What are the grounds for salary deductions?
To withhold part of an employee's salary, there must be a legal basis. For example:
- Art. 137 of the Labor Code: reimbursement of advance payment unspent on a business trip, accounting error, unearned vacation pay.
- Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - transfer of personal income tax by a tax agent.
- Art. 109 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation - withholding alimony from an employee.
- Art. 98 of the Federal Law “On Enforcement Proceedings” No. 229-FZ - foreclosure of the debtor’s income by a bailiff.
All grounds, except for personal income tax withholding, must be documented.
Types of deductions
All deductions can be grouped into mandatory by law, optional at the initiative of the employer, or voluntary at the request of the employee.
The first group of withholdings is mandatory - withholding 13% of the personal income tax, the amounts specified in the court decision, writ of execution or order of the bailiff.
The employee’s consent or the employer’s permission is not required to produce them.
The second group of deductions - at the initiative of the employer - can be in 6 cases.
1. The employee received an advance, but did not work the allotted time and quit . Some employers pay a fixed advance - 50% of the salary. They take into account the actual number of shifts worked only when calculating at the end of the month. If an employee worked few shifts, received an advance and immediately quit, he received too much.
The employer can withhold the money during the final payment or reclassify it as compensation for unused vacation.
2. The employee received advance travel allowances, but did not spend them all and did not return them upon returning from the business trip . For example, Ivanov was given 10,000 rubles in advance to cover the cost of paying for a hotel room. But Ivanov finished his business earlier, returned home, and from 10,000 rubles he still had 1,500 rubles unspent.
The employer can withhold 1,500 rubles from the next salary.
3. A counting error has occurred . This is a very controversial basis, since the law does not define the concept of “counting error”. There is an opinion from Rostrud that the counting error is an arithmetic one.
Whether a technical error is considered a counting error is also unclear - the law does not say anything, the courts say different things (see the ruling of the Sverdlovsk Regional Court dated 04/21/2016 in case No. 33-7642/2016, the Samara Regional Court ruling dated 01/18/2012 No. 33-302/ 2012).
In any case, the law has such a basis, which means the employer has the right to use it to withhold, for example, overpaid wages.
4. The employee did not fulfill the work standard through his own fault, and the labor dispute commission or court confirmed this . For example, an employee must produce 50 products a week, for which he is paid 5,000 rubles. For unknown reasons, he produced only 40 items.
The employer organized a commission on labor disputes, at the meeting they recorded the fact of shortcomings, and the manager had the right to withhold wages from the employee on account of unmanufactured products.
5. The employee took 28 days off, but did not work for a full year . For example, Ivanov got a job in March, worked for six months and went on full leave. After his vacation, Ivanov worked for another 2 months and quit. He received 4 months of vacation pay in excess, so the employer can withhold this money when calculating.
6. The employee caused material damage to the employer . For example, an employee spilled coffee on the keyboard and it stopped working. He caused damage to the employer, so the latter can deduct wages.
The third group of deductions is at the request of the employee. For example, an employee asked an accountant to send part of his salary to the bank to pay off a loan. The Ministry of Labor believes that this cannot be done: the law allows deductions only in certain cases, and this is not on the list.
Types of deductions from wages
Deduction from wages is a part of income accrued in favor of an employee, but transferred (paid) not to the employee himself, but to a third party. What types of deductions are there and what their sizes are – read in this publication.
Based on the standards set out in the Labor Code, deductions from wages are
can be divided into three categories:
1) mandatory
– types of deductions from wages that are made on the basis of legislative norms. Mandatory deductions from wages and other income of an employee include personal income tax, personal income tax, and deductions under executive documents.
The key difference between mandatory deductions and other types is the presence of a legislative or administrative document on the basis of which deductions are made from debtors. An administrative document means a court decision, a writ of execution;
2) at the initiative of the employer
– type of deductions from earnings that are made by order of the employer;
3) voluntary
– any types of deductions from wages made at the request of the employee (for example, for voluntary insurance, charity amount, loan repayment amount).
The main difference between voluntary deductions and other types of deductions is the presence of an application from the employee, which indicates the conditions, amounts and purposes of the withheld amounts.
According to paragraph 1 of Article 115 of the Labor Code, deductions from an employee’s salary are made by court decision, as well as in cases provided for by the laws of the Republic of Kazakhstan and this article of the Labor Code.
Deductions from an employee’s salary to pay off his debt to the organization in which he works can be made on the basis of an act of the employer with written notification to the employee:
1) to repay unspent and not returned in a timely manner amounts of money issued in connection with a business trip, as well as in the event of failure to provide documents confirming expenses related to the business trip;
2) in cases that provide for reimbursement to the employer of costs associated with training an employee, in the presence of a training contract, in proportion to the unfinished period of work in the event of early termination of the employment contract;
3) to reimburse an unpaid advance issued to an employee on account of wages;
4) in cases of transfer or recall of an employee from annual paid leave, with the exception of paragraph 3 of Article 95 of the Labor Code;
5) in other cases - with the written consent of the employee.
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 115 of the Labor Code, when deducting from wages under several writs of execution, as well as in cases provided for by the laws of the Republic of Kazakhstan and this article of the Labor Code, the amount of monthly deduction is not ...
How much can you deduct from your salary?
Salaries can only be partially withheld. In Art. 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states how much can be withheld from each payment:
up to 20% - in all cases,
up to 50% - according to several executive documents,
up to 70% - if alimony, compensation for harm caused to health, and payments for the loss of a breadwinner are withheld.
Account for employees without special knowledge
Elba will prepare all the necessary reports for employers. Forms will be filled out automatically, salary payments and taxes will also be generated.
Try 30 days free Gift for new entrepreneurs The promotion is valid for individual entrepreneurs under 3 months old
When deduction from salary is not possible
An accountant withholds tax or debt from a salary by order of a bailiff without completing other documents. He only needs to remember the restrictions from Art. 138 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In all other cases, two conditions must be met:
- The one-month period established for debt repayment has not expired (Part 3 of Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- The employee gave written consent to the deductions.
If at least one of these conditions is not met, the employer will have to go to court to return the overpaid money.
There is no need to obtain consent from the resigning employee to withhold for unworked vacation days. But if there is not enough money to cover overpaid vacation pay, the employer will not be able to recover the remaining amount through the court. Because there is no such basis in the law.
Can an employer make deductions from an employee's salary?
As a general rule, an employer does not have the right to make deductions from an employee’s wages. But there is an exception to this rule. In this article, we will look at what grounds it is permissible to withhold part of an employee’s salary.
According to Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, deductions from an employee’s salary are made only in cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws, namely:
- to reimburse an unearned advance paid to an employee on salary;
- to repay an unspent and timely unreturned advance issued in connection with a business trip or transfer to another job in another area, as well as in other cases;
- to return amounts overpaid to the employee if the body for the consideration of individual labor disputes recognizes the employee’s guilt in failure to comply with labor standards or downtime;
- upon dismissal of an employee before the end of the working year for which he has already received annual paid leave for unworked vacation days. Deductions for these days are not made if the employee is dismissed on the grounds provided for in paragraph 8 of Part 1 of Art. 77 or sub. 1, 2 or 4 hours. 1 tbsp. 81, sub. 1, 2, 5, 6 and 7 tbsp. 83 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Withholding of overpaid wages
In addition, in some cases it is allowed to withhold overpaid wages. An employer has the opportunity to recover overpaid wages from an employee only in the following cases:
- counting error;
- if the body for the consideration of individual labor disputes recognizes the employee’s guilt in failure to comply with labor standards or downtime;
- if the wages were overpaid to the employee in connection with his unlawful actions established by the court.
What is considered a counting error?
The Judicial Collegium for Civil Cases of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation indicated that a counting error in this case should be considered an error made in arithmetic operations (actions related to counting), and technical errors, including technical errors committed through the fault of the employer, should be considered counting errors. are not (Decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated January 20, 2012 No. 59-B11-17).
Recovery from the employee of the amount of damage caused to the employer
In addition, Art. 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows the employer to recover from the employee the amount of damage caused to his property, but provided that the amount of damage does not exceed the employee’s average monthly earnings.
Deductions from wages by force of law and by executive documents
In addition, deductions may be made from the employee’s wages by force of law (taxes) or by executive documents.
Amount of deductions from salary
The maximum amounts of deductions from an employee’s salary are determined in Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the employer is obliged to comply with them. The total amount of all deductions for each payment of wages cannot exceed 20%, and in cases provided for by federal laws - 50% of wages due to the employee. When deducting from wages under several executive documents, the employee must, in any case, retain 50% of the wages.
The above restrictions do not apply to deductions from wages when serving correctional labor, collection of alimony for minor children, compensation for harm caused to the health of another person, compensation for harm to persons who suffered damage due to the death of the breadwinner, and compensation for damage caused by a crime. The amount of deductions from wages in these cases cannot exceed 70%.
How to withhold money from an employee
For mandatory deductions, orders from the manager or statements from the employee are not needed; a writ of execution or a copy of it with the order of the bailiff is sufficient.
For deductions initiated by the employer, the list of documents depends on the situation. For example, when withholding an overpaid advance, written consent must be obtained from the employee and an order from the manager to withhold. If a shortage occurs, in addition to these documents, a deficiency report must be drawn up, signed by the commission, and an explanatory note from the financially responsible employee.
When can employees challenge wage deductions?
Let us once again draw your attention to the fact that money must be withheld from an employee’s salary strictly in accordance with labor laws.
This applies not only to the registration of the employee’s consent and the employer’s order to withhold; it is necessary to correctly draw up the documents that form the basis of these withholdings.
If the employer incorrectly prepares the supporting documents, there is a high probability that the employee will challenge all “deductions”.
For example, you need to prove that this particular employee is to blame for the breakdown of this particular item, or that there was a shortage, and it occurred precisely because of this employee. For each case, the employer should carry out a number of activities and prepare the necessary documents. Otherwise, the deductions are illegal.
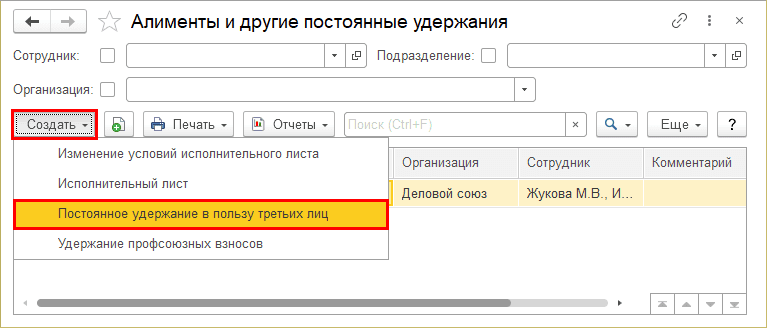
Creating a new hold type
Step 1. In the Holds directory, click the Create button.
Step 2. Specify the name and set the calculation procedure.
For example, let’s create a type of deduction – Material damage, entered as a fixed amount, purpose – deduction in favor of third parties.
Having saved a new type of deduction in the journal, when you click the Create button, a new type of deduction will become available - Permanent deduction in favor of third parties.
When creating other types of retention, indicating the purpose - Permanent retention in favor of third parties, they are combined and entered in one document.
Step 3: Select Permanent Third Party Lien.
Step 4. Fill out the header of the document. The deduction field will display the name of the created calculation type – Material damage. Specify the withholding period and the third party in whose favor the withholding is made.
Step 5. Select an employee and indicate the amount to be withheld.
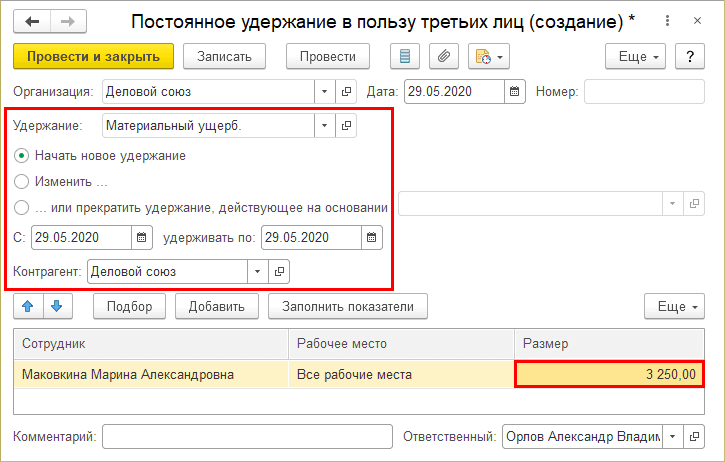
Step 6. Save the document – Post and close.
All created deduction documents are reflected in the Alimony and other permanent deductions journal.
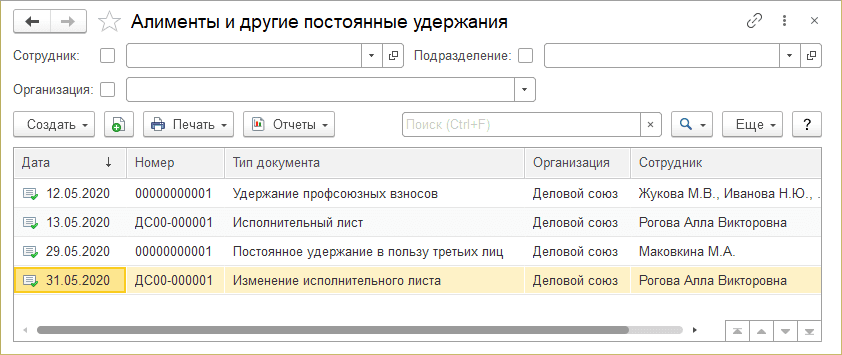
Let's look at how deductions are reflected in the document when calculating wages.