Home / Labor Law / Occupational Safety and Health
Back
Published: 08/10/2016
Reading time: 11 min
0
7343
Although every citizen, in accordance with the Constitution of the Russian Federation, is guaranteed the right to safe work, in some areas of activity such conditions cannot be provided.
This is due to the presence of harmful factors in the workplace, the impact of which on employees is a feature of the activity.
It is worth considering these factors in more detail, including the example of individual professions, and also determining their impact on the human body.
- Legislation
- What it is? Physical
- Chemical
- Biological
- Psychophysiological
- Accountant
What is a production factor
An occupational factor is any substance or exposure that affects a person during work. The impact can be beneficial, neutral or harmful. Anything that does not cause harm is rarely taken into account in hygiene regulations. A harmful production factor is anything that can cause harm to health and therefore must be regulated.
Harmful production factors
Occupational Safety and Health
There are many concepts that refer to harmful and dangerous production factors; they are found in many areas of activity.
The owner’s task is to timely and correctly identify harmful and dangerous production factors and take measures to ensure safety. It is impossible to detect the danger and determine its characteristics on your own.
Identification means identifying all aspects of influence that may have a negative impact, measuring their values and comparing them with standard indicators.
To do this, you need not only to correctly classify different phenomena, but also to be able to measure their level of influence. This requires special equipment and complex analyses.
Such tasks require the participation of professionals. Our expert laboratory has enough experience, competence and the required equipment to carry out all work in this direction. Ecostar specialists will quickly detect all dangerous and harmful production factors; a table with standard values will help to establish their level. After this, if necessary, a plan is developed to minimize or eliminate harmful influences, and optimal means are proposed to protect workers. The owner of an enterprise is obliged to have a general understanding of harmful and dangerous production factors in order to protect his employees from their influence and ensure compliance with legislative requirements, violation of which can lead to large fines and even the elimination of certain workshops or the closure of the entire company. Therefore, we recommend promptly seeking help from specialists and regularly monitoring changes.
Harmful production factors
Harmful factors are the characteristics of the work process and environment that cause diseases. By their origin they are divided into natural and anthropogenic, and by nature - into physical, chemical, biological and psychological. They have a specific or nonspecific effect on humans and cause occupational diseases.
Industrial injuries: what is it, types
Physical factors and diseases to which they lead:
- illumination - visual impairment;
- temperature - burns, heatstroke, hypothermia;
- radiation - radiation sickness, tumors;
- height - injuries from falling;
- noise and vibration - hearing loss and vibration disease;
- dust - respiratory diseases;
- electricity - electrical injuries;
- moving parts - injuries.
The negative effect of these factors leads to injuries and chronic diseases. You can fight them using special clothing that is appropriate for the temperature and protects from moisture, insurance when working at heights, protective gloves, helmets and dust masks. Each protective equipment must comply with GOST.
Chemical factors and the results of their influence:
- general toxic substances - poisoning;
- irritating - chemical burns;
- sensitizing - occupational eczema;
- carcinogenic - tumors;
- mutagenic - harmful effects on offspring.
For your information! Harmful production factors of chemical origin cause chronic diseases and acute poisoning.
Biological effects and diseases caused by them:
- microorganisms and their toxins—infectious diseases;
- biological fluids - infectious diseases.
Pathogens can be present in any substance that has been in contact with a sick person. Each type of pathogen has its own hazard class.
Psychological factors are those to which a worker is exposed when performing stressful and emotionally charged work. Their effect is the most difficult to identify and prove, so they are often not taken into account. The result of their action is neuroses, obsessions, diseases of the heart, blood vessels and digestive system.

Variety of harmful factors
Hazards in the workplace
Special working conditions: what are they?
A key factor in identifying hazards is whether they cause severe or fatal injuries. Even short-term exposure is enough to cause irreparable harm to health. This is the main difference between dangerous factors and harmful ones - harmful factors have a strong but reversible effect, which can be corrected by rest.
