Free legal consultation by phone:
8
Part-time work is quite commonplace for many citizens. This opportunity is used not only to increase profits, but also to implement their own plans. For example, the main job can serve as the main source of income, and the additional one can be for one’s own pleasure and self-development. However, the employment of part-time workers makes the issue of recording their working time both under the employment contract and in the accounting sheet relevant.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation
A part-time employee is considered to be an employee who works at a given enterprise under an employment contract exclusively during the hours that remain free from his main job. A distinction is made between external part-time work, in which an employee who already has a job enters into a contract with another employer, and internal, in which case he is employed in the same organization, but for a different position, both in another and in the same department. At the same time, a part-time worker can conclude more than two work contracts. There is no upper limit for the working hours of part-time workers in the law, and the number of combinations can only be limited by common sense.
It is established that an employee cannot practice internal part-time work in the same profession or specialty. Being employed at the enterprise as an operator or manager on a full-time basis and working additionally, he simply works overtime or on weekends. This is how this work should be viewed and paid accordingly. Working in the same profession in different organizations is considered as external part-time work.
Part-time employment is formalized by order of the employer. An entry in the employee’s work book can be made at the place of his main job by the employer, who has this document at his disposal at the request of the employee. However, no such obligation is provided for him.
In accordance with Article 284 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a part-time worker has the right to be employed in a second job for no more than four hours a day. This time limit applies only to those cases when he is busy at his main job on the same day. If on a certain day he is free from it, then the employee has the right to work at the place where he is employed part-time, full time. It is stipulated that the total working time of part-time workers cannot be more than half of the working time that is established for a given period (month or other) as the norm.
MY RIGHTS: HOW TO PROTECT YOUR RIGHTS

Labor legislation on recording working hours when working part-time
Part-time work (part-time work) as a legal category occupies a special place in labor legislation.
There are features in the organization of labor relations associated with part-time work:
- regarding the conclusion and termination of employment contracts,
- working hours,
- provision of holidays and benefits,
- work restrictions, as well as guarantees regulated by labor legislation.
What is part-time work according to labor law?
Part-time work is the performance by an employee, in his free time from his main job, of another permanently paid job for the same or another employer under the terms of an employment contract:
- in accordance with the norms of labor legislation, when working part-time, it is mandatory to conclude a written employment contract ;
- in the employment contract and in the order (instruction) on hiring, it must be indicated that the work is performed part-time.
Part-time work is regulated by Chapter 44 “Features of regulation of labor of persons working part-time” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with the Labor Code, part-time work (part-time work) is:
- performance by an employee of other regular paid work under the terms of an employment contract in his free time from his main job.
Conclusion by an employee of employment contracts for part-time work:
- allowed with an unlimited number of employers,
- unless otherwise provided by federal law.
Part-time work can be performed by an employee:
- as in the place of his main work,
- so do other employers.
The employment contract must contain a mandatory indication that the job is a part-time job.
Part-time work is not allowed:
- workers under 18 years of age,
- at work with harmful and dangerous working conditions,
- if the main work involves the same conditions,
- as well as in other cases provided for by the Labor Code and other federal laws.
Features of regulation of part-time work for certain categories of workers:
- teaching staff,
- medical and pharmaceutical workers,
- cultural workers
in addition to the specifics established by the Labor Code and other federal laws, they can be established in the manner determined by the Government of the Russian Federation, taking into account the opinion of the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations.
Article 282 “General provisions on part-time work” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (as amended on 02/05/2018)
Do not confuse part-time work with combining professions (positions).
Combination of professions (positions)
Combination of professions (positions) is regulated by specific labor legislation.
When combining professions (positions), with the written consent of the employee, he may be entrusted with:
- performance during the established duration of the working day (shift) along with the work specified in the employment contract,
- additional work in a different or the same profession (position) for additional pay.
