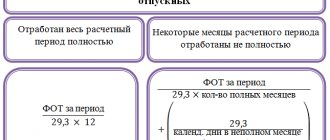
Concept of work injury
Trauma is any damage to the tissues of the human body and disruption of the normal functioning of organs. If the accident is related to the performance of one’s official duties at the enterprise, it falls under the definition of an industrial injury.
Cases of health deterioration specific to a given profession are classified as occupational diseases. Workers receive them as a result of their work in hazardous conditions. The respiratory organs and musculoskeletal system are most often affected. In the Russian Federation there is a list of hazardous professions of categories 1 and 2 and diseases associated with them. It is valid throughout the country, for any organizations, regardless of their size and subordination.
Enterprises, depending on the technological process, have different categories of harmfulness. They negatively affect the body with the following phenomena:
- high and low temperatures;
- release of harmful gases into the atmosphere;
- strong light radiation;
- force fields;
- dustiness of the air;
- drafts;
- vibration;
- increased noise threshold;
- conditions of being underground or at height.
All these factors also relate to the causes of industrial injuries and occupational diseases.
At enterprises of the Russian Federation, all managers are obliged to take measures to prevent and reduce industrial injuries: fencing off dangerous places, providing workers with special clothing, improving working conditions, and others.
There are cases when it is impossible to completely eliminate the negative impact on a person. For example, working in northern conditions, especially in open areas. Most often these are builders, drivers, forestry workers, and sailors.
In the south, agricultural workers are forced to spend all day in the field under the rays of the scorching sun at air temperatures above +30 ⁰C. Under similar conditions, workers construct buildings, lay pipelines and other communications.
Preventive measures
Theoretical foundations of the problem of studying industrial injuries
Measures to prevent industrial injuries are divided into technical and organizational.
All activities must be carried out at the enterprise by managers of different levels. Employees of the labor management and safety department monitor the progress of work and offer their own preventive measures.
Technical measures to prevent occupational injuries include:
- creating a rational work schedule;
- installation of systems to prevent dangerous situations;
- use of collective protective equipment;
- implementation of safe management of equipment and processes;
- use of automation and remote and digital control;
- replacement of old technology that releases harmful substances with a new, clean one;
- eliminating contact of workers with workpieces, finished products and waste that have a negative effect on the body;
- use of waste-free technologies;
- marking hazardous areas with special colors and warning signs.

The legal framework regulates the relationship of the worker with management, the range of his responsibilities and rights. He must refuse to work if safety precautions are violated and special clothing and protective equipment are not provided. Prevention of industrial injuries begins with proper organization of the workplace, good lighting, placement of racks for tools and plates for parts.
For prevention, psychological measures to prevent industrial injuries are of great importance. The work must correspond to the worker's qualifications and character. Too complex leads to overexertion and mistakes. Monotonous and monotonous irritates a highly qualified specialist.
The management of the enterprise is obliged to carry out organizational activities daily at all levels. You should start by reviewing safety procedures with all employees. A shift assignment is issued after the worker has listened to daily instructions on safe work practices.
Trainings and repetition of all fire safety rules are conducted quarterly. Every 6–12 months, the company’s employees take an exam on their knowledge of safety precautions.
Carrying out all measures to reduce industrial injuries does not completely eliminate industrial accidents, but significantly reduces their number.
Occupational and non-occupational injuries
The causes of industrial injuries are classified according to the location where the accident occurred:
- in production;
- outside the enterprise while performing official duties;
- on the way to work and home;
- on the territory of the enterprise not related to production;
- household
Work-related injuries include those sustained on the territory of the enterprise while performing actions related to job responsibilities. When a worker or employee performs his work directly at the workplace. These include injuries sustained during the lunch break.

Occupational injuries can occur outside the enterprise, when a person is on a business trip, driving a company vehicle, going to work and home after a shift. If his movement or activity is related to the performance of duties specified in the employment contract and movement to and from the place of their implementation.
Coming home from work has its limitations. This is not the entire route home, but only the route directly from work to your place of residence. For example, after a worker entered a store and then fell and twisted his ankle, he should no longer leave work. An injury sustained before entering a retail or other establishment may be considered an industrial injury. Official transport and travel in it are considered being at work.
Not all injuries sustained on the premises of an enterprise are considered occupational injuries. Injuries received by a stranger or during free time are not considered industrial injuries and are considered accidental.
Domestic injuries are not related to the worker’s performance of his duties, and the accident occurs outside the enterprise.
Similarly, during a long business trip, occupational injuries include injuries received in a specific place. If it is impossible to strictly delimit the territory for performing his duties, for example, the supplier visits many organizations. In this case, the limitation is made in time.

