From this article you will learn what three-stage labor protection control is, how this system works, how to correctly introduce it at an enterprise, and how to draw up a three-stage control log.
Three-stage labor protection control is an effective way to constantly monitor safety and promptly respond to deviations from the norm. At the same time, control functions are distributed over 3 levels:
• Work managers - foremen, foremen, site managers - are responsible for the implementation of level 1 tasks. This is operational control.
• The implementation of level 2 tasks is organized by department heads - heads, managers, heads of workshops, production facilities, departments. This is control at the level of intermediate managers.
• Level 3 tasks are supervised by an occupational safety commission headed by the head of the enterprise (organization). This is control at the management level.
Therefore, three-stage control over compliance with labor protection is an effective way to involve the entire team in solving labor safety issues. All employees of the enterprise are involved in it: ordinary workers through occupational safety representatives, foremen, engineers, representatives of trade unions, managers of all ranks and even senior management.
Control levels
- I stage. The foreman and the authorized (trusted) person for labor protection of the trade union visit all workplaces daily. Detected problems are corrected immediately;
- II stage. The head of the workshop (large area) and the labor protection representative with a labor protection engineer make a round once a week. The results of the inspection are recorded in a journal with the appointment of performers and the establishment of a deadline for eliminating the discrepancy;
- III stage. The commission (committee) of the enterprise studies the state of labor protection in departments once a month. Based on the results of the inspection, a report on violations is drawn up and an order is issued to eliminate them.
At an enterprise or organization with a small number of employees, two-stage control is used:
- I stage. Daily inspection by the manager of all workplaces;
- II stage. Monthly in-depth examination by the labor protection committee (commission) with the participation of leading specialists of a small enterprise, an authorized (trusted) person for labor protection of a trade union or work collective.
Based on the results of the inspection, the commission enters into a special journal the noted deficiencies, proposals for eliminating them, deadlines for completion and the contractor. The performer responsible for the implementation of the planned event puts his signature.
It should be understood that three-stage control will give noticeable results only if the entire team of the enterprise, organization, from workers to top management, consistently and persistently strives to improve working conditions.
The main condition for an enterprise organizing the implementation of three-stage control is the presence of a trade union or other representative body of workers.
Much depends on the chairman of the trade union organization in matters of labor protection. He must organize public control, manage the work of labor protection commissioners, and negotiate with the head of the organization. It will also be necessary to form a commission (committee) on labor protection at the enterprise or organization, which will organize joint actions of the employer and employees on labor protection. The commission (committee) performs the following duties:
- organizes an inspection of the state of labor protection conditions at workplaces;
- informs employees about the results of these checks;
- collects proposals for the section of the collective agreement on labor protection.
Responsibility for the organization and methodological support for the functioning of three-stage control at an enterprise or organization rests with the department or occupational safety specialist. Each engineering and technical employee, within the scope of authority defined in the job description, participates in monitoring. The content of inspections at all levels of labor protection control can be supplemented depending on the specifics of the work and the technologies used; The frequency and reflection of inspections in documentation are almost identical at all enterprises and organizations.
The three-stage control system provides:
• compliance with labor protection legislation;
• safety of production equipment, technological processes, buildings, structures;
• maintaining the territory in proper condition;
• use of collective and individual protective equipment by employees;
• proper sanitary and hygienic working conditions;
• medical and preventive services for employees;
• training, instruction, special assessment of jobs in accordance with the requirements of labor legislation.
At each enterprise and organization, a Regulation on three-stage control over labor protection is being developed on a voluntary basis. Three-stage control does not exclude the conduct of administrative control in accordance with the job responsibilities of heads of enterprises, organizations, as well as public control in accordance with Art. 20 of the Federal Law “On trade unions, their rights and guarantees of activity” dated January 12, 1996 No. 10-FZ. Management of the three-stage control organization is carried out by the employer and the head of the trade union or other representative body of employees.
Three-stage labor protection control (regulatory document) - what besides it?
In addition to the provisions on three-stage labor protection control itself, the following documents will be required for its organization:
- order to conduct three-stage labor protection control;
- order to create a labor safety commission;
- logs for checking compliance with labor protection requirements (for the first two stages);
- sample act of conclusion of the labor safety commission based on the results of the third stage inspection.
