If, as the number of staff decreases, workers are laid off, this is one procedure for preparing regulatory documents; if there are no layoffs, this is a different situation. Let's take a closer look.
Sample order to reduce personnel and staff
Order to reduce the number of employees, sample 2021 (word)
A local regulatory act on reducing the number of employees is prepared by employees of the HR department on the basis of primary documents, which are:
- decision of the company's owners to optimize the size of the enterprise and reduce personnel costs;
- decision of the company's owners to liquidate a branch, representative office, separate division or legal entity as a whole;
- court decisions on the grounds specified in paragraph 3 of Article 61 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The preamble of the regulatory document is virtually identical to the content of the primary document; the operative part of the order contains:
- timing;
- list of persons responsible for the event;
- name and number of units subject to liquidation;
- the draft of the new staffing table and the period from which it begins to operate.
Reasons for reducing the number of employees
The employer has the right to independently determine the grounds on which staff are being reduced (part 1 of article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 10 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2, Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated July 15, 2008 No. 413-O-O) .
Most often, reductions are the result of:
- low profitability;
- unfavorable economic situation;
- changes in production technology (for example, through automation).
In order to defend their point of view in court, management should obtain the necessary information to explain the reasons why the need for a regular event arose.
Sample order for optimization of numbers
- I : introduction by the employer of a part-time working regime - regulated by Art. 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- employees with time-based wages - in proportion to the time worked;
- workers with piecework wages - depending on the amount of work they perform.
- II : if the employer manages to reach a mutual agreement with the employees, then it is possible to conclude additional agreements with them to the employment contracts (Example 3). In this situation, there is no need to give workers two months' notice, and the duration of part-time work is not limited to six months.
- Order for dismissal under the article How to correctly fill out an order for dismissal for absenteeism See also: Labor legislation classifies absenteeism as a gross violation of labor duties, for a single commission of which an employee can […]
- Grounds for dismissal under the article Procedure for dismissal for absenteeism One of the grounds for termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer is the employee’s commission of a one-time gross violation of labor duties, in particular […]
- Reasons for dismissal from military service at one's own request Dismissal of a military personnel at one's own request Dismissal of a military serviceman at one's own request is a rare and rather complex procedure. Labor relations of military personnel are regulated not by labor [...]
Thus, the employer has the right to make a decision to introduce a part-time regime only if there is a threat of mass layoffs of workers, in particular, in conditions of a financial and production crisis.
The decision to introduce such a regime is made by the employer, taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization and in the manner established by Art. 372 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for the adoption of local regulations.
The employer has the right to introduce one of the following regime options:
a) part-time (shift) with a full work week;
b) part-time work week with full-time work (shift);
c) part-time work week with part-time work (shift).
Remuneration of employees when working part-time, in accordance with Art. 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, produced:
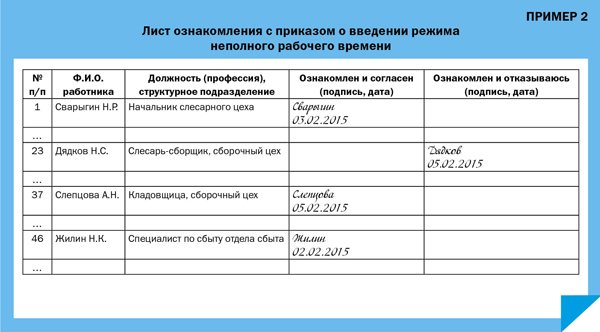
An employer who, in order to avoid mass layoffs of workers, has decided to introduce part-time work in an organization (enterprise), is obliged to warn employees about this at least two months in advance. The employer makes his decision with an order, with which employees must be familiarized with signature (Example 1). In addition, it is necessary for employees to express their consent or disagreement to work part-time. To do this, you need to fill out a familiarization sheet with the order (Example 2).
If the order specified a specific period for transition to part-time working hours, then an order to return to work during normal working hours is no longer required. If the period was not specified specifically (“...up to six months”), then an order to return to normal operation with a date is required.
