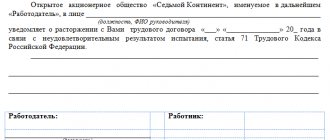
Valid reasons for the release (dismissal) of an employee have a significant impact, first of all, on length of service, date of dismissal, benefits, and tuition fees. This mainly applies to dismissals at the initiative of the employee.
| What does a valid reason affect when voluntarily leaving? | Explanations |
| Dating of dismissal | If there are valid reasons, the two-week work period is canceled, the date of departure is determined by the employee; in relation to this situation, the validity of reasons is established by Art. 80 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Dismissed person's length of service | The work experience is not interrupted over a long period, regardless of the pause in work. Thus, valid reasons include: · retirement; · moving to another area due to the transfer of a spouse to another job, etc. |
| Assignment and payment of benefits | Payment for sick leave is made if the employee has been sick for no more than a month, starting from the first day of dismissal. Unemployment benefits are calculated as a percentage of average earnings (Article 30 of Federal Law No. 1032-1 “On Employment” dated April 19, 1991 in ed. 07/29/2017) |
| Reimbursement of funds spent by the employer on employee training | If the reason is not valid, then the employee is obliged to return the money spent on his studies; If you leave early, your tuition fees will stop |
It is self-evident that in specified situations, justifiable circumstances of dismissal play a dominant role. So, usually the application does not need to indicate the reason for dismissal. But in special cases it is simply necessary to prescribe it. For example:
- the person being dismissed needs to receive payment not on the last working day, but much earlier;
- it is necessary to resign without working;
- An entry in the work book with reference to a valid reason is important, since it gives the right to receive a number of privileges.
In the absence of valid reasons, the dismissed person significantly loses his rights and opportunities.
Employer notice period
As a general rule, an employee who wishes to resign must give his employer two weeks' notice.
However, there are also special deadlines for such warning:
- if the employee’s employment contract establishes a probationary period when hiring, he can inform the employer of his resignation just three days before the expected date of dismissal;
- if the employee holds the position of manager, then the period for notice of dismissal is one month;
- For employees of internal affairs bodies, the notice period for termination of a contract is one month.
The employee and the employer can agree among themselves and not comply with the specified deadlines, then the dismissal will be carried out within the deadlines established by the parties.
In addition, there are special cases when the employer is obliged to dismiss the employee on the exact date indicated by the employee himself in his application:
- cases when the employee is unable to continue working - retirement, enrollment in an educational institution, etc.
- cases where an employee decided to quit because the employer violated labor laws, the provisions of an employment or collective agreement, etc.
After warning the employer about his resignation, the employee is not required to be at work, i.e. he may take a vacation or be on sick leave. The warning period remains the same and is not postponed.
Legal features
Article 278 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is called “Additional grounds for termination of an employment contract with the head of an organization.” Even from the name you can see that managers of enterprises and other organizations can be fired for a more extensive list of reasons than ordinary ordinary employees.
Dismissal is the termination of the employment relationship between an employee of an organization, on the basis of which he is not obliged to further perform his official duties. The employer is relieved of the obligation to pay him remuneration.
Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation describes the reasons why any employment relationship can be terminated:
- mutual agreement of both parties;
- the completed term of the concluded employment contract;
- termination of the contract at the initiative of the employer or the employee himself;
- transfer to another place with his consent or request;
- for other reasons that do not depend on the wishes of either party.
Dismissal must be formalized according to the rules established by federal and regional legislation, since non-compliance will be considered an administrative offense leading to a fine of up to 50,000 rubles.
Article 278 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows you to dismiss, without explanation, any head of an organization working in it on the basis of a concluded and valid employment contract, if the board of directors, shareholders or founders made such a decision at their general meeting, and the data on this was necessarily correctly entered into the minutes.
What to do if the employer refuses to accept and sign the employee’s application?
There are often cases when an employer does not want to fire an employee and in every possible way prevents his dismissal - he refuses to accept an application from the employee.
In this case, you need to do the following:
- You can make a copy of the resignation letter and bring it to the reception, office, personnel service, etc. Require the service employee to register the application, and on the second copy put the number, date and surname of the person who accepted the application.
In this case, the employee will have evidence that he sent the application to the employer, i.e. the employer is warned about his departure, and within the specified period the employer will be obliged to dismiss him, otherwise the employer’s actions will be illegal.
- You can notify your employer of your resignation by mail. To do this, the application should be sent by registered mail with notification, and an inventory of the correspondence sent should be made.
When the letter is received by the employer, the employee will be returned a notification of receipt of the letter, which, together with the receipt and inventory, will serve as evidence of the employee’s notice of his dismissal.
What happens if the employee did not indicate the date of dismissal in his application?
If the employee did not indicate the date of his dismissal in the application for dismissal, then the employer does not have the right to dismiss him after two weeks from the date of filing the application.
The fact is that the Labor Code establishes the obligation for an employee to notify the employer of his dismissal at least two weeks in advance - i.e. An employee can give one or two months’ notice.
The employer himself does not have the right to independently determine the date of dismissal of the employee. Therefore, in this case, it would be more correct to return the application to the employee and explain to him the rules for dismissal and writing an application. This can be done in writing so that it does not look like a refusal to dismiss.
Similar actions will be taken if the employee indicated the date of dismissal without observing the two-week deadline. In case of disagreement with such early termination of the contract, the employer is obliged to warn the employee about this in writing.
What to do in such a situation
Dismissal without providing reasons is a gross violation of labor laws and fundamental rights of the employee. That is why such a decision can be easily appealed if you take the following steps:
- Write an application to the director or founder of the enterprise with a request to provide reasons for termination of the employment relationship with a package of documents proving this.
- If there is a trade union in the organization and the employee participates in it, it is necessary to contact them to protect their rights. This function is part of their main responsibilities.
- Within 1 month after dismissal, you can contact the labor inspectorate. You must write a written request and attach all the necessary documents. A complaint to the prosecutor's office is written using the same system.
- However, the most effective method will be to go to court. Filing a claim leads to results, although it will take quite a long time. If the claim is satisfied, the employer will be obliged to pay wages for downtime and moral compensation. The limitation period is 1 month after dismissal.
The decision of the court or supervisory authority is mandatory for the head of the enterprise, non-compliance with which leads to an administrative fine.
Withdrawal of resignation letter
If an employee for any reason changes his mind about resigning, he can withdraw his application. This can be done before the expiration of the notice period, before the date of dismissal indicated in the application, and if the employee was granted leave with subsequent dismissal, then before the start date of the leave.
The review can be written on the resignation letter itself, or it can be issued in the form of a separate document.
After receiving the withdrawal of the application, the employer does not have the right to dismiss the employee. An exception is the case when another employee has already been invited in writing to take the place of an employee, who, by law, cannot be denied employment (for example, if the employee is invited as a transfer from another employer).
You may be interested in the Termination of Employment Mind Map, which describes this procedure in detail.
Or look HERE at how an employee’s financial liability is regulated.
Dismissal procedure
Upon expiration of the notice period, i.e. on the employee’s last working day, the employer is obliged to:
- issue a dismissal order and familiarize the employee with it;
- issue the employee with a work book with a record of dismissal at the employee’s initiative (i.e. there will be a link to clause 3, part 1, article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- pay the employee all payments due to him (salary, allowances, bonuses, compensation, including for unused vacation).
The employee must sign the work book, confirming that he has read the entry made, in the work book movement log, as well as in the personal card.
Reduction in the number of employees
Dismissal “due to reduction” (Clause 2, Part 1, Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) is currently used quite often. As a rule, the reason for downsizing is a reduction in the volume of work (optimization of the number of employees), and for staff reduction - a change in the type of activity (dismissal of all employees who held the relevant positions). There are no fundamental differences in the procedures for dismissal on these grounds.
Create a staffing table using a ready-made template Try for free
The decision on the need for layoffs is made exclusively by the employer (Part 1 of Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Clause 10 of Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 2, determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated July 15, 2008 No. 413-O-O). However, he must be ready to justify the feasibility of this measure (determination of the RF Armed Forces dated December 3, 2007 No. 19-B07-34).
Under no circumstances can you be fired “due to reduction” (Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article of the Federal Law of June 12, 2002 No. 67-FZ):
- pregnant women;
- women with a child under three years of age;
- single mothers raising a disabled child under the age of 18 or a child under the age of 14;
- workers raising a motherless child under 14 years of age (disabled child under 18 years of age);
- the sole breadwinners of a disabled child under the age of 18 or a child under the age of three in a family where there are three or more young children, if the second parent (legal representative) does not work;
- an employee who is a voting member of the election commission - until the end of his term of office;
- an employee who is a member of the election commission with the right to an advisory vote - during the election campaign.
Next, you need to determine which of the remaining employees has a priority right to keep their jobs. According to Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to retain those who have higher labor productivity and qualifications. And with equal productivity and qualifications, the following persons have protection from reduction:
- family workers with at least two dependents;
- the only breadwinners in the family;
- employees who received work-related injuries and occupational diseases during work;
- employees aimed at improving their skills without interruption from work;
- disabled people of the Second World War and combat operations to defend the Fatherland;
- other employees who are granted such a right by the collective agreement.
Even with a small staff, downsizing involves significant paperwork. First, you will have to determine those who cannot be fired on this basis at all (and for this, you may need to request additional documents from employees). Then, collect data on the productivity and qualifications of other employees. Analyze this information and distribute employees to the appropriate levels. Within each level, select groups of beneficiaries. Then identify those who will remain working and those who will have to say goodbye.
The latter must be given notice of the upcoming dismissal “due to reduction”. The date of termination of the contract indicated therein should not be earlier than 2 months. The notification must also be sent to the employment service authorities.
IMPORTANT
Data about each laid-off employee is transmitted to the employment service, in particular, about his position, profession, specialty and qualification requirements (clause 2 of article 25 of the Law of the Russian Federation of April 19, 1991 No. 1032-1). In 2021, employers were required to post this information in the all-Russian vacancy database “Work in Russia” (clauses 1 and 4 of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 12, 2020 No. 486). It is expected that this duty will be extended into 2021. For more information about the “Work in Russia” service, see “The transition to electronic personnel documents and the “Work in Russia” service: what employers need to know.”
Order an electronic signature to use the “Work in Russia” service Receive in an hour
All layoffs must be offered available vacant positions - both those corresponding to their specialties and qualifications, as well as lower-ranking or lower-paid ones. The main thing is that they are suitable for the employee due to health reasons, and the place of work is in the same area (the possibility of transfer to another area must be agreed upon in advance in a collective or employment agreement). If new vacancies become available during the two-month notice period, they must be offered to redundancy candidates first. And only then can you replace them with new people.
Although the Labor Code does not require confirmation that laid-off employees have been offered vacancies, it is better to issue notifications and hand them to employees against signature. And if you refuse to sign, draw up an act.
ATTENTION
Employees who are on sick leave or on vacation can also be fired “due to reduction.” But only after the period of rest or temporary disability ends.
Also see “Payments when laying off an employee in 2021” and “How, according to the new rules, to pay compensation when reducing staff or liquidating a company.”