Video :
Work of the third stage of labor protection control
Integration of three-stage labor protection control into the OSMS
Three-stage control over labor protection (regulatory document) , also known as the provision on three-stage control over labor protection, can be very organically integrated into the labor safety management system (OSMS). The document can act as a separate procedure, along with control of the functioning and monitoring of the implementation of procedures, or integrated into the procedure for ensuring the functioning of the OSMS (distribution of responsibilities in terms of labor protection).
Integration as a separate procedure
In this case, the provision on three-stage labor protection control becomes consistent with the procedures of the labor protection management system and must comply with the documents of the entire OSMS. To do this, make sure of the following:
- the regulation on the labor protection management system contains information about the procedure for three-stage labor protection control;
- the provision on three-stage control has the structure of an OSMS procedure (contains all the characteristic sections that we discussed above).
Integration into the procedure for ensuring the functioning of the OSMS
In this case, you will need to rework the procedure that distributes duties and responsibilities among the leaders of your organization. It is necessary to add excerpts from the provisions on three-level control over labor protection to the powers of management positions.
First stage of control:
Depending on the specifics of the enterprise, organization, structure and scale of its divisions, three-stage monitoring of the state of labor protection is carried out:
At the first stage - on the site (classes, workshops, training grounds, gyms, offices, etc. (hereinafter referred to as the site)); The first stage of control is a shift or daily check of the safety status of workplaces by line engineering and technical workers: foremen, mechanics, power engineers, heads of lower-level structural units and an authorized (trusted) person for labor protection of a trade union or work collective (resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia “On approval of recommendations on organizing the work of an authorized (trusted) person for labor protection of a trade union or work collective” dated April 8, 1994 No. 30).
During the first stage checks, the following is controlled:
• implementation of measures to eliminate violations identified during previous inspections; • illumination, microclimate in workplaces; • cleanliness of the surrounding area; • serviceability of working tools and equipment; • state of compliance with the requirements of fire and electrical safety rules; sanitary and hygienic standards; • safety of educational or technological equipment, lifting and transport vehicles; • absence of clutter in workplaces and passages to them; • availability of first aid kits and fire-fighting equipment at workplaces; • availability and correct use of personal protective equipment by employees; • absence of hazardous production factors that could harm the health of workers; • compliance by employees with the requirements of labor protection and safety instructions; • employees have occupational health and safety certificates; • condition and correct organization of workplaces (location and availability of the necessary tools, devices, workpieces, etc.); • compliance by employees with electrical safety rules when working on electrical installations and power tools; • serviceability of supply and exhaust ventilation, dust collection devices;
After the inspection, the control person makes entries in a journal of the established form, where he indicates all identified violations and comments on the operation of the equipment. The occupational safety control log is kept by the person checking. An important point is to work through the identified violations with all employees in order to prevent their recurrence.
Elimination of identified violations, as a rule, should be carried out immediately under the direct supervision of the site manager. If the deficiencies identified by the inspection cannot be eliminated by the site, then its manager must, upon completion of the inspection, report this to a superior manager to take appropriate measures.
In the event of a gross violation of labor safety rules and regulations, which may cause harm to the health of workers or lead to an accident, work is suspended until this violation is eliminated.
Working conditions: definition and varieties
In the article we will analyze the concept of conditions in the workplace - one of the main ones in labor protection, we will talk about their varieties, as well as how to keep an inspection log. magazine. This topic may seem simple, but any employer can see the opposite from his own experience. Let's figure out what working conditions are.
This concept includes a set of production factors that can affect the health status, as well as the degree of the employee’s ability to work at his workplace.
This definition is given in. Harmful and hazardous occupational factors (HOF) are a type of negative impact on the body that can lead to high humidity or gas pollution in the room. Good examples.
An occupational hazard has a more serious impact that can lead to injury, sudden ill health, or even death. The goal that every employer faces is to ensure that every workplace has safe working conditions. Under such conditions, there is no impact on workers at all, or such impact does not exceed the standards established by law.
Since the situation in production consists of the entire set of VOPFs, they need to be classified. Based on their origin, exposure to the working environment can be divided into four types:
- physical;
- psychophysiological.
- chemical;
- biological;
The first include: temperature, humidity, radiation, lighting, noise, vibration, and many others.
Second stage of control
At the second stage - at an enterprise, in an organization, in assigned areas by members of the commission (committee) on labor protection, as a rule, weekly, but at least twice a month in areas assigned to members of the commission.