Article 151 “Payment for combining professions (positions), expanding service areas, increasing the volume of work or performing the duties of a temporarily absent employee without release from work specified in the employment contract” of the Labor Code
Additional work assigned to an employee in another profession (position) can be carried out:
- by combining professions (positions);
- additional work assigned to an employee in the same profession (position) can be carried out by expanding service areas, increasing the volume of work;
- to perform the duties of a temporarily absent employee without release from work specified in the employment contract, the employee may be assigned additional work in either a different or the same profession (position);
- the period during which the employee will perform additional work, its content and volume are established by the employer with the written consent of the employee;
- the employee has the right to refuse to perform additional work ahead of schedule, and the employer has the right to cancel the order to perform it ahead of schedule, warning the other party about this in writing no later than 3 working days.
Article 60.2 “Combination of professions (positions). Expanding service areas, increasing the volume of work. Fulfillment of duties of a temporarily absent employee without release from work specified in the employment contract" of the Labor Code
Types of part-time jobs: external and internal part-time jobs
In accordance with labor legislation, an employee has the right to enter into employment contracts to perform other regular paid work during his free time from his main job:
- for the same employer - internal part-time and
- with another employer - external part-time work .
Article 60.1 “Part-time work” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Internal part-time:
- can be carried out by the employee at the employer’s place of main work;
- in this case, in addition to the previously concluded employment contract for the main job, an agreement on part-time work must be concluded.
This type of part-time job is beneficial for both the employer and the employee:
- the employer entrusts the work to the most qualified employee who is able to ensure the implementation of the tasks facing the organization,
- and the employee has the opportunity to increase his income level and realize his abilities more fully.
External part-time job:
- involves the employee performing work in another organization;
- that is, an external part-time worker is an employee who works for another employer in a certain specialty, profession, position, qualification under a second employment contract in his free time from his main job.
At the same time, labor legislation does not limit the number of additional employers with whom an employee has the right to enter into an employment contract for part-time work.
Hiring for external part-time work: Who can be a part-time worker
In general, external part-time work does not require special consent from the employer at the main place of work:
- the employee has the right to independently realize his desire to work part-time.
However, the current labor legislation contains a number of restrictions regarding part-time work.
Thus, in accordance with Articles 282 and 329 of the Labor Code, part-time work is not allowed for the following categories of workers:
- those under 18 years of age - in all jobs without exception;
- workers engaged in heavy work, work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions - if their main work involves the same conditions;
- workers whose work is directly related to driving vehicles or controlling the movement of vehicles - in work directly related to driving vehicles or controlling the movement of vehicles;
- in other cases provided for by federal laws.
Article 282 “General provisions on part-time work”, Article 329 “Working time and rest time for employees whose work is directly related to the movement of vehicles” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Some restrictions on part-time work have also been established for heads of organizations. Thus, according to Article 276 of the Labor Code:
- the head of an organization can work part-time for another employer only with the permission of the authorized body of a legal entity or the owner of the organization’s property, or a person (body) authorized by the owner;
- the head of an organization cannot be a member of the bodies performing the functions of supervision and control in this organization.
In certain cases, the Labor Code refers the employer to other federal laws and regulations that limit the combination of certain categories of employees:
- these are, in particular, Federal laws on state and municipal unitary enterprises, bodies of the judicial community, advocacy and advocacy, magistrates;
- Resolutions of the Government of the Russian Federation, for example, the Resolution regulating the procedure and conditions of part-time service (work) in the system of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia;
- the ban on holding a second job is also contained in paragraph 3 of Article 97 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, which clearly states that State Duma deputies work on a professional permanent basis and, in addition, can only engage in teaching, scientific or other creative activities;
- The conditions for part-time work for teaching, medical, pharmaceutical and cultural workers are also special and are regulated by the Labor Code, other laws and regulations. For example, by the same Decrees of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 4, 2003 No. 197 and the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated June 30, 2003 No. 41 “On the peculiarities of part-time work for teaching, medical, pharmaceutical and cultural workers.”
Required documents when applying for external part-time work
Article 283 of the Labor Code establishes a clear list of documents presented by the applicant when applying for a part-time job with another employer (external part-time job):
- the employee is required to present a passport or other identification document;
- When hiring a part-time job that requires special knowledge, the employer has the right to demand from the employee:
presentation of a document on education and qualifications or a duly certified copy thereof,
- and when hiring a job with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions - a certificate about the nature and conditions of work at the main place of work.
