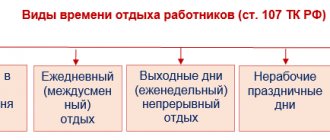
What are working hours
In Part 1 of the new edition of Art. 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation gives the concept of the working period regime.
This is the total time spent performing job or job functions that establish the employment contract and internal regulations.
This concept also includes:
- forced stoppage of the work process for technical or other reasons;
- eating without being absent from the workplace, unless a break is provided;
- a period of time of a special nature for heating;
- break from work to feed the baby.
The administration coordinates the length of time with the trade union committee. For example, drivers are provided with rest and gymnastic exercises.
The work regime provided for by the Labor Code consists of the following standards:
- Standard duration is 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week.
- Incomplete standard.
- Shortened day.
- Overtime, irregular work.
The last point provides for increased pay for working hours.
The daily routine involves being at the workplace 24 hours. It must be remembered that this mode of operation has a different, increased form of payment. Most often, this regime is used by the military, security guards and medical workers.
General provisions
Reduced working hours See
Encyclopedias and other comments to Article 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation Shortened working hours are established: for workers under the age of sixteen - no more than 24 hours a week; for workers aged sixteen to eighteen years - no more than 35 hours per week; for workers who are disabled people of group I or II - no more than 35 per week; for workers whose working conditions at their workplaces, based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions, are classified as hazardous working conditions of the 3rd or 4th degree or hazardous working conditions - no more than 36 hours per week.
Working hours standard
Based on Art.
91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the norm is the number of hours that must be worked out by agreement for a specific calendar period. The maximum standard is established by law. Exceptions are allowed in specified cases under the Labor Code. Limiting working hours contributes to:
- protecting workers' health, preventing physical and psychological fatigue;
- on-the-job training and professional development;
- improvement of working capacity.
The maximum working week is 40 hours. In addition, the duration of the period is influenced by working conditions, age, and health status.
Therefore, an alternative type is an incomplete or shortened week for a specific contingent of workers. The standard monthly, quarterly, and annual level of labor activity is determined by the executive body.
Working hours according to the law are:
- Five working days and two days off.
- Six work days and a day off.
- Flexible schedule with rotating weekends.
The legislation allows for other types of regime that take into account the specifics of production, working hours beyond the norm, and work on free days.
Average working day: formula
Depending on the form in which the value of this indicator is of interest - per employee or generally for all personnel, different formulas will be used for calculation.
To calculate the average working time per employee, the following formula is used:
Average duration = Actual number of hours worked / Number of days in the period
Thus, the average actual working day will be determined as the quotient of dividing the total number of hours worked by the employee by the number of days in the period under review.
If we are talking about the length of the day for the entire team, you should turn to another calculation formula:
Average duration = Actual hours worked total / Total number of employees
Accordingly, the use of a particular formula will depend, first of all, on the need to obtain specific information.
In the process of work of personnel and other departments of the company, there may be a need to obtain other average indicators of the organization’s performance. These include the average established and scheduled working day and other similar indicators, the use of which allows the company to organize labor activities within the framework of the law and carry out analytical activities.
Similar articles
- Sample working time schedule
- Sample working time schedule
- For whom is the 36 hour work week established?
- What is the maximum duration of overtime work?
- An example of calculating total working time accounting
Operating mode
The Labor Code article on working time includes the following characteristics:
- length of the working week;
- period of duty, watches, shifts;
- intervals in work activities of different nature;
- gradation of working and free days;
- use of labor in excess of standards;
- start and end times of the work process every day;
- other questions.
The regime is irregular, shift, flexible or round-the-clock, but at the same time divided into parts (breaks).
It is formalized in local regulations, regulations on labor regulations, and individual agreements for a specific group of workers. For example, in rural areas, irregular days are set for the summer period.
How many hours per week must a person work by law?
If the work takes place in shifts, then all the same, if you add up all the hours, then you should again get 40 hours a week. If a person works in shifts with the following schedule: from 8 a.m. to 10 p.m., then usually people work two days and rest for three days.
