When you first open any 1C program, the Startup Assistant is automatically launched: the user can immediately make the initial setup of the information base by simply checking the appropriate boxes. We are interested in how to activate, configure and introduce a new staffing table
ZUP version 3.1 provides three ways to maintain it:
- It is not kept, so the “Positions” directory is used in personnel records. This is how small commercial firms can keep records, but at the same time they have to generate reports to statistical authorities manually*;
- In personnel records, the corresponding reference book is used to create a printed copy, which eliminates the need to check whether employees are in compliance with the staff.
- One or more employees are “attached” to a staffing position. This is the best option for large companies and government agencies.
*In this case, the “Use...” checkbox is not checked, but the following options require that it be checked.
Fig.1 Maintaining staffing
It is important to note that if you are setting up 1C ZUP 3 for the first time and skipped checking the “Use staffing table” checkbox, you can do this later, but in the “Settings” section, as shown in the figure below.
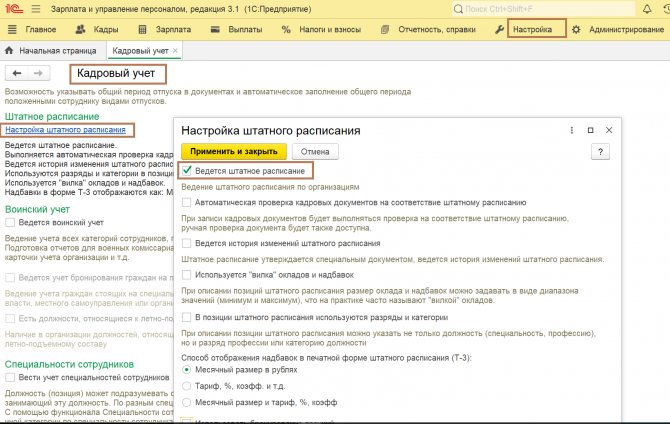
Fig.2 First stage of setup
We suggest taking a closer look at the following options:
The option shown in the figure below is responsible for checking the compliance of personnel documents with the staffing schedule and warns if an error is detected.

Fig.3 Setting automatic check
The next option allows you not only to save the history of maintaining the staffing table, but also to build reports for any period in which all changes will be reflected. If there is no option, only the last value will be stored in the staffing directory. But, based on our many years of experience, I would like to note that keeping records while preserving history is the most convenient and informative.

Fig.4 Activating history
If the system needs to take into account ranks and categories, then you must enable the option shown in the figure below. In this case, the data (category and rank) in personnel records documents are established automatically.

Fig.5 Using categories and categories
To set up a printed form of the staffing table, the option shown in the figure below indicates the method for displaying allowances.

Fig.6 Setting up T-3
The 1C ZUP 3 program allows the user to book staffing positions, indicating the number of days after which the reserved positions will be released. If you would like to use this function in your work, you need to open the staffing settings menu window and check the “Use reservation” checkbox, indicating the number of days of reservation.
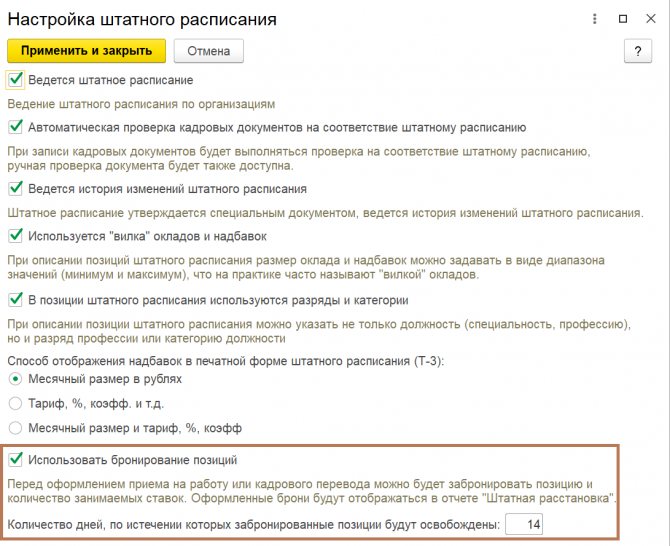
Fig.7 Position reservation
Reasons for change
The reasons why amendments to the staffing table are required may vary. As already indicated, adjustments are made to the act by changing the current schedule or creating a new one. There is no third option.
A complete replacement of the “staff” is carried out if there are serious reasons for this. This could be personnel changes, reductions or expansion of staff, transfer of workers to another department, etc.
Minor adjustments are made to the schedule by issuing an order, which is signed by the head of the organization. An order is issued until the amendments are made. The reasons for issuing such an order may be:
- changing the names of departments and divisions;
- reduction in staffing levels;
- renaming of positions;
- making recalculations regarding wages;
- introduction or removal of a position.
The listed grounds can be used to adjust the current act. The main step in making a change is issuing an appropriate order. Such a document should contain an explanation of the upcoming changes.
If the order is drawn up with violations, then the amendments made to the staff act are recognized as not corresponding to reality if a dispute arises between the employer and the employee or during an audit. In some situations, in addition to issuing an order and making changes to the document, additional measures may be required.
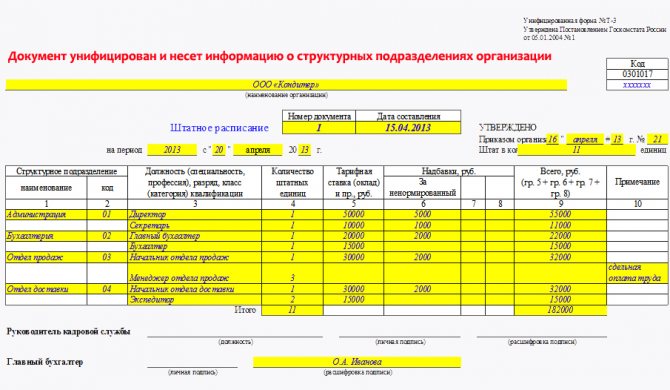
Design example
When changes in the “staff” affect not just a few employees, but the entire enterprise as a whole, a new schedule is issued. This is done to avoid confusion. An example of the issuance of a new act is an increase in the level of the minimum wage in the region where the company is located, provided that the salary of workers depends on this indication.
Situations arise that require forced measures to be taken to provide employees with a shortened working week or day. This happens during crises, a decline in demand for a product and other nuances. The employer's goal in this case is:
- do not close production completely;
- do not leave people without jobs.

Such a decision is agreed upon with the employees of the enterprise, after which they are given notices of the changes. An additional agreement attached to the employment contract is also signed. It is compiled in two copies.
In practice, it is difficult to make adjustments to the entire staff in the schedule, so a new one is created. Before modifications are made to the act, appropriate grounds must appear. Otherwise, the manager does not have the right to change the personnel structure at his own discretion.
Proposals for making adjustments are set out by the heads of divisions and departments and are set out in a memo. A note is drawn up in a free format.
Petition
The reasons for changing the schedule are indicated in the memo (also called a petition). When the document in question is drawn up, it is required to register it in a special journal.
It is not legally established who has the right to draw up notes. Most often, the act is drawn up by personnel department employees. To compile, you need to know what changes are coming to the document. Also, the management of the departments has the right to draw up memos.

Example of a memo
There are no specific requirements regarding the preparation of the document. The compiler must adhere to the general rules for filling out this type of document:
- initially the “header” is written, which contains information regarding the originator and addressee;
- the name of the act is written;
- the document number is indicated;
- describes the content indicating the reasons for the adjustment;
- proposals for resolving this issue are included;
- signature of the author and its transcript.
After writing, the document must be registered in a special accounting journal. This journal is intended to record notes. According to this journal, the note is assigned a number. Next, the act is transferred to the company’s management, who makes the final decision regarding the need to make corrections.
History
There are two options for maintaining a schedule:
- Without keeping history*;
- With change history**.
*View without change history:
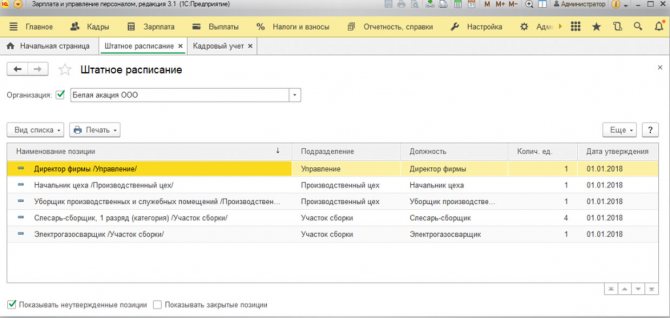
Fig. 16 Two options for maintaining a schedule
**View with change history, with change documents:
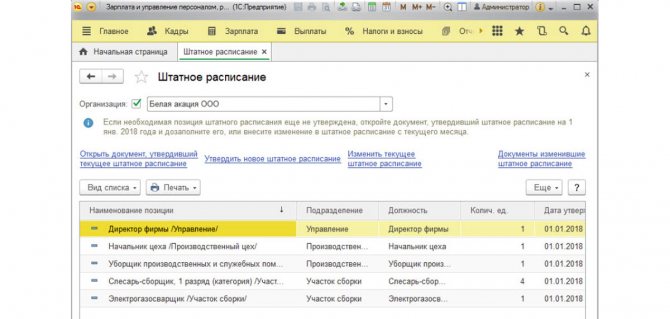
Fig. 17 Two options for maintaining a schedule
Let’s take a closer look at the option with history through the activation “Approve the staffing table with a special document and keep a history of its changes.”

Fig. 18 Option with history
After our actions, changes in the schedule are possible only with the help of special approval documents* and changes, so it will not be possible to simply open a staff unit and change its contents.

Fig. 19 Approval of the staffing table with a special document
*If there are several documents in the list, the previous document can be opened for viewing only, but cannot be edited. To make this possible, you must first disable changes to a later document by canceling posting the document.
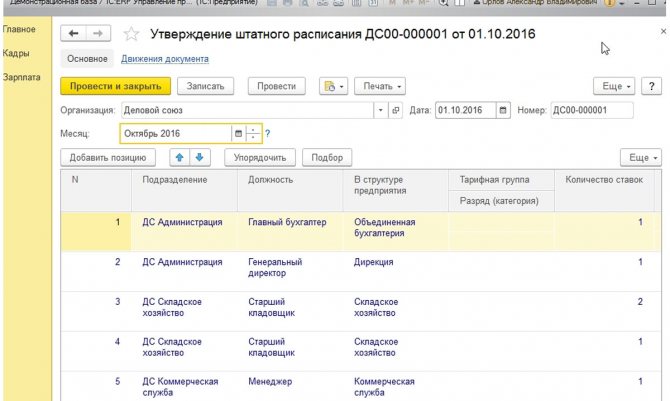
Fig.20 Cancel document posting
Change Order
In practice, two methods have been developed by which adjustments are made:
- an order is issued to modify the document, which lists the adjustments made to the act;
- a new document is approved.
In the case when minor adjustments are made to the act, the first method is considered the most appropriate. Accordingly, the second one is used for fundamental amendments to the schedule.
The order is drawn up in any form. The document indicates, according to what grounds the decision to change was made, and the date when the adjustments begin to take effect.
The grounds that are used to revise the act may be different:
- increase or decrease in production volumes;
- structure optimization;
- reorganization;
- others.

In a situation where an employee is dismissed from a company, this cannot be considered as a basis for removing the position he occupied from the schedule. The exception is cases of staff reduction.
When volumes in a company have decreased and management decided to remove a position from the staff, and after some time it was reintroduced, the employer should not forget about indexing earnings.
When issuing an order regarding any basis for correction, the originator must be extremely careful. This provision especially applies to filling out fields containing details. The order must contain:
- name of the act;
- Date of preparation;
- the date on which the document comes into force;
- description of all changes;
- information concerning the person appointed responsible for the execution of the act;
- management signature.

When errors are made in the order, it is considered invalid.
In this case, the new “staff” will also be recognized as inconsistent with reality.
Change, optimization and renaming
Initially, when an enterprise begins to operate, as a rule, it has a narrow range of activities. This is due to the lack of established connections and regular clientele.
After the company has existed for several years, it becomes capable of providing a larger range of services than previously stated. For this reason, there is a shortage of personnel required to carry out the new amount of work.

Notification of amendments due to change of position
In this case, it is necessary to rewrite the position in the staffing table. Due to this foundation, new positions are added to it. The list of available departments can also be supplemented.
Optimization
The document is subject to adjustment in the event of optimization of the activities of managers or redistribution of obligations. For example, an organization may initially introduce one deputy manager position, but later the need for a second deputy arises.
As a rule, the required volume for the introduction of a new rate is not enough, then one of the department heads is renamed to deputy, while increasing his volume of work and increasing his pay.
Also, additional staff units can be entered into the “staff”, while indicating a rate of 1/2.
Renaming
In case of renaming a position, the legislator provides for a certain procedure that must be followed by the employer. The project is coordinated with the enterprise's trade union.
The reasons for which adjustments are made are attached to the project. The trade union reviews the project for a five-day period, after which it issues its reasoned opinion.
Amendments must be agreed upon in the following cases:
- changes in the names of a large number of positions;
- formation of a new division;
- reduction of staff by more than five percent of the total number of workers.
The procedure is performed in the following order:
- An explanatory note is drawn up containing the rationale for the changes.
- Administrative documentation regarding making adjustments is issued. After reviewing the note, a manager’s resolution is imposed on it, with instructions to change the job title and prepare changes in the employee documentation.
- Changes are being made. Changes are carried out in accordance with the issued order.
Employees whose job titles are changing must be properly notified of the upcoming changes in the prescribed manner.
The manager offers the person a choice regarding agreement or disagreement with the changes, as well as choosing a vacant position to continue working. Notifications are given no later than 2 months before the relevant changes.

Notification of position renaming
Changes are made by issuing a new or adjusting an existing act. After the changes have been made, a number of documents must be completed:
- additional agreement;
- employee personal card;
- job description.
It is also necessary to make adjustments to the work book.
Setting up positions
To create a new position, click “Create” and enter the positions. Entering their names manually is a simple method, but not optimal.

Fig. 11 Creating a new position
It is more correct to enter positions through “Selection from OKPDTR”, selecting them from the list of positions.
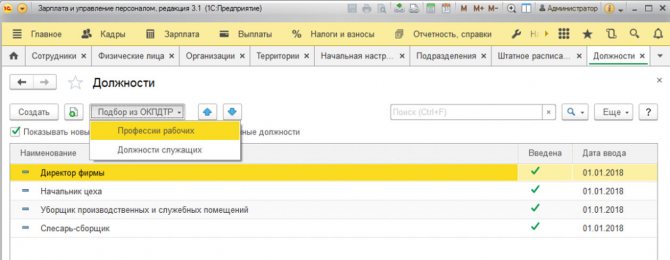
Fig. 12 Selection of a position from OKPDTR
If a position is selected, it becomes gray and inactive in the list.
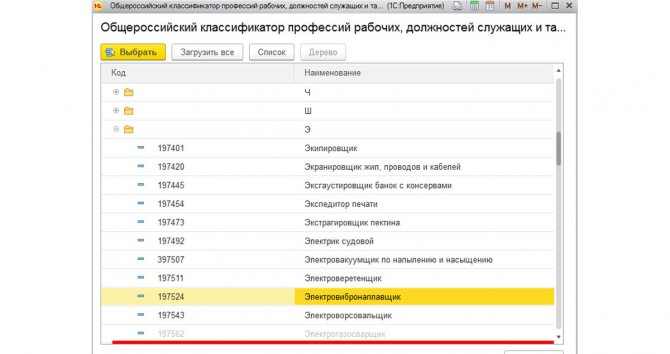
Fig. 13 Already selected position
Having closed OKPDTR, we will see that the new position is highlighted in bold. That is, the program warns us that this is a new, not yet valid entry.
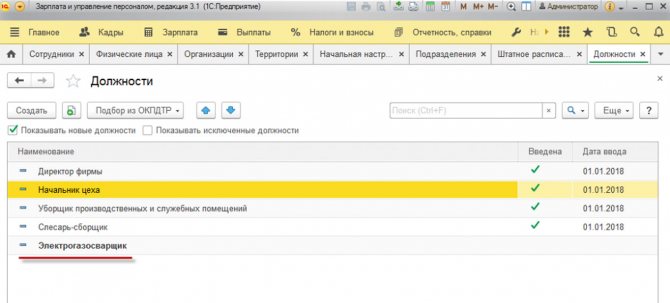
Fig.14 New entry
In order for a position to be used for work, you must open it and enable “Position approved” (from January 1 of the current year). Since version 3.1.5 of the ZUP program, the line “Data for filling out reporting” has been added to the position card:
- OKPDTR code
- Check number
- Category*.
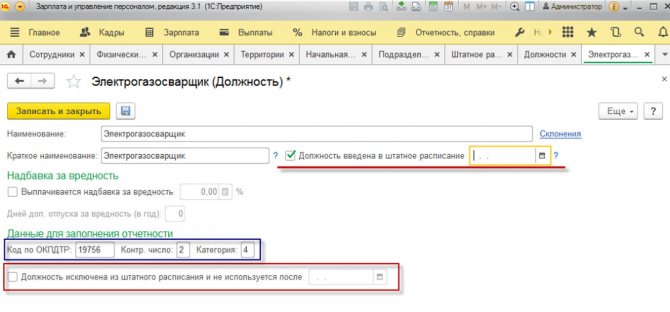
Fig. 15 Position approved
*They are needed when filling out statistics form 57-T, so if you enter a new position simply by clicking the “Create” button, the reporting will have to be generated manually.
To create a schedule, we “linked” “Division” and “Position” to each other (they can be entered in advance or simultaneously with the creation of elements of our “staff”).
Get a free consultation on staffing in 1C: ZUP
Salary change
Initially, the schedule establishes the salary amount due to each position. As the company grows, there may be a need to make adjustments to this point, as the volume of labor increases and the financial capabilities of the enterprise increase.
Also, the grounds for changing the schedule may be provided for in legislation adopted at the federal level. Such acts establish an increase in the minimum wage.
According to labor law, the employer does not have the opportunity to set wages less than the minimum wage. For this reason, when making corrections to the value under consideration, it is necessary to adjust the schedule.
List of replacement and elimination of positions
An explanatory note must be prepared for the schedule, which describes the calculations made regarding the adjustments, as well as a statement of job changes. The head of the organization initially gets acquainted with the project, after which he makes his own adjustments and approves it.
According to the rules in force regarding the schedule, it is possible to replace one position with another. In this case, it is necessary to generate the statement in question. If necessary, some positions are removed from one department and new ones are created using them.
After the schedule is approved and approved, the statement must be drawn up as an integral part of the act or its appendix. Typically, positions that are vacant will be used for replacement.
The statement is drawn up in the form of a table. It consists of two parts. Example:
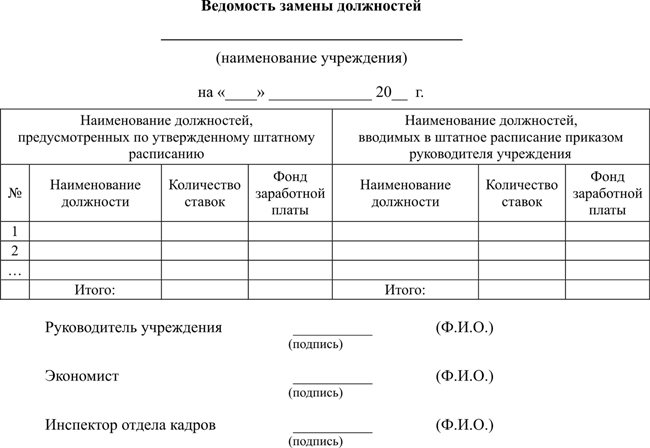
Sample job change sheet
The employer has the authority to exclude positions or structural units from the schedule only when staffing in the organization is reduced. In this case, it is necessary to issue an appropriate order. The compiler will need the following documents:
- employee documentation;
- schedule;
- forms developed for orders;
- company documents;
- legislative acts;
- seal.

A position can be excluded if there are circumstances that are classified as special. An example is a crisis, changes in working conditions, etc. An employee whose position is being eliminated must receive notice two months before the changes take effect.
Next, an order is drawn up, in the header of which the name of the company is indicated. The name is written in accordance with the statutory documentation. The date and number of the issued order and the date when the changes come into force are indicated.
The order reflects the reason for its preparation and specifies the positions that will be excluded. An employee of the HR department is appointed responsible for execution. Next, the act is certified.
The position that is being eliminated is then eliminated from the current schedule. An order is also issued containing information regarding staff reductions. The order indicates the name of the position that is subject to exclusion from the schedule, and also specifies the details of the employee occupying this position.
The order is certified by the signature of the company management. The specialist whose position is being reduced gets acquainted with the document.
The legislator does not stipulate how often the “staffing” can change. This indicates the ability of the company's management to make changes at their discretion. If adjustments are made, the procedure established in the laws must be followed.
Regulatory documents governing changes to the staffing table
| Name of the normative legal act | Document Number | Description |
| Labor Code | Article 8 | Regulates the adoption of internal regulations of organizations that can regulate the legal aspects of interaction between the employer and employees |
| Resolution of the State Statistics Committee | №1 | This resolution regulates unified forms of primary documentation that are necessary for maintaining personnel records and accounting for wages. Here is the unified form T-3, which serves as the basis for maintaining the staffing table |
Change Notice
According to labor legislation, the head of the company has the obligation to familiarize employees with all acts adopted within the organization.
When changes are made to the schedule, it is not necessary to notify employees. The exception is the situation when adjustments affect the employee’s activities.
For example, when several new positions are introduced, familiarization is not required; if a reduction is made, then those whose positions are being reduced become familiar with the act. Also, when changes concern salaries or allowances, the person is notified of the upcoming changes.