The second stage of control is carried out by the head of the workshop (section), the head of the top-level structural unit according to the established schedule, together with a representative of the workforce.
The second stage involves checking:
• organization and results of the first stage of control; • eliminating violations identified by the first stage of control, as well as by previous inspections; • timely execution of orders, instructions, and other regulations regarding labor safety issues; • the state of protection of workplaces from the influence of harmful production factors; • correctness of the technological process; • sanitary condition of household and industrial premises; • compliance with equipment maintenance schedules; • the state of the occupational safety corners, the presence and condition of posters, stands for visual propaganda on occupational safety; • the correctness of issuing work orders for the execution of work, carrying out all types of labor safety briefings within the established time limits; • presence and correct installation of safety warning signs at workplaces; • uninterrupted provision of therapeutic and preventive nutrition to employees and other established means of preventing occupational diseases; • compliance with the established work and rest schedule, labor discipline by employees; • implementation of measures according to the orders and instructions of supervisory and control authorities; • serviceability and compliance of educational and production equipment, vehicles and technological processes with the requirements of labor safety standards and other regulatory and technical documentation on labor protection; • availability and condition of protective, special and fire-fighting equipment and devices, control and measuring instruments;
The results of the inspections are recorded by the person conducting the inspection in a journal of the established form. At the same time, the commission outlines the activities and presents them to the head of the enterprise or organization, who determines the performers and deadlines.

Specifics of filling out occupational safety logs
Now let’s look at what nuances an employer should pay attention to when filling out occupational safety logs.
For both types of training logs, it is important to pay attention to:
- the presence of signatures of the person being instructed and the person instructing opposite each entry on the instruction;
- indication of the full name and positions of the instructed employee and instructor, the date of each briefing.
The procedure for conducting introductory training on labor protection is described in detail in the Guide from K+, access to which can be obtained free of charge.
To fill out the instruction logbook, the following are of greatest importance:
- correct indication of the date of registration of the instruction and the beginning of its use;
- correct title of documents;
- presence of signatures of the responsible employee confirming the fact of acceptance of the instructions for registration.
With regard to the instruction log, special attention should be paid to:
- correct indication of the date of issue of instructions upon request;
- indication of the full name of the employees receiving instructions, as well as the presence of their signatures.
When filling out the accident log, it is important to indicate:
- the exact date, time, location of the incident;
- all necessary information about the victim;
- measures taken to eliminate the causes of the accident.
These nuances of filling out occupational safety logs are among the most critical. This does not mean that other columns or paragraphs of the document need not be filled out at all. It is also necessary to work with them, but errors or omissions of entries in them may not be as critical as in the elements of occupational safety journals reflected above.
Third stage of control
At the third stage - at the enterprise, in the organization as a whole.
The third stage of control is carried out according to the schedule established by the head of the enterprise or organization. The inspection is carried out by a commission headed by the technical director of the organization. The commission includes: chief specialists of the enterprise, employees of the labor protection department, representatives of the workforce.
At the third stage of control, it is recommended to check:
• organization and results of work of the first and second stages of control; • implementation of activities planned as a result of the third stage of control; • compliance with the instructions of supervisory and control bodies, orders and instructions of higher authorities, orders and decisions of the trade union committee on labor protection issues; • implementation of activities provided for by the collective agreement, labor protection agreement and other documents; • implementation of activities based on materials from the investigation of severe, group, fatal accidents and accidents; • the state of affairs in the special assessment of workplaces based on working conditions; • technical condition and maintenance of buildings, structures, premises, condition of roadways and pedestrian parts of roads, tunnels, passages and galleries; • compliance of technological, lifting, transport, energy and other equipment with the requirements of safety standards and other regulatory and technical documentation on labor protection; efficiency of supply and exhaust ventilation, dust and gas collection devices; • implementation of scheduled preventive maintenance schedules for educational and production equipment, availability of communication diagrams and connection of power equipment; • provision of students and workers with special clothing, safety footwear and other personal protective equipment, the correctness of their issuance, storage, organization of washing, cleaning and repair; • provision of workers with sanitary facilities and facilities; • conducting periodic medical examinations; • training and testing of knowledge on labor protection of managers and specialists; • the condition of the corners and labor protection office; • organization and quality of training and briefings for employees on occupational safety; • revision of labor protection instructions; • compliance with the established work and rest regime, labor discipline; • state of compliance with the requirements of fire and electrical safety rules, safety regulations, sanitary and hygienic standards, etc.