It turns out that a person works the required 40 hours a week, just with a different work schedule. This time schedule cannot be exceeded or the employer must pay extra for the hours. Different categories of citizens have their own time schedule. Children under 16 years of age work no more than 24 hours a week. From 16 to 18 years old already 35 hours.
Disabled people must also work 35 hours a week. On weekends, the employee must go out at will, but the employer must pay double for these days. People engaged in mental work, for example, teachers and kindergarten teachers should not work more than 36 hours a week.
Rules for irregular work
Based on Art. 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the need to engage outside of work hours is formalized by order of the head of the enterprise, subject to the admissibility of such a provision by the employment agreement.
The procedure for engaging in work beyond the standard:
- With a written instruction from the manager, the employee’s consent is not required; he is only familiarized with the order.
- Overtime hours are not stipulated by law; overtime is possible before the shift or at the end.
- Involving employees in the work process beyond the norm is possible if such activities are provided for in the employment contract. Such work should be of an occasional nature, but not regular.
If the administration violates the rights of workers, they have the right to appeal to the courts.
Recording work activity means observing standard time. The responsibility to keep track of the period worked is assigned to the administration of the enterprise. For this purpose, there is a working time and payroll journal, which records arrival or absence from work, being late, temporary disability, overtime, and idle hours.
Registration is available daily, weekly and general. The norm is also recorded monthly, quarterly and annually. This is provided for on a rotational basis, when working in the transport sector.
Of particular interest is generalized registration. It is divided into two types.
We recommend you study! Follow the link:
Rules for payment of overtime hours according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- Daily work intervals are unequal in time, which take into account the hours worked for the full accounting period.
- A certain daily routine. If shift hours increase, the number of days off increases. Folded time tracking takes into account different times.
The type of accounting is determined by the enterprise itself due to its type of activity.
Preliminary actions
In addition to the main functional responsibilities, the working period includes questions of the preparatory plan:
- checking constituent documentation and other papers;
- putting things in order in the workplace;
- reporting and delivery of manufactured products.
Other preparatory work time is included in the work schedule. For example, a medical examination of the driver before leaving for the route. Activities such as walking from home to work, changing clothes, and taking a lunch break are not included in working hours.
The schedule is developed taking into account other part-time and reduced modes and volumes of work. The inclusion of such species is carried out by issuing an order. Information about the time worked is reflected in the exit report card.
When determining work intervals, the main point is compliance with the law and the correct execution of regulations. Establishing a normal working period affects productivity, preserves ability to work, and prevents fatigue, which leads to mistakes and affects health.
Duration standards
For all workers, the length of the shift is not specifically defined, but adherence to the weekly limit of 40 hours is important. The maximum working week is established according to the principle of five days for work, and two days off contribute to normal rest.
The body of persons under the age of majority is just being formed, their psyche is more susceptible to stress and overwork. Therefore, the duration of a watch, duty, or shift should not exceed the hourly norm established by law.
So, for children the following number of working hours is required:
- four – for the age of 14-15 years;
- five – for minors 15-16 years old;
- seven – for workers aged 16-18 years;
- two and a half - for persons who combine work and study 14-16 years old, four - for minors 16-18 years old.
The list is legally closed.
Based on a medical decision, a standard for persons with physical disabilities is established. It is determined based on the results of the examination in accordance with Art. 11 of the Law on Persons with Disabilities. For such people, the work schedule depends on the type of injury or illness. Some functional duties are completely prohibited, for example, lifting and carrying heavy objects, working at night.
For work involving danger and risk to life, the shift schedule cannot be more than:
- Weekly regime - 36 hours, per day - 8, up to 12 - with the consent of the worker;
- Weekly - 30 hours, per day - 6, up to 8 - with the consent of the worker.
An increase in shift hours under labor legislation occurs in the form of a deviation from the rules. The working day for employees of cinematography, the media, theater and concert institutions, and circuses is regulated by a collective agreement, taking into account the maximum weekly standard.
The duration of a watch, duty, shift depends on the characteristics of work activity, part-time work, and other circumstances.
Thus, the legislator established the following provisions:
- for part-time workers, 4 hours or less are provided. If they do not have a main job, they can work another full day;
- ships have an eight-hour day. For women in the Far North, as well as persons under the age of majority, 7.2 hours.
