, then the employer will pay for it. Daily allowances are not included in the reports.
If documents are lost
Some documents can be restored. For example, you can request a certificate from the airport or hotel about the cost of tickets or accommodation. If it is not possible to restore the documents, the head of the organization makes the decision whether to pay the expenses or not.
How is a business trip paid in 2021: average earnings
In Art. 167 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that an employee sent on a business trip retains the position held in the company and the average salary (AE). To calculate the amount payable for days on a business trip (C), you must use the formula:
C = SZ* K, where
K – number of days of business trip. When calculating this indicator, the accountant is guided by the company’s work schedule. He adds:
- working days spent at the destination;
- days spent traveling there or back.
For weekends and holidays that fall during the trip, the average salary is not paid in a situation where the employee was on vacation. If these dates were devoted to resolving official issues, the remuneration is calculated in a special manner.
Paying for a business trip based on average earnings involves the following algorithm for calculating it:
NW = W/BH, where:
- Z - the total salary received by the specialist for the billing period - 12 months preceding departure on the trip. For example, if a specialist goes on a business trip in May, the accountant will carry out calculations for the period from May 1 of the previous year to April 30 of the current year.
- K – number of days worked in the billing period.
Payment for business trips in 2021 involves two possible nuances in calculating SZ:
- If a specialist is sent on a business trip in the first month after employment, the SZ is calculated for the period from the first working day to the last date before departure.
- If in the previous 12 months the specialist was on leave for employment or to care for a young child, calculations are made for the year preceding this time.
The “K” indicator includes all days when the specialist was physically present at the service. Dates when the employee was absent for any reason (vacation, time off, temporary disability, business trip, etc.) are not summed up.
To determine wages during a business trip, you need to sum up all the citizen’s income related to work (salary, allowances, bonuses). The calculation does not include social benefits (sick leave benefits), travel allowances, amounts of financial assistance, food allowances, etc.
Average earnings saved while traveling are subject to income tax and insurance contributions. In the 2-NDFL certificate it is reflected using the code “2000”.
What business trip expenses are eligible for reimbursement?
The main expenses of a business traveler include:
- accommodation;
- travel to and from the business trip;
- nutrition.
In this case, travel and accommodation expenses are necessarily reimbursed, and meals are usually paid for from the daily allowance and basic salary.
Payment for accommodation on a business trip in 2021

When booking a hotel, you should familiarize yourself with the living conditions in advance, read reviews, compare the price and the comfort offered
Most often, business travelers choose a hotel to stay - it’s more convenient and easier to confirm expenses. Since the range of prices in hotels is very significant, it is usually prescribed in the internal regulations on business trips what class of hotel the manager, other managers, and ordinary employees can afford.
You can live in a rented apartment while on a business trip, but in order to confirm expenses, the owner of the apartment must conduct business legally, for example, be an individual entrepreneur. In this case, he will be able to issue a confirmation document.
If the host country has its own dormitory, ordinary employees are usually accommodated there.
If a business traveler has a delay on the way (for example, planes are canceled due to bad weather, and therefore the employee cannot make a transfer and fly), the employer pays for his accommodation while waiting.

Expenses due to forced delays in transit are paid by the employer
When staying in a hotel, only accommodation is paid for (drinking in a bar or going to a SPA at the expense of the employer is not possible).
When an employee on a business trip lives with relatives or friends, he is not entitled to compensation.
Payment for travel on a business trip
The employer is obliged to compensate the cost of travel to the place of business trip and back. If the business trip location is far from the main one, most often these are plane tickets. Other travel options are also possible - by train, bus, taxi, private car.
Judicial practice shows that taxi costs are also included in the fare. But at the same time, their expediency is taken into account (for example, night departure of an airplane).

Supervisory authorities will not object if a car is rented for a manager on a business trip
How are expenses reimbursed when traveling on a business trip using personal transport?
When traveling by personal car to a business trip, expenses for gasoline, repairs, and parking are reimbursed. And also the employer can pay compensation, the amount of which is determined independently. There is another option - to arrange a trip in a personal car on a business trip as renting an employee’s car for production needs.

An example of a memo for a business trip in a personal car
Payment for food
The law does not provide for payment for meals for employees, but the employer can pay for meals on its own initiative.
Often in hotels breakfast is included in the price. In this case, you can adjust the daily allowance to the cost of breakfast. You don’t have to do this - in this case, the cost of breakfast is not taken into account when calculating income tax and is taken into account in insurance premiums and personal income tax.
Daily allowance

