Taking into account the physical capabilities of disabled employees, legislators have made more preferential working and rest conditions for this category of workers. For example, their paid vacation time cannot be less than thirty days (unpaid vacation time can last up to sixty days), and such subordinates are allowed to work overtime only after receiving written consent from them. Federal regulations also provide for reduced working hours for people with disabilities. Many organizations are reluctant to comply with this requirement. Although this preference is guaranteed to persons with disabilities by both the Labor Code and the Law on Social Protection of Persons with Disabilities No. 181-FZ of November 24, 1995 (as amended on July 29, 2018).
Shortened working hours for disabled people of groups 2 and 3
People in the second group can get a job, but with certain conditions of activity. Let's take an example: if a person is deaf, he can be used physically or mentally.
Citizens who have received the third group can work almost anywhere. They have only partially lost their ability to work and are not intended to carry out activities with increased loads.
A production manager who has agreed to hire a disabled person of group 2 or 3 as an employee is forced to provide such a person with working conditions in accordance with the Labor Code. Such a worker also has the right to count on being given the opportunity to self-realize and join the work team.
Working hours for an employed citizen with a similar social status differ from those determined by law. The code states that a healthy person can work a maximum of 40 hours per week on a five-day schedule. Regarding persons with disabilities, a quota has been established for them - a maximum of 35 hours. In addition, the employer does not have the right to force such employees to work at night or to work beyond the norm, without their written consent.

In turn, the employer must provide acceptable working conditions so that the disabled person can perform the tasks assigned to him. If legislative acts are violated by the employer in relation to an employee with a disability, the latter has the right to contact the Labor Inspectorate with a written complaint. And if, after an investigation, violations are revealed, the employer will have to answer according to the law.
Working hours for disabled people: legislative norms
When declaring to an employer the right to work a shortened working day, an employee with a disability should be guided by two legal acts:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation – article 92 is devoted to reduced working hours;
- Law No. 181-FZ (dated November 24, 1995) – the working conditions of disabled workers are stated in Art. .
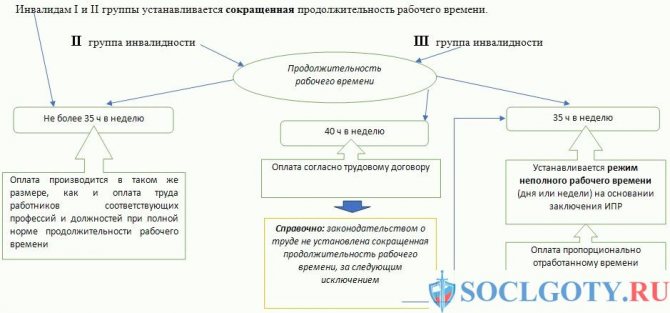
What are the working hours for disabled people is explained in both sources. Law No. 181-FZ and the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that employees with group I/II disabilities must have reduced working hours - they have the right to work no more than 35 hours a week. Let us remind you that a normal, ordinary working week is five hours longer and equals 40 hours.
An important provision is contained in Article 23 of Law 181-FZ: despite the fact that the working hours for disabled people are reduced, an organization or entrepreneur should pay for their work as for a full working day. That is, the salaries of persons with disabilities cannot be cut because they work less than other colleagues.
If a disabled person agrees to work more than thirty-five hours a week (and this is not prohibited by a medical certificate), his work beyond the preferential norm is paid as “overtime” - in an increased amount established by Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Please note that a shortened working week is provided only for employees with disabilities of groups 1 and 2. They are assigned to people with the most severe and irreversible diseases, which was taken into account by legislators when establishing labor benefits. The length of working time for a group 3 disabled person does not differ from the usual weekly norm of 40 hours.
How to reduce working hours for disabled people?
How long a person with a disability must work is determined by law. Reducing time spent at the workplace is possible only in accordance with a medical report provided in conjunction with the requirements of an individual rehabilitation program. The last document is of greater significance, since it is used by the manager to set the length of the working day.
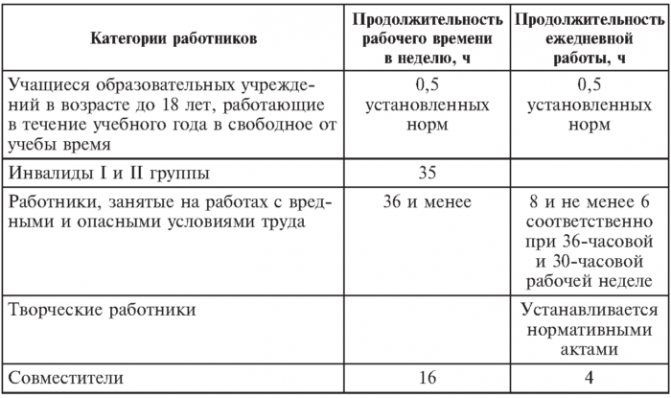
Among the various options, there is usually a work week consisting of five days, 7 hours daily, with days off on Saturday and Sunday. That is, for a disabled person, from Monday to Friday, the time for work is one hour shorter.
If there are no restrictions on the length of the working day, the work schedule can be drawn up as follows: from Monday to Thursday for 8 hours, and on Friday only 3. Regardless of how much time a disabled person spends at the enterprise, he has the right to get a break for rest and meals . What is provided by current legislation.
If there are no other requirements in the rehabilitation program, a week may consist of six working days and a day off. Moreover, from Monday to Friday working hours are 6 hours, and on Saturday - five.
Medical certificates that establish restrictions regarding a person’s capabilities are not particularly significant. The head of the enterprise mostly refers to the instructions that are defined in the individual rehabilitation program. The employer must strictly comply with this condition. Therefore, when establishing a shortened work schedule, he should not take into account the wishes of the employee.