Article 283 “Documents presented when applying for part-time work” of the Labor Code
This list of the Labor Code does not indicate an insurance certificate of state pension insurance, however, it is also a necessary document when concluding an employment contract, since the payment by the employer of insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation for a part-time worker will require the employer to know the SNILS of the part-time worker.
Work book for external part-time work
When hired for an external part-time job, the employee is not required to present his work book, since it is kept by the employer at his main place of work. Accordingly, employers do not keep work books for persons working for them on an external part-time basis.
At the request of the employee at the place of his main job, entries about external part-time work can be made in the work book. Information is entered on the basis of a document confirming external part-time work. These may be copies of orders for external part-time employment, transfers, dismissal, or relevant certificates.
Recording working hours when working part-time: Standard working hours for part-time workers
The standard working time for part-time workers (both for external and internal part-time work) is determined by agreement of the parties and is fixed directly in the employment contract.
The working hours for part-time workers are also determined by agreement between the employee and the employer, secured by an employment contract and can be formalized in the form of a work schedule.
Duration of working hours when working part-time:
- should not exceed 4 hours a day ;
- on days when the employee is free from performing job duties at his main place of work, he can work part-time full time (shift);
- within one month (another accounting period), the duration of working time when working part-time should not exceed 0.5 of the monthly standard working time (standard working time for another accounting period) established for the corresponding category of employees;
- The specified restrictions on working hours when working part-time do not apply in the following cases:
when the employee has suspended work at his main place of work due to a delay in payment of wages for more than 15 days or
Part 2 of Article 142 “Responsibility of the employer for violation of deadlines for payment of wages and other amounts due to the employee” of the Labor Code
- suspended from work for health reasons (in accordance with a medical report) with retention of position in cases provided for in parts two or four of Article 73 of the Labor Code.
Article 73 “Transfer of an employee to another job in accordance with a medical report” of the Labor Code
A full-time working day without a limit of 4 hours of working time can be assigned to part-time workers:
- on their days off at their main place of work;
Article 284 “Duration of working hours when working part-time” of the Labor Code
- during any vacation and in other cases when the employee is free from performing job duties at his main place.
However, in this case, the monthly standard of working time for a part-time worker, as already mentioned, should not exceed half of the standard established for the corresponding category of workers.
Data on working time worked part-time is reflected in the working time sheet. When performing work duties on an internal part-time basis, the time worked by the employee is reflected in the time sheet separately for the main position and part-time, while the employee may be assigned two personnel numbers.
Remuneration for part-time workers
Labor legislation does not establish any specifics regarding the remuneration of employees working part-time.
With a time-based wage system, the wages of part-time workers are determined by:
- in proportion to the time worked.
In the case of piecework wages:
- depending on output or on other conditions specified in the employment contract.
When establishing standardized tasks for employees working part-time with time-based wages:
- remuneration is made based on the final results for the amount of work actually completed.
For employees working part-time in areas where regional coefficients and wage supplements are established:
- remuneration is made taking into account these coefficients and allowances.
Article 285 “Remuneration of persons working part-time” of the Labor Code
Part-time workers, like main employees, have the right to various additional payments and allowances established by labor legislation, local regulations of the employer, and collective agreement.
Article 133 “Establishment of the minimum wage” of the Labor Code requires that the monthly wage of an employee who has worked the full working time must not be lower than the minimum wage:
- however, since a part-time job is effectively a part-time job, monthly wages may be lower than this wage level.
A part-time worker’s salary, like any other employee, must be paid at least every half month.
Part 6 of Article 136 “Procedure, place and terms of payment of wages” of the Labor Code
Payment of sick leave to a part-time worker
Part-time workers, both internal and external, have the right:
- to receive benefits for temporary disability and pregnancy and childbirth,
- provided that they worked part-time for the same employer during the previous 2 calendar years.
To pay benefits for internal part-time work:
- the employee submits one sick leave (sick leave certificate).
In case of external part-time work, a separate sick leave certificate (certificate of incapacity for work) is submitted for each place of work:
- at the place of work on a part-time basis - with the mark “external part-time job” and indicating the details of the main sick leave (certificate of incapacity for work).