From 8 a.m. to 5 p.m., the employee performs official duties. If a dispatched specialist falls in the evening, then it is a domestic injury.
Measures to prevent injury
Prevention of industrial injuries
Measures aimed at preventing and eliminating the causes of accidents at work are divided into two types:
- technical;
- organizational.
Technical measures are achieved through industrial sanitation and safety procedures.
Industrial sanitation measures:
- Formation of a comfortable microclimate through ventilation and heating.
- Thermal insulation of buildings and technological equipment.
- Installation of lighting in accordance with regulatory documents.
- Ensuring the correct work and rest schedule - no part-time work and no additional overtime for work.
Safety precautions:
- Creation and implementation of safe equipment.
- Mechanization and automation of technology processes.
- The use of safety systems that help protect a person from an accident.
- Convenient location of equipment - it is located so that the employee does not waste time covering the distance between it, and also does not expose himself to risk if working conditions are difficult.
- Implementation of an automatic control system and technological process control.
Organizational activities include:
- Proper organization of work process and location.
- Supervision and control over the state of labor protection is achieved with the help of specially trained inspectors, who must constantly fulfill their duties in checking working conditions in production.
- Compliance with the laws of the Labor Code.
- Introduction of safe work organization methods.
- Promotion of basic labor safety rules.
- Organization of transport tests and technical inspections.
To determine the true cause of a person’s temporary loss of ability to work, an analysis of the causes of industrial injuries is carried out. There are special commissions to investigate the situation and compile a package of documents.
Classification of injuries by type
The causes of industrial injuries are divided into objective and accidental. The latter include isolated accidents on the territory of the enterprise that are not related to work or the specifics of production. For example, a person twisted his leg out of the blue or stared at welding and “caught bunnies” and suffered eye damage.
Objective reasons include:
- technical;
- sanitary and hygienic;
- organizational;
- physiological – personal.
The largest number of work-related injuries occur due to technical reasons. This is a malfunction of equipment and tools, poor insulation of power cables.
The workplace must have protective screens and shields that protect against the ingress of chips, scale and other dangerous objects.
Welding stations are fenced around the perimeter to protect the eyes of people passing by. The worker himself must wear a special suit and protective equipment in the form of glasses, boots, and gloves.
Sanitary and hygiene reasons
Reasons that are sanitary and hygienic factors that negatively affect health:
- bad light;
- drafts;
- low and high temperatures;
- air pollution;
- evaporation of harmful substances;
- poor ventilation;
- vibration;
- noise:
- lack of sanitary facilities.

In a poorly lit workshop, you may not notice the dangerous movement of individual pieces of equipment, a crane carrying a load, or an approaching electric vehicle. Drafts and cold provoke colds, inflammation, and the development of occupational diseases. The lack of household premises violates the standards of personal hygiene of people.
With poor ventilation, harmful substances accumulate in the air, which enter the respiratory system, affect the mucous membranes and blood, and cause occupational diseases.
Drafts, vibration and noise gradually cause irreversible processes in the human body: chronic inflammation, tremors, diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Poor organization of work areas
Organizational reasons often lead to injuries due to poorly cleared aisles and paths and unpaved sidewalks in winter. The enterprise administration must take care of:
- correct placement of equipment;
- compliance with transportation standards;
- training in safe working methods;
- fencing hazardous areas;
- creating storage areas;
- all employees have special clothing appropriate to their profession;
- installation of sound and light alarms on all lifting and transport mechanisms.
The organization of labor begins outside the territory of the enterprise. What sidewalks do people use to get to the enterprise? The condition of the tracks at the plant itself. If there are holes and debris everywhere, then the likelihood of foot injury increases sharply.