Based on the results of inspections, employer acts are issued on disciplinary action against persons violating labor safety standards and requirements, measures are developed to improve the working conditions of employees, assigning deadlines and persons responsible for their implementation.
In general, at each stage of three-stage control, independent tasks are solved; each higher level exercises control over the lower level.
The results of the inspection are recorded in a special audit log, which must be kept by the chairman of the commission. At the same time, the commission outlines the activities and presents them to the head of the enterprise or organization, who determines the performers and deadlines.
Experience of the trade union organization of the production association “Start” in public control over labor protection
If the information was useful, leave comments and share the link to this article on your social networks. Thank you!
More articles:
Regulations “On three-stage control over the state of labor protection of an organization”
Public control over labor protection (from work experience)
Rules for labor protection during placement, installation, maintenance and repair of technological equipment
On the procedure for conducting medical examinations of PC users
Composition of control measures
The specific composition of activities is determined by the specifics of the type of activity. For clarity, let us consider three-stage control in the printing industry.
1st. A master with a safety representative controls:
- workplaces and approaches to them;
- ventilation, lighting;
- equipment, tools, devices, their condition;
- alarms, blockers, braking devices;
- electrical safety;
- availability of special clothing, safety shoes, and protective equipment for each employee;
- check the entries in the equipment technical control log, compare them with the actual condition, make a record of the test and its results in the 3-stage control log>;
- eliminate deficiencies if they are found.
2nd. The shop manager and the safety representative check:
- premises, workplaces therein and working conditions;
- how the deficiencies discovered at the first stage of the audit were eliminated;
- similar: lighting, room ventilation, equipment, protective equipment;
- selectively: employee knowledge of occupational safety standards and rules;
- make an entry in the 3-stage control log;
- develop ways to eliminate shortcomings if they are identified.
3rd. The chief engineer and the safety commission headed by him monitor:
- condition of premises and workplaces;
- condition of equipment involved in production;
- operation and condition of protective equipment, safety equipment, including individual ones;
- the process and result of eliminating deficiencies identified at previous stages of control;
- implementation of decisions, orders of management and the trade union committee on occupational safety.
The results of the commission’s work are entered into the 3-stage control log and discussed at a meeting of its members. Ways to improve safety in the field of occupational safety are outlined. The commission draws up and signs a corresponding document, which reflects all the work it has done.
Members of the commission, in addition to the chief engineer himself, may be other chief specialists: a power engineer, a technologist, a mechanic, a representative of the trade union committee who heads its commission on occupational safety; OT engineer. The commission also includes representatives of the fire and medical services of the enterprise (according to the text of Order No. 237).
According to a similar principle, taking into account the type of activity, control is carried out in other production areas.
Regulations and documents
Creating safe working conditions and a labor protection system in an organization is one of the main responsibilities of the employer (Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 212). The same idea is contained in the Regulations on OSMS (Project No. 438n dated 08/19/16, issued by the Ministry of Labor). When developing a separate provision on three-stage control, which is part of the general system of local acts on occupational safety of the organization, industry and departmental regulatory documents are also used, such as the already mentioned Order No. 336n in construction, Order No. 237 of the Ministry of Transport and Industry.
The regulation on three-stage control is based on the specified documents and contains information:
- on the distribution of responsibility;
- on the organization of control activities;
- about samples of local documentation in the field of control.
The organization of 3-stage control is accompanied by the publication of a corresponding order for the enterprise, with the approval of the powers of the special commission on occupational safety. In addition, it is necessary to approve a sample audit trail and a sample act that will be used to formalize the conclusions of the commission at the third stage of control.
What form is used?
In accordance with the law and document flow rules, the journal is filled out in tabular form.
The table consists of the following columns:
- Stage number.
- Date when control was carried out.
- Violations that were discovered.
- Actions to be taken to correct the violation.
- Appoint a responsible person who will follow all instructions in column 4.
- This specifies the deadline by which problems must be resolved.
- Marking of completed work.
- Signature of the responsible person.
As for the title page, it must indicate the name of the organization and its structural unit, as well as the start date of the journal and the end date.
Is it required?