Vacation when working part-time
Employees working part-time are granted annual paid leave:
- simultaneously with leave from the main job;
- if the employee has not worked at a part-time job for 6 months:
then the leave is provided in advance;
- then the employer, at the employee’s request, provides him with leave without pay of the appropriate duration.
Article 286 “Vacation for part-time work” of the Labor Code
The duration of such leave is determined as the difference between leave at the main place of work and leave at a part-time job. The employee has the right to take leave without pay for the entire period or for a shorter period.
To receive leave for a part-time worker with an external part-time job:
- can submit a certificate or a certified copy of the order granting leave from the main place of work;
- however, the employer can grant leave to an external part-time worker based on his application.
Part-time workers have the right to receive both annual basic leave and additional leave provided in the manner prescribed by current legislation and collective agreements (agreements).
Payment for vacation or payment of compensation for unused vacation to part-time employees is made according to general rules.
Business trips while working part-time
An employer who has provided an employee with the opportunity to work part-time has the legal right to send the employee on a business trip. Sending a part-time worker on a business trip is possible only during free time from the main job.
At the legislative level, the question of what to do with the main place of work for a part-time worker sent on a business trip has not been resolved:
- he may be able to get unpaid leave for this time, but the main employer is not obliged to provide him with this leave;
- in addition, if the leave is nevertheless granted, the part-time worker loses earnings.
Therefore, external part-time work at work associated with business trips is almost impossible.
The opposite situation is equally problematic, when an employee who has a part-time job is sent on a business trip for his main job. Therefore, if the main job involves business travel, external part-time work is also not recommended.
An option to solve this problem may be the obligation of the employer, enshrined in the employment contract, to provide the employee with unpaid leave for the period of business trips for his main job.
If an employee is sent on a business trip simultaneously for both his main job and part-time work:
- then his average earnings are retained by both employers, and reimbursable business trip expenses are distributed between the employers sending the employee by agreement between them;
- in this case, the seconded part-time worker is reimbursed for travel expenses on general terms, and the daily allowance in any case must be paid in a single amount, and not for each of the positions occupied.
Dismissal from a part-time job
Employees working part-time can be dismissed on any of the grounds provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In this case, all rules for terminating an employment contract established by labor legislation must be observed:
- in particular, it is impossible to dismiss a part-time worker at the initiative of the employer during the period of his temporary incapacity for work or while on vacation
Part 6 of Article 81 “Termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer” of the Labor Code
- when dismissing due to a reduction in the number or staff of employees, it is necessary to notify the part-time employee personally, against signature, of the upcoming dismissal at least two months in advance.
Article 180 “Guarantees and compensation to employees upon liquidation of an organization, reduction in the number or staff of an organization’s employees” of the Labor Code
However, an employment contract concluded for an indefinite period with a part-time worker:
- may be terminated in the event of hiring an employee for whom this work will be the main one,
- The employer warns the part-time worker in writing about this at least 2 weeks before the termination of the employment contract.
Article 288 “Additional grounds for termination of an employment contract with persons working part-time” of the Labor Code
In this case, the length of working hours of the main employee does not matter:
- will he work full time?
- or he will be assigned part-time work.
When dismissing an employee with whom an agreement has been concluded on an external part-time basis:
- no later than the day of dismissal, a final settlement must be made with him and all wages due to him must be paid;
- if the employee did not work on the day of dismissal, then the corresponding amounts, in accordance with Art. 140 of the Labor Code, must be paid to him no later than the next day after the dismissed person submits a request for payment.
Article 140 “Terms of calculation upon dismissal” of the Labor Code
In addition to the final payment, on the day of dismissal, the part-time employee must be given copies of documents related to work:
- dismissal order,
- income certificate, etc.
In case of delay for the part-time worker in completing the final payment:
- for the entire period of such delay, the employer is obliged to pay interest (monetary compensation) in the amount of not less than 1/300 of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in force at that time on amounts not paid on time;
- this compensation is paid for each day of delay, starting from the next day after the established payment deadline, up to and including the day of actual settlement;
- the obligation to pay the specified monetary compensation arises regardless of the employer’s fault.
Article 236 “Financial liability of the employer for delay in payment of wages and other payments due to the employee”
Summary.
