24.06.2019
0
302
3 min.
In order to find responsible employees, the manager sets a trial period. During this time, you can verify the competence of the new employee. However, when an already employed person transfers, problems arise with this type of checks. The correctness of the legal registration of this period and the legality of all actions during personnel movements are discussed in this article.
Making an entry about the employee's position in the work book

The issue of employment today is open in our country.
Unfortunately, labor laws are not always and everywhere observed, and many employers, taking advantage of workers’ ignorance, seek to benefit from hiring an employee for a position.
Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
Such a cunning move allows employers to use a citizen’s work function for a certain period of time, and later, without paying him what he is due or without paying him at all , dismiss the citizen from his position. Of course, the employee will try to prove something in court, but what can he do if the work book is empty.

Nowadays, in order to insure themselves, employers often hire workers for a probationary period.
Not all employees are familiar with labor legislation, which means that not everyone knows how it is correctly drawn up in the work book.
Employers persistently assure employees that the probationary period is not reflected in the work book in any way and, through systematic persuasion, they obtain labor.
One way or another, but then the workers are left without experience and without earned money, which means that time was wasted and the result was not achieved. In this article, we will look at all aspects related to an employee’s internship, applying for a permanent job and making an entry directly in the work book.
Who are we testing?
Having received a general understanding of the concept of “probationary period”, you need to understand one very important point: it is impossible to establish a probationary period for everyone, there are categories of newcomers with whom it is forbidden to include a condition about this in the employment contract.
- Elected through a competition to fill the relevant position, conducted in the manner established by labor legislation and other acts containing labor law norms
- Pregnant women and women with children under 1.5 years of age
- Under 18 years of age
- Those who have received secondary vocational education or higher education in state-accredited educational programs and are entering work for the first time in the acquired specialty within 1 year from the date of receiving vocational education at the appropriate level
- Elected to an elective position for paid work
- Invited to work by way of transfer from another employer as agreed between the employers
- Those concluding an employment contract for a period of up to 2 months
The Plenum of the RF Armed Forces in Resolution No. 1[1] indicated that provided for in Art.
70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employment testing is not established for pregnant women, women with children under the age of one and a half years, as well as persons under the age of eighteen. This rule also applies to other persons raising children under the age of one and a half years without a mother. If such employees have been placed on probation, then termination of the employment contract with them based on the test results is not permitted. In addition to those mentioned in Art. 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for categories of citizens, there are others. For example, according to Art. 207 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, persons who have successfully completed an apprenticeship, when concluding an employment contract with the employer under the contract with whom they underwent training, are not subject to a probationary period (see table).
| Norm | Categories of persons for whom the test is not established |
| Part 3 Art. 27 of the Federal Law of July 27, 2004 No. 79-FZ “On the State Civil Service of the Russian Federation” | Citizens who have received secondary vocational education under a training program for mid-level specialists or higher education in accordance with an agreement on targeted training with an obligation to subsequently undergo civil service and who are entering the civil service for the first time; employees appointed in accordance with clause 1, part 1, art. 31 of this law to a civil service position in the order of transfer in connection with the reduction of civil service positions or the abolition of a state body; other citizens and civil servants for whom the legislation of the Russian Federation provides guarantees for maintaining their place of work (position) |
| Part 9 art. 34.2 of the Federal Law of December 4, 2007 No. 329-FZ “On Physical Culture and Sports in the Russian Federation” | Persons who have successfully completed sports training on the basis of an agreement for the provision of sports training services, upon concluding an employment contract with the customer of these services |
| Part 10 Art. 24 of the Federal Law of November 30, 2011 No. 342-FZ “On service in the internal affairs bodies of the Russian Federation and amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation” | Citizens: – appointed to positions of senior management; – those entering educational organizations of higher education of the federal executive body in the field of internal affairs for full-time study; – appointed to positions based on the results of a competition |
If an employer includes a probation clause in an employment contract with a person who is prohibited from establishing a trial, this clause is not valid.
Dismissal of such an employee due to failure to pass the test on the basis of Part 1 of Art. 71 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation will be illegal. For example, the Smolensk Regional Court considered the case of reinstatement of an employee who was dismissed due to an unsatisfactory test result. The requirements were satisfied since the plaintiff had a child under the age of 1.5 years and the employer knew about this, but set her a probationary period, although paragraph. 2 hours 4 tbsp. 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation directly prohibits this. Accordingly, dismiss the plaintiff under Art. 71 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer could not (Appeal ruling of the Smolensk Regional Court dated September 23, 2014 in case No. 33-3145). For your information
If, upon hiring, a probationary period was nevertheless established for someone who should not be given one, changes should be made to the employment contract. To do this, an additional agreement is concluded to the employment contract, which cancels the probationary condition. Based on the agreement, a corresponding order is issued.
Therefore, do not impose a test on everyone, much less fire them under Art. 71 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if you are not sure of the legality of this decision, otherwise you may have problems in the form of:
- reinstatement of a dismissed person to his previous job (Part 1 of Article 394 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- payment of average earnings for the entire period of forced absence (Part 2 of Article 394);
- compensation for moral damage in the form of monetary compensation (Part 9 of Article 394);
- other payments in favor of the employee, for example, payment for the services of a representative in a court hearing (Part 1 of Article 100 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
Rules for entering an employee position
An employee who, for some reason, is not assigned to a specific position cannot work in an organization or an individual entrepreneur. If possible, the position should correspond to the employee’s specialty, which is indicated on the title page of the work book.
Also, upon appointment of an employee to a specific position in the organization, a corresponding order is issued. All this taken together means that the employee’s position should not contradict the position mentioned in the order .
What entries about the position need to be included in the work book?

The employment record must include the correct position entry in accordance with the position specified in the order.
Also, do not forget that it is important to correctly indicate not only the name of the position, but also to correctly enter the entry itself. So, when hiring, only one form of entry is allowed - this is an entry that looks like this: “Hired for such and such a position.”
How can I correct the entry?
HR department employees are people too, and sometimes, due to their inattention or due to other factors, they can make mistakes that they will be forced to correct. In the following paragraphs, we will look in detail at ways to correct such errors, and also provide relevant examples.
If there is an error
If there is a mistake in some word or the position is indicated incorrectly, then there is no need to rewrite the entry or, worse, change the employment title. You may well try to correct a mistake in the text or carefully cross out an unnecessary letter and write another one.
All this needs to be done as carefully as possible so as not to spread dirt and bold cross-outs in the work. But we advise you to consult with an employee first. If he insists on completely redoing the recording, you have no right to refuse him.
When renaming

It is enough for you to put the date of the day the entry was made and write the following phrase: “The position such and such has been renamed to such and such.” Do not forget to indicate in accordance with which order you decided to make such conclusions and enter its date and immediate number.
When it changes
According to the rules of the Labor Code, internal transfer is also reflected in the work book. The entry is made as follows: “Transferred to position such and such.” Also, don’t forget about writing an order.
Is the probationary period recorded in the work book?
The probationary period is also the period of performance of the labor function , and therefore, according to all the rules and with the total length of service . Drawing conclusions, we can say that such a period takes place to be reflected in the labor contract.
However, the question of whether it is necessary to indicate that the employee was hired specifically for a probationary period must be answered in the negative.
The fact is that despite the fact that the employee was hired for a probationary period, he is subject to the internal regulations of the organization, and also complies with all orders and acts issued.
Therefore, it would be discriminatory to write that the employee was hired only for a probationary period. The employee must ask the HR department to register his employment record in the proper manner , namely, write in the employment record that he has been accepted as an employee.

Since in the work book we do not indicate the fact that the employee was hired for a probationary period, this means that we should not indicate the fact that the employee was hired for a limited amount of time.
Therefore, the period is prescribed only in the employment contract between the employee and the employer .
Is it possible to do without a probationary record?
This is a gross violation of employee rights by the employer. That is why it is worth paying special attention to correctly filling out the work report, rather than dissuading the employee from receiving it.
Is there a labor report for a temporary employee?
A temporary worker also has every right to be recorded in the work book. Let the contract represent an agreement with him for a specific period, but still this period is the period for the implementation of the labor function, which means it simply must be entered in the employee’s work book. Temporary work, according to all the rules, is included in the total length of service and pension payments are deducted for it.
Who can be the initiator
The desire can be expressed by both the employee and the employer. In both cases, the cadre must provide a written statement: in the first, that he wishes to transfer, in the second, that he has considered the employer’s invitation and expressed his consent. There are certain moments when an employer can send an employee without his consent.
Reference! If an employee has health limitations, before transferring him, you need to make sure that it is not contraindicated for him.
Entry into the work book of a temporary worker
Where is it written?
Typically, temporary work is performed by employees for their absent colleagues . The wording can be completely different, the main thing is the fact that the employee replaces someone for a certain period.

The entry is made in the work book of the temporary worker in compliance with all the rules for making entries in the work book.
Many people mistakenly believe that there is a separate column for entering data for temporary workers. This is all wrong. In fact, a temporary worker should see that a record of his work , albeit temporary, is included in the column of general data about the work performed .
Record wording
A temporary job entry should look like this: “Temporarily hired for such and such a position.” As usual, we do not forget that the HR department employee must have an order that allows the employee to take up the position temporarily.
What entry in the work book during the probationary period is made in case of dismissal?
Where is it written?
In case of dismissal from the probationary period, a record is also required. It is done immediately under the employment notice. There is nothing particularly remarkable in the registration of the record of dismissal from the probationary period, but we will try to take a closer look at this fact and its wording.
Record wording
How is the entry worded? First of all, it should look like a simple dismissal of one’s own free will or by decision of the parties, because the employment record did not indicate that the employee was serving a probationary period.
“Dismissed from such and such a position for such and such a reason” the reason for dismissal is chosen by the employee and the employer jointly.
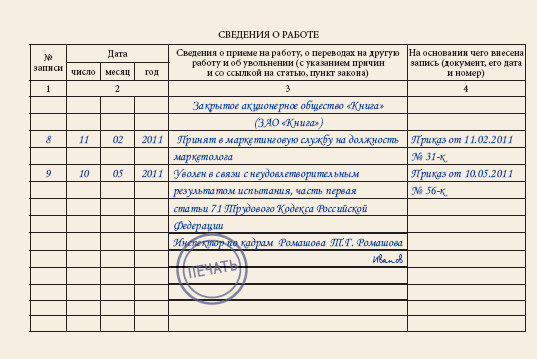
Sample entry in the work book about the dismissal of an employee who has not completed the probationary period
Responsibility of the employer in case of unlawful assignment of a test
An employee who has been placed on a probationary period in violation of the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation has the right to apply to the State Labor Inspectorate. In this case, the employer faces sanctions under Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation:
| Violation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | Officials | IP | Organizations |
| Primary | Warning or fine 1,000-5,000 rubles. | Fine 1,000-5,000 rubles. | Fine 30,000 -50,000 rubles. |
| Repeated | Fine 10,000-20,000 rubles. or disqualification from 1 year to 3 years | Fine 10,000-20,000 rubles. | Fine 50,000-70,000 rubles. |
See the GIT inspection plan for 2021 here.
Temporary transfer. How does it become permanent?
An employee works in a certain position, at a certain workplace, performs the same labor functions... But the legislator has, if necessary, provided for such a procedure as transfer to another position or another workplace. Moreover, there are temporary and permanent transfers. A situation is possible when an employee was transferred to another position temporarily, but remained in it on a permanent basis. We will tell you in the article how this happens, for what reasons and how it is formalized.
Briefly about translations
In accordance with Art. 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, transfer to another job is a permanent or temporary change in the labor function of an employee and (or) the structural unit in which he works (if the unit was specified in the employment contract), while continuing to work for the same employer, as well as transfer to another job to another location with the employer.
Based on this formulation, the following can be distinguished:
1. Transfer can be temporary or permanent.
2. The translation consists of:
3. A change in the structural unit will be a transfer only when this unit was indicated in the employment contract.
The most common type of transfer deserves special attention – in connection with a change in job function.
That is, it is not enough to simply change the employee’s job function; he must be transferred to a position with a different name. To do this, you need to make changes to the staffing table:
If the job duties remain the same, but the title of the position changes, the transfer is not formalized - the position is simply renamed. Then changes are simply made to the staffing table and the employment contract.
In both cases, you need to make entries in the work book. In the first case - about transfer, and in the second - about renaming the position.
Let us note that when transferring to another structural unit, the employer is not obliged to indicate in the employment contract which unit the employee works in, unless it is a separate unit (branch or representative office) (Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, even if the employer, in violation of this rule, did not indicate a separate division in the employment contract, then if the employee’s place of work changes, for example to the head office, a transfer must be completed.
A transfer from the same employer to another workplace, to another structural unit located in the same area, or an assignment of work on another mechanism or unit will not be considered a transfer, unless this entails a change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties (Part 3 of Art. 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
And the rarest case of processing a transfer is when the employer moves to another area and the employees agree to the move.
Probation period according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The terms of the employment contract may provide for testing the employee to determine suitability for the position held. Such a check is not considered mandatory, therefore, if it is not specified in the agreement, the applicant is hired without a probationary period (Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The test is characterized by some features for the parties to the labor relationship:
| Worker | Employer |
| Receives the right to resign at his own request with 3 days of service | Receives an additional basis for dismissal - an unsatisfactory test result, of which the employee is notified 3 days before the termination of the contract (Article 71 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The opinion of the trade union is not taken into account, severance pay is not paid |
The maximum duration of the inspection is established by Art. 70 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- for a fixed-term employment contract of up to 2 months, there is no probationary period;
- for a fixed-term employment contract from 2 to 6 months - a trial period of no more than 2 weeks;
- for an employment contract of 6 months - no more than 3 months, and for managers and chief accountants, their deputies - up to 6 months.
The probationary period does not include periods of employee absence from work (for example, due to illness). This means that the employee’s failure to appear postpones the end of the test to a later date.
At the end of the compliance check period, the employee is recognized as having passed it, and termination of the employment contract is allowed only on general grounds.
Is it possible to change the probationary period? Read here.
Temporary transfer
So, temporary transfer means a temporary change in a job function or structural unit. During a temporary transfer, the employee retains his previous place of work.
Types of temporary transfer
By agreement of the parties
At the initiative of the employee
At the initiative of the employer
By virtue of Part 1 of Art. 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee may be temporarily transferred to another job with the same employer by agreement of the parties, concluded in writing, for a period of up to one year. If the transfer is carried out to replace a temporarily absent employee, who, in accordance with the law, retains his place of work, the transfer period will end when this employee returns to work.
The employee himself can propose a transfer when, for example, another position in the same department or a position in another department is vacated. As a rule, a desire to transfer on a permanent basis is expressed. If the employer does not object, the employee is transferred. However, the Labor Code establishes cases when an employee is entitled to a temporary transfer to another position for certain reasons and the employer cannot refuse him.
In accordance with Art. 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, such guarantees are provided:
1. Pregnant women, if, in accordance with a medical report, they cannot perform the work of their position. Based on the pregnant woman’s application, the employer must reduce her production standards, service standards, or transfer her to another job that eliminates the impact of adverse production factors.
2. Women with children under the age of one and a half years, if they are unable to perform their previous work. This should be understood as cases where such work is incompatible with feeding the child and properly caring for him or when such work has a certain working hours, relates to work with a traveling nature or remote from the place of residence, etc. (paragraph 3 p. 22 Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated January 28, 2014 No. 1 “On the application of legislation regulating the labor of women, persons with family responsibilities and minors”).
If these women are transferred to lower-paid positions, they retain the average earnings for their previous jobs.
However, the initiator of the transfer is often the employer. And here the Labor Code establishes cases when:
1. The employer is obliged to offer the employee a transfer.
2. An employer may transfer an employee without his consent.
Cases when an employer is obliged to offer a temporary transfer
Cases when an employer can temporarily transfer an employee without his consent
Medical indications according to a medical report for a period of up to four months (Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
A natural or man-made disaster, industrial accident, industrial accident, fire, flood, famine, earthquake, epidemic or epizootic and any exceptional cases threatening the life or normal living conditions of the entire population or part of it (Part 2 of Article 72.2 Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
Expiration, suspension of a special right (Part 2 of Article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
Downtime (temporary suspension of work for reasons of economic, technological, technical or organizational nature) (Part 3 of Article 72.2)
The need to prevent destruction or damage to property and to replace a temporarily absent employee (Part 3 of Article 72.2)
If, according to a medical report, an employee cannot hold his position at all, or if he has been deprived of special rights, he is offered not a temporary, but a permanent transfer. There are many other cases where a permanent transfer should be offered. For example, if an employee refuses to work under new conditions when there is a change in organizational or technological working conditions, resulting in a change in the terms of the employment contract (Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), a reduction in the number or staff of employees (Part 2 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), or the employee’s inconsistency with the job positions (part 3 of article 81), etc.
Please note: in cases where the employer is required to offer an employee a temporary transfer according to the table, the employee will be required to transfer to the offered position. Otherwise, the employer will have to remove him, since he can no longer perform the work of his position.
In other cases, in addition to these and those listed in Art. 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (for example, production necessity), the employee’s consent to a temporary transfer is required.
What to do if an employee’s suitability for a new position needs to be checked?
The provision for verification during transfer cannot be fixed in an agreement, even if the employee agrees to it. If the test is nevertheless stated in the agreement, such a clause is not enforced as it worsens the employee’s position by virtue of Art. 9 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
If an employer needs to make sure a subordinate’s suitability for a new position, he has the right to use one of the options:
- issue a temporary transfer (Article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), and if the employee successfully performs new duties, a permanent transfer. All this is possible only with the consent of the employee;
- dismiss the subordinate by agreement of the parties, and then rehire him with the establishment of a probationary period.
What if the transfer is required before the end of the trial period?
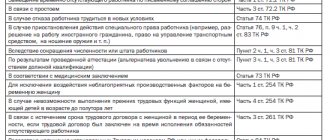
With the transfer, the labor function changes: verification was assigned in relation to the first, but in relation to the second it is no longer allowed.
It all depends on the nature of the translation:
| Permanent (Article 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) | Temporary (Article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) |
|
|
Is it possible to transfer an employee to another position without his consent? Read the material.
Registration of temporary transfer
So, if an employer wants to replace a temporarily absent employee and transfer another to his place, he sends the latter a proposal for a temporary transfer. The offer can also be made orally, since there are no special requirements for it. And if the employee agrees, an agreement to the employment contract is drawn up in writing in two copies.
If the transfer deadline is known in advance, it must be indicated in the agreement. However, if an employee is transferred to replace a temporarily absent employee, it is better to define the period as “until N returns to work.” When concluding a transfer agreement, fix in it the basis for the transfer, its duration, the employee’s new responsibilities, as well as other conditions that differ from those established by the employment contract.
Here is a sample of such an agreement.
Additional Agreement No. 2
to the employment contract dated May 23, 2015 No. 23/05-td
Yaroslavl May 13, 2021
Municipal budgetary institution "Department of Improvement" (MBU "Department of Improvement"), hereinafter referred to as the "Employer", represented by the director Viktor Ivanovich Kolesnikov, acting on the basis of the Charter, on the one hand, and Marina Vladimirovna Kopeikina, hereinafter referred to as the "Employee", on the other hand, collectively referred to as the “Parties”, have entered into this additional agreement to the employment contract dated May 23, 2015 No. 23/05-td as follows:
1. Due to the temporary absence due to temporary disability of the chief accountant, the Employee, with his consent, from the position of “accountant” is temporarily transferred to the position of “chief accountant”.
2. Transfer period: from May 14, 2021 until L.V. Babkina returns to work.
3. During the specified period, the Employee performs work in accordance with the job description for the above position.
4. For the period of temporary transfer, the employee is set the official salary provided for in the staffing table for the position of chief accountant in the amount of 70,000 rubles. per month, as well as bonuses, additional payments and bonuses provided for in the Regulations on remuneration and bonuses.
5. In all other respects that are not provided for in this additional agreement, the terms of the employment contract remain in effect.
6. This additional agreement is drawn up in two copies, one for each Party, and comes into force from the moment of signing.
Kolesnikov/V. I. Kolesnikov/Kopeikina/M. V. Kopeikina/
A copy of the additional agreement has been received. 05/13/2019, Kopeikina
Based on the agreement, a transfer order is drawn up in the unified form T-5 (approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 5, 2004 No. 1 “On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for labor accounting and payment”). In the line “Type of transfer” it is necessary to indicate that the transfer is temporary, and the employee must be familiarized with the order against signature.
Then you should make an entry about the transfer in section. III personal card “Hiring and transfers to another job” (f. T-2).
But an entry about a temporary transfer is not made in the work book (part 4 of article 66 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 4 of the Rules for maintaining and storing work books [1]).
If an employee is transferred to another job or position, he must be familiarized with the job description and other local regulations relevant to the performance of work for this position, and, possibly, undergo safety training and conclude a liability agreement.
Keep in mind that if, at the end of the transfer period, the employee’s previous job is not provided, and he did not demand its provision and continues to work, then the condition of the agreement on the temporary nature of the transfer loses force and the transfer is considered permanent (Article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
How to formalize this if the deadline for the transfer was unknown is not explained in the Labor Code. We think that first the employees can be notified that the main employee is returning to his place, and the temporary one is given his position, and then an order can be issued. You can immediately issue an order to terminate the performance of duties in a temporary position and return to the performance of duties in the main position, which the employee should also be familiarized with and signed. This order is drawn up in any form (see sample).
Municipal budgetary institution "Department of Improvement"
(MBU "Department of Improvement")
about the expiration of the temporary transfer period
Yaroslavl 06/13/2019
Due to the end of the transfer period
1. M. V. Kopeikina, who previously temporarily held the position of chief accountant on the basis of additional agreement No. 2 dated May 13, 2019, will begin performing her main duties as an accountant from June 14, 2019.
2. To accrue M. V. Kopeikina’s salary in the position of accountant from June 14, 2019 in accordance with the staffing table.
Director Kolesnikov /V. I. Kolesnikov/
I have read the order. Kopeikina, 06/13/2019
Test condition
First of all, let's say that a probationary period can only be established upon hiring, that is, at the time of concluding an employment contract.
According to the norms of labor legislation, the purpose of including such a condition in the contract is to check the employee’s compliance with the assigned work (Part 1 of Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). We draw attention to an important nuance: the test clause is included in the contract only by agreement of the parties. Of course, the employer may doubt the candidate’s professionalism if he is against the test. However, disagreement with such a condition will not be a valid reason for refusing to hire.
Part 2 of Art. 70 it is determined that the absence of a probationary clause in an employment contract means that the employee was hired without a trial. Even if this condition is in the contract, but the employee did not sign it, it is considered that the employee was accepted without testing. And here's an example.
S. was hired on April 2, 2015, which is confirmed by the hiring order. In accordance with this order, she was given a probationary period of 2 months. She read the employment order on April 2, 2015, but did not sign an employment contract with a similar condition.
On May 27, 2015, the employee contacted the employer with a resignation letter of her own free will, without indicating the desired date of dismissal. The defendant employer, believing that the plaintiff was on a probationary period, fired her three days later. However, the plaintiff did not agree with the date of dismissal, so she went to court, demanding to change it. The court granted the request, and here's why.
The court established and was not disputed by the parties that the probation clause was included in the employment contract, which the plaintiff (employee) did not sign. The inclusion of a test condition in the employment order (which the plaintiff familiarized herself with under signature) has legal significance within the meaning of Part 2 of Art. 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not have it. In such circumstances, the provisions of Art. 71 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, including Part 4, establishing a 3-day notice period for dismissal, were not subject to application to the relations of the parties and, at the initiative of the employee, the employment contract in this case could be terminated according to the general rules of Art. 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - 14 days after filing the application (Appeal ruling of the Sverdlovsk Regional Court dated December 2, 2015 in case No. 33-17309/2015).
note
During the probationary period, the employee is subject to the provisions of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts, collective agreements, agreements, and local regulations.
It also happens that an employer is in no hurry to conclude an employment contract with a newcomer, hoping that if he is not suitable for the job or he himself does not like the work, he can part with him without completing any documents. However, this is an unjustified step: an employment contract that is not drawn up in writing is considered concluded if the employee began work with the knowledge or on behalf of the employer or his authorized representative (Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, administrative liability is provided for evading the conclusion of an employment contract (Part 3 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
If, nevertheless, the employee is actually allowed to work without an employment contract, a probationary clause can be included in this contract (which must be concluded within 3 working days) only if the parties formalized it in the form of a separate agreement before the start of work. Accordingly, if no agreement was concluded, then all subsequent steps of the employer to conduct the test are illegal.
Some employers believe that an oral agreement to establish a probationary period is acceptable in this case. This is wrong. In particular, A.K. challenged the dismissal due to unsatisfactory test results. The court of first instance (which refused to satisfy the requirements), having questioned witnesses, examined the evidence presented by the defendant, came to the conclusion that when hiring the plaintiff was familiar with the condition of the probationary period, he actually started work, and there was an agreement between the employer and the plaintiff employment agreement with a probationary period of 3 months. However, the appellate court overturned this decision and satisfied A.K.’s demands, noting that the content of Art. 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation indicates the need to draw up a separate written agreement on a probationary period before starting work in the absence of a signed employment contract with information about the probationary period, which was not the case in the case of A.K. (Appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court dated November 24, 2015 in the case No. 33‑43726/2015).