Salary with shortened working hours for disabled people
When applying for a job or subsequently, by agreement with the head of the company, a shortened working day may be established for the employee. The accrued salary in this case is determined by the actual time worked or the amount of work done. That is, according to the order for the enterprise, signed by the head of the organization, on the formation of a 7-hour work schedule instead of the required 8, payment will be accrued accordingly for the period worked (7 hours a day). Such rules also apply to employees with 2nd and 3rd disability groups.
Minimum wage
In accordance with Article 133 of the Labor Code, earnings must be accrued in full, that is, no less than the minimum determined by the state. This applies to workers of any category. Namely, disabled people of groups 2 and 3, working 35 hours a week, cannot receive less than the salary established by law.
Features of calculation: how the salary of a disabled person is calculated
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the salary of a partially capable employee cannot be less than 1 minimum wage for the established number of hours per month (Article 133).
Minimum wage
In accordance with Article 133 of the Labor Code, earnings must be accrued in full, that is, no less than the minimum determined by the state. This applies to workers of any category. Namely, disabled people of groups 2 and 3, working 35 hours a week, cannot receive less than the salary established by law.
With a reduced schedule
It does not matter how many hours a disabled person works per week:
- 40 hours, as holders of III class;
- 35 hours as disabled people I and II.
In any case, he has the right to full payment for his work, which any other employee in his place would receive. That is, a shortened working week should not affect the salary of a disabled person.
Any work that goes beyond 35 hours/week (for the first and second groups) is overtime and is paid separately - in accordance with the Labor Code.
With a shift schedule
If the enterprise has established a shift work schedule, then difficulties may arise: long-term activities are often contraindicated for disabled people of groups 1 and 2. Therefore, the management of the enterprise is forced to introduce individual work schedules. In accordance with them, wages will be calculated.
If an employee has a group 3 disability, then he can work on a general basis (in the absence of medical contraindications).
When working remotely
An employee’s remuneration for remote work is made in proportion to the time worked.
Transfers to state funds for group III. Example
- 22% - to the Pension Fund;
- 2.9% – to the account of the Social Insurance Fund;
- 5.1 – to the Compulsory Health Insurance Fund.
Plus, income tax will be deducted from the employee.
Note. Employees with more severe illnesses (grades I-III) will receive slightly higher payments - thanks to proper tax deductions.

Nuances of remuneration for disabled people (different groups 1,2,3)
Legislative framework (Labor Code of the Russian Federation) Regulation of issues regarding wages for disabled people is based on the following regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation:
- Federal Law No. 181 of November 24, 1995 “On the social protection of disabled people in the Russian Federation”;
- Federal Law No. 143 of November 15, 1997 “On acts of civil status of citizens of the Russian Federation”;
- Federal Law No. 195 of December 10, 1995 “On the fundamentals of social services for the population of the Russian Federation”;
- Federal Law No. 178 of July 17, 1999 “On State Social Assistance”;
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation, article No. 133;
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation, article No. 92.
Based on these laws, a minimum wage level is established for disabled workers, which must be paid proportionally in accordance with established rules.
Does the shortened working week apply to disabled people in the first group?
Employees with disabilities in group I have the right to a shortened working week (up to 35 days). And the duration of one shift is also established by the rehabilitation program.
Working conditions
The “Sanitary Rules” provide for working conditions for citizens with disabilities. Persons with a similar status cannot work:
- at high or low temperatures, noise or poor lighting;
- with electromagnetic radiation, static electricity;
- with increased gas pollution, air pollution with dust;
- in the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the air;
- if the work involves prolonged physical activity, or the workplace is inconveniently equipped;
- if work activity involves excessive psychological stress (monotonous work, night shifts, irregular working hours).
Also, work should not cause aggravation of the disabled person’s well-being or provoke the development of any pathologies.
Guarantees and benefits
Disabled people have the right to receive certain benefits and guarantees:
- Possibility to take 60 days of vacation without pay. But all days must be taken off during the current year. The remaining days will not be rescheduled.
- They have an advantage during contraction. If the employee has received a disability due to direct work duties. And it wasn't his fault.
- In the event that an employee has been injured and his disability has not yet been established, he is required to be given a different place of work or position, with the condition that he will be able to cope with new responsibilities without harming his health.
- Distribution of jobs in accordance with Article 21 of the Federal Law.
- Prohibition on receiving an unjustified refusal when applying for a job that is related to the category.