When applying for part-time employment, both with the main employer (internal part-time job) and in another organization not related to the main place of work (external part-time job), one should not forget about the regulatory side:
- on concluding an employment contract with a part-time worker,
- about the contents of this employment contract,
- on compliance with all conditions prescribed by labor legislation (vacation, benefits, compensation, etc.).
Guided by the content of this material, you will be able to apply your knowledge, avoiding unnecessary questions and disputes with the employer in the future.
If you have any questions about the violation of your rights, or you find yourself in a difficult life situation, then an online duty lawyer is ready to advise you on this issue for free.
WORK TIME
Accounting Features
An external part-time worker works at the enterprise in a single position during working hours, free from performing duties at the main job. This category of employees is assigned its own details - the number under which it appears in the time sheet. There, the part-time worker’s working hours are written down on one line. It will be noticeably less than that of employees for whom this organization is the main place of work.
An internal part-time worker can be considered as an employee employed in a given organization in two positions at the same time. Therefore, two lines should be allocated for him in the working time sheet. At the same time, as a part-time worker, he can have as a requisite the same number that was assigned to him at his main workplace, as well as a different one from it. In the first case, its time is taken into account in one place, an additional line is placed under the main one. In the second case, his indicators are reflected in two different places, in each of which he appears under a different number.
Employment contract
In accordance with Article 57 of the Labor Code, information such as the time when the employee starts work and when he completes it does not apply to the mandatory conditions of the employment contract. Therefore, the requirement to specify the working hours of a part-time worker in the agreement is not established; the parties can do this of their own free will. This norm is very convenient for company employees who have an unstable schedule.
The working hours should be specified in the employment contract only in one case. This becomes an obligation if the employee’s schedule does not coincide with the general rules adopted at the given enterprise regarding the start and end times of work.
If a part-time worker works at different working hours on different days, a schedule is developed for him. This document describes the working hours of the part-time employee; the employee himself gets acquainted with this plan and signs this fact. An appropriate provision is included in the employment contract, for example, that “The employee’s work schedule is determined in accordance with the schedule approved by the manager.” If necessary, a copy of the plan can be presented in the personal file of the part-time worker.
In this case, in any case, the contract must mention that, under this agreement, the employee will work with the organization as a part-time employee.
Rights and obligations of the employer
3.1. The employer has the right:
— conclude, amend and terminate an employment contract with the Employee in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— conduct collective negotiations and conclude collective agreements;
— encourage the Employee for conscientious, effective work;
— require the Employee to fulfill his job duties and take care of the property of the Employer (including the property of third parties owned by the Employer, if the Employer is responsible for the safety of this property) and other employees, and compliance with internal labor regulations;
— bring the Employee to disciplinary and financial liability in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— adopt local regulations;
- create associations of employers for the purpose of representing and protecting their interests and join them;
— create a works council;
— [other rights provided for by the current Labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreement, local regulations].
3.2. The employer is obliged:
— comply with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, local regulations, terms of the employment contract, agreements, collective agreement [if any];
— provide the Employee with work stipulated by the employment contract;
— ensure safety and working conditions that comply with state regulatory requirements for labor protection;
— provide the Employee with equipment, tools, technical documentation and other means necessary to perform his job duties;
— provide the Employee with equal pay for work of equal value;
— pay the full amount of wages due to the Employee within the terms established in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the collective agreement [if any], internal labor regulations, and the employment contract;
— conduct collective negotiations, as well as conclude a collective agreement in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
— provide employee representatives with complete and reliable information necessary for concluding a collective agreement, agreement and monitoring their implementation;
— familiarize the Employee, against signature, with the adopted local regulations directly related to his work activity;
— timely comply with the instructions of the federal executive body authorized to exercise federal state supervision over compliance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, other federal executive bodies exercising state control (supervision) in the established field of activity, pay fines, imposed for violations of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms;
— consider the submissions of the relevant trade union bodies, other representatives elected by employees about identified violations of labor legislation and other acts containing labor law norms, take measures to eliminate the identified violations and report on the measures taken to the specified bodies and representatives;
— create conditions that ensure the Employee’s participation in the management of the organization in the forms provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws and the collective agreement [if any];
— provide for the Employee’s everyday needs related to the performance of his job duties;
— carry out compulsory social insurance of the Employee in the manner established by federal laws;
— to compensate for damage caused to the Employee in connection with the performance of his labor duties, as well as to compensate for moral damage in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation;
— [other duties provided for by the current Labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreement, local regulations].
