Labor protection agreement: what kind of document?
An agreement on labor protection is a legal form for planning and carrying out labor protection measures, indicating deadlines for implementation, sources of financing and those responsible for their implementation.
Since 1995, the Agreement on Labor Safety has been an independent legal document. However, the order of the Ministry of Labor dated March 25, 2013 canceled its legal status. However, the need to regulate the scope of labor protection has not disappeared, and this document has become part of the collective agreement, drawn up as an annex to it. If there is no collective agreement, it is recommended to conclude a labor protection agreement to protect the interests of both the employee and the employer.
Organization of a collective security treaty
For workers, a collective agreement acts as a kind of security guarantee that they will not be deceived by the employer. It establishes rights and guarantees that make the situation of workers better than the law.
Today the situation on the labor market is such that the majority of workers cannot independently achieve the working conditions that a collective agreement can provide them with. In addition, this is the only document, failure to comply with which can be considered in court.
Conclusion procedure
Negotiations between the parties usually take place before closing. Their initiator can be either an employee or an employer. Neither party, after receiving notification of negotiations, has the right to evade them, and is obliged to begin them within seven days. This notice is sent three months before the end of the old contract.
The negotiation procedure has several stages: A decision is made on the need to draw up a collective agreement. A notification note is sent for further decision-making.
An order on the organization and formation of a commission for conducting negotiations is issued within seven days from the date of receipt of the notification. A commission consisting of representatives of the parties is formed. If, for example, not one person, but many, speaks from workers, then within five days a single body is first formed.
The draft of the new document is discussed and finalized in accordance with comments and suggestions. Next, the unified project is approved at a general meeting of employees and signed. The new document, along with attachments, is sent to the labor body within seven days after signing.
When does it take effect?
The Labor Code gives each party the right to choose. It may be established that the collective agreement begins to operate from a certain moment or from the date of signing. Theoretically, the effective date could be linked to a specific event, but, as a rule, such cases do not occur.
Who develops the Occupational Safety and Health Agreement in the organization?
The development of the agreement and the corresponding section of the collective agreement is organized by the labor protection committee (commission) at the enterprise, institution, or organization.
The committee consists of representatives of the employer and the trade union on a parity basis. Representatives of the employer and elected representatives of the trade union are approved by order of the employer.
The Committee collects information and creates a data bank on the state of labor protection and life safety at an enterprise, institution, or organization.
If the organization does not have a labor protection commission, then the labor protection agreement is developed by a labor protection specialist. If the organization has less than 50 people and the staffing table does not include the position of a labor protection specialist, the function of ensuring labor protection is assumed by the manager or another employee authorized by the order.
Main sources of legal regulation Agreement on labor protection
- Constitution of the Russian Federation. It enshrines the employee’s right to work in conditions that meet safety requirements and sanitary and hygienic standards.
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The main priorities of the state labor protection policy are identified, the rights and responsibilities of employers and employees to comply with labor protection requirements are explained.
- Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ “On compulsory social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases.” Approved the mandatory nature of insurance against accidents during work, as well as for diseases caused by harmful working conditions.
- Federal Law of March 30, 1999 No. 52 -FZ “On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population.” Obliges the employer to organize regular medical examinations for employees, as well as to ensure the satisfactory condition of the workplace in terms of sanitary standards.
- Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated March 1, 2012 N 181n “On approval of the Standard List of measures annually implemented by the employer to improve working conditions and safety and reduce levels of occupational risks.” (Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on March 19, 2012 N 23513). Recommends that employers have a list of measures to improve working conditions and safety and reduce levels of occupational risks.
Section Conditions and labor protection in the collective agreement
Want to create a site? Find Free WordPress Themes and plugins.
RECOMMENDATIONS ON THE SAMPLE CONTENT OF THE SECTION “WORKING CONDITIONS AND SAFETY” IN THE COLLECTIVE AGREEMENT, PROVIDING THE OBLIGATIONS OF THE EMPLOYER TO THE EMPLOYEES IN THE FIELD OF LABOR CONDITIONS AND SAFETY
Recommendations on the approximate content of the section “Working Conditions and Safety” in the organization’s collective agreement have been developed in order to more fully take into account the requirements of the current norms of the legislation of the Russian Federation on labor protection concerning the employer’s responsibilities to employees to ensure labor protection in the organization and create healthy and safe working conditions at production.