Violation of transportation rules, improper slinging and stacking of cargo leads to its fall. Clogged aisles and driveways threaten to bring down everything that has accumulated in them onto people passing and driving by.
High-risk areas should be fenced and accessible only to people working there. For example, the crane cabin must be closed. The key is kept by the workshop mechanic and is given only to the crane operator who starts her shift. Similarly, chemical equipment, electrical devices and vibration stands are installed in separate rooms.
The availability of regularly issued protective clothing and the use of protective equipment are important factors in reducing occupational injuries.
Regular training of workers in safe work practices should not be neglected. In addition to information, constant verification of this knowledge is necessary. Each employee should know the scope of their responsibilities and not try to do someone else’s work. The machine operator should not independently remove and install large parts on the machine if he does not have a sling operator’s license. Likewise, the crane operator listens to commands and works only with persons who have passed a special exam and have a document.
With the noise of the equipment, it is difficult to hear approaching vehicles. Loads moving at height are especially dangerous. Therefore, all cranes, machines, electric trolleys must be equipped with signals that are sharply different in nature from the hum of machine tools, welding installations and other units.
Sanitary
At the beginning of the shift, the worker must change into overalls in normal conditions, where there are no drafts and it is warm. After your shift, wash yourself and remove any dirt that has ingrained your skin and contains harmful substances. During the shift, depending on the profession and working conditions, rest breaks are taken. The worker should be able to spend 10 to 15 minutes in comfortable conditions.
If the enterprise does not have a canteen, rooms for meals must be equipped. In addition to the table and chairs, they are equipped with equipment for heating food, a boiler or an electric kettle with boiling water.
Psychophysical
Physiological causes of injuries are called personal. They depend on the state and mood of the person. For example:
- accumulation of fatigue;
- bad feeling;
- nervous overload;
- stressful state;
- monotony of work.
When assigning a job, the physical characteristics of the body and anthropometric data should also be taken into account. For example, in schools for training machine operators, the height and gender of the graduate were always taken into account during the distribution. The tallest and strongest guys were placed on large machines. The girls received turning machines DIP 100 and small single-column planing and drilling units. On them, the weight of the workpiece does not exceed 10 kg, the tool 2 kg.