In this case, the situation is regulated only by Art. 93 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:

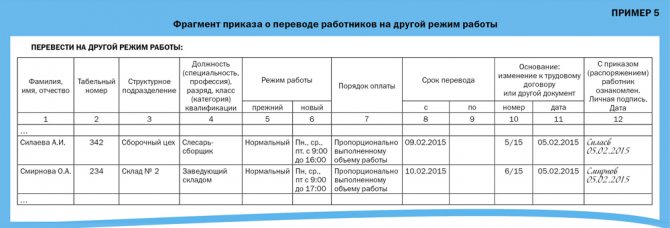
Based on the additional agreement, the employer issues an order to transfer an employee (Example 4) or a group of employees (Example 5) to the appropriate working hours.
II. Suspension of production (downtime)
Suspension of the employer's activities is not provided for by the Labor Code, however, labor relations are regulated not only by this document, but also by other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms (Article 5 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The term “suspension of proceedings” is contained in Law No. 1032-1.
In particular, as already mentioned, in accordance with paragraph. 2 parts of the second art. 25 of this Law, when production is suspended, the employer is obliged to notify the employment service authorities in writing within three working days after the decision is made to carry out the relevant measures.
What is the suspension of production in the context of the Labor Code? The answer to this question is found in part three of Art. 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, where temporary suspension of work for reasons of an economic, technological, technical or organizational nature is recognized as downtime .
Payment for downtime is regulated by Art. 157 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
• downtime due to the fault of the employee (personnel code VP ) is not subject to payment;
• downtime for reasons beyond the control of the employee and the employer (personnel code NP ) is paid in the amount of at least two-thirds of the employee’s salary or tariff rate, calculated in proportion to the downtime time;
• downtime due to the fault of the employer (personnel code RP ) is paid in the amount of at least two-thirds of the employee’s average earnings.
Even during the crisis of 2008, judicial practice developed that unambiguously answers the question of what type of downtime should be considered downtime that arose as a result of crisis problems: courts and inspection authorities do not consider the crisis a sufficiently serious circumstance that relieves the employer of blame, therefore “crisis downtime” » is recognized as downtime due to the fault of the employer and is subject to payment in the amount of at least two-thirds of average earnings. However, if the downtime is caused by the suspension of work at the customer, under whose contract the employer’s activities are carried out, then such downtime can be recognized as independent of the employee and the employer and paid in the amount of at least two-thirds of the salary.
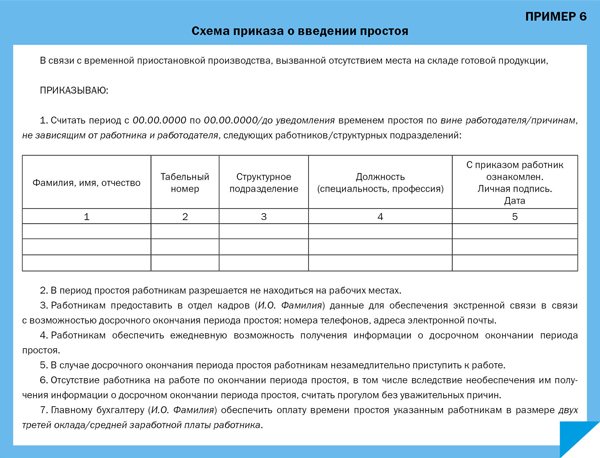
Under normal conditions, downtime is not formalized by order; it is reflected in the working time sheet after the fact. However, in cases where the employer becomes aware of the suspension of production in advance and he considers it possible that employees will not be at work during the period of suspension, an appropriate order may be issued (Example 6).
III. Leave without pay
According to Art. 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer can issue an order to grant leave without pay only on the basis of statements from employees:
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation (LC RF) approached this issue in a similar way[2]. The situation is far from new in our country, therefore, back in 1996, the Ministry of Labor approved an explanation on this issue, which remains relevant today:
Explanation
“On leaves without pay at the initiative of the employer”
(approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated June 27, 1996 No. 40)
In connection with incoming inquiries about the legality of sending employees on “forced” leave without pay at the initiative of the employer, the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation explains:
Leave without pay can be granted only at the request of employees for family reasons and other valid reasons (Article 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)[3].