Since all these factors have an adverse effect on the body, they are taken into account together. Moreover, the same factor by nature can cause harm to health of varying degrees, it depends on the strength of the impact. Thus, exposure to vibration can be harmful (if it is not strong) or dangerous (if it is strong and causes disability).
Influence of psychophysiological factors on occupational safety
The main indicators of a person’s work activity are considered to be his ability to work, i.e. the ability to perform formed, purposeful actions. From a physiological point of view, this is the ability of the human body to withstand a given physical and emotional stress during the work process.
Changes in physiological functions that cause a decrease in human performance during labor are called industrial fatigue. The psychological state of a person associated with fatigue is called fatigue. In the absence of overloads that cause fatigue, the body’s performance when stopping work or changing the type of activity is completely restored.
Intellectual load
Mental work is considered easy, in which there is no need to make a decision. If the employee makes a decision within the framework of the instructions, then such working conditions are acceptable. Stressful working conditions include work that involves solving complex problems using multiple instructions.
In the process of production activity, a person performs tasks of varying degrees of complexity. Processing any information or performing a task without evaluating its results is less complex work, which allows it to be assessed as optimal. If, in addition to these actions, the need to verify the result obtained is added, then such working conditions are acceptable.
The functions performed under time pressure and if responsibility for the final result is added, determine the work performed as intense.
Sensory loads
They are assessed by the duration of concentrated observation, the density of signals and messages, the number of production facilities being monitored, as well as the load on the visual and auditory analyzer. The duration of concentrated observation as a percentage classifies this indicator as follows:
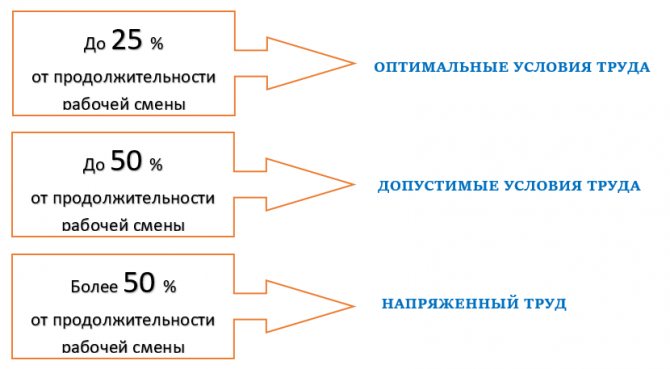
The intensity of labor also depends on the number of simultaneously observed objects. In this case, objects mean a technological process, instrumentation, production product, etc. With an increase in the number of objects of simultaneous observation, labor intensity increases.
The load on the visual analyzer is determined by the size of the object in question and the observation time. The smaller the size of the object in question and the longer the observation time, the higher the load on the visual analyzer and the labor intensity increases accordingly.
Working with video display terminals for up to two hours per shift is considered optimal, up to three is acceptable.
Working at a computer or monitoring the process via a video terminal for more than the specified time is defined as stressful.
Emotional stress
The degree of responsibility for the result of one’s own activities and the significance of an error indicates the extent to which an employee can influence the result of one’s own work at various levels of complexity of the activity performed. With increasing complexity, the degree of responsibility increases, since erroneous actions lead to additional efforts on the part of the employee or the whole team, which, accordingly, leads to an increase in emotional stress.
If there is no risk to one’s own life in the process of performing one’s duties, the performer’s work is considered optimal, but if it is likely, then the working conditions are considered stressful. Working conditions are similarly assessed according to the degree of risk for the safety of other persons.
Return to content
Sources of harmful chemical factors
Working conditions in the workplace: what is it?
The main source of harmful chemical substances is the railway. Tanks and freight cars transport petroleum products, mineral fertilizers, fluorine compounds and other substances. During loading and unloading, gases are released into the environment, and if handled carelessly, leaks occur.
The second harmful source is oil and chemical production. It is impossible to ensure the complete absence of interaction between workers and harmful factors. Despite the use of special clothing and protective equipment, workers inhale toxic fumes. The greatest danger is accidents at such factories.
