Rest time on a daily schedule
Rest time according to labor legislation is the time during which an employee is free from performing work duties and which he can use at his own discretion (Article 106 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Types of rest time are listed in Art. 107 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
These are general rules established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for all employees, regardless of their work mode. However, the activities of many employers have certain specifics in which employees have to work outside the usual eight-hour working day or on days provided for rest. Working on a daily schedule is one of the special cases of such specific activities.
In such circumstances, specific types of rest, their duration and the procedure for alternating working time and rest time should be prescribed in local regulations of employers (for example, in internal labor regulations - PVTR), provided for in vacation schedules and daily schedules, as well as in collective agreements and agreements. The texts of these documents may prescribe additional holidays of longer duration than those provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the possibility of providing additional days of rest, guarantees and compensation.
To ensure that the working and rest conditions for employees with a daily work schedule provided for by local regulations of the company are within the framework of current labor legislation, some requirements, restrictions and prohibitions should be taken into account.
Rights of an employee during daily duty according to Labor Code
The Resolution of the Secretariat of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions states that workers can be called to duty only in exceptional cases and in agreement with the trade union committee. What is considered “exceptional cases” is not specified in the Resolution. This document defines functions that should not be assigned to duty officers.
This is interesting: Labor veteran of the Kostroma region benefits
Nevertheless, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation speaks of the application of this norm to rescuers who are on standby at home (Regulations on recording the working time of citizens accepted into professional emergency rescue services, professional emergency rescue units for the positions of rescuers, approved by the resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated 08.06 .98 No. 23) Consequently, the requirement of the Regulations on service puts us in obviously worse conditions compared to the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Requirements, restrictions and prohibitions
In order for the work of employees working on a daily schedule to fall within the framework of the law, the employer needs to focus on the requirements established for such work and comply with a number of restrictions (Articles 91, 103, 110 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
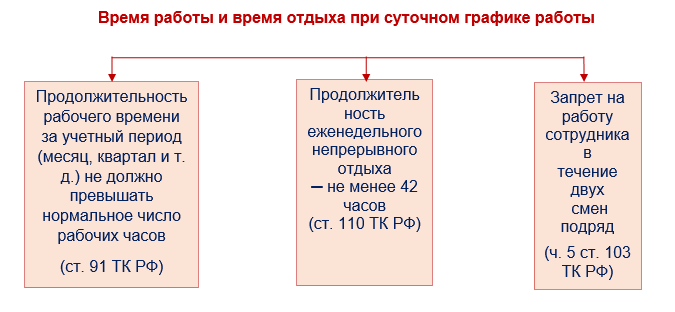
If the employer, when organizing work on a daily schedule, ignores existing requirements and prohibitions, the efficiency of the company and the productivity of employees, as well as their health, will deteriorate. And violation of labor laws may result in administrative penalties under Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Breaks during the working day
During the working day (shift), the employee must be provided with breaks for rest and food (Article 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The duration of such a break, according to the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is no more than 2 hours and no less than 30 minutes. These breaks are not included in working hours.
The specifics of the work of specific employees in certain companies may impose certain features on the provision of such intra-shift breaks. These nuances should be reflected in the PVTR. The law does not prohibit setting during working hours, for example, two breaks of an hour, four breaks of 30 minutes, or in another suitable mode.
If difficulties arise in establishing regulated breaks common to all employees working on a daily schedule, the time and duration of the breaks are established by agreement between the employee and the employer.
Art. 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation determines that in those jobs where, due to production (work) conditions, it is impossible to provide a break for rest and food, the employer is obliged to provide the employee with the opportunity to rest and eat food during working hours. The list of such work and places for rest and meals must be prescribed in the company’s local regulations.
Basic rules for daily work according to the Labor Code
Currently, some professions and positions have a 24-hour work schedule. Currently, the Labor Code does not directly regulate such a work schedule, but does not prohibit it either. This means that subject to certain legal requirements, a 24-hour work schedule is quite possible. The most common period for recording working hours is a month, since it is more convenient to adjust it, as well as familiarize the employee with it without violating legal requirements. The standard time in each month will be different, since the number of working days in the “standard” 5-day working week will be different.
Please note => Benefits for veterans of military operations in the Nizhny Novgorod region
Special breaks
Workers may be given special breaks due to the technology and organization of production and labor (Article 109 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The types of such work, the duration and procedure for providing special breaks are established by the PVTR.