back to contents
Working hours of part-time workers on the pre-holiday day
Working hours for all categories of employees on the day preceding a holiday are reduced by one hour. The corresponding norm is contained in Article 95 Part 1 of the Labor Code. At the same time, this legislative act does not contain specific provisions relating to working hours on the pre-holiday day of part-time workers.
A more general rule states that all guarantees provided to employees apply to all employers and to all employees. This implies that part-time workers have the right to a reduction in working hours on a pre-holiday day in the same way as other employees in the amount of one hour.
How many rates and hours can there be for internal part-time work?
Legislative acts do not reflect restrictions on how many places a citizen can work in part-time conditions. It is provided that one person has the opportunity to simultaneously have several jobs, at each of which he takes half the working rate.
If we talk about internal part-time work, this applies to situations when a person works in one company, but in several positions. The formation of this type of relationship requires the execution of a separate employment agreement. It states:
- how many hours does a person work
- bet amount
- obligations and powers of the parties
- amount of monetary reward
It is legally stipulated that the duration of the working day cannot be more than 4 hours. In addition, it is unacceptable to establish internal part-time work on a full-time basis. The limit value is half of the specified value. The employment contract must reflect the number of hours that must be worked by a person in an additional position. In a week this figure cannot be more than 20 hours.
Before hiring a person, the positions of the company management and the future employee are agreed upon. As a result, a work schedule and a table are formed where special data is entered. The last option is associated with the action of shift work in the company.
The provisions of the employment agreement also specify the procedure for making payments. Several options are allowed:
- payment for time actually worked by a person;
- payments as a certain number of orders are completed.
Currently, companies most often use the first payment option. This is due to the fact that it greatly simplifies the calculations and transfers of amounts to employees.
Part-time worker's time sheet
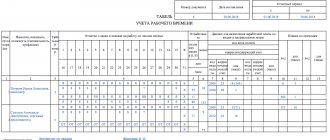
A part-time worker’s time sheet is a document that records the time actually worked under this form of employment.
The working time sheet is presented in two standard forms:
- Form T-12 is a time sheet that takes into account working hours and also calculates the amount of wages; in the future, this article will be about it.
- Form T-13 is a report card, which takes into account only the hours worked by the part-time worker.
Both of these forms were approved by the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation.
Along with them, each enterprise has the right to create its own forms for these purposes.
Below is Form T-13, which records the working hours of an internal part-time worker.
Working hours for a part-time worker in an employment contract
As stated in the Labor Code, when working part-time, it is necessary to draw up an employment contract at the second workplace. It must contain all the details related to this activity.
The main requirement for this agreement is an indication of the fact that according to it the employee is employed as a part-time worker. In other details, this version of the employment contract is completely similar to the standard ones, which are drawn up at the place of primary employment.
Rights and responsibilities of an employee
2.1. The employee has the right to:
— conclusion, amendment and termination of an employment contract in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
- providing him with work stipulated by the employment contract;
— a workplace that meets state regulatory requirements for labor protection and the conditions provided for by the collective agreement [if any];
— timely and full payment of wages in accordance with their qualifications, complexity of work, quantity and quality of work performed;
— rest provided by the establishment of normal working hours, reduced working hours for certain professions and categories of workers, the provision of weekly days off, non-working holidays, paid annual leave;
— complete reliable information about working conditions and labor protection requirements in the workplace;
— training and additional professional education in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— association, including the right to create trade unions and join them to protect their labor rights, freedoms and legitimate interests;
— participation in the management of the organization in the forms provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws, if any, and by the collective agreement;
— conducting collective negotiations and concluding collective agreements and agreements through their representatives, as well as information on the implementation of the collective agreement and agreements;
— protection of one’s labor rights, freedoms and legitimate interests by all means not prohibited by law;
— resolution of individual and collective labor disputes, including the right to strike, in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
- compensation for harm caused to him in connection with the performance of his job duties, and compensation for moral damage in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— compulsory social insurance in cases provided for by federal laws;
— [other rights provided for by the current Labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreement, local regulations].