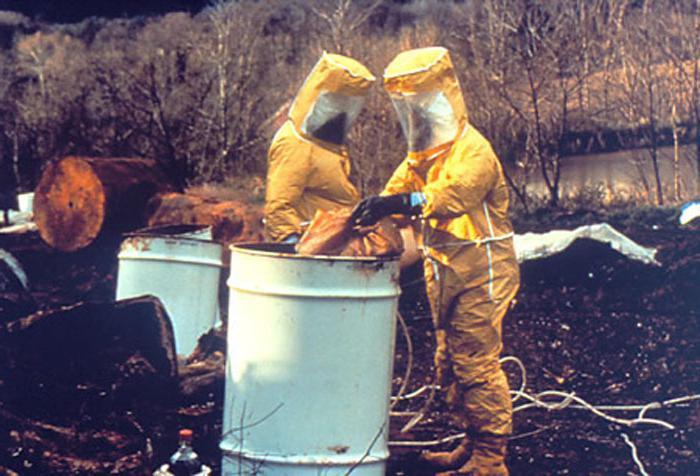

Chemical hazards
The third most dangerous profession is workers in the paint and varnish industry. The danger is posed by fumes from products and their components that workers inhale. Volatile compounds pose a threat to those employees who work directly with them, and also penetrate into neighboring workshops and offices of engineering workers.
In most industries, various reagents are used at one stage or another, even if the plant is not a chemical plant. Therefore, each enterprise undergoes certification and regularly confirms the safety of its workshops.
Physical factors
Physical harmful factors in the working environment are the most heterogeneous group of harmful influences. When the impact is weak, they are perceived as common occurrences, and employees often neglect occupational safety rules. In addition, physical factors are the most frequently changing ones, which is why it is necessary to change the means of protection against them (for example, put on gloves when cleaning the work area and take them off when working with moving parts). The most studied and widespread of physical factors are noise and vibration.
Noise and its impact on humans
Noise includes any constant and uninformative sounds, regardless of their volume. This could be the sounds of operating equipment, moving equipment, or loud music. Noise, to one degree or another, accompanies any human activity, causing harmful consequences. Noise has the greatest effect on the hearing and nervous system.
With constant exposure to noise, a person’s hearing in general deteriorates or certain frequencies are lost.
Note! People whose profession involves working in noisy environments are required to undergo audiometry - a test that indicates the degree of hearing damage. If such violations are recorded, the employee is suspended from work temporarily or permanently (depending on the extent of the injury).
Long-term exposure to loud noise leads to irreversible hearing loss. The simplest protective equipment is earplugs.
Determining the effects of noise on the nervous system is more difficult. Its result is sleep disturbances, irritability, headaches, and neuroses. The decisive factor is not the volume, but the duration of exposure. Earplugs and normalization of work and rest schedules ease the impact of noise on the psyche.
Impact of vibration and its elimination
Working conditions in which the impact of harmful and dangerous factors on workers is most significant also includes vibration. Its impact causes harm to health of varying intensity, causing vibration disease. Its manifestations range from mild to severe. A mild degree is manifested by mood disturbances and a temporary decrease in the sensitivity of parts of the body that interact with vibrating devices.
Severe degree means persistent impairment of tactile sensitivity, pathology of vascular tone and emotional sphere. Patients lose their ability to work, their blood supply to their fingers deteriorates, spontaneous spasms occur, and trophic ulcers may develop.