If employees are forced to work outdoors during the cold season or in closed, unheated rooms, as well as in other necessary cases, special breaks are provided for heating and rest.
At the same time, the employer is obliged not only to equip premises for heating and rest of employees, but also to include special breaks during the employee’s working hours (Rostrud Letter No. PG/2181-6-1 dated April 11, 2012).
Three days later: set the mode correctly and pay
For timesheets, it is necessary to take into account not only the duration of daily work, but also the periods that can adjust it. The timesheet reflects the hours actually worked. Their number may differ from the number according to the schedule, since it indicates the planned days and hours of work and rest. During the accounting period, an employee can go on a business trip, get sick, take leave without pay, etc. 2. For overtime work. Since the first 2 hours of each shift are paid at one and a half times the rate, let’s check whether 16 hours (184 - 168) of overtime fit into this norm. To do this, multiply 8 shifts by 2 hours. We received 16 hours - the amount of the first 2 hours of overtime work on average for each of 8 shifts.
06 Jan 2021 marketur 1212
Share this post
- Related Posts
- What's on the receipt?
- Is it possible to provide documents from the Russian Register to outsiders?
- Benefit code 2887 for labor veteran
- Sample survivor certificate for destination
Weekend
Involving workers in working on a daily schedule should not deprive them of proper rest between shifts. Such workers have the right to legal days off guaranteed by Art. 111 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Their days off will not coincide with the usual Saturday and Sunday for most employees, but will be determined by their work schedule.
The number of days off may vary in different companies and for different categories of employees. For example, days off with a daily work schedule can be two or three days after 24 hours worked.
Rest on non-working holidays
Working on a daily schedule does not always allow employees to rest at generally established times. 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation non-working holidays. Working days coinciding with such non-working holidays will be considered regular working days for the employee.
What should an employer take into account regarding the organization of work and its payment on holidays:
- there is no need to request the employee’s consent to be hired to work on a non-working holiday if this day is scheduled for him to be a working day;
- pay for work on a non-working holiday at least double the amount or, at the employee’s option, single with the provision of time off;
- if only part of an employee’s work shift fell on a holiday, then only the hours actually worked that he worked on that day are paid at an increased rate (from 0 to 24 hours of a non-working holiday (Part 3 of Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation));
- if an employee was hired to work on a non-working holiday outside of the schedule (according to the schedule, this day was a day off for him), he must be paid for such a day in the same way as if this day was a working day for him (part 1, 3,4 of article 153 of the Labor Code RF).
The calculation of payment for work according to a daily schedule on a non-working holiday depends on the remuneration system established for the employee and the type of compensation chosen by him (double payment or single payment with time off).
Working at night without the right to rest
I work in a flower shop on the night shift. Since the salon does NOT close for a minute (for some reason the key is lost, or so they tell us), and I am alone in the salon plus surveillance cameras, there is no way to even go to the toilet, we work without the right to sleep, except for the duties of a florist, assigned duties cleaning ladies. The shift lasts 12 hours. For everything they pay 800 rubles per shift. When asked about increasing pay, the administration answers: if you want to earn more, take more shifts. But the subsistence minimum in our region is already 11,000, to earn even that, you have to work 14 nights a month, which is simply unbearable in this situation. Tell me, what health protection standards can be referred to in a dispute with the administration? Are there any regulations regarding working hours when working night shifts? And according to the calculation of payment for them, since daily workers receive a salary 3-4 times higher than the salary of night workers? What can you refer to in a dispute with our administration? During the working day (shift), the employee must be given a break for rest and food lasting no more than two hours and no less than 30 minutes, which is not included in working hours. And according to the calculation of payment for them, since daily workers receive a salary 3-4 times higher than the salary of night workers? Hope
Please note => Sample performance specification for MSE for driver
Let's sum it up
- With daily work schedules, all requirements for rest time according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation must be observed: a ban on working for two daily shifts in a row, compliance with the minimum legally established standards for the duration of intra-shift, inter-shift and continuous weekly rest.
- An employee on a daily schedule has the right to intra-shift breaks for rest and meals, and in some cases - to special breaks.
- The rest time between daily shifts should be twice the duration of the work shift.
- Employees working on a daily schedule are entitled to all types of leave provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: annual paid basic and additional leave, leave at their own expense without pay. Local regulations of the company may additionally provide for other types of leave.