2.2. The employee is obliged:
— conscientiously fulfill his labor duties assigned to him by the employment contract;
— comply with internal labor regulations;
— maintain labor discipline;
— comply with established labor standards;
— comply with labor protection and occupational safety requirements;
— take care of the property of the Employer (including the property of third parties held by the Employer, if the Employer is responsible for the safety of this property) and other employees;
— immediately inform the Employer or immediate supervisor about the occurrence of a situation that poses a threat to the life and health of people, the safety of the Employer’s property (including the property of third parties held by the Employer, if the Employer is responsible for the safety of this property);
— [other duties provided for by the current Labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreement, local regulations].
back to contents
Accounting
The Labor Code states that the employer has an obligation to keep track of the working time that all employees actually worked. This rule also applies to part-time workers. When taking into account the working hours of part-time workers, it is unacceptable that the load assigned to them exceeds the norm established by law.
Accounting for a part-time employee’s working hours is carried out according to the following rules:
- Time is counted from the moment when the part-time worker actually began working in his place and up to the moment when he was relieved of his own duties.
- Time is taken into account on a monthly basis, recording the duration of the part-time worker’s work every day, as well as other employees, in the time sheet.
- This timesheet is kept by the head of the company department in which the part-time worker or other person who has been assigned this responsibility works.
- In the time sheet, the use of working time is taken into account by the method of recording the appearance of part-time workers at a place or absence from it, regardless of the type of accounting and the form of part-time work. Another accounting option is associated with recording exclusively deviations (in the case under consideration - hours of part-time work)
- All part-time workers, like other employees, have mandatory details entered into their time sheet. These include, first of all, a personnel number, which is assigned to all employees, including part-time workers, after hiring. In addition, the report card contains the first and last name, position and profession. Finally, the details include the number of days worked at a given place, as well as hours worked. Special emphasis is placed on night and overtime hours and hours related to work on weekends and holidays. They also indicate the number of days on which the employee did not show up for work, specifying such acceptable reasons as vacation or temporary disability.
- If a part-time employee does not show up for work, then the validity of his reasons must be confirmed in the same way as for an employee at his main place. To certify that the reasons are valid, there must be an order granting the employee leave, or a certificate of incapacity for work, or a certificate stating that during the period of absence he was engaged in the performance of duties to the state or society.
In the timesheet, the accounting time of employees working part-time is reflected by general rules applicable to all employees. The number of hours that an employee worked on a certain working day is indicated in a cell marked with the same date. Its duration may be indicated as a fraction. In this case, write 4 hours 24 minutes as 4.4 hours.
In the cells relating to weekends, enter the letter “B”, in the cells relating to the time when the part-time worker was on vacation - the code “OT”. If documents confirm that the employee was sick during a certain period, “B” is entered in the appropriate cell. Finally, the days when the employee reported to work are marked
The difference in drawing up a timesheet for a part-time worker is that he has the right to work only at half the rate. Therefore, the timesheet is assigned reduced time. However, with a rotating or rotating schedule, the number of hours indicated for a particular day may vary.
Recording the working hours of an internal part-time worker
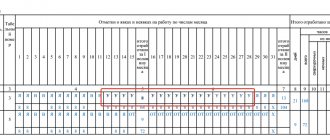
An internal part-time worker is an employee who takes a second job with the same employer. There are two methods to keep track of his working time in the timesheet.