The master should not allow a person in poor health to perform his duties. His inattention will lead to industrial injuries. The patient should be referred to a doctor.
Special attitude towards persons under the influence of alcohol. They should be immediately suspended from work and an act of violating safety regulations and being drunk at work should be drawn up. This is as serious an offense as driving while intoxicated.
Road traffic injuries.
Road transport injuries are injuries caused by various types of vehicles during their use (movement) in cases not related to the production activities of the victims, regardless of whether the victim was in the vehicle (driver, passenger) or outside it (pedestrian) at the time of the incident. A vehicle is any means used to transport goods, objects, people (car, motorcycle, bicycle, airplane, steamship, trolleybus, tram, railway, horse-drawn transport, etc.). Injuries in road traffic accidents are due to a large complex of reasons. Every year about 40 thousand people die on the roads and another 300 thousand are injured and often become disabled.
Experts recognize negligence in following traffic rules as the main cause of death and injury to people on the roads:
- over speed;
- driving on red;
- driving while intoxicated;
- unfastened seat belt;
- jaywalking and running a red light, etc.
The greatest number of road accidents occurs in the summer and in the first autumn months. Road traffic injuries become more frequent during the last days of the week and in the afternoon. They occur less frequently at night, but their consequences are much more severe. In cities, the main cause of traffic injuries is considered to be collisions with pedestrians, mainly by cars; collisions with motor vehicles predominate on highways. In rural areas, road accidents are more likely to involve motorcycles and trucks.
The fight against road traffic injuries and its consequences is one of the most pressing problems of our time. Our country provides for the implementation of national measures aimed at preventing road accidents; improving the state system of providing medical care to victims of road accidents and expanding scientific research in the field of road safety.
Causes of occupational diseases
Occupational diseases are a type of industrial injury, but they arise gradually, usually of the same type in people working in equally harmful conditions. They are provoked by:
- outdated technologies;
- unequipped workplaces;
- poor sanitation;
- failure to use protective equipment;
- retreat from technology;
- the need for contact with harmful substances.
When creating casting molds, the mixture is compacted by vibration. Molders fill the following boxes directly between the shakers. The floor is constantly shaking. Similarly, there are large machines with platforms for installing parts and turning on equipment. The lack of modern instruments showing the exact coordinates of the cutter and load forces the worker to stand on a vibrating metal platform for a long time. This gradually leads to industrial injuries - damage to the musculoskeletal system.
Galvanic baths and containers for electrolysis must be covered with lids on top. Vapors are removed into ventilation ducts. Active forced ventilation is installed in the room. Older equipment does not have such protective measures. Workers inhale harmful fumes.
A large percentage of diseases are caused by drafts and working at low temperatures indoors or outdoors in freezing temperatures. For work in winter conditions, in addition to special clothing, a schedule of heating and hot meals, and warm bathrooms are provided.
Types and categories of occupational diseases
Occupational diseases are divided into types according to the influence of external factors:
- chemical toxic substances;
- high dust content in the air of the working area;
- consequences of vibrations;
- nervous overstrain;
- biological substances.
The nature:
- chronic – caused by prolonged exposure to harmful factors;
- acute – occurring suddenly due to exposure to chemical or biological substances.
The categories of occupational diseases include:
- vibration diseases;
- lung diseases;
- varicose veins;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- hearing impairment;
- osteochondrosis and other diseases associated with loss of health, established by medical examination.
Classification of industrial injuries
To simplify analysis and statistics, all types of industrial injuries are classified according to several parameters:
- degree of severity;
- type of injury;
- one person or 2 or more are injured;
- according to the place where they occur most often.
In accordance with GOST on industrial injuries, the degree of severity distinguishes between mild, moderate and severe injuries. Separately, they are fatal. Special commissions are created for them and prosecutors are involved in the investigation.
According to the type of injury, they are distinguished:
- cuts;
- bruises;
- fractures;
- burns;
- poisoning
Cuts of varying severity most often occur when working with sharp instruments or piercing objects. For example, cooks using knives when cutting and cutting food. Construction workers installing barbed wire fencing or working with glass. Machine operators have sharp edges on their cutters. Drain shavings cut deep into the body.
Slippery floors, spilled oil, parts and containers protruding into the passage lead to varying degrees of bruises.
Fractures occur when a person falls, as well as heavy objects on him. A loose part, a hole in the road or poor lighting can cause serious damage.
Burns are divided into: thermal, chemical, electrical. Thermal ones occur upon contact with hot objects. Chemical burns are caused by contact with acids, alkalis and other harmful substances that corrode skin and tissue. In case of electric shock, an electrical burn appears at the site where the wire touches.
For example, in metallurgy, workers most often suffer thermal burns. It is not necessary to touch the hot workpiece. Standing nearby without appropriate felt clothing is enough to cause burns to exposed skin. The temperature of the molten metal is 1500 ⁰C and higher.
Each enterprise has an occupational safety department that investigates and properly records every accident. In addition to the type, the severity, cause of injury and location are indicated. All data is analyzed, statistics are compiled that identify the most dangerous places and professions.
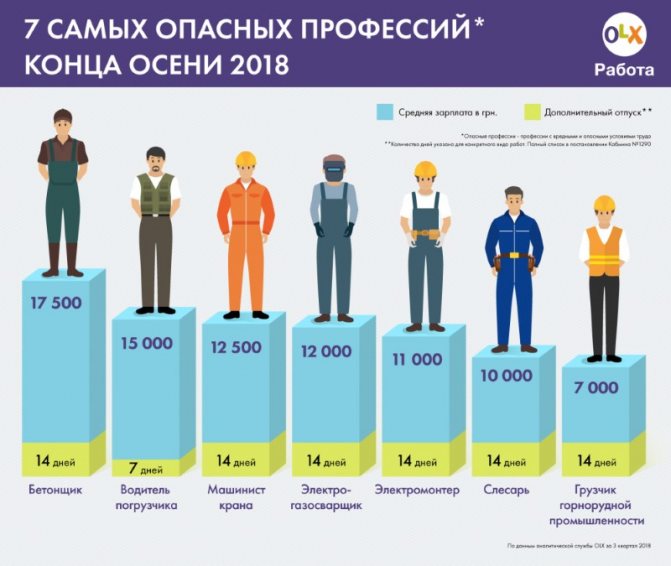
Traumatic professions
The US Department of Labor regularly publishes data on the most dangerous occupations in the country. The data is based on the number of work-related injuries resulting in death per 100,000 employees. Thus, the most dangerous professions are pilots (90 deaths per 100,000 people), lumberjacks (115 deaths per 100,000 people) and fishermen (129 deaths per 100,000 people).

In Russia, the situation is somewhat different, and the most dangerous professions are considered to be construction worker, transport worker (driver) and manufacturing industry specialist. If you believe official statistics, the level of injuries at work in Russia is 4.5 times higher than the average for the countries of the European Union. There are several reasons for this: drunkenness in the workplace; poor technical organization, use of old equipment that has served its purpose; lack of proper attitude to safety on the part of the employer and employee.