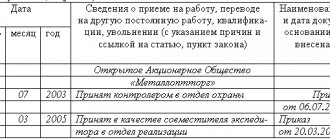
New edition of Art. 264 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Guarantees and benefits provided to women in connection with maternity (limitation of night work and overtime work, involvement in work on weekends and non-working holidays, assignment on business trips, provision of additional leaves, establishment of preferential working conditions and other guarantees and benefits established laws and other regulatory legal acts) apply to fathers raising children without a mother, as well as to guardians (trustees) of minors.
Part-time work
The employer is obliged to establish a part-time working day (shift) or a part-time working week at the request of one of the parents (guardian, trustee) who has a disabled child under the age of 18 (Part 1 of Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
To do this, the employee must write a statement.
To confirm his right, the employee must provide the employer with:
- birth (adoption) certificate of a child or a document confirming the establishment of guardianship or trusteeship of a disabled child;
- a certificate confirming the fact of disability, issued by the bureau of medical and social examination;
- documents confirming the place of residence (stay or actual residence) of a disabled child;
- other documents.
Part-time working time is established for a period convenient for the employee, but no more than for the period of existence of the circumstances that were the basis for the mandatory establishment of part-time working time, that is, for the period of time that the employee’s child has the status of “disabled child.”
Labor guarantees and benefits
When providing preferences, employees are partially exempt from performing certain rules and certain official duties, and are also created easier working conditions. Such preferences are granted to the following categories of employees:
- students who work and study on the job;
- employees who have 1 or more children with disabilities;
- single mothers;
- women raising children under 18 years of age;
- retired employees, etc.
In addition to preferences, according to the law, employees are entitled to a variety of labor guarantees. These are the means, methods and conditions, upon provision of which certain rights are exercised (Article 164 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Labor guarantees come in two types: intangible and tangible. When providing the first of them, employers perform the following actions:
- maintain a job when the company's workforce is reduced;
- extend the main vacation;
- give 1 or more additional days off;
- limit the duration of overtime for various jobs and night shifts;
- send an employee on a business trip (with the employee’s consent);
- give sick leave;
- provide and pay for a certificate of incapacity for work when caring for 1 or more children or a sick family member;
- if necessary, transfer the employee to part-time work;
- postpone the main vacation to a more convenient time;
- provide the opportunity to work remotely - via the Internet, etc.
When providing labor specific material guarantees, employers perform the following actions:
- maintain the average salary during the period of study leave;
- do not reduce an employee’s salary when transferring to another position due to urgent production needs;
- maintain the average salary during 1 or several forced absences of the worker;
- arrange various payments to employees who have lost their ability to work;
- pay compensation to employees who have suffered a work injury or occupational disease, etc.
Important! During hard work with a variety of harmful working conditions, they provide such a labor guarantee - they reduce the length of the working week from 40 to 36 hours (Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Article 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Reduced working hours”
Benefits for working pensioners
Working retirees receive several employment benefits. Employees of retirement age are provided with the following privileges:
- are not fired due to retirement;
- draw up a fixed-term contract. This is done when a working pensioner retires due to age or takes early retirement due to certain harmful working conditions. If you refuse to draw up such a document, an open-ended contract is drawn up with the worker;
- at the request of a working pensioner, they provide an additional second leave on any day, regardless of the vacation schedule. The duration of such a vacation is 14 days as a maximum, but it is not paid.
Read also: Housing subsidy for military personnel
Also, at the personal request of a retired employee, they are transferred to part-time work. After early dismissal due to the closure of a particular company or enterprise, this employee is given a severance pay in the amount of salary and is paid the basic salary for another 2 months.
Attention! In 2021, working pensioners with a “veteran of labor” certificate will also be provided with various benefits based on long work experience (for men - 25-40 years, for women - 20-35 years).
For example, these citizens receive an additional payment to their pension (in Moscow - 1,000 rubles). The exact list of documents and conditions for receiving such state assistance can be found in the local Department of Social Protection of the Population (at the place of registration).
Benefits for working single mothers
Single mothers are also provided with various labor benefits.
In this situation, such employees are given part-time work, transferred to remote work, and the length of their vacation and length of service are not reduced. A single mother is not fired from her job at least until her 1 or more children turn 14 years old. Early dismissal is carried out in the following exceptional situations:
- Upon liquidation of the company. In this situation, a single mother is employed in another company, where they pay approximately the same salary as in the previous organization;
- In case of repeated failure to fulfill specific official duties;
- In case of gross violation of internal labor regulations.