You can spend your daily allowance on anything
Daily allowances are issued to business travelers for related needs - most often food. At the same time, the employee is not required to report daily allowances. Daily allowances are paid even for days on the road (as well as forced stops along the way) and for holidays and weekends when the business traveler does not work.
The amount of daily allowance can be any, but there are amounts that are not subject to personal income tax:
- 700 rubles - within Russia;
- 2500 rubles - abroad.
The daily allowance may be higher, but then income tax must be collected from the amount exceeding the specified amount.
When the employer pays the taxpayer expenses for business trips both within the country and abroad, the income subject to taxation does not include daily allowances paid in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, but not more than 700 rubles for each day of a business trip in the territory of the Russian Federation and no more than 2,500 rubles for each day of travel abroad.
Clause 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
https://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_28165/625f7f7ad302ab285fe87457521eb265c7dbee3c/
For the days of departure and arrival, daily allowances are also paid in full - even if the employee left at 23.59.
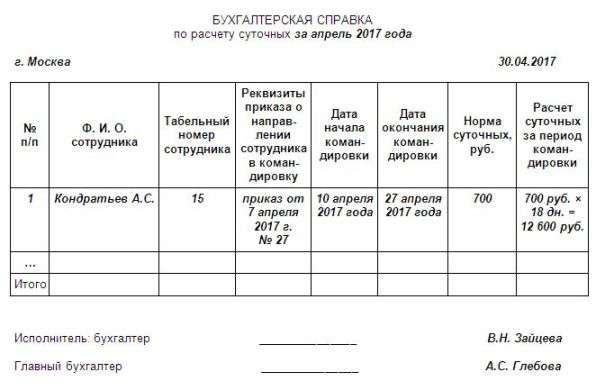
Calculation of daily allowance is confirmed by an accounting certificate
An example of calculating daily allowance for traveling abroad
Manager P.L. Bukhankin was sent on a business trip from Moscow to the Minsk branch (Belarus) to improve sales figures for heaters. The daily allowance at the enterprise is standard. P. L. Bukhankin departs from Moscow on March 25 at 23.00 and arrives on March 26 at 01.30. On March 26–27, P. L. Bukhankin carries out his assigned tasks in Minsk, then on March 27 at 16.00 he flies back to Moscow. For March 25 and 27, the manager will be paid a daily allowance in the amount of 700 rubles, for March 26 - at the foreign rate (2,500 rubles). The daily allowance will be 700*2+2500=3900 rubles.
For one-day trips, per diem is not required, although the employer may provide compensation at its discretion.
Other expenses
All additional business trip expenses are reimbursed based on their production necessity. For example, if an employee decides to spend money on entertainment on a business trip, then he pays for it out of his own pocket, and if, due to the nature of his work, he needs to take significant luggage with him, the employer will pay for it. In general, any additional expenses approved by the employer are subject to compensation.
Since insurance is included in the cost of travel tickets, the employer usually pays for it. If, due to business needs, an employee is forced to use public transport (metro, trolleybuses, minibuses), the employer usually reimburses them. The same applies to mobile communications and the Internet - they are paid for when necessary for production.
Passport and visa
On a foreign business trip, the employer is obliged to bear the costs of obtaining a visa and a foreign passport. Daily allowances abroad are converted into the currency on the date of accrual. Other business trip expenses are reimbursed at the foreign currency acquisition rate. If there is no certificate of currency exchange, then at the Bank of Russia exchange rate.
If an organization attracts a foreigner who is not an employee of the company, this is not considered a business trip, and accordingly, associated expenses are not reimbursed.
Sick leave payment
When a business traveler falls ill, the employer is obliged to pay him temporary disability benefits, additional living expenses (if he had to stay late due to illness and the treatment is not carried out on an outpatient basis) and daily allowance.
Labor Code: payment for business trips on weekends
Average earnings for weekends and holidays spent on a business trip are paid in two situations:
- If the specialist actually worked on these dates.
- If the specified days include travel time, departure to your destination or return to your hometown.
These dates include the rules on payment of overtime work formulated in Art. 153 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Salary calculations during a business trip are made in one of two options:
- The employee is not given additional rest time and is paid for the day worked at double the rate.
- The employee is given one day off and is paid in the “standard” way: in the amount of one average daily salary.
The company has the right to increase remuneration for overtime work in accordance with the provisions of local regulations. The amount due to the specialist is subject to income tax and contributions. It is shown in the 2-NDFL certificate with the code “2000”.
The procedure for paying for business trips assumes that for weekends and holidays during which the specialist was on vacation, the transfer of average daily earnings is not provided. Employee compensation is limited to per diem.
Tax and accounting of business trips
Travel expenses within the established norms are classified as other expenses and are taken into account when calculating income tax. However, they are not taken into account when calculating insurance fees and income taxes. An exception to the collection of personal income tax is daily allowance for an amount of more than 700 rubles within Russia (2,500 rubles abroad) and expenses that are not supported by documents. Additional payments before salary on a business trip can also be taken into account when calculating income tax.
Insurance premiums from daily allowances are charged for amounts over 700 and 2500 rubles (for Russia and abroad, respectively).
Table: accounting entries for travel expenses
| Type of expenses | Debit | Credit |
| Issuing an advance to a business traveler | 71 | 50 |
| Writing off expenses on a business trip | 20, 26, 44 | 71 |