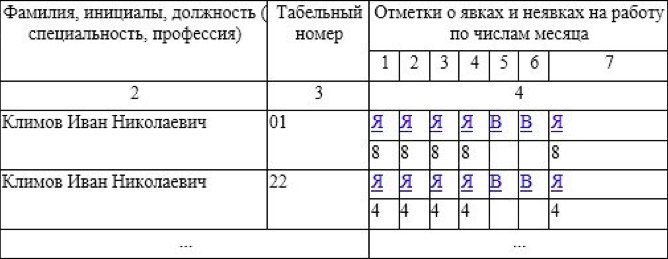
1. One of them is to add an additional line to the timesheet. It takes into account the hours and minutes worked by the employee as a part-time employee, in contrast to the time he worked at the same enterprise as a regular employee. An additional number for the time sheet is not assigned to it. Below is a timesheet for an internal part-time worker with a single number for the main and additional positions. In this document, under the lines with the code indicating the days of attendance and days off, there is a line indicating his working hours at the main position (8 hours each), and then a line with part-time work is added. It is noteworthy that in the first half of the month he worked as a part-time employee for 34 hours, which fits within the 20-hour limit for these employees. In addition, during both weeks it also did not exceed this indicator, the hours are evenly distributed.
| Serial number | Full name, position (specialty, profession) | Personnel Number | Notes on attendance and absence from work by day of the month | Total worked for the first half of the month | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | Kosarev I.P. manager | 5 | I | I | I | I | I | IN | IN | I | I | I | I | I | IN | IN | I | |
| 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 72 | |||||||
| 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 34 | |||||||
2. The second method consists of assigning an additional number. In this case, two lines are also devoted to the employee’s employment at this enterprise, but he appears in them under different numbers.
The choice of one of the two indicated methods is determined by the number of employees in the company as a whole and in particular the number of part-time workers, both internal and external, the number of divisions and other considerations.
It is worth noting that part-time work does not have a specific code, so for it the employer can enter any suitable letter combination, for example “RS”.
It is necessary to separate the hours that the employee spent at the main workplace and as an internal part-time worker. When summing them up, the controlling authority may come to the conclusion that this is a part-time job, which is paid accordingly.
Maximum working hours for part-time workers
The working hours of part-time workers cannot exceed 4 hours. It is also indicated that in certain types of work where it is difficult to comply with the standard norm of working no more than 4 hours a week, it is allowed to take into account working hours in aggregate with the consent of the trade union committee.
It is also established that during the month the working time of part-time workers cannot exceed half of the monthly working time standard for an employee. The restrictions provided for by this norm are canceled if the employee’s main place of work is suspended from performing duties under Article 73, Part 2 or 4 of the Labor Code. Also, restrictions are lifted if the employee voluntarily suspended work in accordance with Article 142 part 2 of the same law.
This means that the weekly working hours of part-time workers cannot exceed 20 hours. The above-established norm of 4 hours a day follows from this. Taking into account the above clause about the possibility of taking into account work time cumulatively, for companies in which it is difficult to comply with the norm of a 4-hour working day, part-time work for more than 4 hours a day is allowed. In this case, it is necessary to fulfill the condition of a weekly working time limit of 20 hours in a part-time position. For this time period, cumulative recording of working time is not provided.
Terms of payment
5.1. The employee is paid a salary of [amount in figures and words] rubles.
5.2. The Employee's remuneration is made [in proportion to the time worked/depending on output or/on other conditions].
5.3. Additional payments and allowances of a compensatory nature, including for work in conditions deviating from normal conditions, systems of additional payments and incentive allowances and bonus systems are established by a collective agreement, agreements, local regulations and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
5.4. Wages are paid to the Employee [indicate specific dates of the calendar month]./ Wages are paid to the Employee at least every half month on the day established by the internal labor regulations.
5.5. When performing work outside the normal working hours, at night, on weekends and non-working holidays, when combining professions (positions), when performing the duties of a temporarily absent employee, the Employee is paid appropriate additional payments in the manner and amount established by the collective agreement and local regulations.
5.6. During the period of validity of this employment contract, the Employee is subject to all guarantees and compensation provided for by the current labor legislation of the Russian Federation.
back to contents
Transfer to part-time
Part-time work is time that is less than the normal duration accepted for the working week. If part-time, transfer to this position means that the employee will work not 4 hours a day, but only 2 or 1 hour.
Such a change in the labor relations of the parties is permitted, but must be introduced by agreement. The transfer is required to be approved by both the employer and employee. Following this, the manager is allowed to issue an order of appropriate content, which establishes part-time employment. In this case, the part-time worker must be familiarized with this order against signature after its release. In the future, in the working time sheet, his accounting for the part-time worker is carried out according to the time he spent on performing his duties.