“Forced” leaves without pay at the initiative of the employer are not provided for by labor legislation.
If employees, through no fault of their own, are unable to fulfill the duties stipulated by the employment agreements (contracts) concluded with them, then the employer is obliged in accordance with Art. 94 Labor Code of the Russian Federation pay for downtime in an amount not less than 2/3 of the tariff rate (salary).[4]
If the employer does not pay for downtime through no fault of the employees, then the employees have the right to appeal the employer’s actions to the labor dispute commission or to the court.
Many employers are able to reach a common language with employees and persuade them to apply for unpaid leave, explaining that this will help preserve jobs to which people are guaranteed to return. However, it is necessary to warn employees that only 14 calendar days of long-term leave without pay are included in the length of service giving the right to annual basic paid leave, and the length of service giving the right to leave for harm does not include all leave without pay.
IV. Reduction in the number or staff of an organization's employees
Reducing the number or staff of an organization is an extreme measure that employers sometimes have to use.
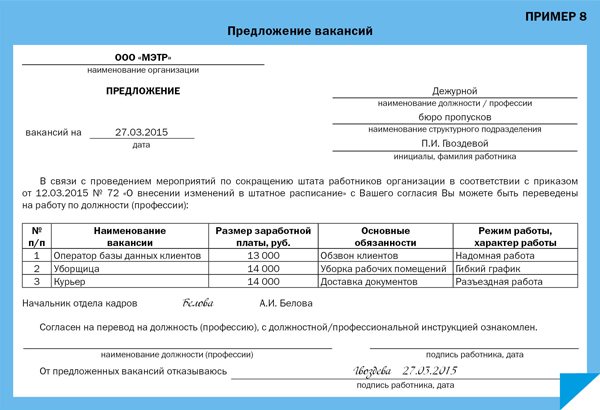
The employer has the right to dismiss an employee on these grounds only after he is convinced that it is not possible to transfer the employee to another job with his written consent. The impossibility of a transfer is determined either by the absence of vacancies suitable for the employee’s competencies (i.e., taking into account his education and work experience, knowledge and skills) and state of health - in this case, the personnel service is recommended to draw up an appropriate certificate (Example 7), or the employee’s refusal proposed work. If the employee agrees to the proposed job, a permanent transfer is issued. If there are vacancies, the employee is presented with an offer indicating the available vacancies and basic information about them (Example 8).
Employees must be notified of dismissal on the basis in question - personally and against signature - at least two months before dismissal[5]. We do not recommend indicating the exact date of dismissal in the notice, because it happens that on this day the employee is on sick leave or on study or other leave, and in such cases the notice with the exact date of dismissal becomes invalid, and the employer is obliged to notify the employee again of the upcoming dismissal, and again - two months in advance. If the notice states that dismissal will occur “no earlier than two months later” or no earlier than a certain date, then the notice remains valid, and the employee may be dismissed on the first day after sick leave or vacation (Example 9).

Despite the fact that the employee has already been notified of the upcoming dismissal, if a suitable vacancy for him appears in the organization, he must be offered this vacancy before a new employee is hired for it.
According to part three of Art. 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in a notice of dismissal, an offer may be made to an employee to terminate the employment contract before the expiration of a two-month period with payment to him of additional compensation in the amount of his average earnings, calculated in proportion to the time remaining before the expiration of the notice of dismissal:
With your written consent, the employment contract with you may be terminated before the expiration of the two-month notice period for dismissal, with the payment to you of additional compensation in the amount of average earnings, calculated in proportion to the time remaining before the end of the notice period.
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 25 of Law No. 1032-1, an employer-organization no later than two months, and an employer-individual entrepreneur no later than two weeks before terminating an employment contract with an employee must notify the employment service authority about this.
For failure to submit or untimely submission of information to the employment service, the employer may be held administratively liable under Art. 19.7 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offences. The fine for officials ranges from 300 to 500 rubles, for legal entities – from 3,000 to 5,000 rubles.
According to part one of Art. 82 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation no later than two months before the start of the relevant activities, the employer is obliged to send a notice of reduction in number or staff and possible termination of employment contracts with employees to the trade union body - if there is one (Example 10).