Basic provisions
The employer, in accordance with the current legislative and regulatory legal acts on labor protection, undertakes to: 1. Allocate funds in the amount of ……….. rubles for labor protection measures provided for by this collective agreement. 2. Complete within the established time frame a set of organizational and technical measures provided for in the labor protection agreement, in accordance with Appendix No. ………… 3. Form a labor protection fund for the organization and allocate funds for these purposes in the amount of ……….. rub. 4. Conduct a special assessment of working conditions in the following departments (list): ……….. 5. Conduct training and testing of knowledge on labor protection of workers, managers and technical employees of the organization within the time limits established by regulatory legal acts on labor protection. 6. Organize, in a timely manner, a medical examination of the organization’s employees who are required to undergo periodic medical examinations. 7. Ensure: - timely provision to employees of special clothing, special shoes and other personal protective equipment, detergents, lubricants and neutralizing agents in accordance with established standards for the list of professions and positions in accordance with Appendix No. ………..; - workers sent to perform work in other workshops (other sections), with special clothing and special footwear provided for by the established standards for professions and positions of the workshop (section); — repair, washing, drying of special clothing and special footwear, as well as their neutralization and restoration of protective properties; — issuing special clothing, special shoes and other personal protective equipment to employees in excess of the established standards at the expense of the organization according to the list of professions and positions in accordance with Appendix No. ………..; - issuing technological uniforms to employees at the expense of the organization according to the list of professions and positions in accordance with Appendix No. ………… 8. Provide employees engaged in work with harmful and dangerous working conditions with the following benefits and compensation: - additional leave and reduced working hours according to the list of professions and positions in accordance with Appendix No. ………..; — additional payment to the tariff rate (salary) for work with harmful and dangerous working conditions according to the list of professions and positions in accordance with Appendix No. ………..; - milk or other equivalent products according to the list of professions and positions in accordance with Appendix No. ………..; — therapeutic and preventive nutrition according to the list of professions and positions in accordance with Appendix No. ………… 9. Provide workers in hot shops and areas with carbonated salted water and tea. 10. Establish a one-time cash benefit to employees (members of their families) for compensation for damage caused to their health as a result of an accident or occupational disease during the performance of work duties in cases of: - death of an employee - ……….. minimum wages, as well as payment of bills and funeral expenses; — the employee receives a disability — ……….. minimum wage; - the employee’s loss of ability to work, which does not allow him to perform work duties at his previous place of work, - ……….. minimum wage. 11. Establish, at the expense of the organization’s funds, the payment of a monthly cash benefit in the amount of 100% of the established (on the day of payment) minimum wage for children who have lost a breadwinner (each child) until they reach 18 years of age, and in cases of continuing education - up to 23 years of age . 12. Timely index the amounts of compensation for harm caused to employees by injury, occupational disease or other damage to health associated with the performance of their job duties. 13. Introduce mandatory medical insurance for employees at the expense of the organization and insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases in accordance with Federal Law of July 24, 1998 N 125-FZ “On compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases”, Federal Law of December 15, 2001 N 167-FZ “On Compulsory Pension Insurance in the Russian Federation”, Federal Law of November 29, 2010 N 326-FZ “On Compulsory Medical Insurance in the Russian Federation”, Federal Law of December 15, 2001 N 167-FZ “On compulsory pension insurance in the Russian Federation”, Federal Law dated December 29, 2006 N 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity”, Federal Law dated July 16, 1999 N 165-FZ “On the fundamentals of compulsory social insurance"). 14. Ensure working conditions and protection for women, including: - limit the use of women’s labor at night; — implement a set of measures to remove women from heavy physical work and work with harmful and dangerous working conditions; — organize home work for women whose labor cannot be temporarily used in the organization; - allocate jobs in departments ……….. exclusively for the employment of pregnant women who need to be transferred to light work; - carry out measures to mechanize manual and heavy physical work in order to introduce new standards of maximum permissible loads for women established by Resolution of the Council of Ministers - Government of the Russian Federation of February 6, 1993 No. 105. 15. Provide working conditions for young specialists, including: - exclude the use of labor of persons under the age of 21 in heavy physical work and work with harmful and dangerous working conditions; — establish, at the request of persons studying on the job, individual work schedules. 16. Together with the trade union, organize control over the state of labor conditions and safety in departments and the implementation of the agreement on labor protection. 17. Regularly consider at joint meetings with the trade union, joint committees (commissions) issues of implementation of the agreement on labor protection, the state of labor protection in departments and inform employees about measures taken in this area. 18. Ensure guarantees of the right of workers to labor protection, provided for by the norms of current legislation, and the consolidation of these rights in employment contracts. Note. At the discretion of the employer and employees, the section “Occupational Conditions and Safety” may include additional clauses that expand the employer’s obligations in the field of labor protection, which do not contradict the requirements of current legislative and regulatory legal acts on labor protection.
Did you find apk for android? You can find new Free Android Games and apps.
What measures should be included in the Occupational Safety and Health Agreement?
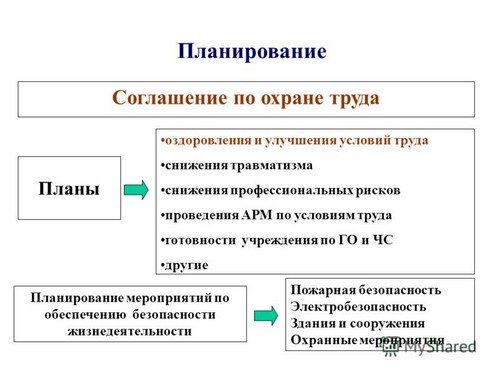
Planning of occupational safety measures is aimed at preventing accidents at work, occupational risks and diseases, improving working conditions and safety, sanitary and welfare provision for workers.
Occupational safety measures are formalized by agreement, taking into account proposals from the Rostrudinspektsiya and other federal supervisory authorities, employers, employees in labor relations with employers, and other representative bodies authorized by employees. Proposals are made based on an analysis of the causes of industrial injuries and occupational diseases, based on the results of an examination of the technical condition of production equipment, as well as taking into account work on a special assessment of working conditions.
Based on these data, the committee (commission) develops an agreement on labor protection. Verifies the implementation of the activities of this agreement, the correct use and expenditure of funds specified in the agreement.
Is it necessary to have an Occupational Safety and Health Agreement in an organization?

The State Labor Inspectorate asks for this document during inspections.
In accordance with Article 45 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an agreement is a legal act regulating social and labor relations and establishing general principles for regulating related economic relations, concluded between authorized representatives of workers and employers at the federal, interregional, regional, sectoral (intersectoral) and territorial levels social partnership within their competence. The agreement may include mutual obligations of the parties on the following issues: wages; labor conditions and safety; work and rest schedules and other issues determined by the parties
For quite a long time in Russia, Resolution No. 11 of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation of February 27, 1995 was in force, according to which the employer was recommended to conclude an agreement on labor protection with the organization representing the interests of the employee (most often a trade union). This agreement contained a list of measures aimed at improving labor safety, indicated the timing, cost of their implementation, as well as full name. and positions of employees responsible for the implementation of relevant activities.
Resolution No. 11 was canceled by order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated March 25, 2013 No. 15, and therefore such a legal category as an agreement on labor protection was excluded from the legal field. However, employers still have a practical need to conclude such agreements.
So, in accordance with the amendments to Art. 219 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, approved by Law No. 421-FZ of December 28, 2013, every employee working in harmful and dangerous conditions has the right to guarantees and compensation established by the Labor Code, collective agreement, agreement, or local regulations. In addition, in Art. 219 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that an employee has the right to a workplace that meets labor protection requirements.
The specifics of providing certain guarantees and compensation to employees are regulated by the provisions of Art. 92, art. 117 and art. 147 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Each of them states that the employer is obliged to provide employees with established guarantees and compensation in the manner established in the collective agreement, and in some cases in agreements.
Thus, the subjects of the labor protection agreement can be the employer, on the one hand, and the employees, or the organization representing their interests, on the other.
In addition, Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated March 1, 2012 N 181n “On approval of the Standard List of measures annually implemented by the employer to improve working conditions and safety and reduce levels of occupational risks,” recommends that employers have a list of measures to improve working conditions and safety and reduce levels of occupational risks .
Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated March 1, 2012 No. 181n On approval of the Standard List of measures annually implemented by the employer to improve labor safety conditions and reduce occupational risk levels
If the information was useful, leave comments and share the link to this article on your social networks. Thank you!
More articles:
Industrial accident: actions of the trade union organization
Conducting SOUT: methodological recommendations
Agreement on labor protection in an organization carrying out educational activities: an approximate list of measures - recommendations of the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia
Regulations “On three-stage control over the state of labor protection of an organization”
Occupational Safety and Health Commissioner: forms and work planning
Collective agreement sample 2021 for a budgetary institution
If we talk about an employment contract, it is concluded with each employee separately. As a rule, the employer imposes his own opinion on him. The collective one is different in that it is better thought out and protects the employee. It is prepared with the participation of all employees, so everyone can make their own proposal.
The finished document is approved at the general meeting and after its adoption it is binding. This is a kind of charter of LLC, JSC and any other organization, regardless of the place of execution - in Ukraine, the Republic of Belarus, Kazakhstan, Moscow and so on.
Even any individual entrepreneur can include this document in his work. In addition, this agreement between the employee and the employer describes in more detail the payment for overtime and downtime, as well as the working hours. Therefore, entering into it is beneficial for both the employee and the employer.
What's happened?
The concept of a collective agreement is a legal act that regulates social and labor relations within an organization, concluded between employees and the employer. Its goal is to improve employee-employer relations.
At its core, it is a document that contains the obligations assigned to the administration and staff of the organization. Here all the interests of each party are agreed upon, rights and guarantees that are softer than those under the law are stipulated. But at the same time, the team has certain responsibilities.
In addition, the employer determines only those obligations that he can actually fulfill. Thus, a collective agreement is also a method of eliminating conflicts of interest, which makes it possible to prevent harsh forms of labor struggle, for example, strikes.
The document never indicates unnecessary things that are not related to the team and the employer. Any such provision shall be excluded. If we talk about who can develop and extend this document, then these are representatives of employees (trade union) and the employer directly, or his representative.
How to make changes?
To make changes, first of all, you need to convene a meeting of the administration and the trade union, and at the end of it, draw up a voting protocol with the signatures of the participants. So, at the meeting, the agenda should be announced and recorded in writing in the minutes. Record all suggestions and arguments regarding the proposed changes in the minutes.
A vote is taken for each item. The number of all votes is entered into the protocol. Changes can be made if, based on the voting results, more than half voted for the initiative. If it is necessary to make any changes, a meeting must be convened, a vote is held and the signatures of the participants are collected. No decision made should be to the detriment of employees.