- for drivers - an eight-hour schedule for five days of work, a seven-hour schedule for six days.
Based on Art. 110 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, rest per week must be at least 42 hours. Time starts from the end of the work process before the weekend.
When establishing a schedule, the following parameters are determined:
- length of the working week;
- time for rest and vacations;
- the beginning and end of a watch, duty, shift;
- time interval.
The provisions are fixed in the collective agreement and internal labor regulations.
How long should a person work according to the labor code?
If you distribute this over a 5-day work week, it turns out that a person works 8 hours every day.
If the work takes place in shifts, then all the same, if you add up all the hours, you should again get 40 hours a week.
If a person works shifts with the following schedule: from 8 a.m. to 10 p.m., then usually people work for two days and rest for three days.
It turns out that a person works the required 40 hours a week, just with a different work schedule.
This time limit cannot be exceeded or the employer must pay additional hours. Different categories of citizens have their own time schedule. Children under 16 years of age work no more than 24 hours a week.
From 16 to 18 years old already 35 hours. Disabled people must also work 35 hours a week.
Breaks by law
There are various breaks throughout the day. According to labor laws, some are paid because they are included in the working period, while others are not; the employee uses them for personal purposes, for lunch, for example.
Special intervals are also provided:
- for heating citizens when performing work in cold weather;
- for sleep, for example, an air traffic controller gets a free hour;
- technological intervals associated with production needs.
Such breaks must be specified in the employment contract.
The following periods of time are paid:
- For mothers to breastfeed their baby every 3.5 hours, which can be folded and taken away at the end of the working day.
- Special breaks for air traffic controllers.
- Time intervals for heating.
A break from work is provided to reduce fatigue and increase working capacity.
The beginning of the working day according to the Labor Code is clearly defined by law. If work begins at 09.00, then all personal activities cease at this point. For being late by a quarter of an hour, punishment for violation of labor discipline is applied. Absence from work for more than four hours is considered absenteeism and may result in dismissal.
We recommend you study! Follow the link:
7 kinds of working modes
The duration of breaks is established by Art. 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation 30-10 minutes, which are not included in working hours and are not paid. If the shift is four hours, then no break is allocated.
If the production situation does not provide workers with time for lunch, then the administration must provide the opportunity to eat food during a paid interval, which is shorter than half an hour.
Mandatory medical examination
Based on Art. 213 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, medical examinations are of two types:
- In order to confirm professional suitability for a specific work activity, the absence of occupational diseases and timely identification of symptoms: in harmful and dangerous types of work, as well as those related to the transport of passengers and cargo.
- To prevent the spread of diseases.
These two types can be combined.
Timely medical examinations are especially important for citizens who work:
- in the food industry and trade, catering establishments;
- at waterworks;
- in medical and children's institutions.
Medical examinations are carried out at the expense of the company, which is obliged to compensate for personal funds spent.
Part-time work
The administration, with the consent of the trade union, can establish a shortened schedule on its own initiative. The principles for establishing a part-time working week are set out in Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Various options can be implemented by agreement with the administrations.
The head of the enterprise does not have the right to refuse this treatment to the following category of persons:
- pregnant women;
- employees who care for sick citizens in accordance with medical findings;
- parents who have disabled children or children under fourteen years of age;
- women who are on maternity leave.
A part-time working period is established for a time that is beneficial to the employee, but the period ends when the conditions are terminated, for example, a disabled child has become an adult.
The Labor Code does not oblige you to indicate in personal documents what working hours are established.
How long do women have to work by law?
Pregnant women, workers under the age of eighteen, and other categories of workers are not allowed to work overtime in accordance with this Code and other federal laws.
Involvement of disabled people and women with children under three years of age in overtime work is allowed only with their written consent and provided that this is not prohibited for them due to health reasons in accordance with a medical report issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulations legal acts of the Russian Federation.
At the same time, disabled people and women with children under three years of age must be informed of their right to refuse overtime work upon signature. Important Federal Law of June 30, 2006 N 90-FZ) The duration of work (shift) at night is not reduced for workers who have a reduced working time, as well as for workers hired specifically for work at night, unless otherwise provided by the collective agreement.