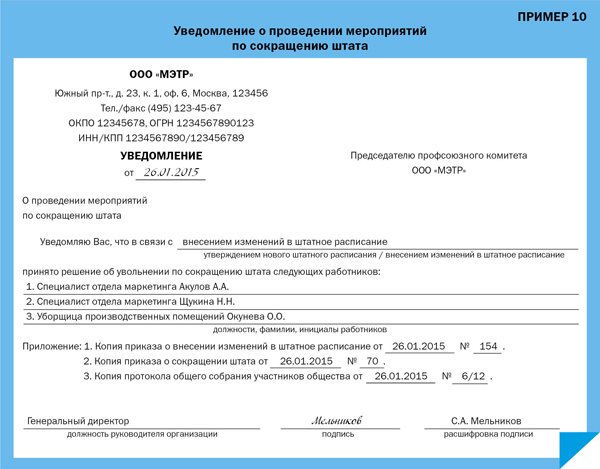
Attention should be paid to the following: if the constituent documents do not provide for the transfer of powers of the executive body of the organization to another person, then documents signed by an improper person related to the reduction of personnel or staff may be recognized as having no legal force. This, in turn, will entail the cancellation of the order to dismiss the employee and his reinstatement at work with payment of compensation for the period of forced absence.
Upon dismissal, the employee is paid severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings, which is reflected in the dismissal order (Example 11), and a corresponding entry is made in the employee’s work book (Example 12, Example 13).
If, two months after dismissal, the employee presents the employer with a work book without a record of hiring a new job and thus indicating that the employee was not employed during this period, he must be paid the average salary for the second month of employment. It is possible that the employee will present a certificate of employment during the second month, in which case he is paid the average salary in proportion to the part of the second month of employment during which he did not work. The payment is formalized by an appropriate order (Example 14).

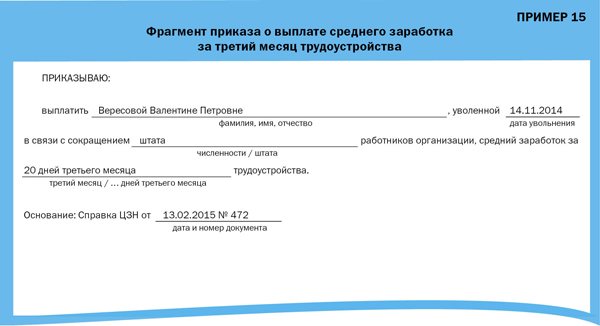
Finally, if three months after dismissal the employee submits a certificate from the employment authorities about the need to pay him the average salary for the third month of employment, the employer is obliged to issue a corresponding order (Example 15) and make the payment.
According to parts three and four of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if a separate unit located in another area is excluded from the organization’s staffing table, the dismissal of employees is carried out according to the rules provided for cases of liquidation of the organization. We emphasize that workers should be fired precisely in connection with staff reduction, and not in connection with the liquidation of the organization. The employer is obliged to offer them work only in the same area [6] where the liquidated unit is located - if, of course, in the same locality there are other separate structural units of this organization, and the employment contract is terminated with all employees, without benefits and restrictions ( including pregnant women, employees with small children, on vacation and sick leave).
[1] That is, reasons associated with changes in organizational or technological working conditions (changes in equipment and production technology, structural reorganization of production, other reasons).
[3] The current norm on this issue is contained in Art. 128 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
[4] In accordance with part one of Art. 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, downtime due to the employer’s fault is paid in the amount of at least two-thirds of the employee’s average salary.
[5]Part two of Art. 180 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
[6] That is, according to paragraph 29 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court dated March 17, 2004 No. 2 “On the application by the courts of the Russian Federation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation” (as amended on September 28, 2010), in the same locality.
I.V. Zhuravleva, consultant on labor law and personnel records
The Ministry of Justice of Russia, by Order No. 123 of June 19, 2018 “On approval of forms of civil registration forms and forms of forms of certificates of state registration of acts of civil status,” updated the forms of civil registration forms.