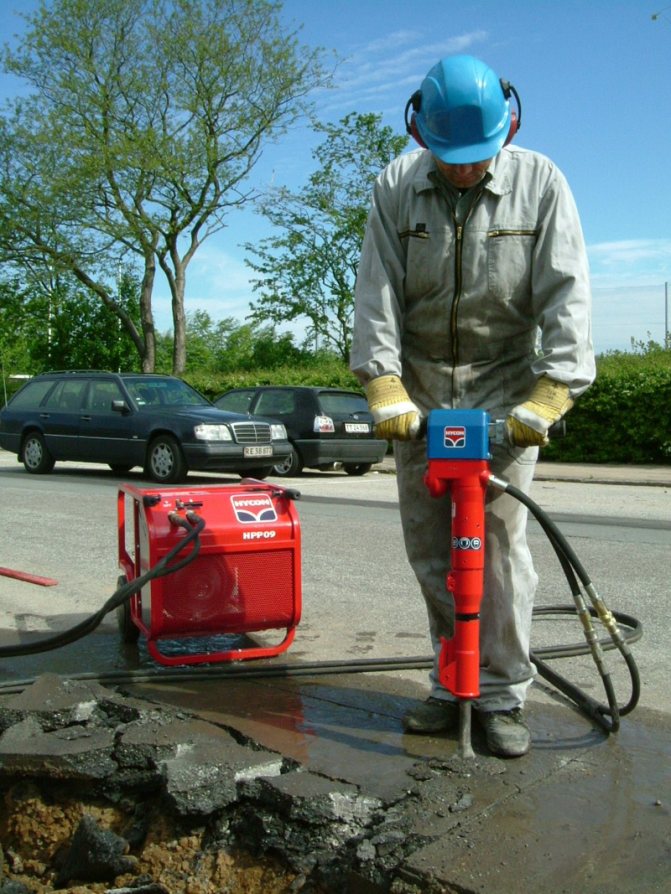

Vibration is harmful to health
To avoid vibration at work and the diseases it leads to, vibration and noise insulation is used - special materials that absorb vibration. Workers are provided with anti-vibration gloves, and the time spent at work must be strictly taken into account. Be sure to take breaks so that the body can compensate for the damage caused.
Other classifications
If the body is affected by several aspects at once, then division into the following groups is used:
- independently acting - each phenomenon has its own influence, which does not depend on others and is clearly visible;
- cumulatively acting - completely different conditions can have a similar effect, increasing negative consequences;
- antagonistically acting - allowing to level each other’s load;
- synergistically acting - with their joint influence, the damage is much greater than the total separately.
By the nature of detection, we can distinguish those that a person can determine organoleptically (temperature, smell, light, sound) and those that require special equipment for detection (electromagnetic radiation, current strength, gases, etc.).
List of harmful and dangerous production factors by source of origin:
- ergonomic – related to convenience, natural suitability of the necessary work for the characteristics of the human body;
- natural – climate, regional characteristics, weather phenomena;
- technical and technological – directly related to equipment, technology.
The same phenomenon can be assigned to different groups, therefore the division into groups itself, and even the distinction between the main dangerous and harmful production factors, is conditional.
The list of harmful production factors shows that they affect almost every sector of human activity to varying degrees. Negative impacts can be encountered even when working as an accountant, since in this case there is close contact with computer equipment, and the employee also experiences nervous and emotional stress. The monotony of such work is also harmful.
Harmful and dangerous occupational factors are those conditions and features of the working environment that lead to an increase in the load on the physical health or psyche of personnel, and are also characterized by an increased degree of risk. Moreover, depending on the type of work activity and working conditions, the negative impact may be different. Certain professions are identified as particularly dangerous by the very description of the labor process. Examples could be firefighters, roofers, industrial climbers, and mountain foremen.
Today, legislative bodies are considering including workplace violence in the classification, the risk of which is quite high in professions related to military service, work in law enforcement, in correctional institutions, etc.
Protecting workers from hazardous substances
Personal protective equipment prevents hazardous substances from coming into contact with human organs. This concept includes PPE for the skin, respiratory system and eyes. Rubber gloves are used to protect the skin of the hands. They are required when working with any caustic substances. Protect your face with plastic shields or goggles to avoid splashes.
Respirators are used against inhalation of toxic substances, and gas masks are used in difficult conditions. Protective suits are used to fully protect the entire body. They are necessary for working in emergency conditions and in particularly hazardous industries. Each employee who is issued such equipment must be familiar with the instructions for its proper use.
Important! According to the rules for providing workers with PPE, enterprises provide employees with cleaning products: soap, protective creams that do not allow contaminants to be absorbed into the skin, products for cleaning and neutralizing various substances.







