What is an abbreviation?
This type of dismissal is a forced measure on the part of the employer. In other words, this is a reduction in the number of subordinates, which is carried out to optimize the number of employees in the enterprise. Job layoffs can happen for several reasons:
- liquidation of the enterprise;
- reduction in the number of people in the state;
- change of company owner;
- abolition of the department.
In the first case, absolutely all subordinates are fired from their jobs; there are no privileged groups of employees. In other circumstances, the boss must keep some people, since by law they cannot be terminated.
Note! In the era of coronavirus, everyone is looking for additional opportunities to earn money. It’s surprising that you can earn much more using alternative methods, up to millions of rubles a month. One of our best authors wrote an excellent article about making money on games with reviews from people.
Legal process of reduction
What to do if they want to lay you off? The most important thing at the moment when an employee finds out that he is being laid off is to remain calm and not give in to emotions, and also to show all his best qualities. It is quite possible that if the employer sees which employee he may lose, he will leave this candidate in another position, while maintaining the basic salary.
If we are talking about staff reductions, you can immediately go to point 4. If there is a reduction in numbers, analyze which of your colleagues who occupy the same position as you and who are not immune from reductions are more experienced and qualified. To do this, conduct a comparative analysis using the following criteria:
Dismissal procedure
If a person has been laid off, then he should know that the manager is obliged to warn his subordinates 2 months before the start of the procedure (Article 180).
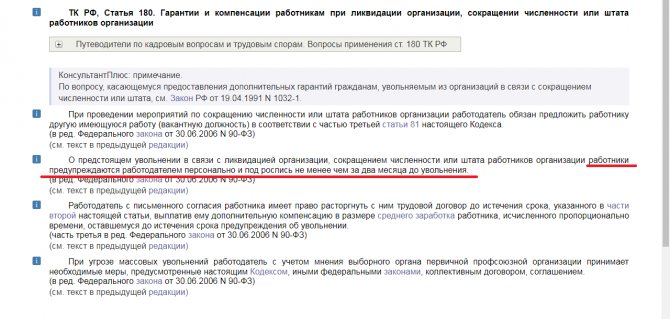
Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Procedure for terminating employment relations:
- An order is issued to dismiss the person.
- All subordinates being laid off are notified.
- Each of them is offered in writing other positions in the company.
- Employees write a refusal if they are not satisfied with the vacancy.
- Notifications are sent to employees about the absence of vacancies.
- The director or human resources department issues a formal dismissal order on the specified date.
If the organization is disbanded, then the employer’s actions during layoffs will be different - in this case, the boss does not offer vacant positions in the company.
Important! If the manager fails to comply with the law: notice of termination of the contract less than 2 months in advance, lack of offers of other places if available, the dismissed person has the right to sue him.
Within two months from the date of receipt of the notification, a subordinate who is being laid off can take a vacation if he has unused days off.
Who gets fired next?
Dismissal procedure
- A single mother with a child under 14 years old (Part 4, Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- A pregnant employee with whom an open-ended contract was concluded (Part 1, Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Head of the trade union (part 1, article 374 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- The only breadwinner of the family, and there are children under 14 years old or a disabled child (Part 4, Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- A single father or guardian in whose care a child is under 14 years old (Part 4, Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- An employee on sick leave (Part 6, Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- A person on vacation (Part 4, Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Reorganization of the company, due to which the number of jobs is reduced;
- Reduction of staff.
In what cases does one not have the right to fire?
How to avoid layoffs at work? According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, certain groups of subordinates do not have the right to terminate the contract on the basis of the following facts:
- staff reduction;
- abolition of the department;
- change of ownership of the company.
If layoffs are being made for one of these reasons, employees should know whether they are part of a privileged group or not.
Who can't be fired?
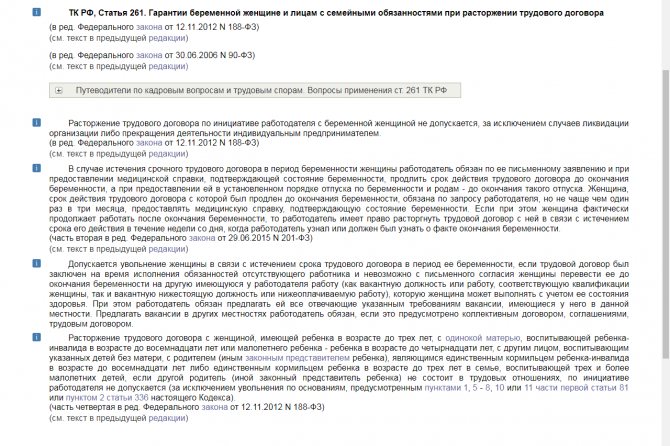
Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
What categories of employees are eligible to retain their positions?
List of subordinates with benefits:
- A single mother with a child under 14 years old (Part 4, Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- A pregnant employee with whom an open-ended contract was concluded (Part 1, Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Head of the trade union (part 1, article 374 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- The only breadwinner of the family, and there are children under 14 years old or a disabled child (Part 4, Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- A single father or guardian in whose care a child is under 14 years old (Part 4, Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- An employee on sick leave (Part 6, Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- A person on vacation (Part 4, Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
All these employees can be laid off only upon dissolution of the organization.
Note! In the era of coronavirus, everyone is looking for additional opportunities to earn money. It’s surprising that you can earn much more using alternative methods, up to millions of rubles a month. One of our best authors wrote an excellent article about how thousands of people make money in the gaming industry on the Internet. Read material with people's reviews about the best games to win money.
Who gets fired next?

There are subordinates with whom you can terminate the contract only after the first layoffs.
Categories of such workers:
- A serviceman of the Russian Armed Forces is in the reserve if this is his first job after service.
- A person who cares for more than 2 dependents, including a disabled child, an incapacitated family member...
- The mother of a serviceman, if she raised a child alone, or if her son (daughter) is currently serving.
- An employee injured as a result of a man-made disaster, for example, a liquidator of the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant.
- A person who has received an occupational illness or was injured at an enterprise under the current management.
In addition to this, on the basis of the 2nd part of Article 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employees who are studying but are going to work can be fired only in the second place.
In addition, according to Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the boss must offer another vacancy or transfer people with high qualifications and good labor productivity to part-time work. However, between a specialist and a subordinate with certain life circumstances, a manager is supposed to choose the second.
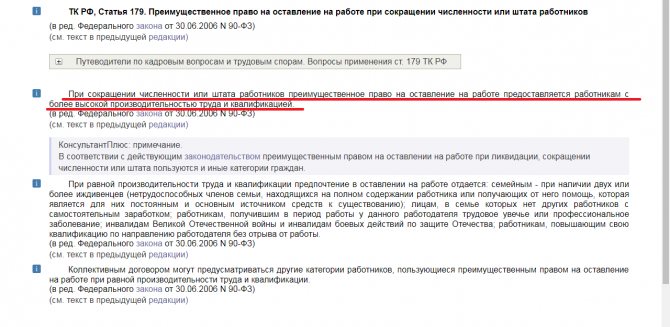
Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
How to insure yourself against layoffs at work?
Retrenchment is an unpleasant and often unexpected procedure for the vast majority of employees. Especially for employees aged 45+. For some time, financial stability is lost, we urgently need to figure out what to do next and change our usual way of life, including convenient routes to work and the family budget.
In a classic dismissal, the employee, as a rule, knows the circumstances due to which he is forced to leave his job. Due to an inconvenient schedule or relocation, misunderstanding with management, for violation of the work schedule, for poor performance of job duties. Alas, there are also unscrupulous employees. Reduction, as opposed to dismissal, occurs for reasons beyond the employee’s control.
Read our article about what you can do to protect yourself as much as possible from the threat of layoffs.

- Reasons for layoffs
- Categories of employees who cannot be laid off when reducing staff
- Who gets laid off first?
- 4 important rules to avoid layoffs or their unpleasant consequences
Reasons for layoffs
- Automation of production
- Repurposing the organization’s activities or abandoning one of the areas
- Decrease in demand for products
- Change of management of the organization
For example, in 2011, the largest Russian company completely abandoned the outdated method of metal smelting - in open-hearth furnaces. At the time of closure, about 400 people worked in the workshop, some of them were laid off.
With the arrival of a new manager, not only the course of development of the enterprise may change. For example, a manager may decide that to complete one project it is advisable to involve not 5, but 3 specialists.
A reduction does not involve replacing a fired employee with a new employee, but rather the complete exclusion of certain positions or the number of employees from the staffing table.
Categories of employees who cannot be laid off when reducing staff
The labor legislation of the Russian Federation does not have clear criteria by which an employer must select employees for layoffs. But there are a number of recommendations that the organization’s management usually adheres to.
According to the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, candidates for reduction cannot be:
- Women pregnant or on maternity leave;
- Single mother or father with a child under 14 years old;
- Head of the trade union;
- The sole breadwinner of the family;
- An employee who is on sick leave or on vacation.
There are categories of workers who can be legally laid off only in the “second wave” of layoffs:
- Military personnel;
- An employee who has a dependent incapacitated family member;
- The mother of a serviceman, if she is raising a child alone;
- Workers injured as a result of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant accident;
- An employee who received an occupational illness or was injured at the enterprise.
If you do not find yourself on the list of those who cannot be reduced by law, or the Labor Code of the Russian Federation has included you in its second part, read on.
Who gets laid off first?
Typical criteria by which employees are assessed for the “redundancy list”:
- education;
- level of professional competence;
- labor productivity;
- personal qualities.
When laying off, there are points that the employee can influence himself, gain an advantage and keep his job. For example, an employer needs to reduce the number of employees in a department that employs two accountants who perform approximately the same functions. One of them has a specialized education, recently completed advanced training, and can work quickly and without errors in 1C. The second one also has a specialized education. But he received it a long time ago, since then he has not been specifically engaged in self-education, he only knows his own area, if he needs to do an additional operation or non-standard wiring, he gets confused and makes mistakes. Who will be retained in the organization: Of course, the first one - the one who will be more useful to it.
Therefore, you should not classify yourself as a “risk group” and give up if your age or work experience is inferior to your opponent. Much more important is your professionalism, ability to learn, desire for development and attitude to work.
So how can you avoid layoffs at work in Russia without violating the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
4 important rules to avoid layoffs or their unpleasant consequences
- Be prepared for it in advance.
Monitor the situation in the organization. Information about upcoming personnel changes often becomes known to the team much earlier than the procedures themselves begin. If you feel insecure in the workplace, develop a plan B. Obtain an additional in-demand profession through professional retraining programs. Now this takes at least 2 months. The cost of such distance learning is very affordable and will not burden your family budget. When you have an additional diploma in hand, even if layoffs occur, you will not have much stress about finding a new job. Having received the required payments, you will comfortably change your field of professional activity and will continue to work calmly.
2. Focus on professional development.
To become indispensable, you need to know something that others don’t know much about. And to do this, you need to expand your professional boundaries - improve your skills, follow trends in the industry. This way you will not only learn a lot of useful things for yourself, but also become competitive among your colleagues and show interest in the work in the eyes of the employer.
Improve your skills at special courses, attend seminars, participate in conferences, webinars. Many of them are now free. ABiUS regularly organizes such events for listeners. Follow our announcements on social networks and come for information.
3. Take on additional responsibilities.
The professional value of “universal employees” is much higher than those who hide behind a job description. If you hold an HR position and have been asked to help out in the legal department during a crisis in the organization, it may be worth getting involved. Or better yet, take the initiative and offer your help yourself.
4. Love your job
When thinking about who to lay off and who to keep, the employer cannot completely ignore personal relationships. It is much easier to say goodbye to a person who is always dissatisfied with something. He was given the wrong shift, the uniform was not comfortable, or the work chair was not so soft. It is more difficult to let go of someone who works in the interests of the organization, loves his job and does it with pleasure, is satisfied with himself and those around him.
The rules are very simple, but very effective, try it.
I wish you stability at work, and we at the Academy are always happy to see you in our online audience!
More than 100 educational programs in popular areas of training.
Rights of a subordinate upon dismissal
What to do if you were laid off illegally? In this case, a person can contact the appropriate authorities:
- court;
- labor inspection.
The employee can contact the first organization within a month from the date the dismissal order is issued. The statement of claim is filed in court at the place of registration of the employer. Labor disputes are not subject to state duty.
There is no time limit for filing a complaint with the inspectorate. Based on the person’s request and the attached evidence, an inspector visits the company and checks for violations. No more than 30 days should pass from the receipt of the complaint to the outcome.
Compensation for layoffs
If a layoff procedure is planned, the employer must follow all points of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. According to article one hundred and eightieth of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee who is planning to be fired must be notified of this fact two months before the start of the layoff. Moreover, in writing against the signature of the dismissed employee himself. It should be noted that the employer may change his mind and not lay off the employee if he deems it necessary. It all depends on the employee himself.
- How to protect yourself from layoffs
According to labor legislation, any employee who has been laid off has the right to receive compensation:







