Split working day: legal principles of the concept
A person's working day should not exceed 8 hours. The total weekly duration is at least 41 hours. But what to do if for some categories of employees the main activity is carried out for 2-3 hours, then he is forced to remain idle, waiting for the next order, client or something else. This is a typical situation for the application of Article 105, which must be applied:
- if such a work schedule is introduced;
- establishing a maximum time defined as working time.
Labor legislation provides detailed explanations and grounds for when such actions can be taken. If such a situation occurs, then the employer is not prohibited from using this article. It roughly looks like this: If the working day is divided into two time periods, between which there is a lunch break (at least 2 hours), then the use of such schedules is inappropriate. If the break is more than two hours, you can use a broken work schedule. This is exactly how the labor code explains it.
Important! A split day cannot be considered shift work. This is regulated only by internal regulations.
And if the order states that the day is considered divided, then so it will be. For shift work, there is a different order that clearly defines the time frame for each shift. This should not be confused, although many of my friends do not see much of a difference.
The video below shows the peculiarities of regulating discontinuous schedules in labor legislation:
In what cases is it necessary to split the working day?
Orders and other normative documents define professions and positions for which a split working day can be established. For example, the Order of the Ministry of Communications defines the following list of professions:
- head of the communications department, belonging to groups 5-7;
- operator for receiving/issuing items, including telegrams;
- the operator who is responsible for postal delivery;
- postman;
- parcel sorter;
- station equipment electrician;
- telephone operator of a call center or help desk, etc.
The possibility of dividing working hours is provided for drivers by the Regulations on the peculiarities of the working hours of drivers. Similar provisions provide for the division of working time for:
- metro employees, namely, employees who are directly related to accompanying and servicing passengers;
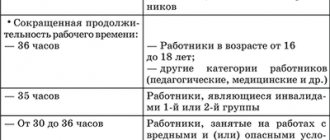
- teachers and other specialists from educational institutions (for example, boarding schools), which provide for round-the-clock stay of pupils or students.
Author of the article
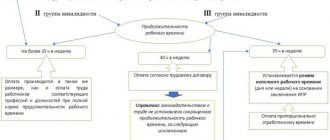
Situations when it is necessary to divide the working day
During one working day, the intensity of work may change. For example, in the morning there is so much work that there is no time to even sit down. But as lunch approaches, there are fewer orders, calls, and other things. It’s one thing when employees just sit and do nothing, counting down the time until the end of the working day. And it’s completely different when they go home for a few hours and go to work at a time when the amount of work will increase significantly.
This cannot be a random fact. This should happen all the time. This is the only way to implement a discontinuous schedule. Typically, such situations arise in transport companies, in public utilities, among employees of aviation companies, on the railway, and so on. Therefore, the TC article precisely specifies the prerequisites for the introduction of a discontinuous schedule:
- specifics of activity;
- work of varying intensity, which changes throughout the day;
- the company has a special resolution adopted by the trade union;
- inability to carry out duties from a large number of people (for example, a cleaner in an office, in a bank branch, in a store, and so on).
The employer has the right to divide the working day by hours at his own discretion. But in the event of a dispute, the employer must provide evidence that such actions were aimed at improving the working conditions of employees.
General procedure for dividing working time
From the norms contained in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a mandatory procedure follows that must be observed when deciding to divide the working day into parts. Violation of this order can lead to a conflict between the administration and employees, complaints to regulatory authorities and proceedings, including litigation.
Order:
- Development of LNA regulating the division of working time during the day.
- Familiarization of members of the trade union organization with LNA and plans for dividing working time. Coordination with the trade union. LNA approval.
- Approval of the local document by the administration.
- Bringing the new work routine to the attention of team members. It is advisable to do this under signature. Explanations regarding the nature and nuances of work in the new conditions.
- Conclusion and execution of additional agreements to the employment contract regulating the division of the working day.
What documents should I fill out if the division of the working day (time) into parts is introduced when applying for a job ?
As we can see, it is impossible to introduce a division of the working day into parts by a single volitional decision, by order of the company’s management, according to labor legislation.
Important! An employee's split working day is not a basis for working without a lunch break. The right to a break is secured by Art. 108 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Its duration is from 0.5 to 2 hours. By agreement with the administration, a break may be added to a period separating parts of the working day. A working day can be considered divided only if there is a break between its two parts of more than 2 hours. Otherwise, the schedule is considered normal.
Features of such breaks

The break between working hours is not paid. The employee receives payment only for the time actually worked. But there are professions where breaks are not comparable to the length of the working day. It can be:
- employees of airlines, railways, bus drivers, whose working day can be much more than 8 hours;
- subway employees;
- educators, teachers, nannies of child care institutions working around the clock;
- veterinarians and livestock farm employees;
- specialists who maintain electrical networks or other utility lines.
An unexpected call to work, as well as long overtime periods, place a strain on the human body and are a gross violation of labor legislation. But in order to officially change the work schedule, the manager must obtain consent from the trade union. And if such an organization does not exist at the enterprise, it is necessary to make decisions taking into account the opinion of the majority of workers.
conclusions
The division of the work regime is the use of a schedule in accordance with which employees perform their work duties during a work shift, divided into at least two main parts with a break lasting more than 2 hours.
The application of the presented schedule must be determined by the specifics of production and must be agreed upon with the primary body of the trade union organization operating at the relevant enterprise (organization).
How to determine time for lunch

Persons whose working hours are split are not deprived of the right to a legal lunch. It is taken into account in the time period that is formed between going to work. The duration of such lunch breaks should not be less than 30 minutes and no more than 2 hours. The same time can be included in working hours.
Question answer. Consultation.
| We receive a 20% increase in wages for broken working hours. I work daily from 8:00 to 20:00, lunch from 13:00 to 16:00. I heard that if this mode of operation is daily, then 30% should be paid for the gap. Please explain whether the actions of our leadership are legal? |
| According to Art. 105 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in those jobs where it is necessary due to the special nature of the work, as well as in the production of work, the intensity of which is not the same during the working day (shift), the working day can be divided into parts so that the total working time does not exceeded the established duration of daily work. This division is made by the employer on the basis of a local regulatory act adopted taking into account the opinion of the elected trade union body of this organization. |
Is there an additional payment for a less convenient schedule?
Splitting the workday is not entirely convenient for many employees. For example, a janitor goes to work early in the morning, and makes a second exit in the evening. Or an office cleaner who prepares the room before the work day and cleans it after all the employees leave. But this mode is inconvenient for everyone. Many people say that this gives them a lot of free time for household chores.
But most agree that it is inconvenient. Therefore, the law provides for additional payment for such working conditions. It is not even considered an additional payment, but compensation, and the amount is calculated as a percentage of the rate. For some categories it looks like this:
- senior employees at the railway – 30%;
- housing and communal services personnel – 30%;
- women working in rural areas (mainly milkmaids) – 30%.
This is a standard compensation indicator, which can be changed in both directions at the discretion of the employer. The amount of compensation and its percentage must be noted in internal regulations and orders.
Payment for broken working hours for additional education teacher
105 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows the employer to introduce a broken working day in other cases, in addition to those provided for by centralized regulations. However, there must be reasons for this (the organization carries out work in which division is necessary due to the special nature of the work, or work, the intensity of which is not the same during the working day (shift)) and the procedure must be followed. The division of the working day into parts is carried out by the employer on the basis of a special local regulatory act, adopted taking into account the opinion of the elected trade union body of the organization. This local normative act must provide: - grounds for introducing a broken working day, - the circle of workers for whom a broken working day is introduced, - the number and duration of parts into which the working day is divided, the duration of the break between them, - the period for which a broken working day is introduced working day (or the period is not specified), etc. Since the broken working day regime is not convenient for the employee, incentive additional payments may be included in the local regulatory act (see Article 144 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The absence of an elected trade union body is not an obstacle to the introduction of a broken working day regime, however, if employees do not agree with such an introduction, they can file a complaint against the employer’s actions with the labor dispute commission operating in the given organization or with the court.
| © 2008-2018, Labor Consulting LLC |
If the amount of compensation is deliberately underestimated
This situation is a gross violation of the law. If an employee believes that the head of the enterprise has illegally underestimated the amount of compensation payments, he needs to write a statement and submit it to the inspectorate for the protection of workers' rights or GIT (State Labor Inspectorate). The complaint will definitely be accepted, and the employer will receive an official notification.
If the manager does not consider it necessary to correct the situation in the near future, then a thorough check is carried out and, if the facts are confirmed, he faces:
- a fine of 1 to 5 thousand rubles for government officials;
- legal entities will have to part with large sums - from 30 to 50 thousand rubles.
If amendments are made to the Government resolution, the amount of fines may change, but not less. Such proceedings do not deprive the employee of the opportunity to continue his work. If the manager does not blurt out the missing amount of compensation, you can safely go to court. There is already a smell of infringement of rights and discrimination here, and I am ready to provide legal support in resolving such a dispute.
The employee has the right to demand not only the amount of underpaid compensation, but also a certain day for moral damage. Dealing with this on your own is quite difficult.
How does separation occur?

The employer understands that some vacancies at his company require a split working day. But he doesn’t quite understand how to do it correctly. A certain procedure will help you undergo the procedure painlessly:
- develop a normative act specifying the distribution procedure;
- sending the document to the trade union committee;
- internal affirmation;
- familiarization with the document of the employees in respect of whose activities this was done;
- concluding an additional agreement with the employee.
These are necessary actions that will protect a person from violations on his part by the employer. The trade union is conducting a check to see how the standards specified in the announcement are being observed.
Commentary on Article 105 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The division of the working day into parts is regulated by Article 105 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In those jobs where this is necessary due to the special nature of the work, as well as when performing work the intensity of which is not the same throughout the working day (shift), the working day can be divided into parts so that the total duration of working time does not exceed the established duration of daily work .
Such work is usually associated with serving the population (for example, in urban passenger transport, in communications and trade organizations). In this case, the total working time should not exceed the established duration of daily work. This division is made by the employer on the basis of a local regulatory act adopted taking into account the opinion of the elected trade union body of this organization.
The law does not determine how many parts a working day can be divided into.