Important! To the basic leave for a single mother with a child under 14 years old, another 14 days of rest are added once a year - all days at once or several times for a certain number of days. This point is indicated in the collective labor agreement.
The work schedule for the night shift (from 22:00 to 6:00) is approved only after the consent of the working single mother. In this situation, a written refusal to engage in such activities is not considered a violation of internal labor regulations.
Benefits for working mothers of many children
Working mothers of many children are provided with the following labor preferences:
- upon personal request, reduce the working week or establish a flexible schedule;
- exempt from paying various insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs;
- No early dismissal. This is done if the mother is the sole breadwinner of 3 or more children under 14 years of age. Moreover, the youngest of them is not even 3 years old;
- they are not sent to work on night shifts and are not given certain overtime work (until 1 or more children are 3 years old);
- transferred to part-time work (if there is a child under 14 years of age or 1 or more disabled children under 18 years of age);
- are hired without passing a certain probationary period (if the child is under 1.5 years old);
- provide additional, but unpaid leave for 14 days (under a collective labor agreement), if 1 or more children are under 14 years of age;
- sent on leave for up to 14 days to accompany their 1 or several children to another city when enrolling in a university;
- receive an early retirement pension.
Attention! Unemployed mothers with many children are given the right to emergency employment and training at the local Employment Center.
Benefits for working parents of disabled children
Working parents of disabled children are also provided with various labor preferences.
For example, during an interview, these citizens do not notify the potential employer that they are raising a child with a disability group. In this situation, after successful employment, they go to their boss or the personnel department and provide an ITU certificate, according to which the employee, in connection with raising 1 or several disabled children, is entitled to various benefits. Such labor preferences remain in force until the expiration of this document (after the removal of disability) or until the child reaches adulthood.
Read also: Tax benefits in 2021
Working parents of 1 or more disabled children are provided with:
- give an additional 4 days of rest for 1 month. Days off are provided only to the mother or only to the father, or they are alternated according to any scheme (1+3 or 2+2). As a result, both or one of the parents are provided with 4 additional monthly days of rest as a maximum;
- When only the mother or father of a disabled child is employed, the second unemployed parent is given all the days off that are due to the first employee. In this case, certain documentation is collected and a separate application is drawn up;
- when constantly caring for 1 or several disabled children or staying with them in a hospital, the working parent is paid sick leave (no more than 120 days per year for 1 minor).
Important! If labor rights are violated, they go to the local state labor inspectorate, the prosecutor's office at the place of registration, or file a claim in court.
Benefits for working students
Students who combine study and work are provided with the following benefits:
- take out an additional second leave with preservation of salary. This time is given to prepare for passing the intermediate and (or) final annual certification at the specific place of study;
- sent on unpaid leave for successful admission and enrollment in a local university and passing the examination session;
- Once a year they pay for travel to a specific place of study (to a university or college).
Attention! Working students have their working hours reduced or given an additional day off (in addition to Saturday and Sunday) to prepare for a specific exam.
Benefits for working disabled people
According to Art.
23 Federal Law No. 181 of November 24, 1995, disabled workers are provided with the necessary comfortable working conditions. This is done according to an individual rehabilitation program. Disabled employees are provided with the following preferences:
- disabled people of groups I and II have their working hours reduced from 40 to 35 hours a week while maintaining the same salary;
- are involved in overtime work or daily work duties on weekends or at night only with the consent of the employee and the group and provided that such work does not harm his health (Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- provide annual leave of at least 30 days;
- when involved in overtime work, the working day is extended by 4 hours for 2 days in a row and by 120 hours per year as a maximum.
Important! In accordance with Art. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation, specific terms of the employment contract (agreement) and transfer to another specific job are carried out only under a separate agreement between the disabled employee and the employer.
Such a document is concluded in writing. If, according to a medical report, a disabled working person is temporarily transferred to another job for 4 months. or forever, then if the employee refuses such a transfer or the employer does not have a certain vacancy, the employment contract is terminated in accordance with clause 8 of Part 1 of Art. Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Federal Law of November 24, 1995 No. 181-FZ “On social protection of disabled people in the Russian Federation”
Article 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Night work”
Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “General grounds for termination of an employment contract”
Article 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Changing the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties”
Features of annual leave
One of the parents (guardians, trustees, foster parents) raising a disabled child under the age of 18 has the right to be granted annual paid leave at his request at a time convenient for him (Article 262.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
A collective agreement can establish annual additional leaves without pay at a time convenient for them, lasting up to 14 calendar days. Such leave, upon written application of the employee, can be added to the annual paid leave. This leave cannot be transferred to the next working year (Article 263 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Read in the berator “Practical Encyclopedia of an Accountant”
Providing annual leave
Commentary on Article 264 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Persons raising children without a mother, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, include fathers raising children without a mother, men raising children adopted by them without a mother, guardians and trustees raising children without a mother, stepfathers raising children without a mother, adoptive fathers raising children without a mother. In practice, they may be an adoptive parent, a stepfather, as well as an adoptive parent (adoptive father).
Guarantees and benefits related to raising a child are provided regardless of the reasons why the mother is absent (death, deprivation of parental rights, serving a sentence, long-term illness, long business trip, etc.).
Guarantees and benefits in the field of labor relations:
in accordance with Part 3 of Article 64 of the Labor Code - prohibition of refusal to conclude an employment contract for reasons related to the presence of a child;
restriction of work at night (part 5 of article 96, article 259 of the Labor Code);
restriction of involvement in overtime work, on the basis of Part 4 of Article 99 and Article 259 of the Labor Code;
Part 5 of Article 113 and Article 259 of the Labor Code limit employment on weekends and non-working holidays;
transfer to another job of persons raising motherless children under the age of one and a half years, if it is impossible to perform the previous job (Part 4 of Article 254 of the Labor Code);
provision of parental leave for a child up to three years of age and benefits for the period of parental leave for a child up to one and a half years old (Article 256 of the Labor Code);
Article 258 of the Labor Code provides for the provision of breaks for feeding a child under the age of one and a half years;
in accordance with Article 259 of the Labor Code, restrictions have been established on business trips;
guarantees when establishing the priority of vacations (Article 260 of the Labor Code);
guarantees upon termination of an employment contract (Article 261 of the Labor Code);
additional days off when caring for a disabled child (Article 262 of the Labor Code);
additional leaves without pay established by the collective agreement (Article 263 of the Labor Code);
restrictions on work on a rotational basis (Article 298 of the Labor Code).
The given list of guarantees and benefits that can be enjoyed by persons raising children left without maternal care is not exhaustive, and these persons can also enjoy other rights and guarantees provided to women with children. If the collective agreement establishes additional guarantees and benefits for women in connection with raising children, they should also apply to the persons specified in Article 264 of the Labor Code.
Additional days off
An employee has the right to be provided with 4 additional paid days off per month to care for disabled children (Part 1 of Article 262 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The procedure for providing additional paid days off is established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 13, 2014 No. 1048.
To be granted additional days off, the employee must also submit a written application.
Read in the berator “Practical Encyclopedia of an Accountant”
Payment for days off to care for a disabled child
Characteristics of Art. 220 TK
At the beginning, it is emphasized that the state provides workers with protection of their rights to work in conditions that meet current labor protection criteria.
It is indicated that the work parameters specified in the employment contract must meet current labor protection criteria.
The following are options in which, in a situation where work is suspended due to a violation of labor safety standards through no fault of the employee, he retains his position and average salary. This is possible if the activity:
- administratively suspended;
- was placed under a temporary ban.
While this situation is being resolved, the employee, with his consent, is moved to another position, but with a salary that is not lower than the average in the previous position.
The situation of an employee refusing to work if a dangerous situation arises is also considered. It is indicated that the employer is obliged to provide him with other work for the period of elimination of this danger. Exceptions are possible in cases provided for by the Labor Code and relevant legislation. If it is impossible to provide an employee with work, then the time of forced downtime is paid by the employer in accordance with the Labor Code and relevant legislation.
A situation was separately analyzed when the employer was unable to provide staff with the protective equipment required by them. In this case, he cannot require his subordinates to start work and must pay them for forced downtime based on the provisions of the Labor Code.
Cases were examined when an employee’s refusal to work does not entail disciplinary liability for him. This is possible if he refuses to work:
- if a danger arises for him due to violation of labor protection parameters;
- in harmful conditions - unless this is specifically provided for in the employment contract.
It is emphasized that in a situation where harm is caused to an employee at work, the compensation due to him is paid on the terms stipulated in the relevant Federal Law.
It is indicated that in order to prevent violations of labor protection requirements, the state undertakes to organize supervision in this area. It also prescribes the parameters for the responsibility of managers for such violations.