The use of three-stage control is not a mandatory requirement. The management of the organization or the relevant supervisory authority may determine a different system for monitoring occupational safety and health.
Example:
MBU “Kirishi Center for Methodological and Psychological-Pedagogical Support”, due to the specifics of its activities, structure and number of employees, has established a two-stage system as a method for monitoring labor safety.
Example of a two-stage control provision
conclusions
When considering the structure of the organization of three-stage control, it becomes clear that this method is suitable for large enterprises, with a large number of employees, and the presence of structural divisions. Although the introduction of three-stage control is not a mandatory measure, this technique will help cover all aspects of labor protection at the enterprise, while control is carried out at all stages of production, which helps to instill labor discipline in workers and leads to the development of measures to improve working conditions. Thanks to three-stage control, the head of the organization will regularly receive information about the functioning of the labor protection system at his enterprise and will be able to select the right strategy for managing labor protection.
Sources
- https://profi-cpr.ru/biblioteka/stati/kak-vesti-zapisi-v-zhurnale-trexstupenchatogo-kontrolya.html
- https://olgasofronova.ru/mnogostupenchatyj-trexstupenchatyj-kontrol-po-oxrane-truda.html
- https://www.protrud.com/2016/04/19/%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%B3%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%B0%D1 %86%D0%B8%D1%8F-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%82%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BB%D1%8F-%D0%B7%D0 %B0-%D1%81%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BE%D1%8F%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5%D0%BC-%D0%BE%D1 %85%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%BD%D1%8B-%D1%82%D1%80%D1%83%D0%B4%D0%B0-%D0%B2-%D0%BE% D1%80%D0%B3%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%B0%D1%86%D0%B8%D0%B8/
- https://consot.ru/three-stage-control/
- https://emelyanov-dokin.ru/zhurnal-proverki-sostojanija-uslovij-truda-kak-zapolnjat-88050/
- https://olgasofronova.ru/polozhenie-o-trexstupenchatom-kontrole-za-sostoyaniem-oxrany-truda.html
- https://assistentus.ru/forma/prikaz-o-trehstupenchatom-kontrole-po-ohrane-truda/
- https://pgc-expert.ru/trehstupenchatyj-kontrol-po-ohrane-truda-normativnyj-dokument/
- https://nalog-nalog.ru/ohrana_truda/kak_pravilno_zapolnyat_zhurnaly_po_ohrane_truda_obrazec/
- https://assistentus.ru/sotrudniki/trehstupenchatyj-kontrol-po-ohrane-truda/
- https://azbukaprav.com/ohrana-truda/kontrol/forma-zhurnala-kontr-za-sostoyaniem-ot.html
- https://assistentus.ru/forma/zhurnal-trehstupenchatogo-kontrolya-po-ohrane-truda/
How to make journal entries correctly
The form of the document is not fixed by law. An enterprise can create its own form, the main thing is that it reflects all the necessary information and complies with GOST standards for document management in the company. Fill out the paper by hand. Corrections are not allowed.
The title page indicates the name of the company or enterprise, structural unit, and the period for which the journal is kept.

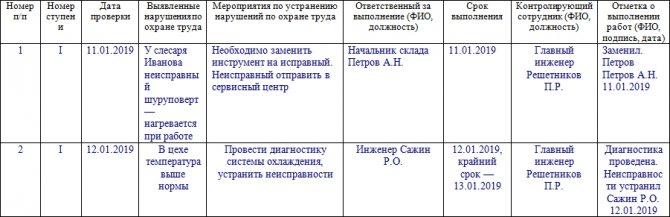
The log itself is a table with the following columns:
- Serial number of the record.
- Stage number (put in Roman numerals).
- Date of inspection.
- Identified violations of labor protection. You need to write briefly, but at the same time you need to fully reflect the nature of the violation.
- Measures to eliminate violations. Here you need to list what needs to be done by the employee who has been assigned this task.
- Responsible for implementation (full name and position of the employee).
- Deadline.
- Full names of supervisory employees, signatures.
- A note on the completion of work (full name of the person who performed it, date, signature). The employee who eliminated the violations reports in this column.
The journal must be stapled before filling out and certified: indicate how many pages it contains. Then the manager confirms this fact: puts his signature, indicates the position, full name and date.
Once completely filled out, the log must be kept in the organization for 10 years, like every document related to the field of labor protection.