August 03, Moscow, Time Out Bar, st. Bolshaya Sadovaya, building 5
A new section has appeared on the website of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, in which department specialists have collected key information about the pension reform project. It explains who gets early retirement and other issues.
www.profiz.ru
See also:
Reducing headcount and staff: understanding the concepts
Clause 2 art.
81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows for termination of an employment contract when the number or staff of employees is reduced. But the Code does not specify what the difference is between such cases. HR specialists use the following terminology:
| Staff event | The essence of the event |
| Reduction in numbers | Dismissal of an employee whose position remains on the staff list |
| Staff reduction | Exclusion from the staff list of vacant positions |
| Reduction of number and staff | Dismissal of an employee with subsequent exclusion of his position from the staff |
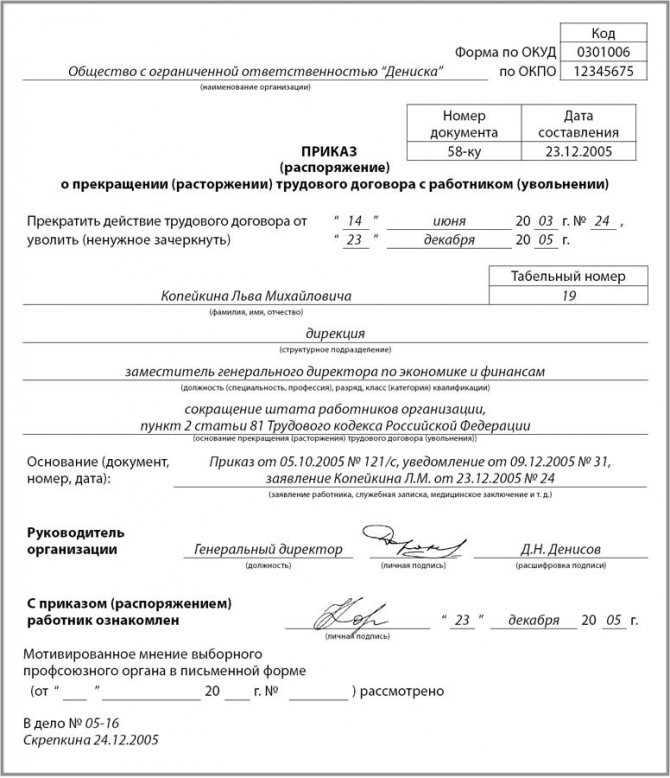
The reduction procedure is regulated by law. Its first stage is the issuance of an order.
How to write an order correctly?
If a unified form is used to draw up an order, then no difficulties should arise.
You need to fill in the blank lines. This can be done manually or on a computer. In any case, the manager must sign personally. If the order is written in free form or a company letterhead is being developed, then you need to know what information to reflect in it. A4 size office paper is tried on. At the top of the sheet, in the center, the company details are written. Under this data the name and number of the document are indicated.
The place of issue of the order is written just below and the date is written opposite it. The following is basic information: who is fired, when and for what reason. At the end the manager’s signature is placed. The order may be issued in connection with job reduction or early dismissal or payment of benefits. Based on the reason for which the order is drawn up, its content changes.
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilyeva
Civil law expert
Current legislation does not oblige managers to use forms T-8 and T-8a when drawing up an order for dismissal due to reduction. Employers may use letterhead that is developed and approved locally.
Due to job reduction

The decision to reduce a position is usually made due to automation of production processes, closure of branches, etc. If an enterprise is on the verge of bankruptcy, then its manager can remove individual staff positions, thereby increasing the load on the remaining employees.
The decision is formalized by order. Such an order is usually drawn up on company letterhead or in any form.
It provides information about which position needs to be eliminated. The date of change and approval of the staffing table is noted.
Instructions are given to the heads of personnel and accounting departments to notify employees, the trade union and the employment center about planned changes within a certain period. The surnames and initials of dismissed employees may be provided. A sample order for job reduction is given below.

With benefit payment
In accordance with current legislation, an employee who is laid off due to the liquidation of an enterprise is entitled to severance pay in the amount of average earnings. This is a kind of compensation for loss of income due to the fault of the employer. The average salary for a subordinate can be maintained for two months.
If after this period the citizen does not find a job and brings the corresponding certificate from the employment center to the former management, then he will be paid for the third month of unemployment. This is stated in Article No. 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.

The accrual of money is formalized by an appropriate order. The order is drawn up in any form or on company letterhead.
The order contains the following information:
- Full name of former employees who are entitled to benefits;
- for what reason were the employees fired;
- amount of compensation;
- reference to labor legislation (Article No. 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), on the basis of which benefits are paid;
- indication of the details of the certificate or decision of the employment center;
- who is responsible for monitoring the execution of orders.
An example of an order for payment of severance pay is given below.

If an order is issued to lay off an employee with payment of severance pay, then the unified T-8 form can be used. It is filled out in the standard manner. In the grounds for termination of the employment contract, a note is made regarding the accrual of compensation in the amount of average earnings. A sample dismissal order due to staff reduction with severance pay is given below.

Due to the early dismissal of an employee
According to the law, an employee, after receiving notice of a layoff, may resign early on his own initiative. To do this, he needs to submit a corresponding application to management.
On the basis of such a document, an order for early termination of employment relations will be issued. Such an order is usually drawn up on a T-8 form in the standard manner. The details of the employee’s application are noted in the grounds. An example of such an order is given below.
Dear readers! To solve your problem right now, get a free consultation
— contact the on-duty lawyer in the online chat on the right or call:
+7
— Moscow and region.
+7
— St. Petersburg and region.
8
- Other regions of the Russian Federation
You will not need to waste your time and nerves
- an experienced lawyer will take care of solving all your problems!
Form of order for layoff of employees
There is no standard order form, but some details must be indicated:
- name of company;
- name “Order”, its number;
- date of compilation no later than 2 months before dismissal;
- reasons for the reduction;
- actions taken as part of a regular event, the timing of their implementation and responsible persons;
- manager's signature;
- signature of employees familiar with the order and responsible for its implementation.
Sample order for layoffs in 2020
A reduction order, taking into account all the recommendations for its preparation, may look like this:

Order to reduce the number and staff of employees
Clause 2.6 is included in the order if the organization has a trade union.
Our example involves reducing both numbers and staff. In other cases, the content of the order is adjusted:
- when reducing staff (excluding vacant units), paragraphs 1, 3 and 4 remain relevant;
- when reducing the number of employees (dismissal), paragraph 1 lists the employees dismissed due to reduction with a further distribution of tasks according to paragraphs 2 and 4.
Sample order form
When using the standard T-8 form applied to one employee, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
| Field | Filling procedure |
| Name of company | The name of the company reflected in the statutory documentation is entered in abbreviated or full form. Additionally, the company's OKPO is provided. |
| Document No. | A number is affixed that corresponds to the numbering that the company uses when preparing administrative documentation. The number is assigned during the registration of the order in the journal for similar personnel-type documents. May include alphabetic, digital and symbolic signs; the company must focus on its own needs. There should be no repetitions of numbers within the same reporting period. |
| Document date | The day the order was issued. The document must be registered in the journal on the same day. |
| Contract number and date | Details of the employment agreement subject to termination. |
| date of dismissal | The last day of work of the dismissed person is determined based on the date the employee receives the notification paper from the employer. If desired, the employee can complete the work process with this employer at an earlier date, without waiting for the end of the notice period. In this case, the date of the last working day is set. |
| Employee data | A standard set of details of the dismissed person is provided - full name, personnel number, department and position. |
| Grounds for termination | The phrase from the Labor Code of the Russian Federation about the grounds for dismissal is transferred, taken from clause 2, part 1, article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. |
| Foundation documents | All the documents that made it possible to legally dismiss an employee due to redundancy are listed. |
| Signatures | It is necessary to put:
|
| Union opinion | If there is such a body in the organization, then a request is sent to it to obtain an opinion on the possibility of reduction. The trade union formalizes its opinion in writing; the details of this paper should be entered at the very bottom of the T-8 form. |
If a group of employees is subject to reduction, then it is possible to use the standard form T-8a, which contains a list of those persons who are subject to reduction in tabular form.
An example of an order:








